108.5 Microscopic Examination Chapter07 2022.23
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What kind of elements are seen in a microscopic examination?
Red blood cells (RBCs)
WBC
Epithelial cells
Casts
Bacteria
Yeast
Parasites
Mucus
Spermatozoa
Crystals
Artifacts
What field should casts be look on
Low power field (10x)
Sediment Stains
Increases the overall visibility of sediment using bright-field microscopy by changing refractive index
imparts identifying characteristics of cellular
structures = Nuclei, Cytoplasm, Inclusions
Supravital Stains
Sternheimer-Malbin stain : crystal violet /Safranin O
Useful in the differentiation between WBCs and renal tubular epithelial cells
provides clearer delineation of structure and contrasting colors of the nucleus and cytoplasm
Acetic Acid
Acidic acid will enhance nuclear detail of WBC and epithelial cells
RBCs are lysed by the acetic acid
Lipid Stains
Oil Red O and Sudan III stains are used and polarizing microscopy
Triglycerides and neutral fats stain orange-red
Cholesterol does not stain and capable of polarization
Gram Stain
Used primarily for the differentiation between gram-positive (blue) and gram- negative (red) bacteria
Identification of bacterial casts
Hansel Stain
Preferred stain for urinary eosinophils
Consists of methylene blue and eosin Y in methanol
Prussian Blue Stain
Hemosiderin granules seen with hemoglobinuria
Prussian blue stain for iron is used and stains the hemosiderin granules a blue color
Bright Field
Most often used in routine urine testing
Low light with condenser in low position
Phase-Contrast
phase-contrast objective lens and a matching condenser
enhances visualization of elements with low refractive indices, such as hyaline casts, mixed cellular casts, mucous threads, and trichomonas vaginalis
objects with low refractive index
Polarizing
Used to identify crystals, fat elements which are bifringent
Aids in identification of cholesterol in oval fat bodies, fatty casts, and crystals
Dark- field
Aids in identification of Treponema pallidum
Fluorescence microscopy
allows visualization of naturally fluorescent microorganisms or those stained by a fluorescent dye, including labeled antigens and antibodies
Interference- contrast
produce a three- dimensional microscopy image and layer- by- layer imaging of a specimen
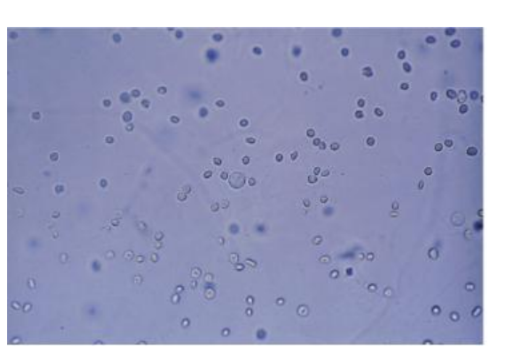
RBC ( red blood cells)
Smooth, nonnucleated, biconcave disks ~7 µm
Crenated in hypersthenuric urine
Ghost cells in hyposthenuric urine
Identify using high power
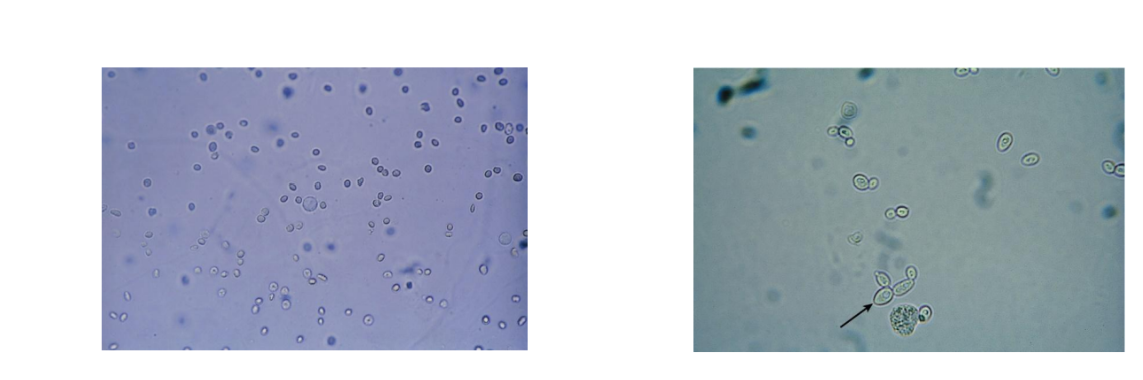
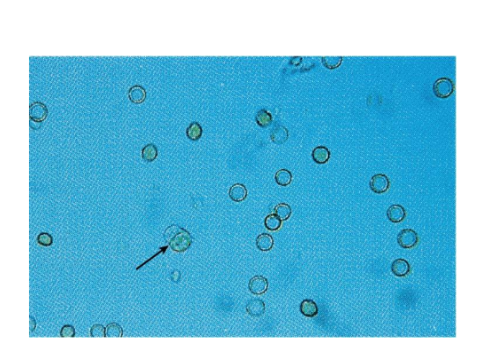
WBC (White blood cell)
12 µm
Neutrophil is predominant
Identify under high power
Glitter cells
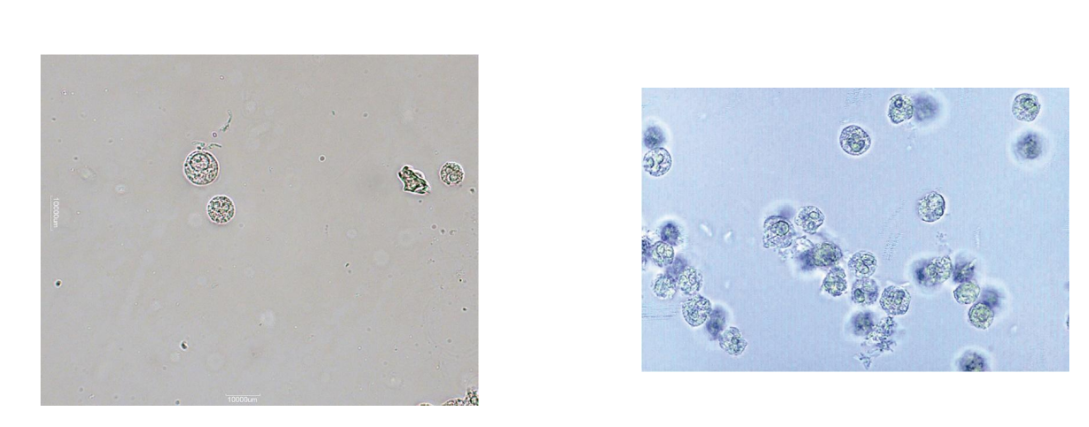
What are the three types of epithelial cells
squamous, Transitional, Renal tubular epithelial
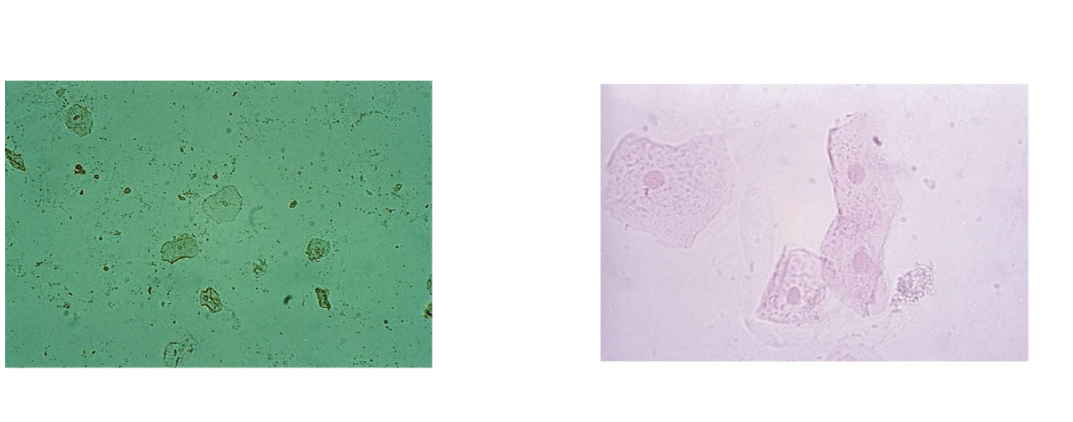
Squamous
Largest cell in urine
Good for focusing microscope
Rare, few, moderate, many
lpf or hpf per laboratory
Normal sloughing
Contamination if not midstream clean-catch
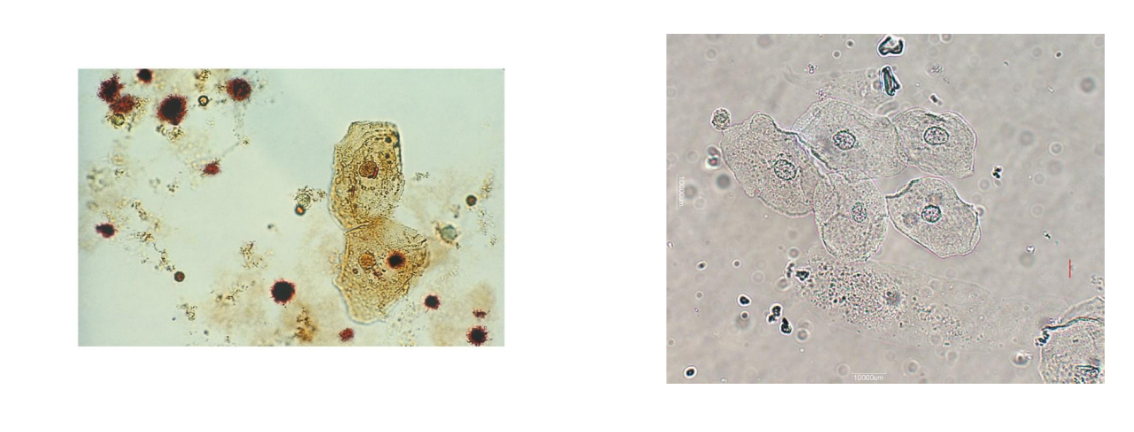
What are the three forms of a transitional epithelial cells
Spherical, Polyhedral, Caudate
Spherical
absorb water in bladder and become
large and round
polyhedral
multiple sides
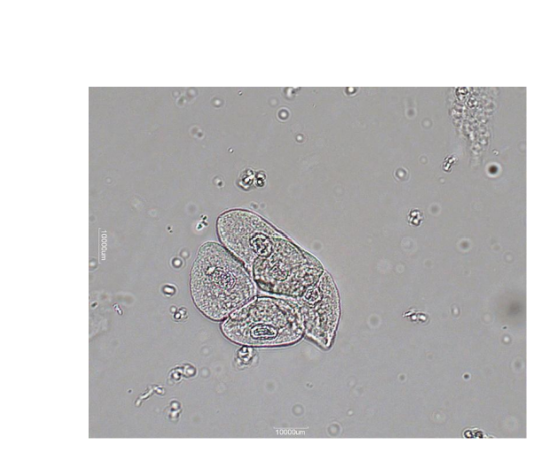
Caudate
has a tail
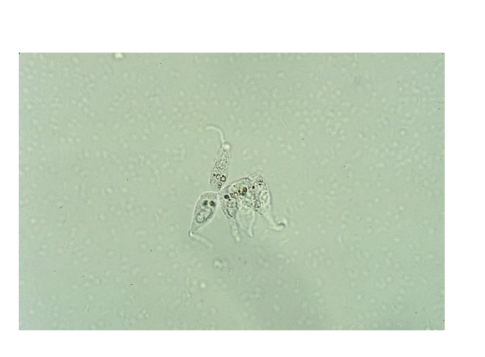
Transitional epithelial cell
Centrally located nucleus
Reported as rate, few, moderate, many
Syncytia = clumps
Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells
Size and shape vary with renal tubular area
Columnar = (larger)proximal convoluted tubule
(PCT)
Round, oval = (smaller) distal convoluted
tubule (DCT)
Cuboidal = collecting duct, never round
Three or more cuboidal cells = renal fragment
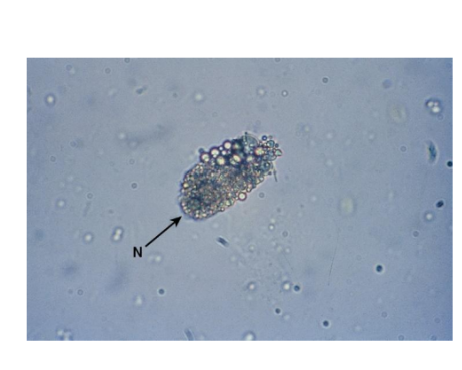
RTE in Proximal Convoluted Tubule Cells
Larger
than other RTEs
Columnar, convoluted,
rectangular
May resemble casts
Coarsely granular
cytoplasm
Examine for presence of
nucleus
RTE in Distal Convoluted Tubule Cells
Round or oval shaped,
smaller
May be mistaken for
WBCs or spherical
transitional cells
Observe the
eccentrically placed
nucleus to differentiate
from spherical
transitional
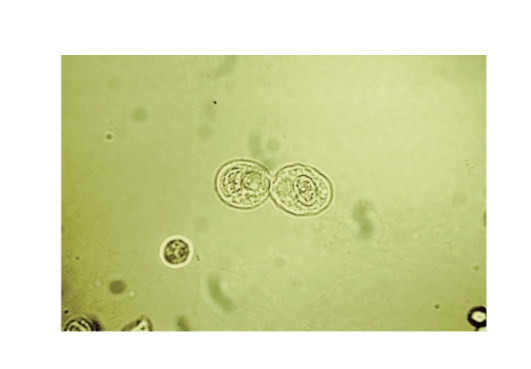
RTE in the Collecting Duct
Cuboidal, never round
At least one straight edge
Eccentric nucleus
Three or more cells in clump is renal
fragment; often large sheets
PCT and DCT not seen in clumps
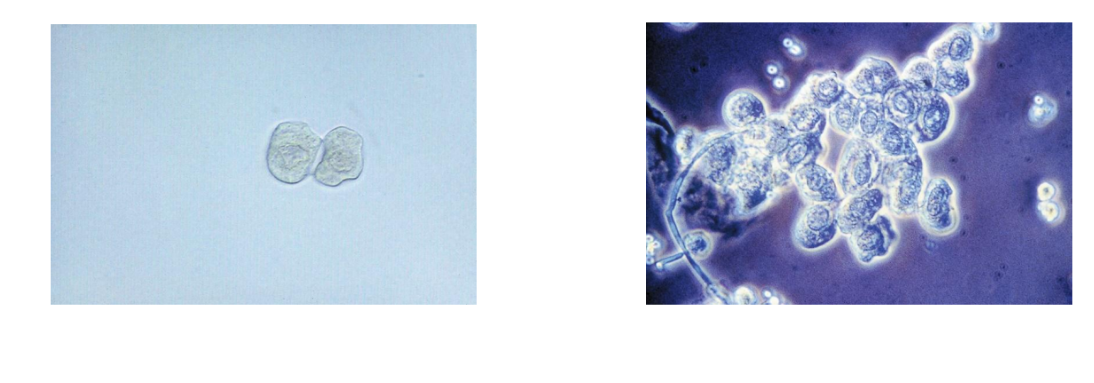
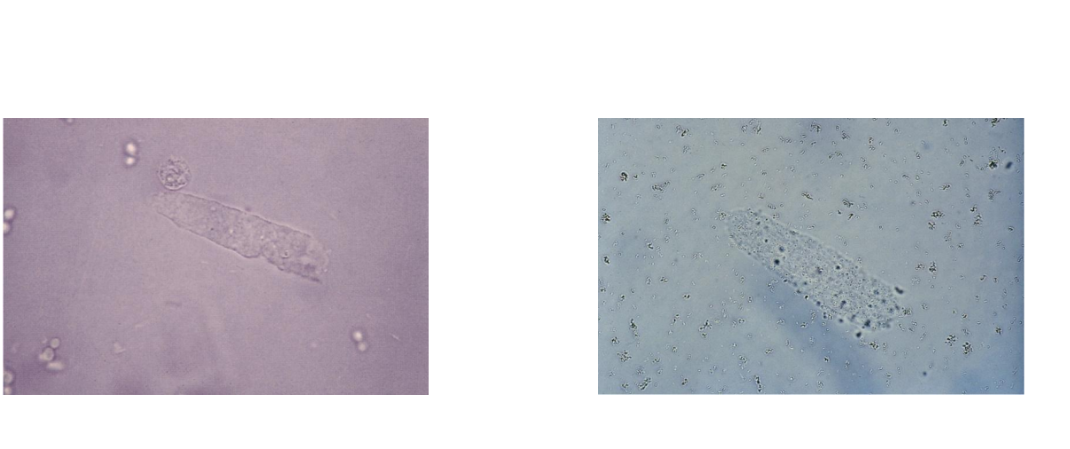
Hyaline Casts
Nonpathologic: stress,
exercise, heat exposure,
dehydration
Pathologic: acute
glomerulonephritis,
pyelonephritis, chronic
renal disease,
congestive heart failure
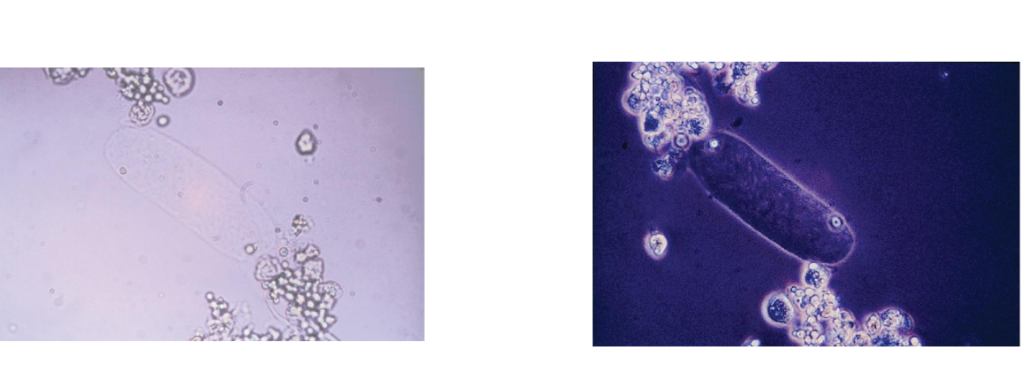
RBC Cast
Glomerular damage or nephron capillary
damage
Glomerular damage: dysmorphic RBCs and
elevated protein
May be seen following strenuous exercise
orange to red color
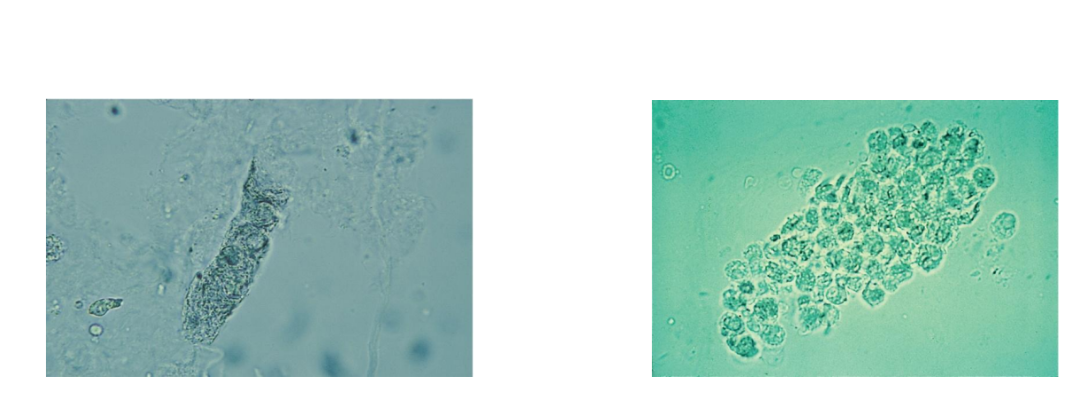
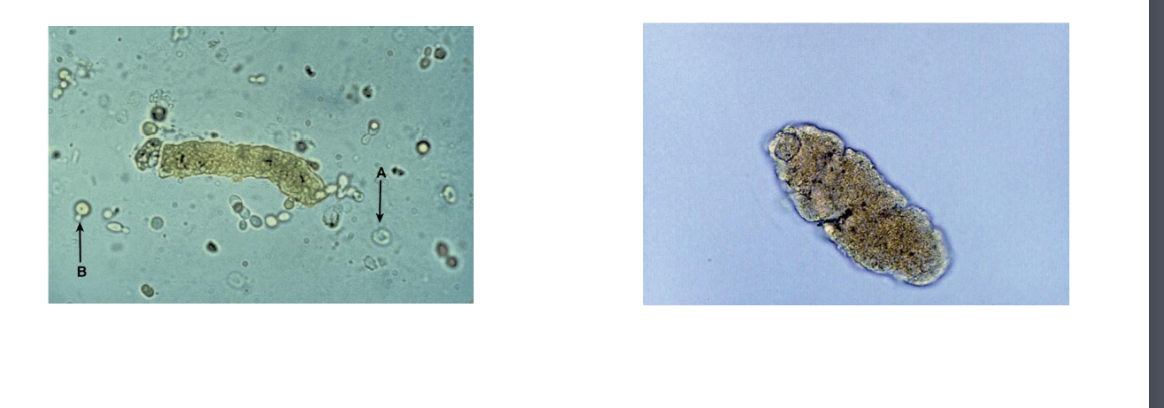
WBC Casts
WBC casts are seen with infection and
inflammation of the nephron
Pyelonephritis: WBC casts, bacteria
Acute interstitial nephtitis: WBC casts, no
bacteria
May accompany RBC casts in
glomerulonephritis
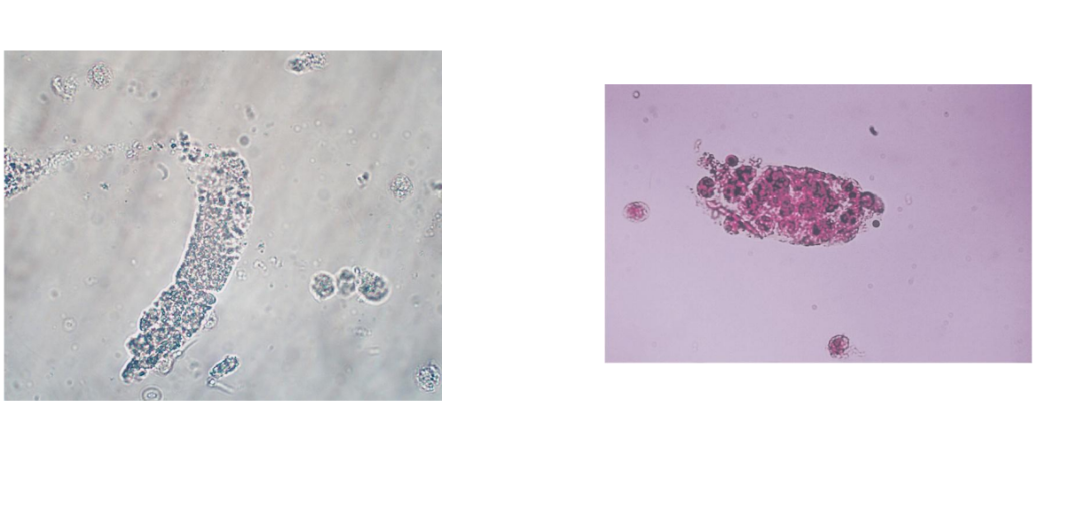
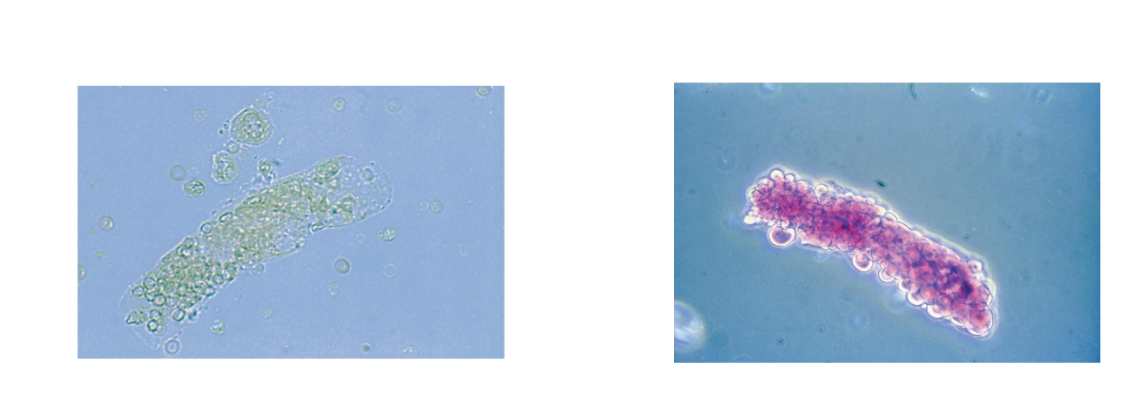
Bacterial Casts
Seen in pyelonephritis
May be pure bacteria or mixed with WBCs
Identification is difficult, resemble granular
casts
Look for free WBCs and bacteria
Confirm with Gram stain
Seen in pyelonephritis
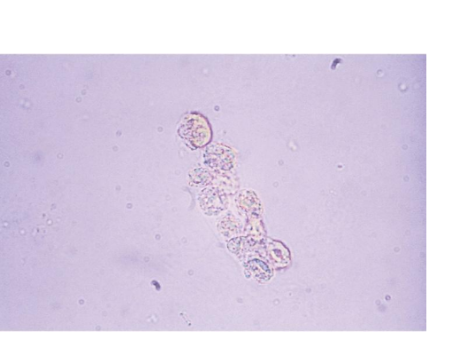
Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Casts
Tubular damage, heavy
metals, viral infections,
drug toxicity, graft
rejection, pyelonephritis
Cells may appear
bilirubin stained
Look for matrix to
distinguish fragments
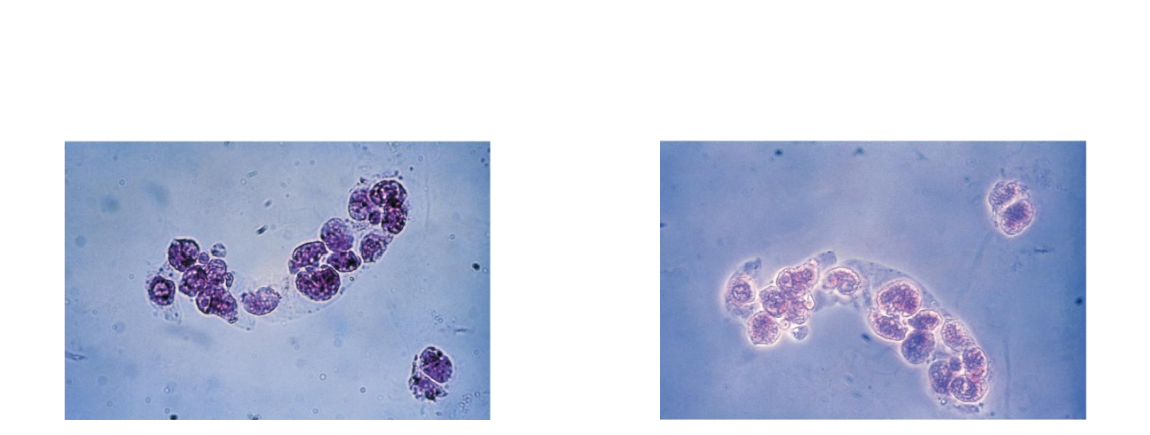
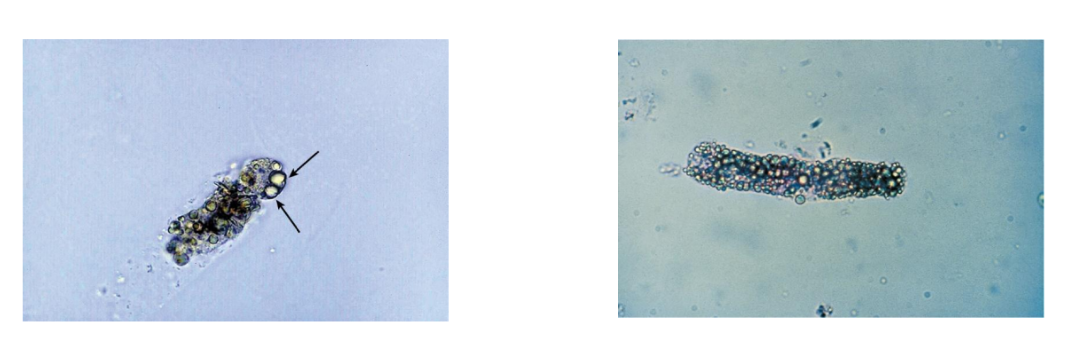
Fatty Casts
Nephrotic syndrome, diabetes, crush
injuries, tubular necrosis
Seen with oval fat bodies (OFBs) and fat
droplets
Highly refractile, OFBs may attach to matrix
Polarized microscopy and lipid stain
Triglycerides and neutral fats stain orange
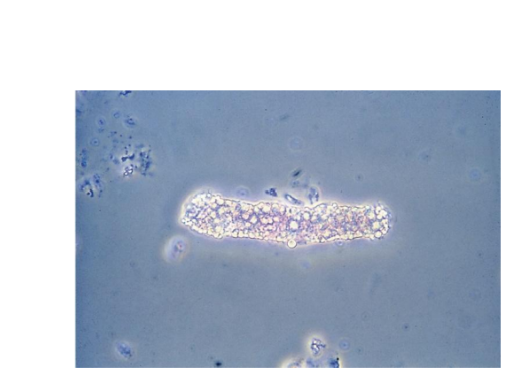
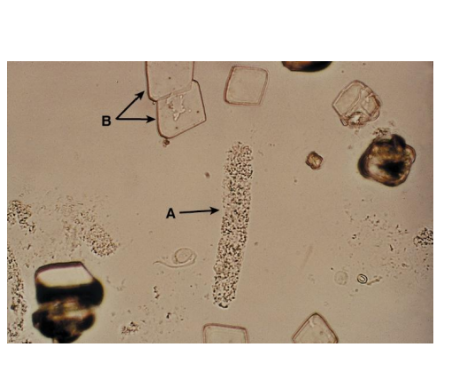
Granular Casts
Coarse and finely
granular
Granule origin
RTE lysosomes, excreted in
normal metabolism, more
after exercise and activity
Disease states:
Disintegration of cellular
casts and tubule cells or
protein aggregates filtered
by the glomerulus
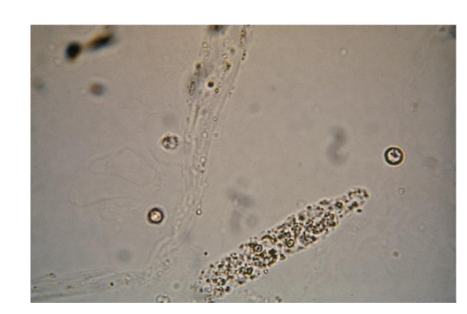
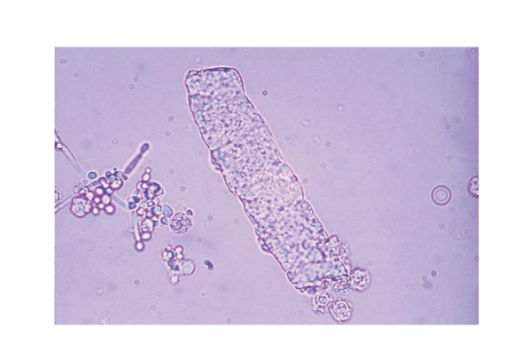
Waxy Casts
Brittle, highly refractile
Often fragmented with
jagged ends and
notches
Stains a homogenous
dark pink
Degenerated hyaline
and granular casts
Extreme urine stasis
Renal failure
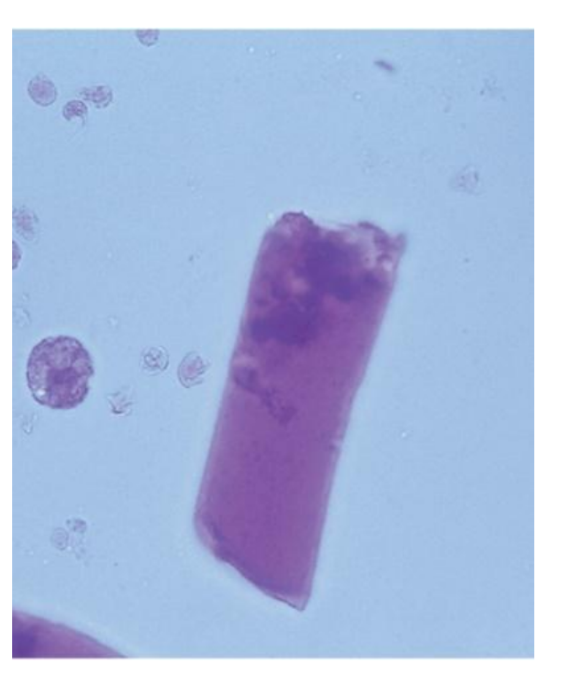
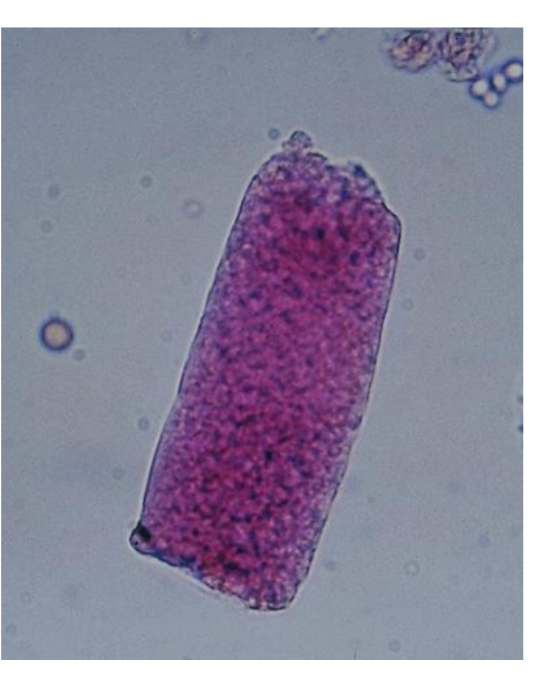
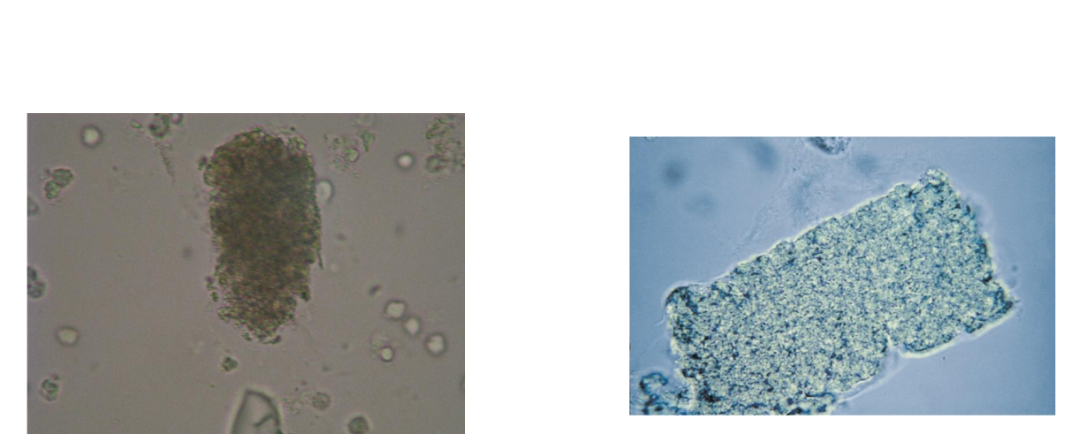
Broad Casts
Renal failure casts
Destruction and
widening
of the DCTs
Formation in the upper
collecting duct
All types of casts may be
broad
Most common are
granular and waxy
Bile stained from viral
hepatitis
What crystals are seen in Acidic Urine
Amorphous urates
Uric acid
Acid urates
Sodium urates
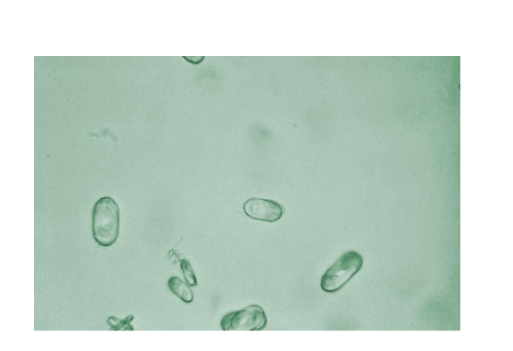
Calcium Oxalate
Amorphous urates
Yellow-brown granules microscopically
pH usually greater than 5.5
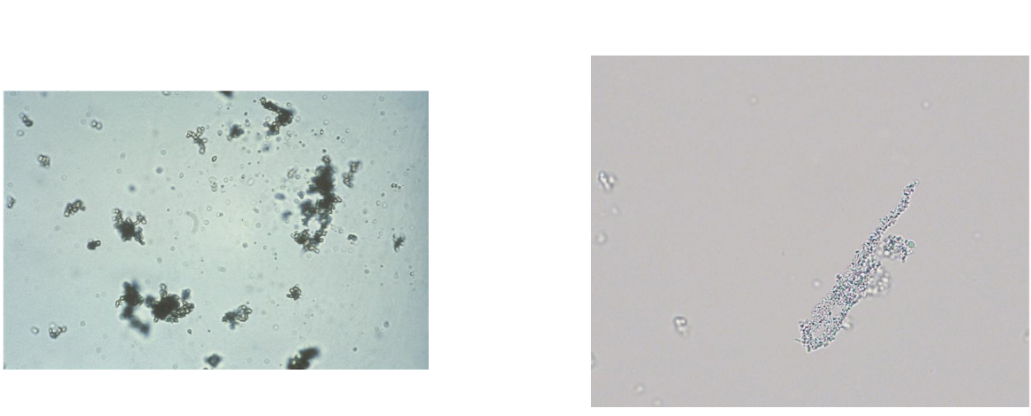
Uric acid crystals
Rhombic, whetstones, wedges, rosettes
Yellow-brown color
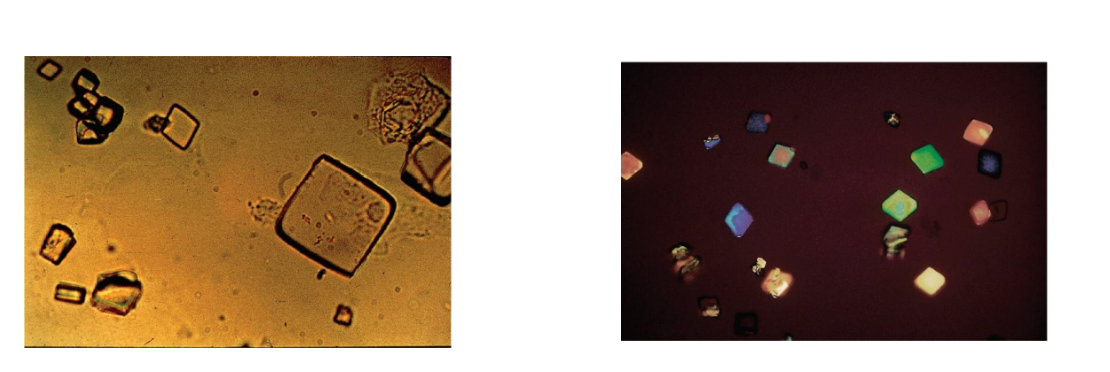
Calcium oxalate crystals
Acid and neutral pH
§
Dihydrate is envelope or two pyramid–shaped
Most common
§
Monohydrate is oval or dumbbell shaped
Antifreeze poisoning
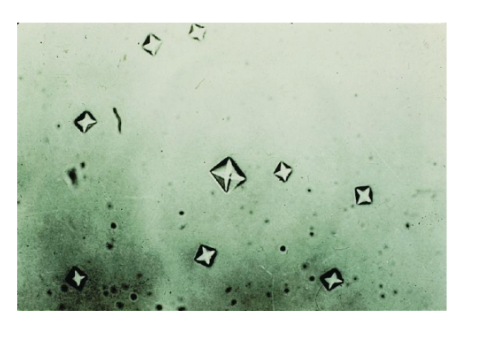
What crystals are seen in Alkaline Urine
Amorphous phosphates
Triple Phosphate
Calcium Phosphate
Calcium carbonate
Ammonium biurate
Amorphous phosphates
Alkaline pH and heavy white precipitate after
refrigeration
Granular in appearance
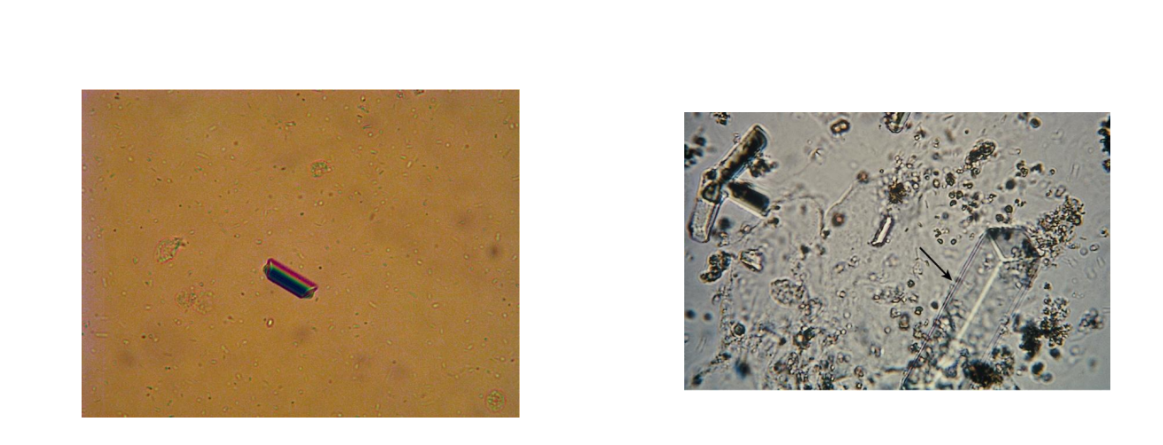
Triple phosphate
Colorless, prism, or coffin-
lid shaped
Highly alkaline urine and
urinary tract infections
(UTIs
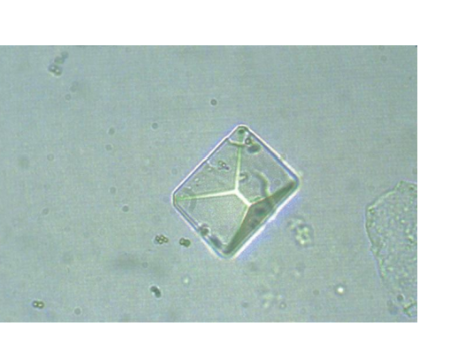
Calcium phosphate
Colorless, flat rectangles
and thin prisms in rosettes
Calcium carbonate
Small, colorless, dumbbell,
and spherical shapes
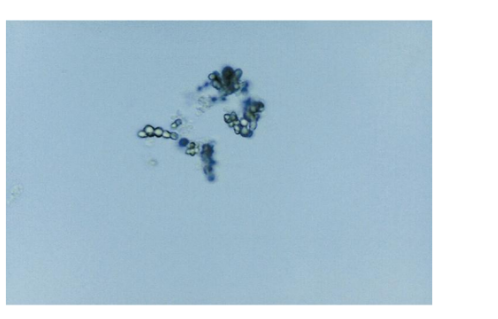
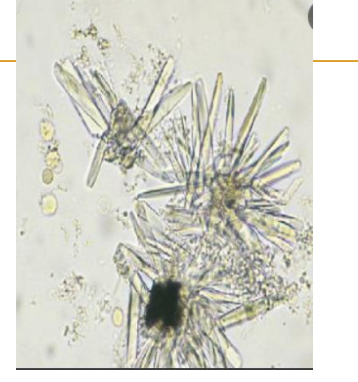
Ammonium biurate
Yellow-brown, spicule-
covered spheres;
“thorny apples”
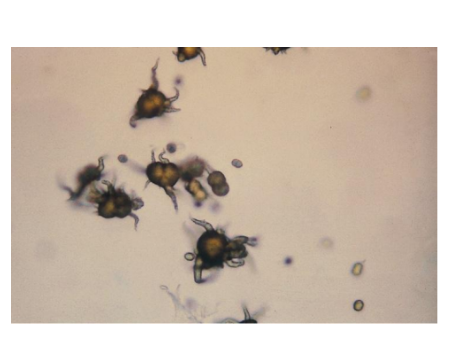
What pH is abnormal urine crystals are found on
Acidic urine
What are abnormal Urine Crystals
Cystine crystals
Cholesterol
Radiographic Dye
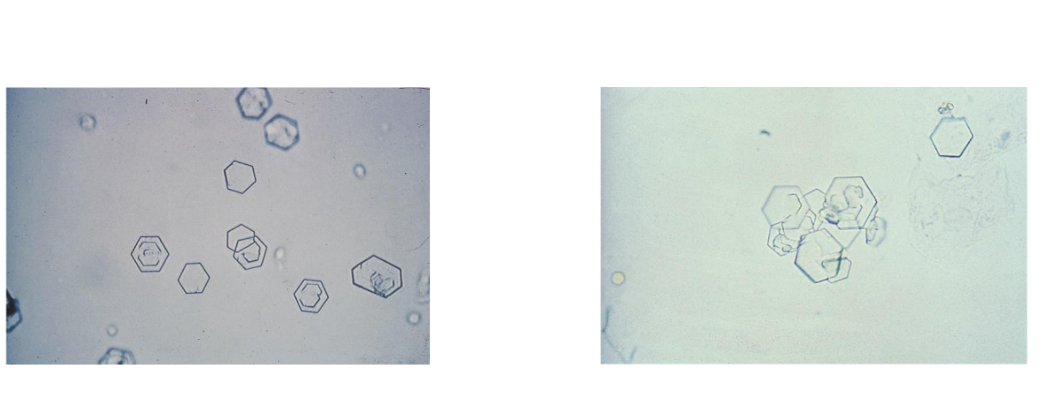
Cystine crystals
Colorless, hexagonal, thin and thick plates
Cholesterol crystals
Rectangular plates with characteristic
notched corners
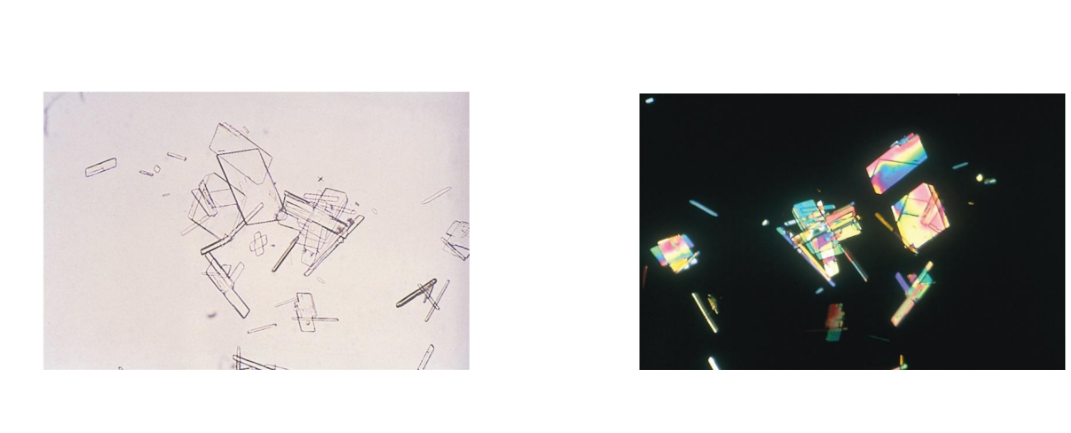

Radiographic Dye Crystals
Similar to cholesterol crystals, polarize
Patient history and comparison of results of
other UAs
Very high SG with refractometer
What crystals are associated with Liver Disease
Tyrosine Crystals
Leucine Crystals
Bilirubin Crystals
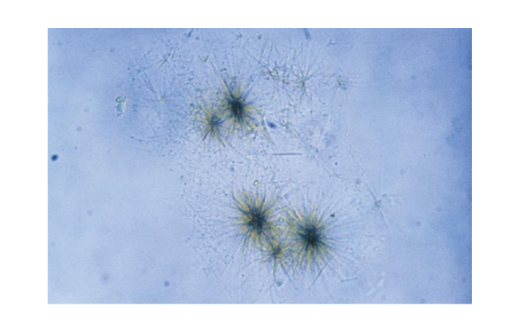
Tyrosine Crystals
Fine colorless to yellow needles in clumps or
rosettes
Leucine crystals
Yellow-brown spheres with concentric circles
and radial striations
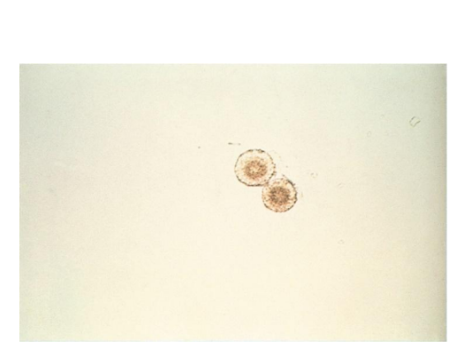
Bilirubin crystals
Hepatic disorders
Clumped needles or granules
Characteristic bright yellow color
Viral hepatitis with tubular damage
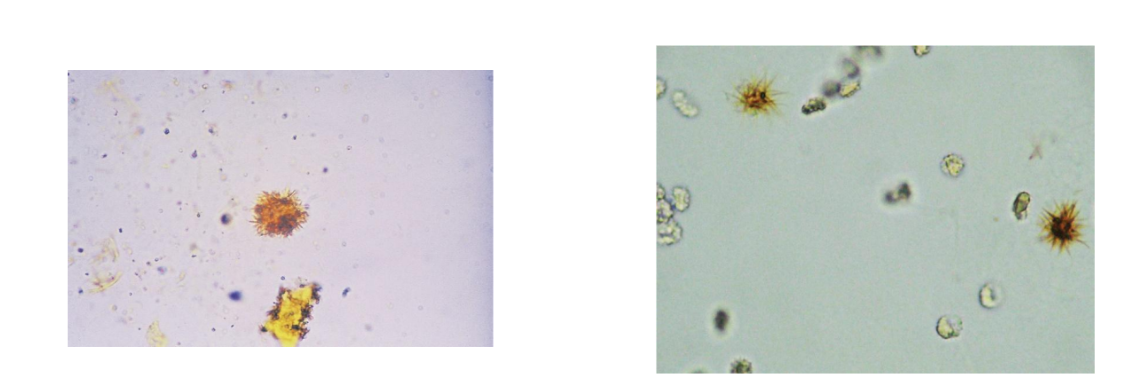
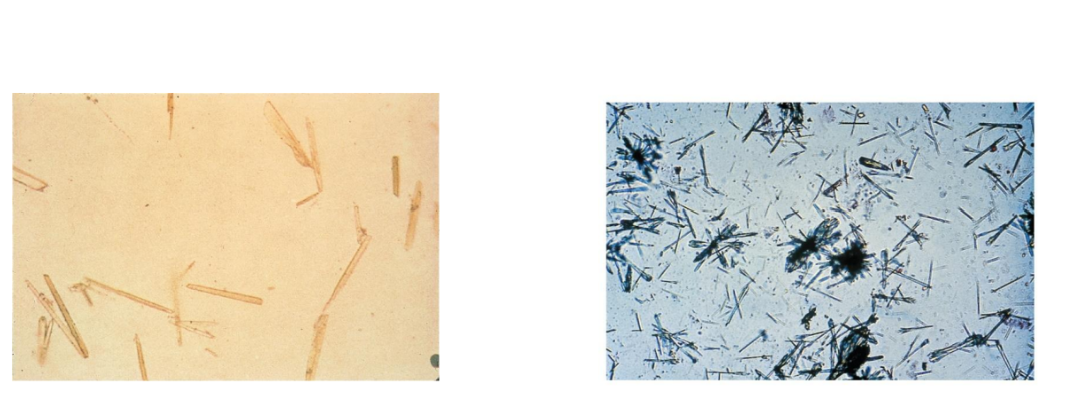
Ampicillin Crystals
Ampicillin crystals appear as colorless
needles that tend to form bundles following
refrigeration
Extreme dehydration