Body Systems- TISSUE + NEURON
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
order & organization
cell —> tissue —> organ —> organ system
4 major types of tissues
Epithelial Tissue
Connective Tissue
Muscle Tissue
Nervous Tissue
Epithelial Tissue (Func, structure, shapes, classificaion)
FUNC: cover and line other tissues and organs to protect them
STRUC: types are named by the shape and number of cells in the tissue
SHAPES: Squamous, Cuboidal, Columnar
# CLASSIFICATION: Simple, Stratified, Pseudostratified, Transitional
EX: Skin (stratified squamous)
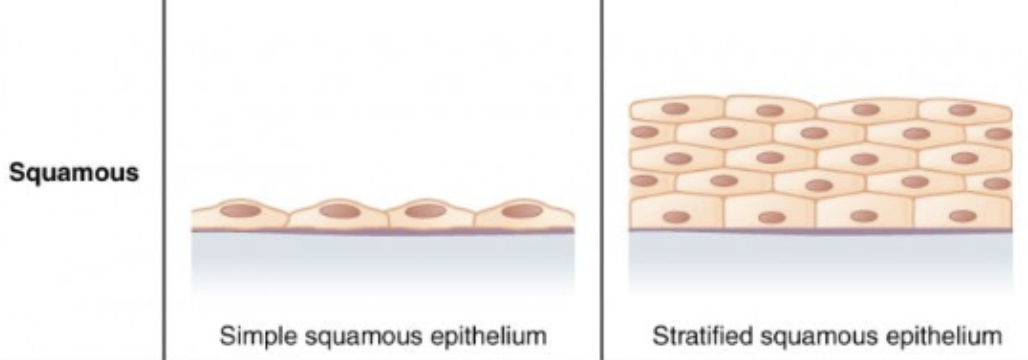
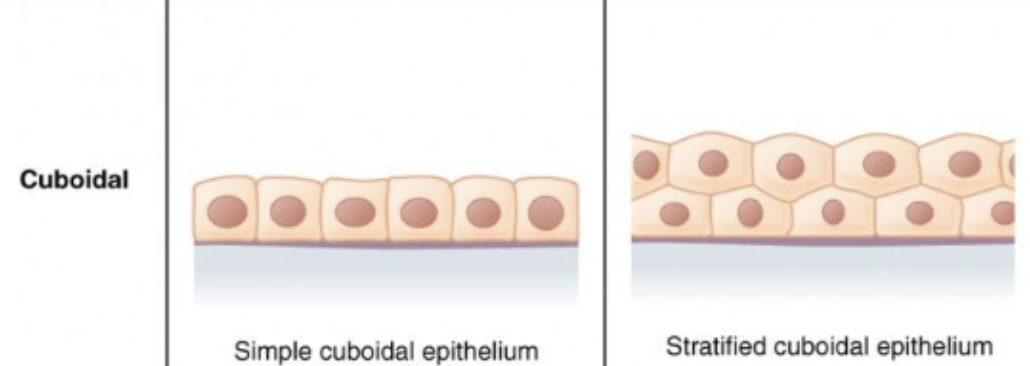
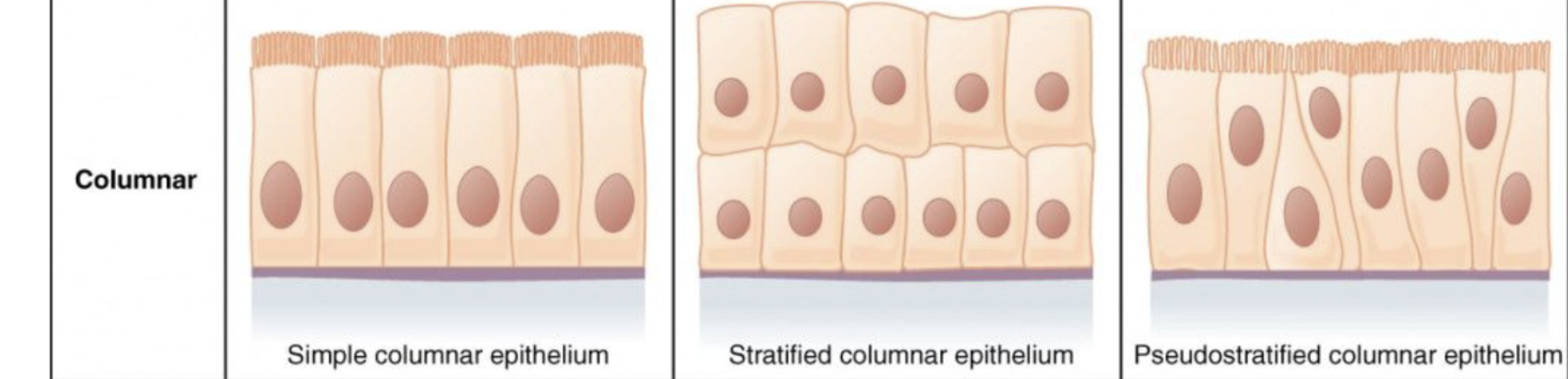
Simple
# Classification of Epithelial Tissue
Having ONE layer
Stratified
# Classification of Epithelial Tissue
Having MULTIPLE layers
Pseudostratified
# Classification of Epithelial Tissue
Having an ABNORMAL single layer where the nuclei do not line up (look zig-zaggy), so it looks like there are multiple layers (when there is not)
mostly with the columnar shape
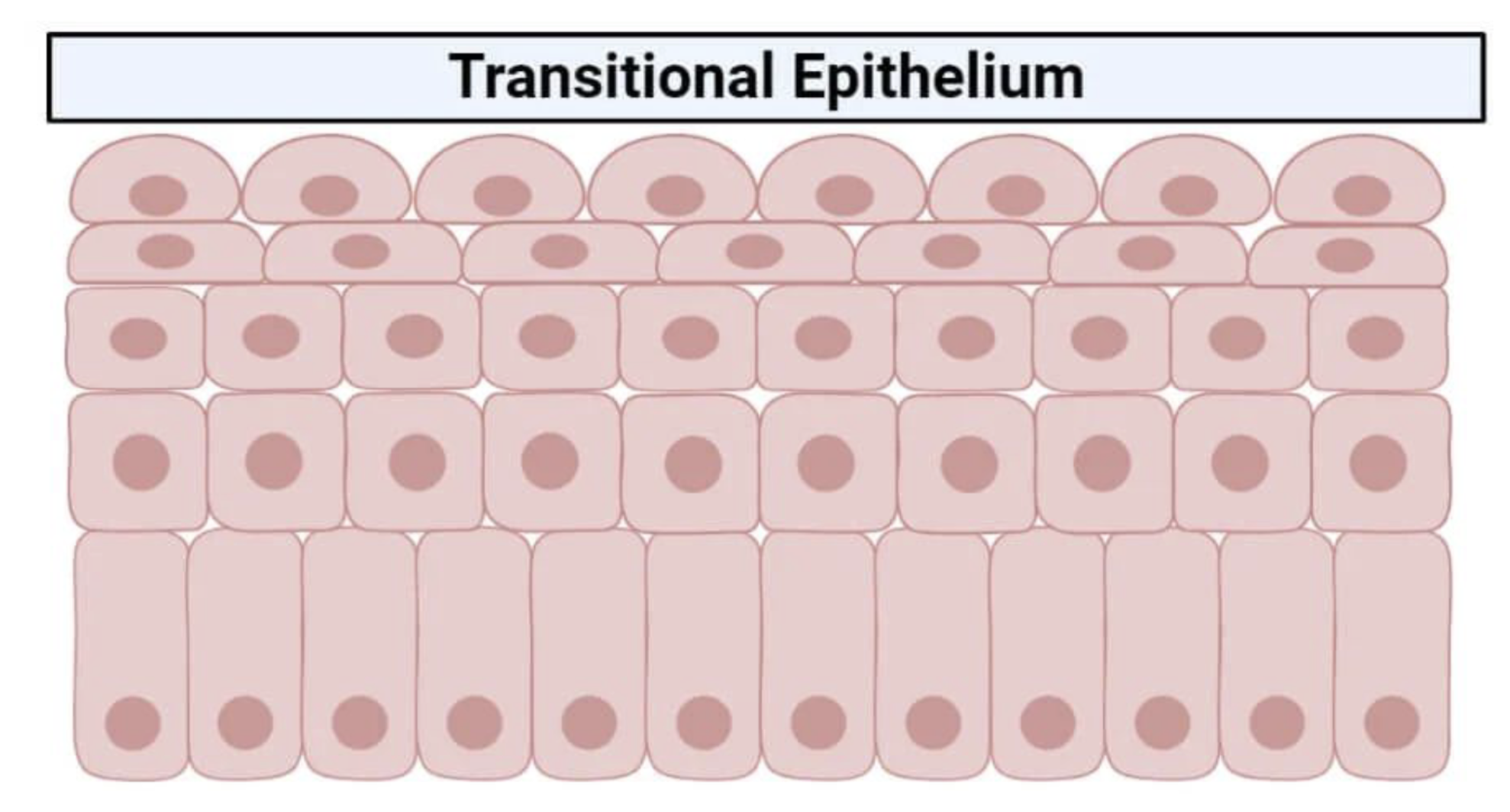
Transitional
# Classification of Epithelial Tissue
Having a top layer that is a DIFFERENT SHAPE than the bottom layers
Squamous
An Epithelial Tissue shape that is flat in shape
Cuboidal
An Epithelial Tissue shape that is shaped like a cube
Columnar
An Epithelial Tissue shape that is shaped like a column
Connective Tissue (Function, 6 Types)
FUNC: Bind and support other structures
TYPES: Loose Connective Tissue, Fibrous Connective Tissue, Adipose Tissue, Cartilage, Bone, Blood
Loose Connective Tissue
A type of connective tissue that holds organs in place
Fibrous Connenctive Tissue
A type of connective tissue that 1. connect muscle to bone (Tendon) or 2. connects bone to bone (Ligament)
Adipose Tissue
A type of connective tissue that stores fat and insulates the body
Cartilage
A type of connective tissue that absorbs shock to protect bones
Bone
A type of connective tissue that provides structure and movement
Blood
A type of connective tissue that carries substances throughout the body
Muscle Tissue (Funciton, 3 Types)
FUNC: Contract and generate force that can produce movement and other functions
TYPES: Skeletal, Smooth, Cardiac
Skeletal
Type of muscle tissue that does voluntary movements
EX: things you think about doing (walking, writing, raising your hand, running)
Smooth
Type of muscle tissue that does involuntary movements and is found in organs
EX: things you DO NOT think about doing (breathing, blinking, digesting)
Cardiac
Type of muscle tissue that does heart functions, involuntary
Nervous Tissue (Function, Structure, 3 Types)
FUNC: Senses stimuli (5 senses) and transmits information (EX: feeling it’s cold outside (sensing) —> getting a jacket (transmitting ))
STRUC: made of neurons
TYPES: Motor Neurons, Sensory Neurons, Interneurons

parts of a Neuron (7 terms)
Dendrites, Soma, Nucleus, Axon, Myelin Sheath (w/ Schwann Cell), Nerve ending
Make up the Nervous Tissue

Dendrites
INTAKE neurotransmitters using endocytosis
Soma
houses the neuron’s organells, neuron’s body
Nucelus
houses the neuron’s DNA
Axon
transmit the neurotransmitters from the dendrites to the nerve ending
Myelin Sheath
lines the Axon and functions as insulation
schwann cells
make up the myelin sheath
Nerve Ending
sends out neurotransmitters using exocytosis
Motor Neurons
Type of nervous tissue that creates movement
EX: does voluntary and involuntary movements
Sensory Neurons
Type of nervous tissue that intakes sensory stimuli
EX: detects the 5 senses
Interneurons
Type of nervous tissue that connects the motor or sensory neurons to the central nervous system (brain, spinal cord)
EX: interneurons in the spinal cord coordinate the knee-jerk reflex and allow the leg to kick