Chemical Bonding Part 4: BOND POLARITY
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
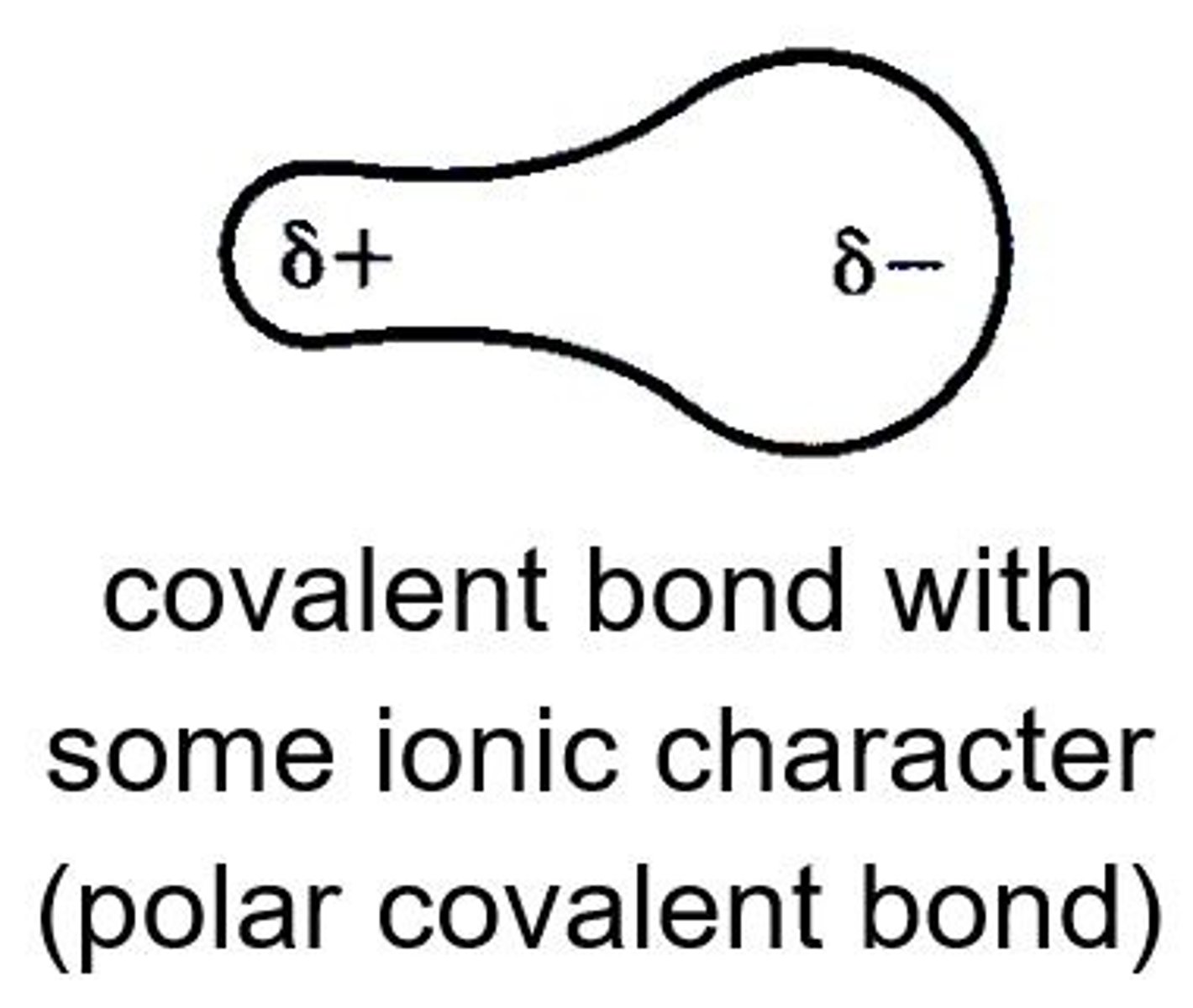
polar bond
a covalent bond between two atoms where the electrons forming the bond are unequally distributed.
This causes the molecule to have a permanent dipole moment where one end is slightly positive(d⁺) and the other is slightly negative(d⁻).
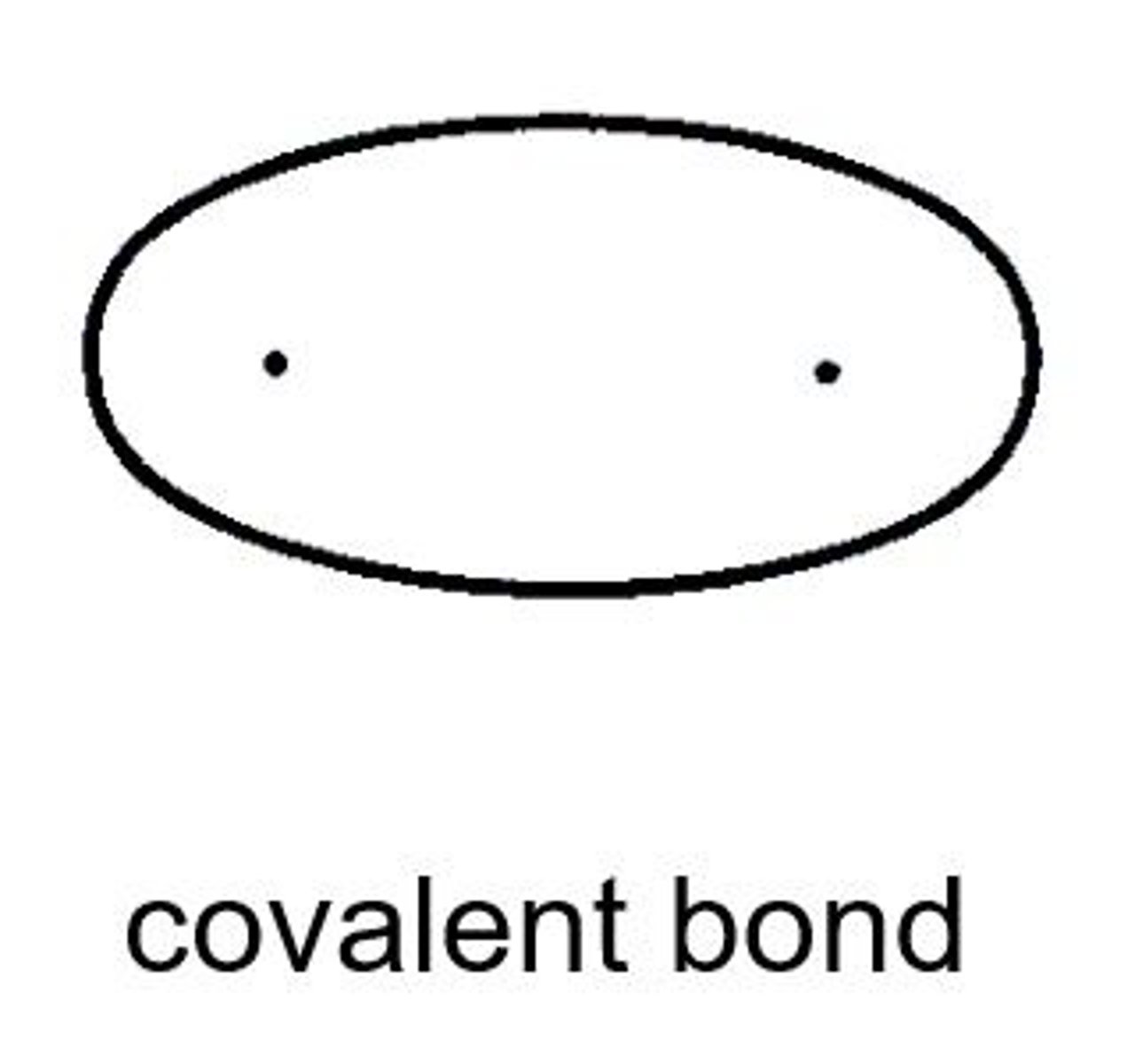
non polar bond
a covalent bond between two atoms where the electrons forming the bond are equally distributed.
The molecule will have a temporary dipole moment where one end is slightly positive(d⁺) and the other is slightly negative(d⁻) when there is another molecule nearby.
Are diatomic gases polar or non polar/why?
Non-polar, since the atoms have equal electronegativity so the electrons are equally attracted to both nuclei
Why is C-H non polar?
They have similar electronegativities
Why is C-C non polar
They have the same electronegativity
What happens in polar bonds
The bonding electrons move towards the more electronegative atom in the pair
Common Non Polar Molecules
CCl₄, CO₂ (linear and dipole moment will cancel out ), noble gases, homonuclear diatomic elements and any molecules that contains only C-H bonds
permanent dipole
A small charge difference across a bond resulting from a difference in electronegativities of the bonded atoms.
What is a dipole? What is a dipole moment?
A dipole is a separation of opposite electrical charges. A dipole is quantified by its dipole moment (μ).
A dipole moment is the a product of the charge and the distance between the charges.
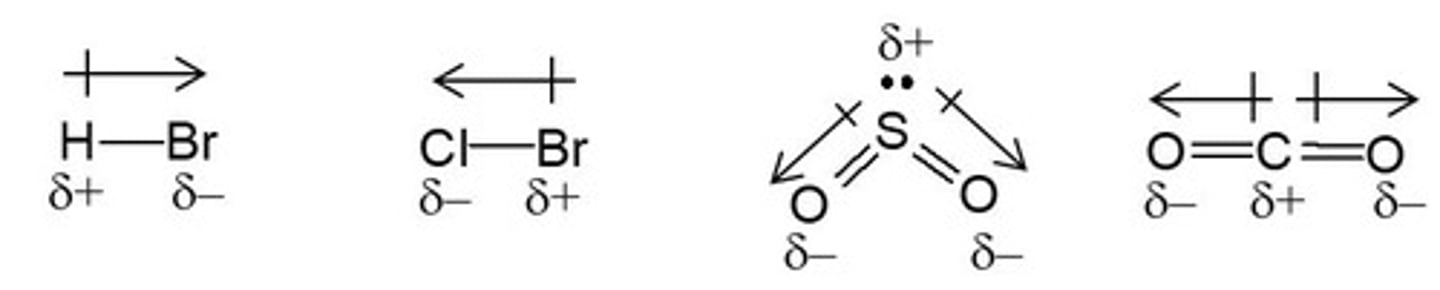
The larger the difference in the electronegativity between the two atoms, the greater the magnitude of the dipole moment the more polar the bond.
The direction of an electric dipole moment is represented by arrow and it points towards the more electronegative atom,
Bond Polarity
is determined by the difference in electronegativities of the bonding atoms.
The greater the difference in electronegativity, the more polar the covalent bond.
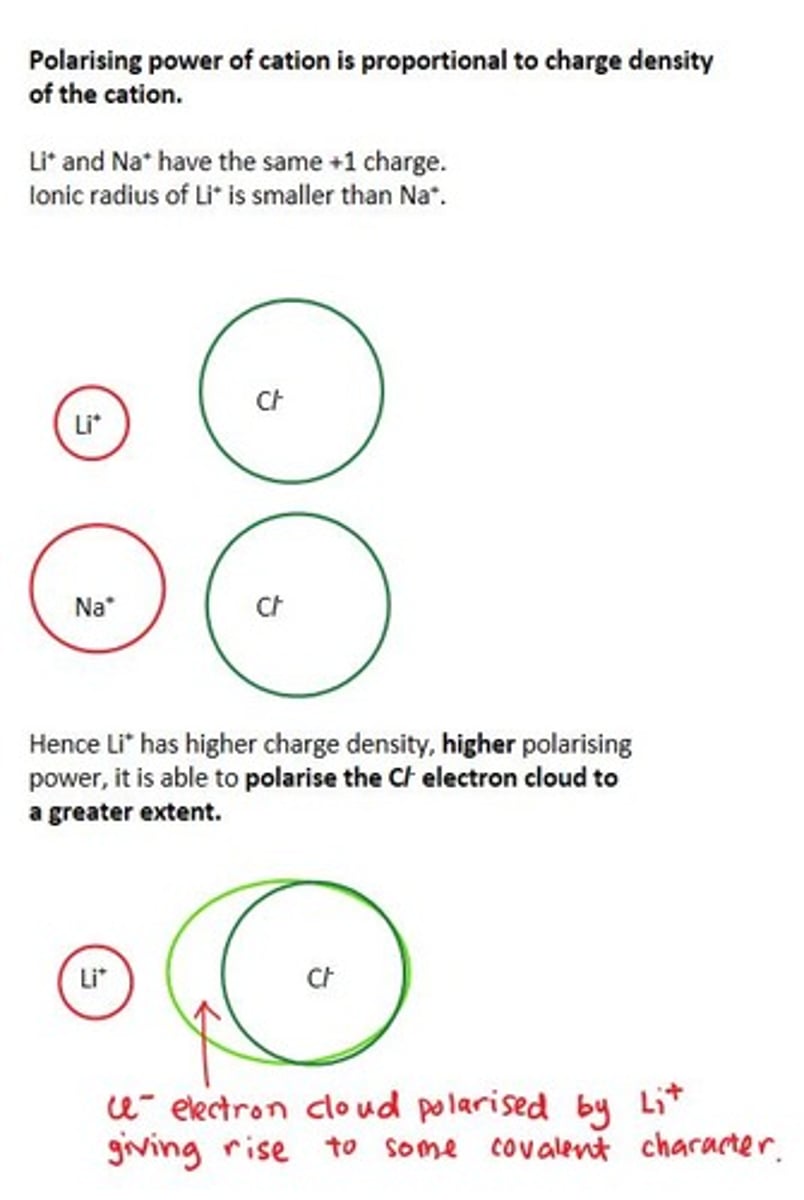
Polarising power of cation
refers to polarisation/distortion of the anion electron cloud.
depends on charge density (charge/size) i.e. the higher the charge and the smaller the cation, the stronger is its polarising power.
Polarisability of anion
refers to the ease of being polarised/distorted by the cation.
depends on charge and size, electron clouds of large anions are easier to distort than those of small anions.
C-H bond and P-H bond are
non-polar (small difference in electronegativity between two atoms)
Example of polarising power of Li⁺ vs Na⁺ in LiCl vs NaCl
Li⁺ is more polarising than Na⁺