chapter 9 key concepts
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
how do fatty acids enter mitochondria
how are the following involved:
CoA-SH
carnitine
carnitine-palmitoyl transferases I & II
carnitine carrier proteins
small FAs (<12 C) can diffuse through the membrane
larger FAs → transported via carnitine transporter
CoA-SH carries the acyl group in the cytosol and the matrix
carnitine carries the acyl group through the carrier protein
carnitine-palmitoyl transferase I transfers the acyl group from CoA-SH to carnitine in the cytosol
carnitine-palmitoyl transferase II transfers the acyl group from carnitine to CoA-SH in the matrix
carnitine carrier proteins facilitate acyl-carnitine transport through the inner mitochondrial membrane
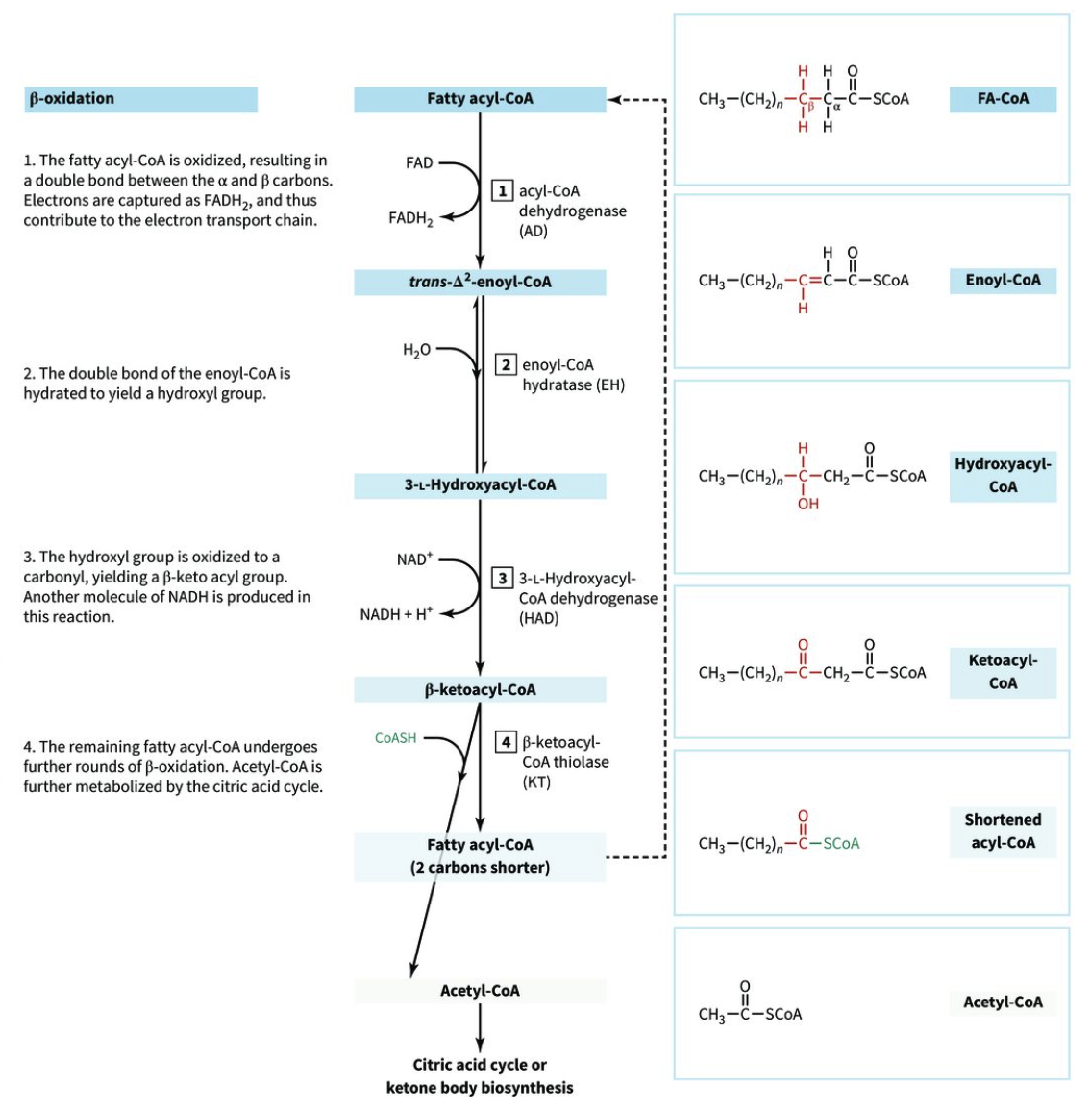
steps of beta-oxidation for saturated fatty acids with an even number of carbons
enzymes and cofactors
products made
oxidation
acyl-CoA dehydrogenase
consumes 1 FAD
makes trans-∆2-enoyl-CoA
hydration
enoyl-CoA hydratase
makes 3-L-hydroxyacyl-CoA
oxidation
3-L-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase
consumes 1 NAD+
makes beta-ketoacyl-CoA
thiolysis
beta-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase
makes fatty acyl-CoA that undergoes further beta-oxidation
uses CoA-SH to make acetyl-CoA for the citric acid cycle or ketone body biosynthesis
what are the products of saturated fatty acids with an odd number of carbons
propionyl-CoA (3C) that can be converted to succinyl-CoA (4C)
what are some important biological functions of lipids
phospholipids → membranes
cholesterol → membrane fluidity
steroid hormones → development, reproduction, mineral balance
triacylglycerols → in adipose tissue, insulate/cushion vital organs
eicosanoids → signalling molecules
where in cells does lipid synthesis occur
the cytosol
what is required for lipid synthesis
sources of carbon, electrons, and energy
reducing equivalent NADPH
energy source
electron source
malonyl-ACP
carbons source
thioester bonds → energy source
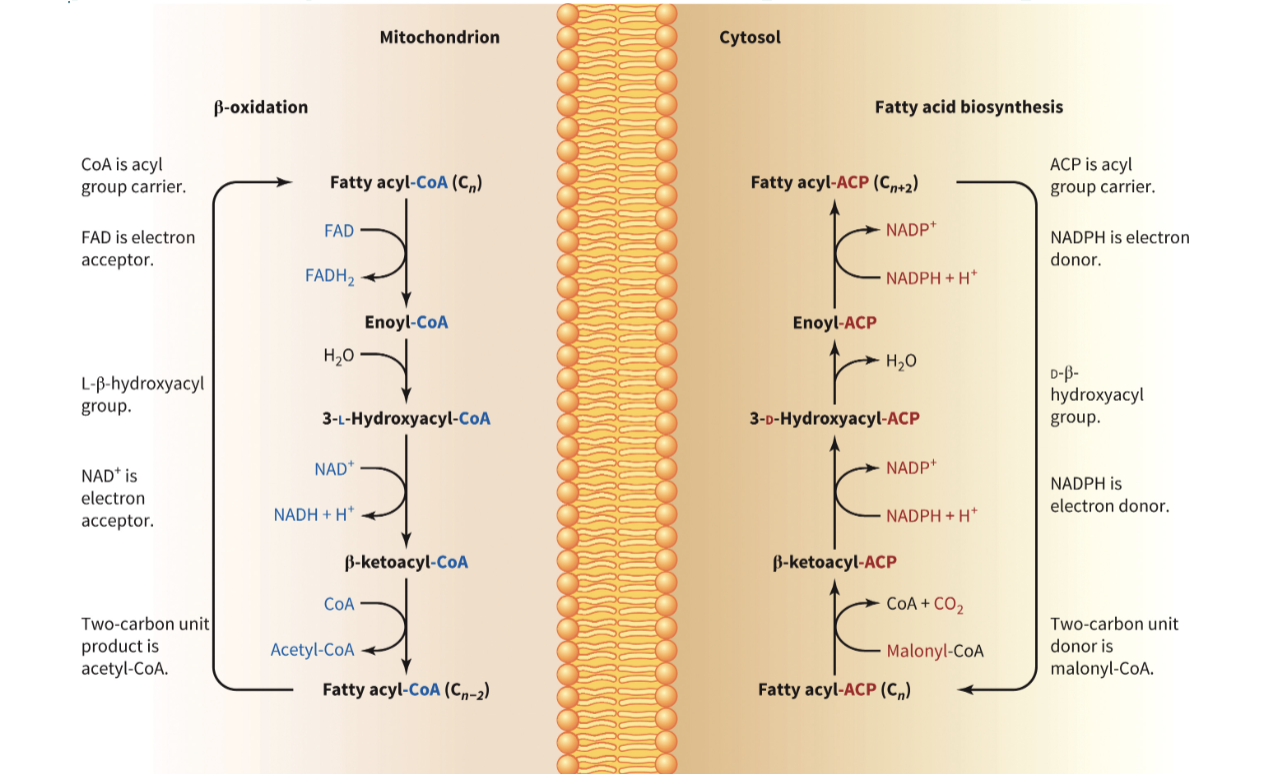
lipid synthesis vs. lipid catabolism
synthesis
requires acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA
requires reducing power (NADPH)
takes place in the cytosol in animals, chloroplast in plants
catabolism
produces acetyl-CoA
produces reducing power (NADH)
occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
how is malonyl-CoA made and what is the source of the three malonyl carbons
carbon sources
CO2 (1C)
acetyl-CoA (2C)
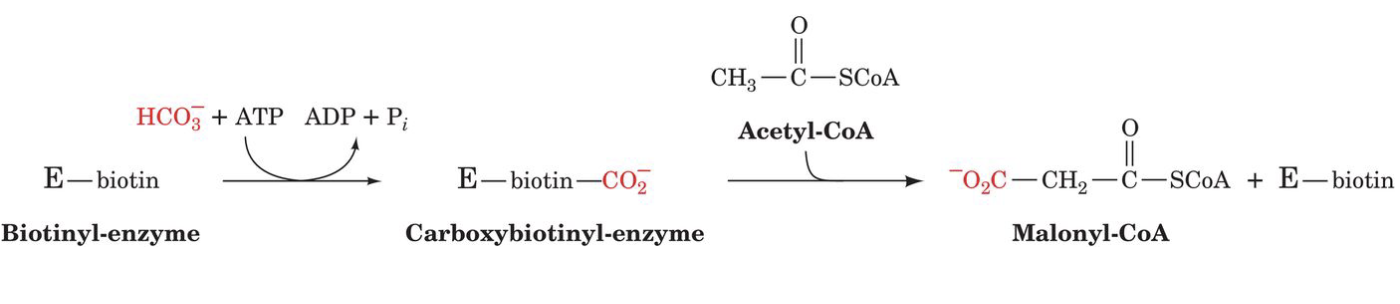
where does malonyl-CoA synthesis occur
smooth ER
describe how malonyl-CoA is involved in the regulation of fatty acid metabolism
why is it better for regulating FA synthesis than acetyl-CoA
malonyl-CoA inhibits FA import into the mitochondria
inhibits CPT1
better for regulating FA synthesis than acetyl-CoA since it is not used for other pathways but acetyl-CoA is
what is the function of fatty acid synthase
synthesize fatty acids → palmitate (16:0)
how is palmitate (16:0) synthesized in mammalian cells
roles of:
acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC)
fatty acid synthase (FAS)
acyl carrier protein (ACP)
summarize reactions
where do they occur
acetyl-CoA is transferred to the ACP domain of FAS
acetyl-ACP transfers the acetyl group to the KS domain of FAS
malonyl-CoA is transferred to the ACP domain of FAS
ACC synthesizes malonyl-CoA in the smooth ER and releases it into the cytosol
condensation of malonyl- and acetyl-ACP by NADPH/H+ in the KS domain of FAS
beta-keto group is reduced to a beta-hydroxyl group by the KR domain of FAS
dehydration of the alcohol to an alpha-beta double bond
reduction of the double bond by NADPH/H+ in the KR domain of FAS
repeat 3-7 six times to generate palmitoyl-ACP
palmitoyl-ACP is cleaved by thioesterase to release palmitate and ACP
why are only 7 malonyl-CoA required for palmitate synthesis
the other two carbons needed to form palmitate come from acetyl-CoA
describe/diagram how acetyl-CoA from mitochondria is moved to the cytosol for FA synthesis, include:
intermediates
enzymes
return of intermediates to the mitochondrial matrix
relate the cellular location of FA synthesis with pathways that serve as sources of NADPH
FA synthesis occurs in the cytosol
consumes NADPH
pathways that generate NADPH in the cytosol provide it for FA synthesis
describe how FA synthesis in cytosol can be reciprocally regulated by malonyl-CoA
malonyl-CoA is needed to proceed through the first step of FA synthesis since it is the 2C donor
describe how citrate and palmitoyl-CoA act as regulators
how is acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity affected by glucagon and epinephrine
citrate activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase
signals that excess energy must be converted to fat
palmitoyl-CoA inhibits acetyl-CoA carboxylase through feedback inhibition
glucagon and epinephrine stimulates PKA which phosphorylates acetyl-CoA carboxylase, making it less active
what are two modifications to palmitate that can form additional kinds of fatty acids
elongation
desaturation
in what cellular compartment are fatty acids elongated
endoplasmic reticulum
describe the activity of fatty acid desaturases
oxidative desaturation
directly removes two e- and associated H from stereoyl-CoA (18:0) to create oleyl-CoA (18:1∆9)
briefly describe the overall pathway in the liver leading from acetyl-CoA to the ketone bodies:
acetone
acetoacetate
D-beta-hydroxybutyrate
acetone = breakdown product formed by the spontaneous decarboxylation of acetoacetate
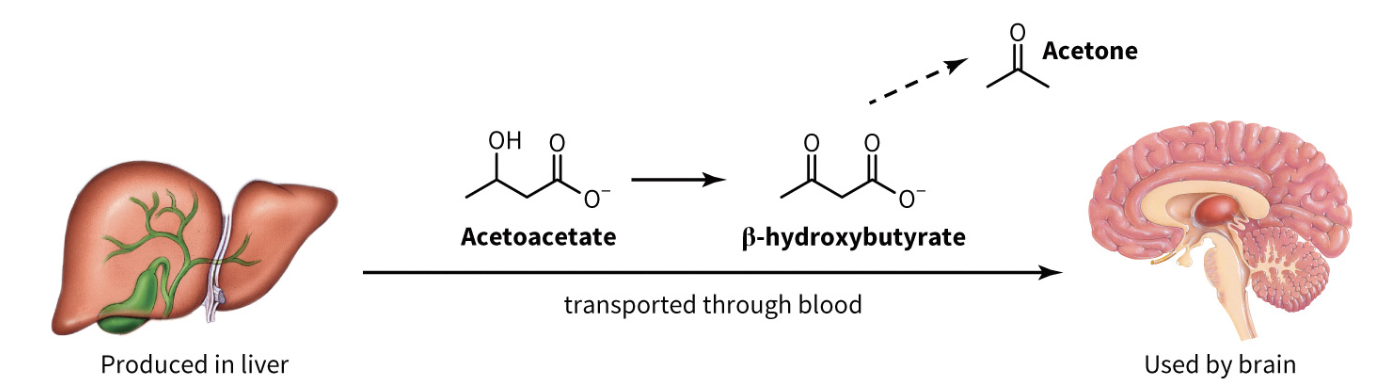
what is one serious physiological consequence of the overproduction of ketone bodies
ketoacidosis
how are steroids made from cholesterol, is it the same pathway as FA synthesis
overall pathway
oxidative cleavage of the cholesterol side chain
oxidation of the hydroxyl group → progesterone
most other reactions of steroid hormone biosynthesis happen in the ER during cleavage
why are HMG-CoA reductase and mevalonate important in cholesterol synthesis
HMG-CoA reductase catalyzes the irreversible reduction of HMG-CoA to mevalonate
committed step in cholesterol synthesis
key regulation point
mevalonate levels regulate HMG-CoA reductase
inhibits active HMG-CoA reductase through negative feedback
directly inhibits cholesterol synthesis
describe one example of how an eicosanoid signalling molecule can be synthesized from a membrane phospholipid
overal pathway
role of phospholipase A2
phospholipase A2 destroys cell membranes to liberate arachidonic acid from phospholipids
arachidonic acid can be converted to various eicosanoids
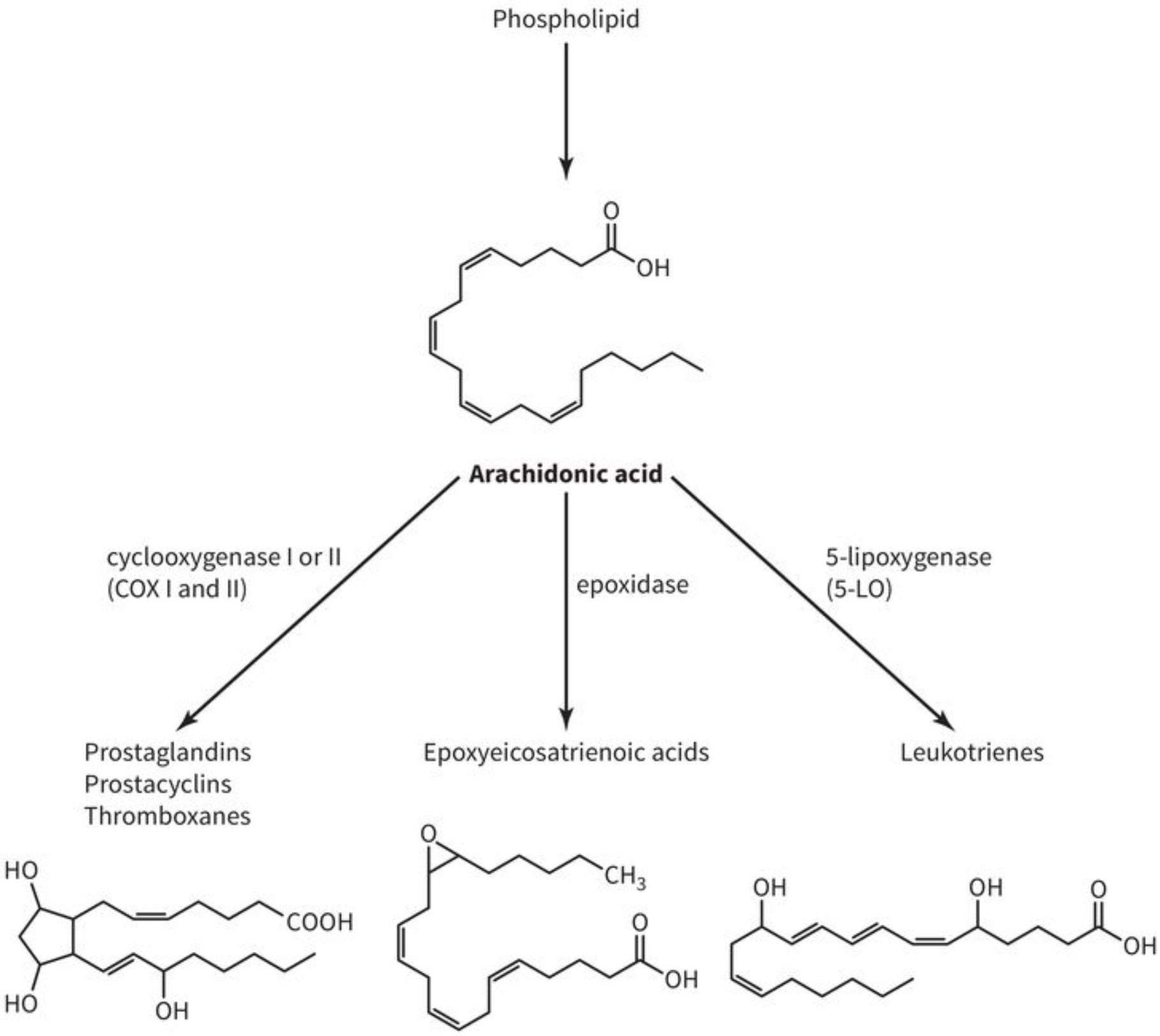
which class of enzyme converts arachidonic acid to prostaglandins (with cyclic structure)
cyclooxygenases (COX)
which class of enzyme converts arachidonic acid to leukotrienes
5-lipoxygenase (5-LO)