Marketing Final
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
means-end theory
seeks to understand how consumers translate product or service characteristics and consequences of use into personal, self-relevant
values.
Means-end value chain
a way to understand what drives consumers by
linking attributes of products with particular consequences to an
underlying value.
Zone Diagram
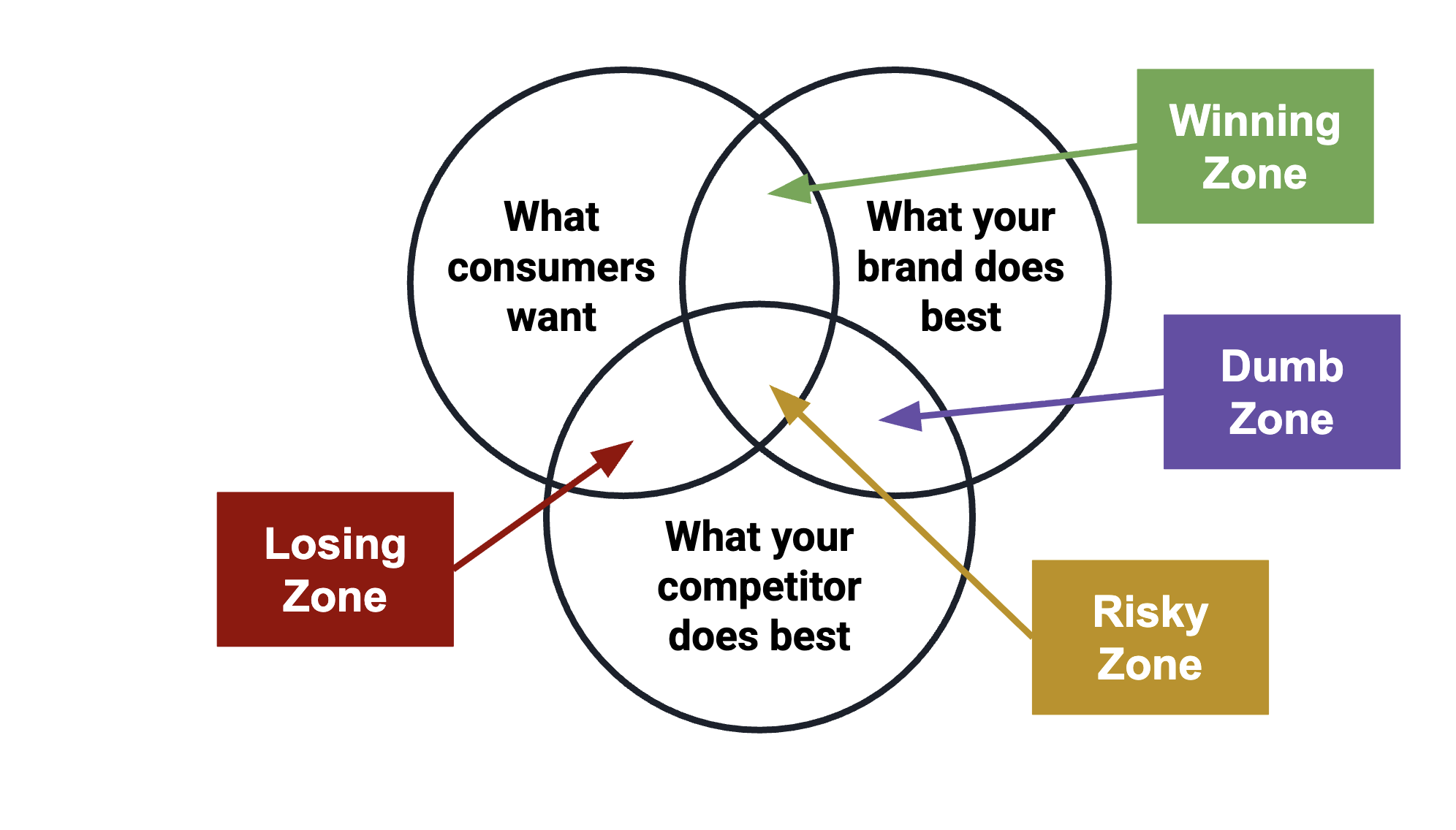
An effective marketing strategy
targets the _____ of their key
target market.
Values
Brand Equity
is a company’s reputation in the marketplace.
Positioning
is the process by which your business
creates an image or identity in the minds of your core market.
Strategic positioning enhances brand equity.
SWOT analysis
a qualitative tool. It provides a process for
making meaning out of an organization’s most prominent characteristics
SWOT Strengths
(Internal factor)Characteristics of the business or a team that give it an advantage over others in the industry.
● Positive tangible and intangible attributes, internal to an organization.
● Beneficial aspects of the organization or the capabilities of an organization, which includes human competencies, process capabilities, financial resources, products and services, customer goodwill and brand loyalty.
SWOT weaknesses
(Internal factor) Characteristics that place the firm at a disadvantage relative to others.
● Detract the organization from its ability to attain the core goal and influence its growth.
● Weaknesses are the factors which do not meet the standards we feel they should meet. However, weaknesses are controllable. They must be minimized and eliminated.
SWOT Opportunities
Chances to make greater profits in the environment
● External attractive factors that represent the reason for an organization to exist & develop.
● Arise when an organization can take benefit of conditions in its environment to plan and execute strategies that enable it to
become more profitable.
● Opportunities may arise from market, competition, industry/government and technology.
SWOT Threats
External factors, beyond an organization’s control, which could place the organization’s mission or operation at risk.
● Arise when conditions in external environment jeopardize the reliability and profitability of the organization’s business.
● Compounded vulnerability when relate to weaknesses.
● Threats are uncontrollable. When a threat comes, the stability and survival can be at stake.
Limitations of SWOT analysis
Produces vague and oversimplified lists of general priorities.
● Does not provide sufficient context for strategy
optimization.
● Quality depends on the brainstorming team.
● A company’s “true” situation is constantly changing.
Segmentation
is about IDing the different types of consumers in the
market.
Targeting
is about finding the right consumers for your product.
Positioning
is about the follow-through (i.e., making sure
Your target customers see the value of your product).
Market segmentation
dividing the mass market into subsets of consumers who share common needs, characteristics, or behaviors
Target Market
the segment(s) toward which a firm’s marketing efforts are directed.
Positioning
differentiates a product from competitors
and explains how it satisfies consumers’ needs.
Demographic segmentation
Based on vital population statistics.
Age
● Gender
● Income
● Education
● Occupation
● Marital status
● Ethnicity/race
Geographic segmentation
Based on physical location of consumers.
● Total population
● Population density
● Regional differences
● Climate
Psychographic segmentation
divides a population based on psychological traits, values, interests, lifestyles, and personality characteristics.
● Lifestyle and habits
● Values and beliefs
● Personality traits
● Activities and interests
● Challenges
Behavioral segmentation
divides a population based on behaviors or decision-making patterns.
● Purchase behavior
● Usage rate
● Usage occasion
● Customer Loyalty
● Benefits sought
How do you determine a target market?
Option 1: Look at your current customer base. Who are your current customers, and why do they buy from you?
Option 2: Evaluate your competition. Who are your competitors targeting? Don't go after the same market. You may find a niche market that they are overlooking.
Option 3: Analyze your product/service. Next to each feature, list the benefits it provides (and the benefits of those benefits). Once you have your benefits listed, make a list of people who have a need that your benefit fulfills.
Option 4: Choose specific demographics and psychographics to target. Figure out not only who has a need for your product or service, but also who is most likely to buy it.
primary target audience
The group you envision thinking, feeling, or behaving differently after interacting with the organization
secondary target audience
The people who are most likely to communicate with your primary target
marketing
the activity, set of institutions, and
processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.
Source: American Marketing Association (2022)
key consumer benefit
is the one benefit that is unique to the client’s product or can be positioned as big or important.
goal of marketing campaign
creatively convey a key consumer benefit (to a target) to achieve some marketing objective(s).
Visual uniformity
happens when layouts, representative
characters, slogans/taglines, and representative color combinations cohesively center around the key consumer
benefit.
Semiotics
The study of meaning making. (eg: a sign, we see octogonal stop sign and know it means stop)
Signifier
The form that the sign takes (e.g., a rose)
Signified
The concept or meaning that the sign represents
(e.g., a rose can signify passion)
Semiotics: Advantages
Breaks down a message into
meaningful components.
Allows us to look for patterns
within a message.
Helps determine cultural and
social conventions.
Placement
Consider where the product is in relation to
the camera. Placement defines what the consumer needs to see to understand the
message.
Color
Color also reflects emotion. Spot color is an excellent way to highlight critical areas. A lack of color can also draw the eye.
Typography
Type also reflects emotion. It can be used to maximize understanding of a message.
Verbal Uniformity
_______________happens when creative
messages promote one idea or key consumer
benefit.
Search Engine Optimization
(SEO)
is the process of taking a web page and improving it in order to increase visibility on search engines via unpaid (“organic”) results (SEOMoz 2010).
Common user intent types
Informational: Searching for information. Example: “What is the best type of laptop for photography?”
Navigational: Searching for a specific website.
Example: “Apple”
Transactional: Searching to buy something. Example:“good deals on MacBook Pros”
Organic link-building
Internal links are links you insert throughout your
website to link to other relevant pages or content. What is the quality of your links within the website?
● Design / Link structure
● Keywords (in title, links, etc.)
● Page content
Black Living Data
Black living data is data on and for black lives and experiences
Bonding social capital
connects people based on a sense of common identities, such as family, close friends, and people who share our culture or ethnicity.
Bridging social capital
connections that stretch beyond a person's immediate circle of friends and family.
creative brief
ROI Formlua
(money gained- money spent)
—------------------------------------ x100
(money spent)
KPI formula
Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
Cost of sales+cost of marketing
—----------------------------------------
New customers acquired
Customer lifetime value
How much can one customer provide over a lifetime
Average total order amount x average number of purchases per year x retention rate
If we are not achieving the return we may want to choose other strategies to increase this ratio
Linking social capital
is social connections to people or groups that are further up or lower down in the social ladder
Quantitative market research
Key Performance Indicator (KPI)
A measurable component that can be used to
demonstrate the efficiency with which a company achieves their business objectives.
ethnographic research
IMC campaign
consists of a connected series of deliverables running for a set period of time centered around a key consumer benefit, addressing the objectives, and is implemented through tactics.
Promotional mix
includes any combination of the
following:
● Public relations
● Advertising (newspaper, magazine, radio, television)
● Direct marketing and sales promotion
● Internet and social media
● Mobile Knowing the strengths and
Weaknesses of different mediums
is essential.
IMC
works to interactively engage a specific individual, using
a specific message through specific media outlets.A planning process designed to assure that all brand
contacts received by a customer or prospect for a product,
service, or organization are relevant to that person and
consistent over time.
IMC plan
One visual/verbal message, multiple media.
● Situation analysis (SWOT)
● Marketing objectives
● Marketing strategy
● Target market analysis
● Creative strategies
● Implementation tactics
● Evaluation
reflexivity
turning the researcher’s lens back onto oneself to recognize and take responsibility for one’s own situatedness within the research and the effect that it may have on the setting and people being studied, questions being asked, data being collected, and its interpretation” (berger, 2015, p. 220)
Graph theory
incorporates mathematical structures used to
model pairwise relations between
objects.
Social Networks
is a social structure made up of a set of social
actors (such as individuals or organizations), sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactions
between actors.
SMART
Specific: Have you stated the objectives in a clear and precise manner that also defines what your organization is interested in achieving
Measurable: Is there a way to quantify your progress and success while working to achieve your objectives
Achievable: Are the marketing objectives you are setting reasonable and doable? Are u making sure the goals aren't set too high to achieve
Relevant: Does this objective help the organisation achieve its overall goal or fulfill its mission? Is it in line with the identity and branding of the organisation
Time-specific: when would u prefer to achieve the goals you have set? Each specific objective should have a date of completion.
Strategy should match the overall goal we've established as needed. If the goal is to grow brand equity, our objective might be to increase satisfaction scores on 5 websites
STP marketing model
S- segmentation
Divide the market into groups of customers
T- Targeting
Select the most attractive segments to focus marketing on
P- positioning
Determine how to position your product for each target segment
Verbal uniformity
happens when creative
messages promote one idea or key consumer
benefit.
Visual uniformity
happens when layouts, representative
characters, slogans/taglines, and representative color combinations cohesively center around the key consumer benefit.