LING100 Phonetics
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Phonetics
______: The study of human speech sounds
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA)
______: A comprehensive system for transcribing the sounds of the worlds languages
Pulmonic egressive airstream
“going out from the lungs,” used by all languages to speak,
Speech begins in the lungs, we need breath to make sounds
Consonants
Made with some sort of closure/obstruction in the vocal tract
Voiced or voiceless
Vowels
No obstruction of air in the vocal tract
Always voiced
Stop
______: Complete closure in the oral cavity
Fricative
______: Continuous airflow through narrow opening
Affricate
______: A stop released with friction (stop + fricative)
tʃ
dʒ
Nasal
______: A stop with air released through nasal cavity
Liquid
______: Produced with contact + free passage of air.
Glide
______: A vowel that behaves like a consonant
Bilabial
______: Sounds are made using both lips, usually the lower lip is the articulator, as it is raised to meet the upper lip
Labiodental
______: Sounds are made using the lower lip and upper teeth
Interdental
______: Sounds involve the front of the tongue against the upper teeth
[ð] [θ]
Alveolar
______: Sounds are made at the alveolar ridge, with the tongue tip or blade
[t] [d]
Alveopalatal
______: Sounds are made behind the alveolar ridge.
Palatal
______: Sounds are produced using the tongue body against the hard palate
[j]
Velar
______: Sounds are produced using the tongue dorsum raised towards the velum or soft palate, its softer
[g] [ŋ] [k]
Glottal
______: Sounds made at the glottis, which is the space between the vocal folds inside the larynx.
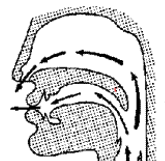
Nasal Sounds
Velum is lowered
Air flows through mouth and nose
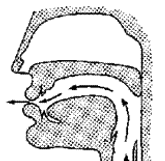
Oral Sounds
Velum is raised
Air flows through mouth only
/p/
Voiceless
Bilabial
Stop
/b/
Voiced
Bilabial
Stop
/m/
Voiced
Bilabial
Nasal
/f/
Voiceless
Labiodental
Fricative
/v/
Voiced
Labiodental
Fricative
/θ/
Voiceless
Interdental
Fricative
/ð/
Voiced
Interdental
Fricative
/t/
Voiceless
Alveolar
Stop
/d/
Voiced
Alveolar
Stop
/s/
Voiceless
Alveolar
Fricative
/z/
Voiced
Alveolar
Fricative
/n/
Voiced
Alveolar
Nasal
/r/
Voiced-retroflex
Alveolar
Liquid
/ʃ/
Voiceless
Postalveolar
Fricative
/ʒ/
Voiced
Postalveolar
Fricative
/tʃ/
Voiceless
Postalveolar
Affricate
/dʒ/
Voiced
Postalveolar
Affricate
/j/ JAY
Voiced
Palatal
Glide
/k/
Voiceless
Velar
Stop
/g/
Voiced
Velar
Stop
/ŋ/
Voiced
Velar
Nasal
/w/
Voiced
Velar
Glide
/h/
Voiceless
Glottal
Fricative
/ʔ/
Voiceless
Glottal
Stop
/i/
Front
High
Unrounded
Tense
/e/
Front
Mid
Unrounded
Tense
/u/
Back
High
Rounded
Tense
/o/
Mid
Back
Tense
Rounded
/ɑ/
Back
Low
Unrounded
Tense
/aj/
diphthong
/aw/
diphthong
/oj/
diphthong
/ɪ/
Front
High
Unrounded
Lax
/ɛ/
Front
Mid
Unrounded
Lax
/æ/
Front
Low
Unrounded
Lax
/ʊ/
High
Back
Rounded
Lax
/ʌ/
central
mid
unrounded
lax
Stressed
/ə/
Central
Mid
Unrounded
Lax
Unstressed
Stress
______: Cover term for the combined effects of pitch, loudness, and length— the result of which is perceived as prominence
Primary stress
______: Most prominent stress, marked with acute accent [ˊ]