Aca Deca (2025-2026) - Science - Equations
1/27
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Ampere's law
B (2𝝅r) = μ₀ I
I = current passing through the Amperian loop
B = magnetic field
2𝝅r = length around the Amperian loop
μ₀ = permeability of free space
Coulomb constant
8.99 x 10⁹ N m²/C²
Coulomb's law
Fᴇ = k ( q₁q₂ / r² )
q = amount of charge of the two objects
r = distance between them
k = Coulomb constant
Electrical force
Inverse square law
Electric field
E = σ / 2ε₀
σ = surface charge density
Electric Field
Fᴇ = qE
Faraday's Law
V = -N ( ∆Φʙ / ∆t )
Φʙ = magnetic field flux
N = amount of loops
∆ = change in quantity
Frequency
f = c / λ
c = speed of light
λ = wavelength
Gauss's law
Φᴇ = q / ε₀
Amount of electric field that passes through a Gaussian surface
ε₀ = permittivity of free space
Φ = "phi", electric field flux
Gravitational Field
Fɢ = mg
Gravitational Force
Fɢ = G ( m₁m₂ / r² )
m = masses of the two objects
r = distance between them
G = gravitational constant / Newton's constant
Kinetic energy of a particle
∆E = q x V
V = voltage (change in height of a ball)
q = charge (weight of a ball)
Lorentz factor
γ = 1 / √ (1 - v²/c²)
The effects of relativity
Magnetic field in a Solenoid
B = μ₀ I (N/L)
L = length of solenoid
N = number of loops
Magnetic Force
Fᵦ = q v B
q = electric charge of the particle experiencing the force
B = strength of the magnetic field (measured in teslas)
v = velocity of the particle
Maxwell's 1st equation
How an electric field is created around charge
Full mathematical form of Gauss's law
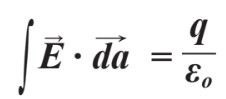
Maxwell's 2nd equation
How a magnetic field is created around charge

Maxwell's 3rd equation
Faraday’s law
A changing magnetic field gives rise to an electric field

Maxwell's 4th equation
The changing electric field between the plates of a discharging capacitor
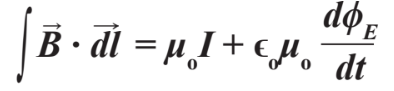
Newton's constant
6.67 x 10⁻¹¹ N m²/kg²
Ohm's Law
I = V/R
V = voltage
I = Current
R = resistance, measured in ohms (Ω)
Current in a circuit
Oscillating circuit
f = 1 / (2𝝅 √LC)
C = capacitance of the capacitor
L = inductance of the inductor
Resistance of a Parallel Circuit
1/Rₜₒₜₐₗ = 1/R₁ + 1/R₂ + 1/R₃ + …
Resistance of a Series Circuit
Rₜₒₜₐₗ = R₁ + R₂ + R₃ + …
Speed of Light
c = ( 1 / √ ε₀μ₀ ) = 3 x 10⁸ m/s
Strength of proton's electric field
E = kq / r²
Velocity of a wave
v = λf
λ = wavelength
f = frequency
Wavelength
λ = c / f
c = speed of light
f = frequency
ε₀
1 / 4𝝅k
Permittivity of free space