water balance and urine formation
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
how does urine form? general 3 step process
glomerular filtration
tubular reabsorption and secretion
water reabsorption
glomerular filtration
first step of urine formation
water, salt, nutrients and waste molecules move from glomerulus to bowman’s capsule
extreme pressure creates filtrate: liquid waste
large macromolecules not pushed through
why is filtrate needed?
waste removal, without it we would become sick and die
renal medulla
middle, salty area since salt is being pumped out of loop of henle to ensure water is reabsorbed by body
tubular reabsorption and secretion: proximal tubule
occurs in cortex
reabsorb nutrients into circulatory system
nutrients, water, salt, and bicarbonate reabsorbed
hydrogen ions, some drugs and poisons secreted into proximal tubule
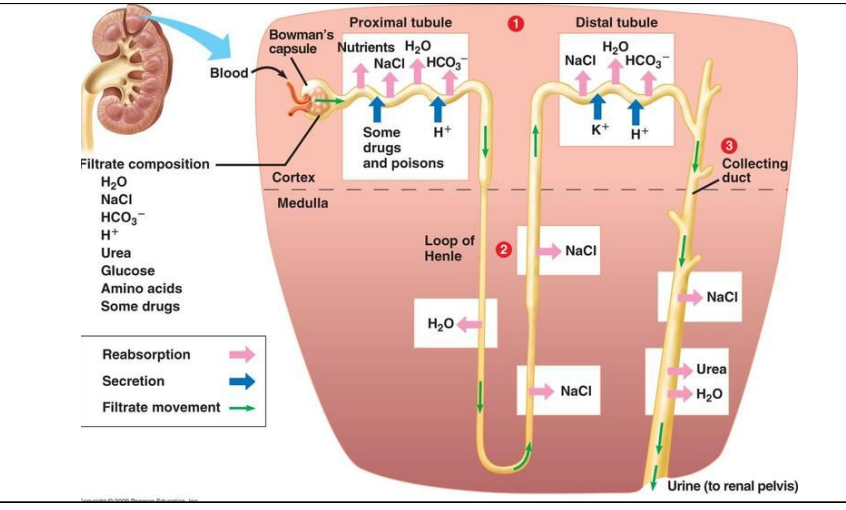
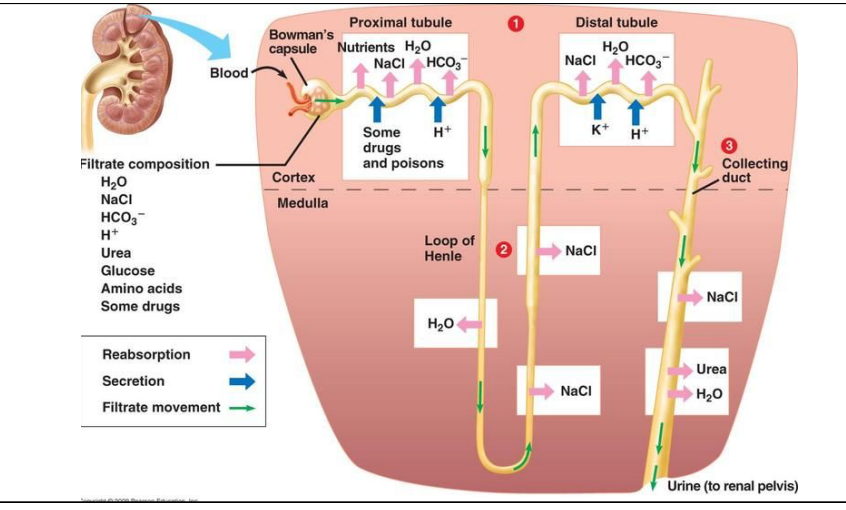
tubular reabsorption and secretion: loop of henle
occurs mainly in medulla
descending: passive transport of water
ascending: active transport of salt
both absorbed into circulatory system
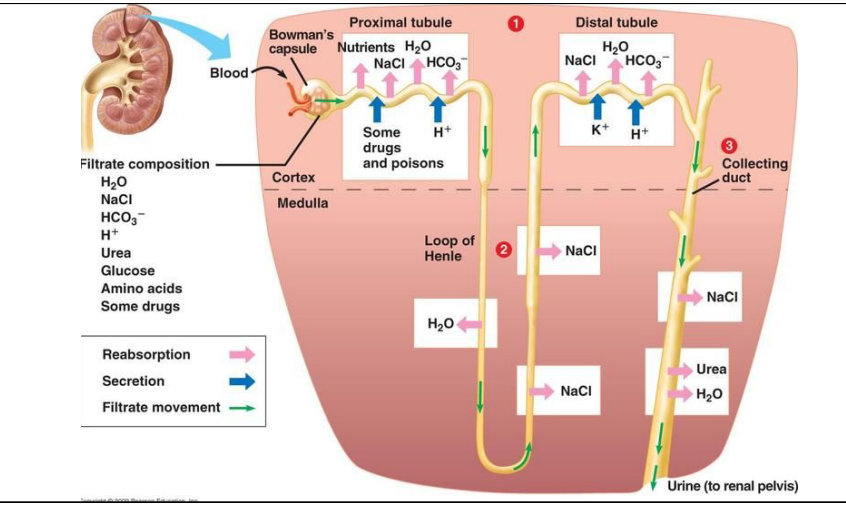
tubular reabsorption and secretion: distal tubule
occurs in cortex
salt, water, bicarbonate absorbed by body
potassium and hydrogen ions secreted into distal tubule

water reabsorption
opportunity for body to reabsorb salt and water through osmosis
increases concentration of filtrate → now urine
environmental and what you consume: dehydration, hot temps
collecting duct can change permeability regulated by ADH
reabsorption of salt, water, urea
to maintain water balance, humans must consume how much fluids?
1.5 to 2 L daily
A decrease in fluid intake by as little as 1% of ____ will cause..
your body mass will cause thirst
a decrease in fluid of 5% of your body mass will cause
extreme pain and make you collapse
a decrease in fluid of 10% of your body mass will cause
death
ADH
antidiuretic hormone
release of ADH allows body to conserve water, producing more concentrated urine
how is ADH released?
osmoreceptors in hypothalamus detect change in osmotic pressure
osmotic pressure: high is dehydration, low is overhydration
pituitary gland releases or prevents release of ADH into blood depending on current fluid amount
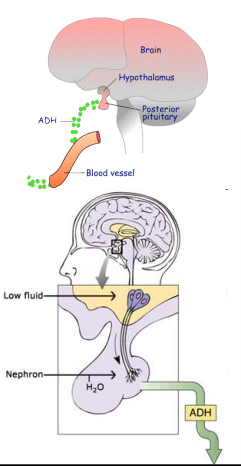
high blood osmotic pressure
blood is too concentrated = dehydration
osmoreceptors in hypothalamus detect change
you feel thirsty and hypothalamus send signal to pituitary gland
pituitary releases ADH
ADH travels to kidney
increases permeability of collecting duct, more water reabsorption
drink water due to thirst
lowers osmotic pressure

ADH not present
85% of water reabsorbed into body from proximal tubule and descending loop of Henle regardless of ADH presence
Distal tubule and collecting duct cannot reabsorb since no ADH
15% of water is lost in urine
Diluted, watery, pale urine
ADH present
makes upper part of distal tubule and collecting duct permeable
Water diffuses into peritubular capillaries
High concentration of salt in interstitial fluid here
Interstitial fluid
watery fluid filling spaces between cells that delivers oxygen and nutrients from capillaries to cels and caries away waste
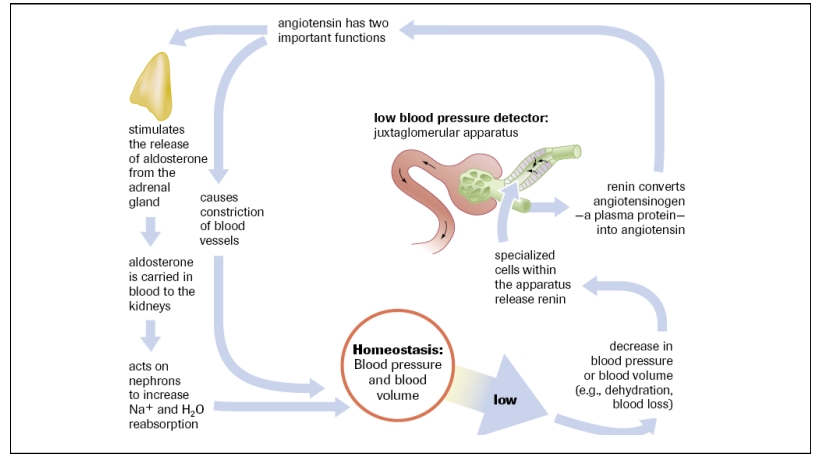
Low blood pressure and blood volume
RAAS system
dehydrated
JGA detects low bp and releases renin
Renin converts a protein in blood to angiotensin
Angiotensin increases bp signals adrenal gland to secrete aldosterone
Aldosterone carried in blood to kidneys
Aldosterone increases sodium and water absorption
Urinalysis
non invasive tests for kidney function
Tests for kidney damage
Diabetes mellitus
Kidney stones
Bacterial infections
Pregnancy
Dehydration
Acetone and ketones, albumin (protein), bilirubin, calcium, colour and clarity, glucose, pH, urea, Uris acid values in accepted healthy urine test
Acetone and ketones, albumin (protein), bilirubin, glucose: 0
Calcium: less than 150 mg/day
Colour and clarity: pale yellow to light amber; transparent