Particles
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
* which holds the particles closer together
* but in a gas the forces between the particles are neglagible
* so the particles spreads out furthur apart.
* In a solid:
* The particles are **closely packed**
* The particles **vibrate** about fixed positions
* In a liquid:
* The particles are **closely packed**
* The particles can **flow** over one another
\
* The particles are **far apart**
* The particles move **randomly**
* so tyere are more frequent collosions of gas particles within the container walls
* each particle will cause a force
* so there is a greater force within the walls
for the experiment which Measures the Density of Regularly Shaped Objects
What are the independent and dependent variable?
Indpendent variable: type of shape/volum
Dependent variable : mass of the object
1. Place the object on a digital balance and note down its mass
2. Use eitcher the ruler or Vernier callipers to measure the objects dimensions
3. Repeat these measurements and ake an average of these readings before calculateing the density.
4. Calculate the volume of the object
(dependent on its shape)
5. convert cm to m (by diving by 100)
6. Then use the formula for density to calculate the density.
What are the variables?
dependent: volume of displaced water
Dependent variable: volume of displaced water
1. place the object on a digital balance and note down its mass
2. fill the eureka can with up to a point just below the spout (to make sure it is exactly till then let one of two drops of water wall from the apout)
3. Place an empty measuring cylinder below its spout
4. carefully lower the object into the eureka can
5. measure the volume of the displaced water in the measuring cylinder
6. repeat these measurements and take an average before calculating the density.
7. the volume of the water displaced is the volume of the object.
8. then use the formula for density to calculate the density.
* This includes when measuring the density of the liquid – remove the measuring cylinder and zero the balance before adding the liquid
* Ensure to take repeat readings and calculate an average to keep this error to a minimum
* Place the irregular object in the displacement can carefully, as dropping it from a height might cause water to splash which will lead to an incorrect volume reading
* Water should not be poured into the measuring cylinder when it is on the electric balance
* This could lead to electric shock
\
* Make sure to stand up during the whole experiment, to react quickly to any spills
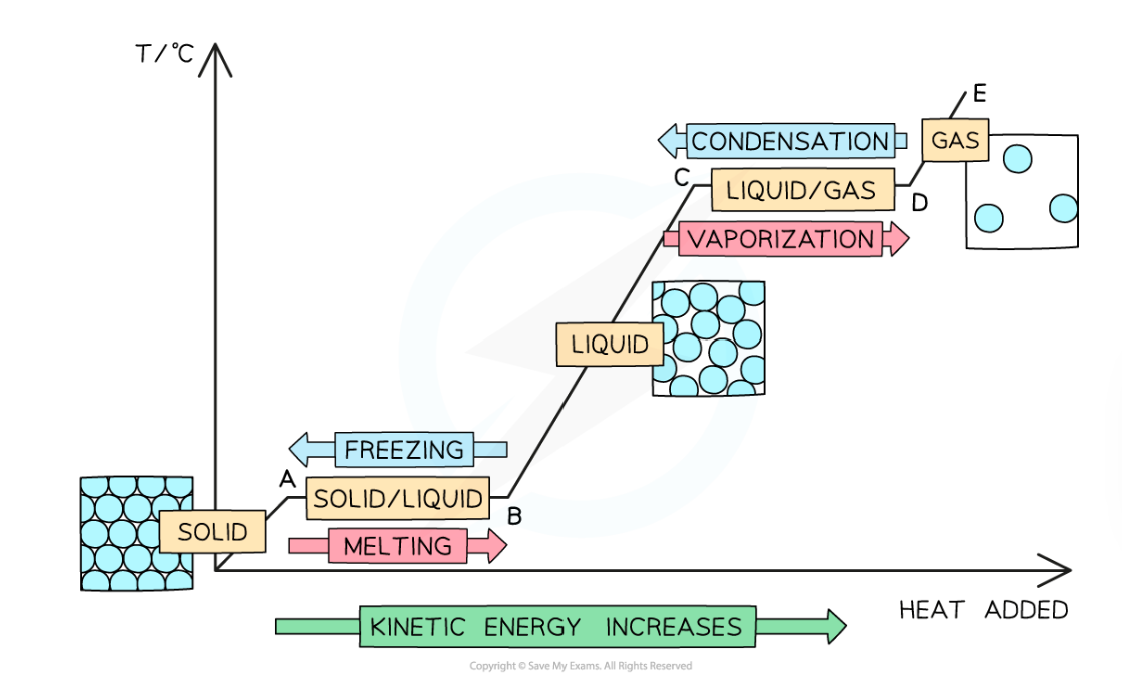
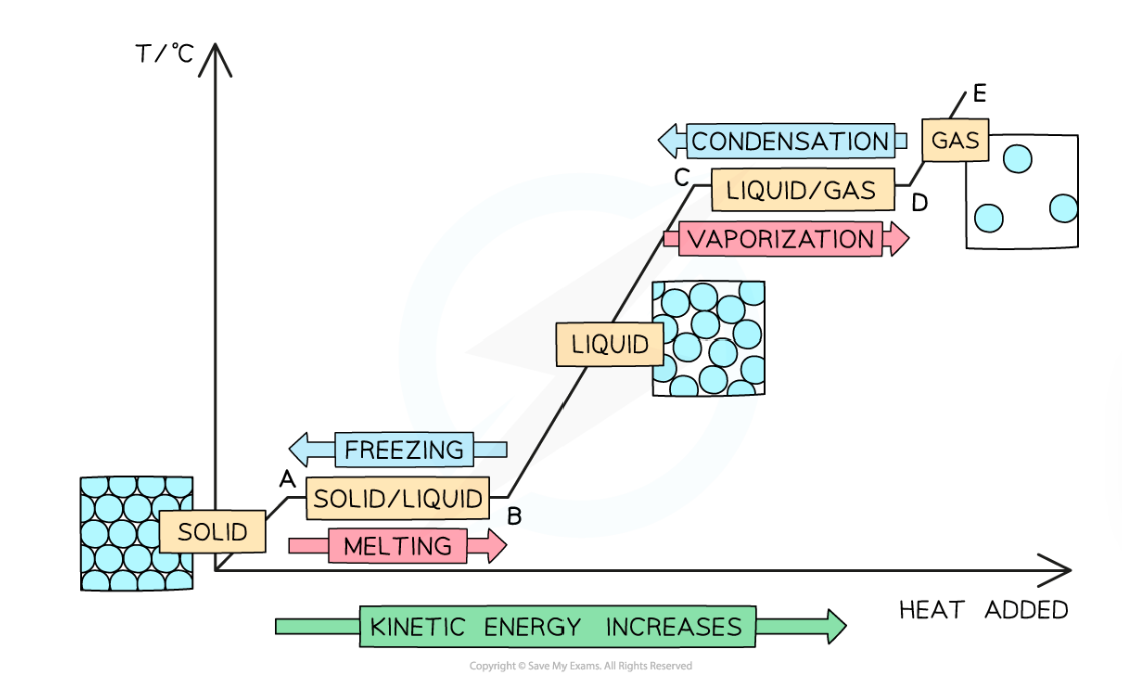
What is hapening in each stage of the heating cooling graph?
ORIGIN to A: Energy transferred to the substance is being used to increase the kinetic energy of the particles while it is a solid
A to B: Energy transferred to the substance is being used to overcome the intermolecular forces of attraction, increasing the potential energy and melting the substance
B to C: Energy transferred to the substance is being used to further increase the kinetic energy of the particles while the substance is a liquid
C to D: Energy transferred to the substance is being used to overcome the intermolecular forces of attraction, further increasing the potential energy and boiling the substance
D to E: Energy transferred to the substance is being used to further increase the kinetic energy of the particles while the substance is a gas