chap 5
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Sensation
The process of the sense organ receptor cells being stimulated and relaying information to the brain for further processing.
Perception
The selection and interpretation of sensory input to give it meaning.
Olfactory
Relating to the sense of smell, detecting airborne chemicals called odorants.
(smell)
Somatosensory
Relating to the sense of touch, heat, and pain, detecting pressure or damage to the skin.
(Touch, Heat, Pain)

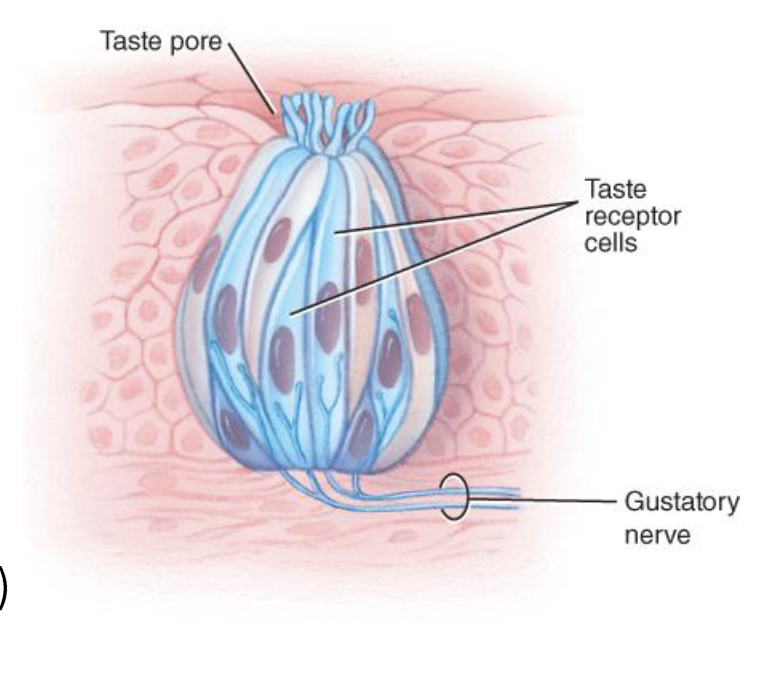
Gustatory
Relating to the sense of taste, detecting chemicals typically found in food.
(taste)
Auditory
Relating to the sense of hearing, detecting sound waves.
(Hearing)
Visual
Relating to the sense of sight, detecting light (photons).
(Sight)
Sensory Transduction
The process of converting environmental stimuli into neural activity.
Sensory Receptor Cells
Specialized cells that convert specific forms of environmental stimuli into neural impulses.
Psychophysics
The study of how physical stimuli are translated into psychological experiences.
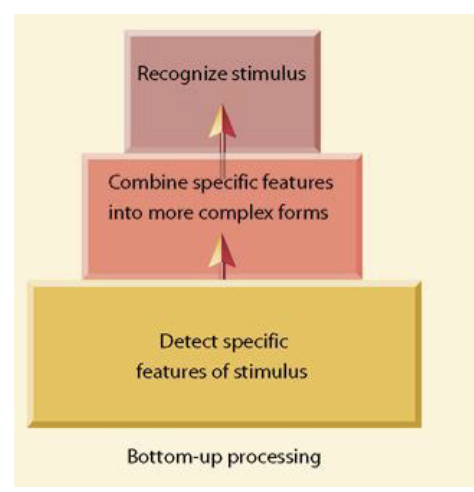
Bottom-Up Processing
A progression from individual elements to the whole.
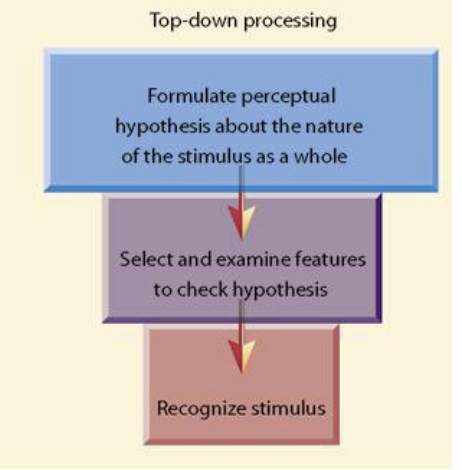
Top-Down Processing
A progression from the whole to the elements.
Stimulus
Any detectable "thing" in the environment.
Threshold (Individual Differences)
The value of a sensory event at the point where things are perceived as different, varying among individuals.
Absolute Threshold
The minimum amount of stimuli needed to notice something, occurring 50% of the time.
Just Noticeable Difference
The amount of stimuli needed to notice a difference in the environment.
Signal Detection Theory
An observer's perception depends not only on the intensity of a stimulus but also on their motivation.
Subliminal Perception
Perception below the threshold of conscious awareness.
Signal Adaptation
Losing conscious awareness of a sensory stimulus.
5 Taste Receptors
Sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami.
Ageusia
Inability to taste, a rare disorder.
Anosmia
Inability to detect odors.
Hyposmia
Reduced ability to smell.
Reflex Epilepsy
A seizure occurs only after exposure to a specific odor.
Migraine Headaches
Specific odors can trigger migraines.
Tactile or Somatosensory System
Combination of skin senses like pressure, touch, temperature, vibration, and pain.
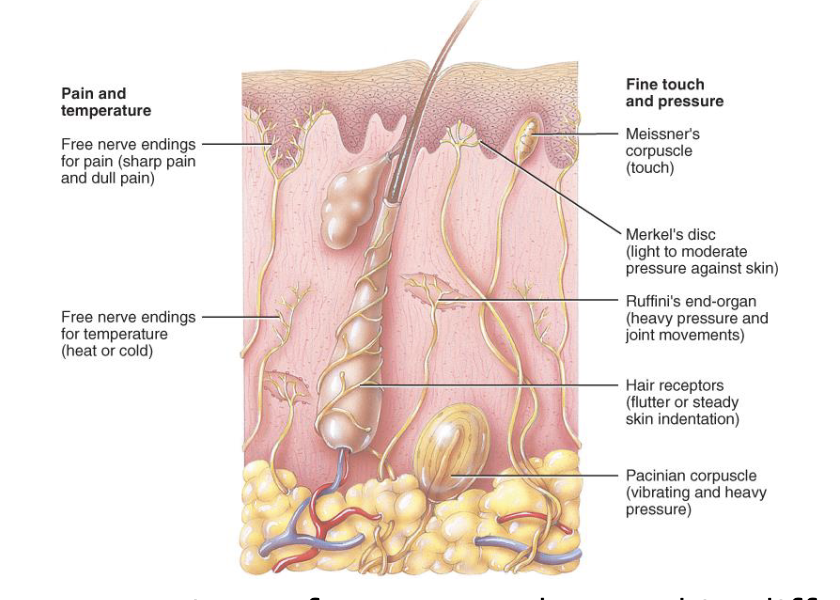
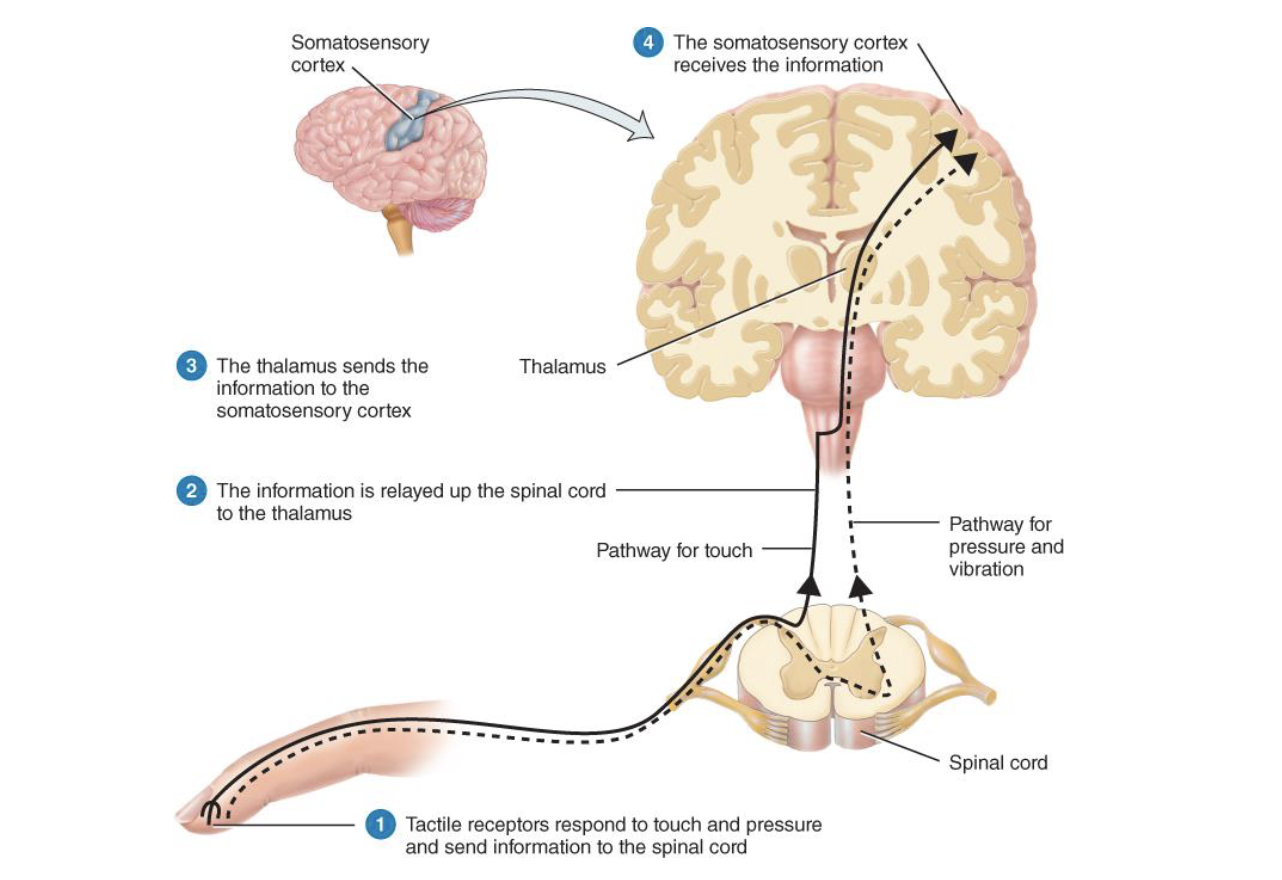
Touch Process
1) get a tactile stimulus that is then sent to the spinal cord (one for touch and one for pressure+vibration)
2) Then it gets sent to the thalamus (relay sensory information)
3) Then sent to the somatosensory cortex which then processes the info
No Pain (Familial Dysautonomia)
A rare genetic condition associated with an inability to detect pain or temperature and produce tears.
Phantom Limb Sensations
Tactile hallucinations of touch, pressure, vibration, and pain in a body part that no longer exists.
Reflex Epilepsy
A seizure occurs only after exposure to a specific odor.
Migraine Headaches
Specific odors can trigger migraines.
Tactile or Somatosensory System
Combination of skin senses like pressure, touch, temperature, vibration, and pain.
Deafness
Partial or complete loss of hearing, which can be caused by various factors.
No Pain (Familial Dysautonomia)
A rare genetic condition associated with an inability to detect pain or temperature and produce tears.
Phantom Limb Sensations
Tactile hallucinations of touch, pressure, vibration, and pain in a body part that no longer exists.
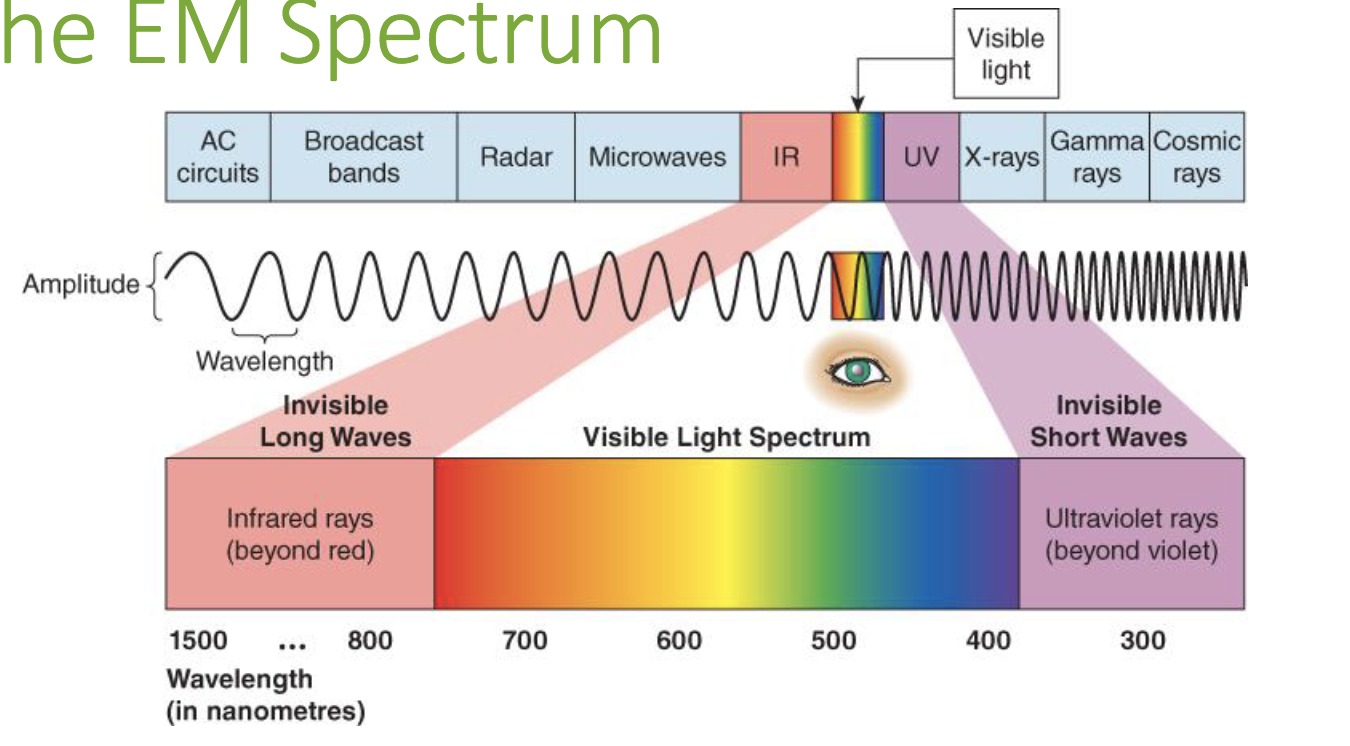
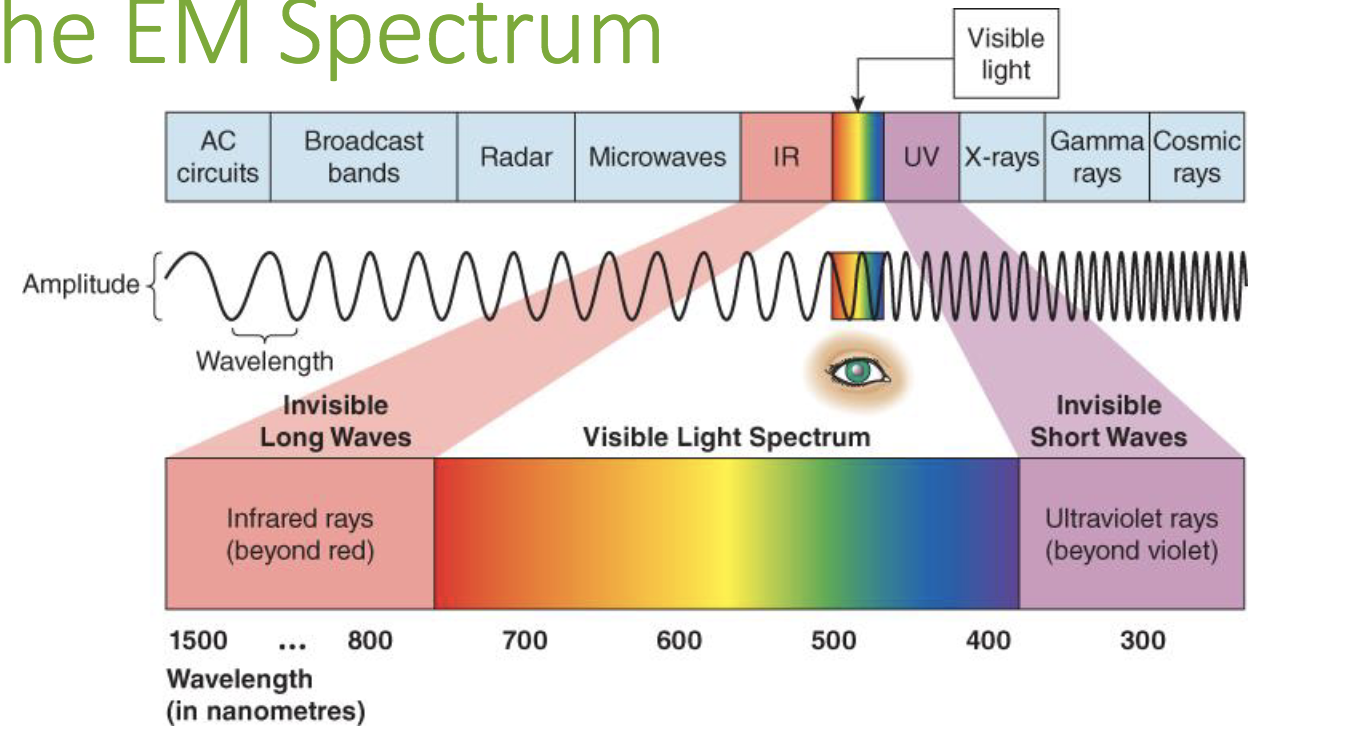
Sound Waves
Vibrations of air that are within the frequency of hearing.
Amplitude
The perception of brightness.
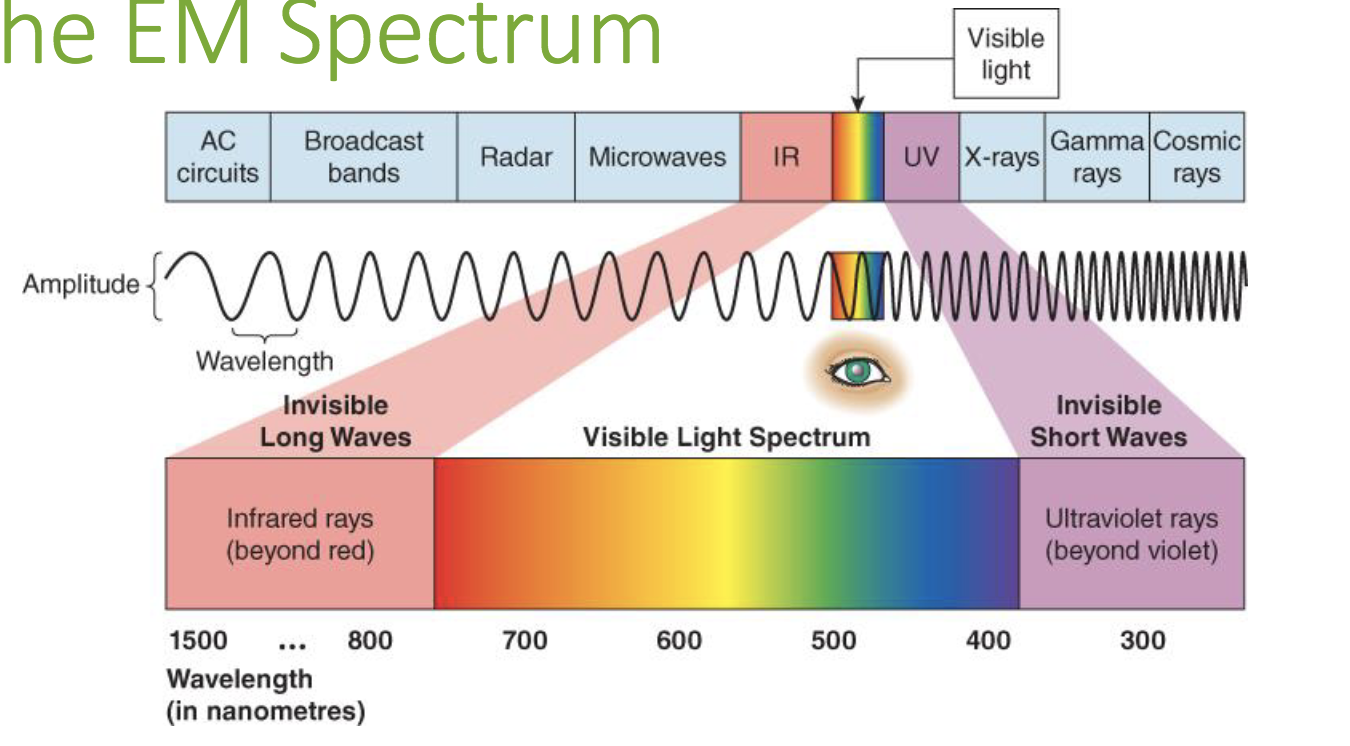
Wavelength
The perception of color.
Deafness
Partial or complete loss of hearing, which can be caused by various factors.
Perception of Saturation
The richness of colors.
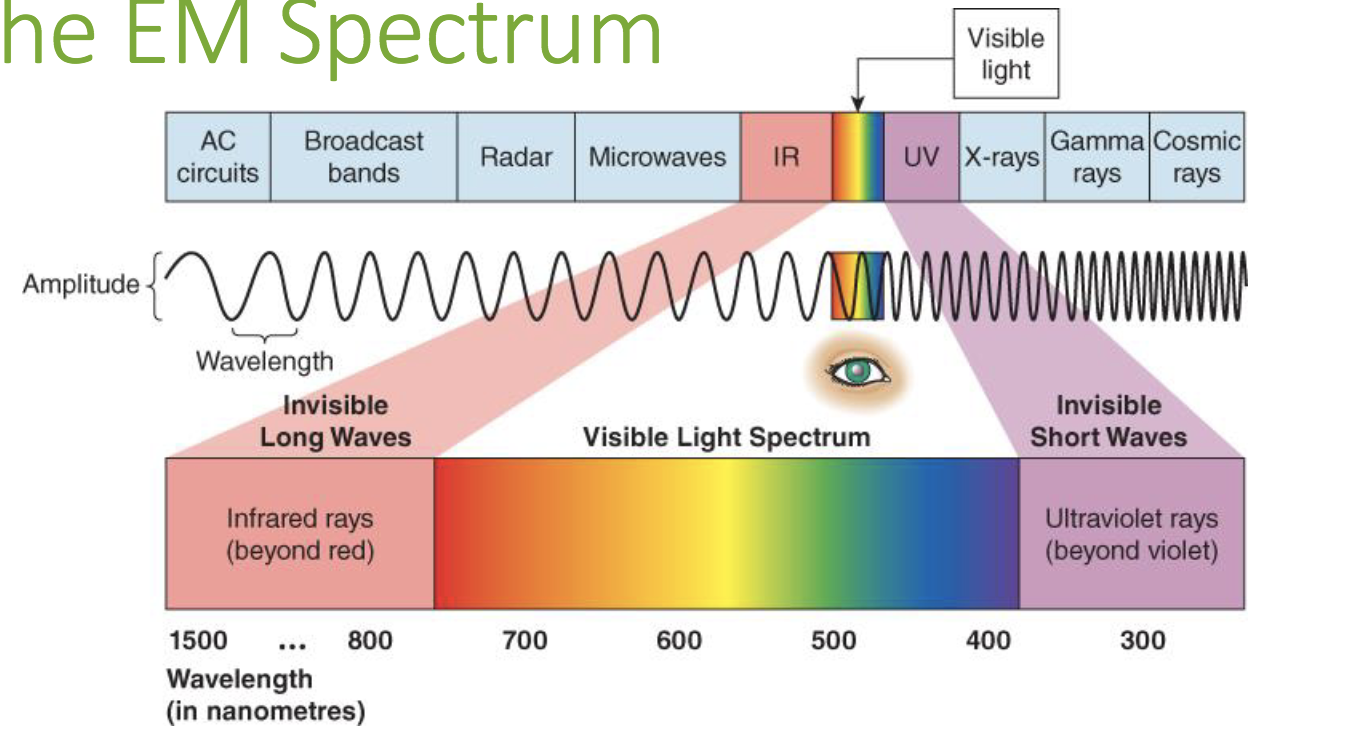
Cornea
The transparent portion of the eye's front surface that refracts light and allows it to enter the eyeball.
Pupil
The aperture in the eye formed by concentric bands of muscle.
Iris
The layered ring of tissue that gives the eye its characteristic color.
Lens
The transparent eye structure that focuses light rays onto the retina.
Visual system step 1
light enters the eye → iris adjusts the size of the pupil so more or less light can go in
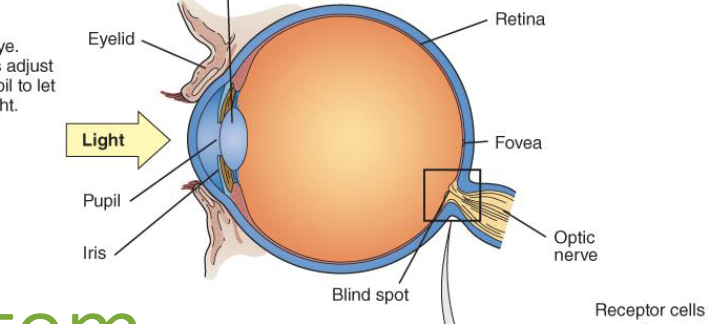
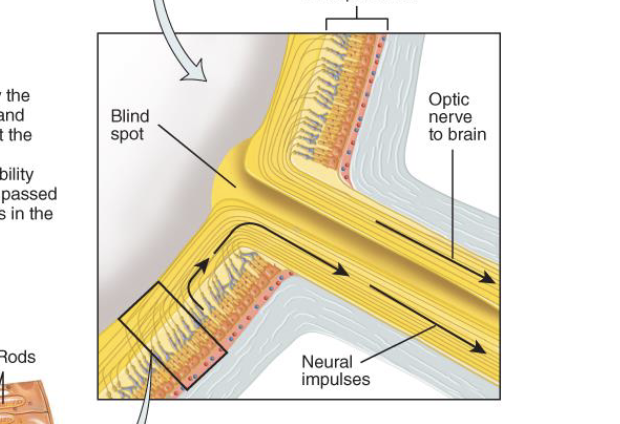
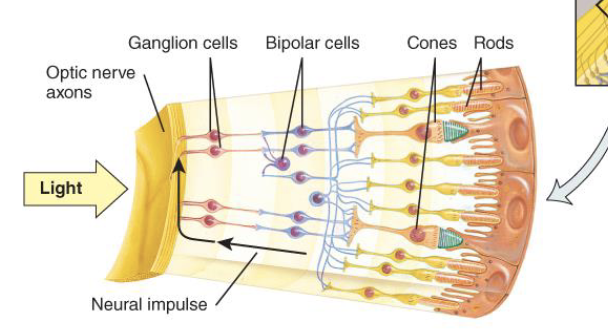
Visual system step 2
light is transduced by the photoreceptors (rods and cones) in the retina at the very back of the eye → changes form the photoreceptors get passed down to other neurons in the retinal circuitry
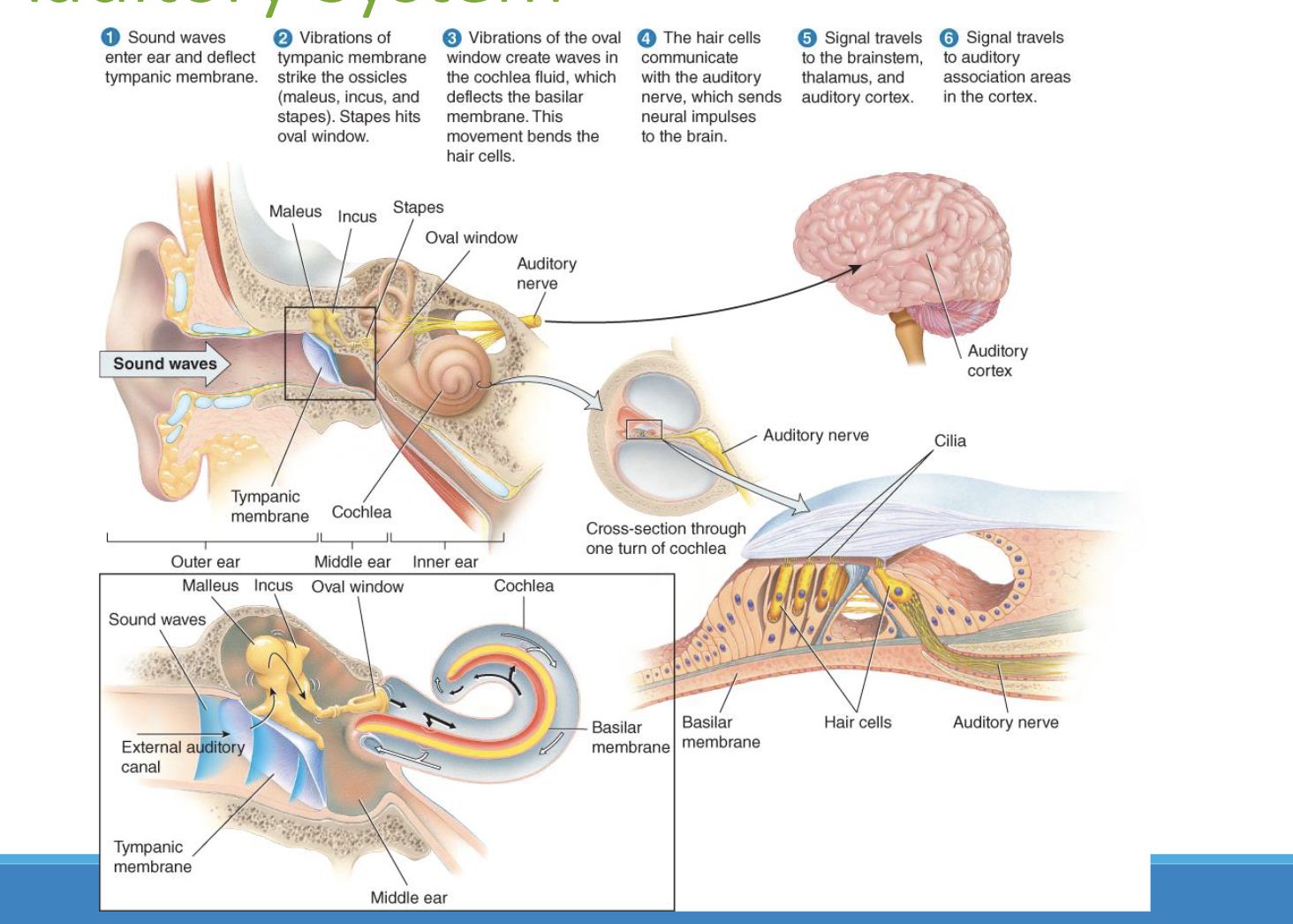
How the sound moves through the ear
Tympanic membrane —--> ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) —--.> oval window —--> choclea —--> basilic membrane (bends cillia over) —> cillia —-> signal impulse to auditory nerve
Tinnitus
Ringing in the ear due to abnormalities in the ear.
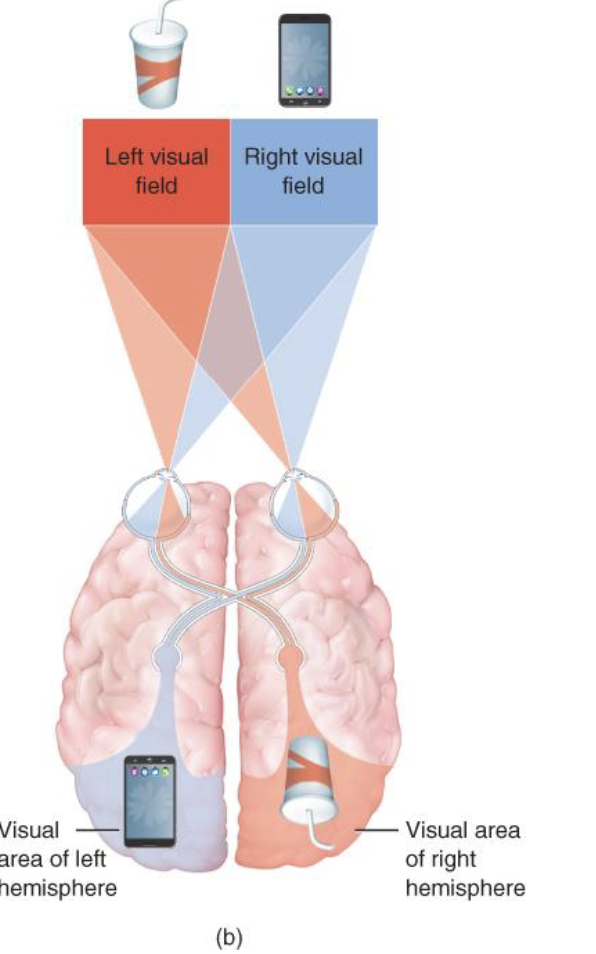
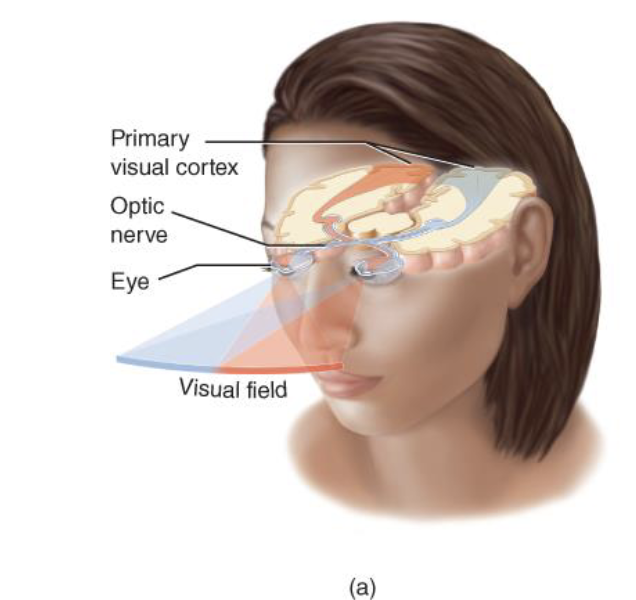
Visual System
light enters the eye → iris adjusts the size of the pupil so more or less light can go in → light is transduced by the photoreceptors (rods and cones) in the retina at the very back of the eye → changes form the photoreceptors get passed down to other neurons in the retinal circuitry → photo projectors project to interneurons which communicate through ganglion cells in retina → ganglion cells send visual input from retina to brain via optic nerve
Amplitude
The perception of brightness.
Wavelength
The perception of color.
Purity
The mix of wavelengths.
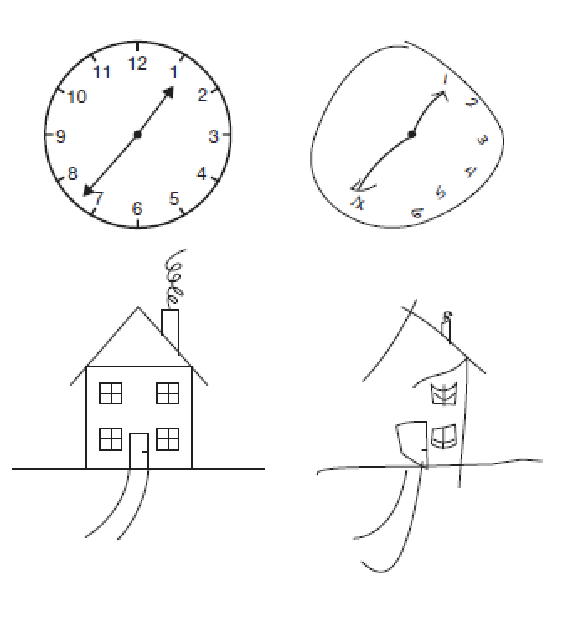
Figure-Ground
The tendency to perceive one aspect as the figure and the other as the background.

Proximity
Objects that are physically close together are grouped together.

Continuity
Objects that continue a pattern are grouped together.
Closure
The tendency to see a finished unit from an incomplete stimulus.
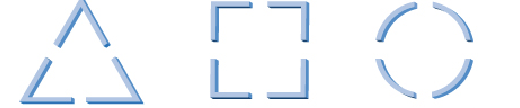
Similarity
Similar objects are grouped together.

Gestalt Law
How we perceive stimuli as whole forms or figures rather than individual lines and curves.
Retinal Disparity
The slight difference in images processed by the retinas of each eye.
Convergence
The inward movement of the eyes to view objects close to oneself.
Binocular Cues
Cues from both eyes.
Illusions
Perceptions of physical stimuli that differ from measurable reality and normal expectations.
The Muller-Lyer Illusion
One line appears longer, but both are the same length.
Ponzo Illusion
The converging lines make the upper bar seem larger, but both are identical in length.
Gestalt's Law of Organization
The whole is greater than the sum of its parts.
Law of Pragnanz
When items or stimuli can be grouped together or seen as a whole, they will be.
Strabismus
Lack of coordinated movement of both eyes.
Amblyopia
A loss of visual abilities in a weaker eye due to abnormal development of the brain's visual cortex. (eyepatch)
Braille
A form of reading skill used by individuals with visual impairments.
Kinesthetic
Receptor cells in muscles that tell the brain about movement and body part location.
Vestibular
Located in the inner ears' semicircular canals, the
movement of fluid tells us if we are standing up or swaying from side to side