Modelling Competitive Supply
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
W3L3
Last updated 3:34 PM on 6/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
1
New cards
What do supply decisions depend on?
Supply decisions depend on the external environment, especially the strategic environment in which the firm finds itself
* Monopoly (only firm in market) → only external constraint faced is market demand curve
* Perfect competition (one of a large number of firms in the market) → heavy constraints
* Oligopoly (among a handful of firms) → must consider other firm’s responses
* Monopoly (only firm in market) → only external constraint faced is market demand curve
* Perfect competition (one of a large number of firms in the market) → heavy constraints
* Oligopoly (among a handful of firms) → must consider other firm’s responses
2
New cards
What are the assumptions of perfect competition?
1. Many small firms
2. Profit-maximisers
3. Price takers
4. Homogenous products
5. No barriers to entry or exit
6. Perfect information
3
New cards
What is residual demand?
Residual demand refers to the demand curve faced by an individual firm operating in a market where there is perfect competition.
* For an individual firm in a perfectly competitive market, the firm is considered a price taker
* As a result, the individual firm's demand curve is perfectly elastic, or horizontal (the aggregate demand curve slopes downwards). This implies that the firm can sell as much output as it wants at the prevailing market price without affecting the price itself.
* For an individual firm in a perfectly competitive market, the firm is considered a price taker
* As a result, the individual firm's demand curve is perfectly elastic, or horizontal (the aggregate demand curve slopes downwards). This implies that the firm can sell as much output as it wants at the prevailing market price without affecting the price itself.
4
New cards
What is the first order and second order condition?
FOC: states that firms should set output level where MR = MC such that p = MC (because MR is same as price under perfect competition where firms are price takers) → derivative of py - c(y) = 0
\
SOC: helps determine whether the output level obtained from the FOC indeed leads to maximum profit by assessing concavity → second derivative of py - c(y) less than or equal to 0 (meaning that the FOC is a maximum)
\
SOC: helps determine whether the output level obtained from the FOC indeed leads to maximum profit by assessing concavity → second derivative of py - c(y) less than or equal to 0 (meaning that the FOC is a maximum)
5
New cards
Which costs matter more in determining whether profit-maximising, price taking firms should stay in business: fixed or variable costs?
Variable costs matter more. If p < AVC then the firm will close. If price is above minimum AVC, firm can cover variable costs and make some contribution to fixed costs
6
New cards
What is the formula for producer surplus?
Producer surplus = Revenue - Variable costs
7
New cards
What is the formula for profit?
Profit = Revenue - Total Costs
or
Profit = Producer Surplus - Fixed Costs
or
Profit = Producer Surplus - Fixed Costs
8
New cards
What are the implications of long-run competitive supply?
* There are no fixed costs, so AVC = AC → shutdown conditions depend entirely on AC
* Entry and exit are possible → these conditions imply there are zero economic profits
* Entry and exit are possible → these conditions imply there are zero economic profits
9
New cards
How does more entry of firms into the market influence the supply curve?
More entry makes aggregate supply more and more flat (more price elastic)
10
New cards
Draw diagrams illustrating the long-run impact when firms make profit in the short-run
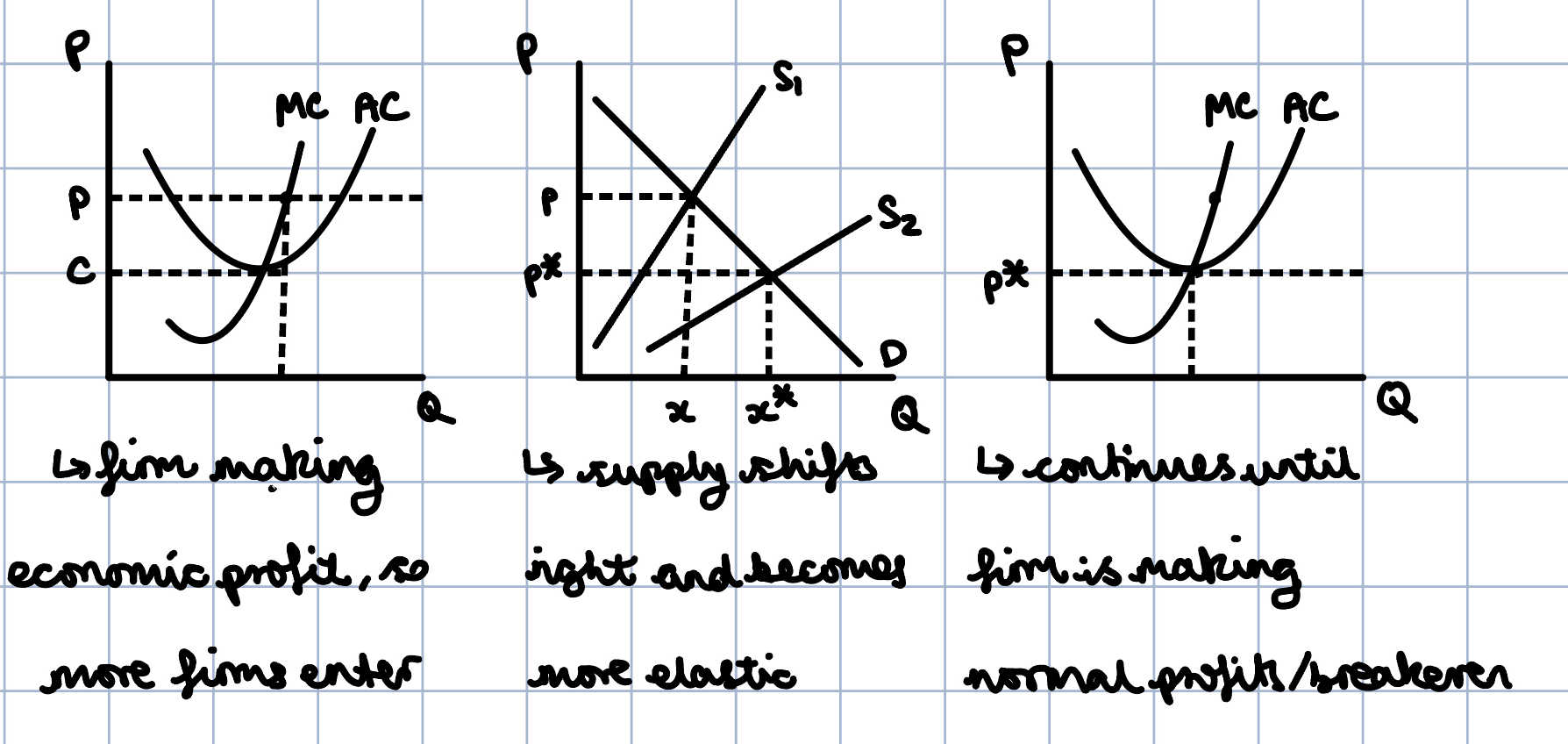
11
New cards
Define long-run equilibrium
Long-run equilibrium is a state where there is neither net exist or entry and so all firms make zero profits