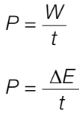Physics - P1 Motion, Forces and Energy
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physical quantities and measurement techniques - doesn't have graphs
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Newton’s Law of Gravity:
F = G m1m2/r2

to measure small lengths
either measure multiple to find the average or use a specialized tool such as a micrometer or vernier caliper
1 ml =
1 cm3
volume of cylinder
pi radius squared times height
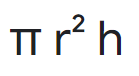
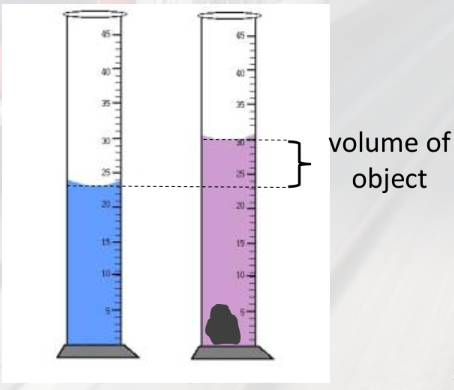
to measure the volume of an irregular object
displacement method
Period (time for one oscillation)
measure multiple oscillations and find the average
mass (m)
the amount of matter in an object, units kg
weight (w)
the force of gravity on an object in a gravitational field, units Newtons (N)
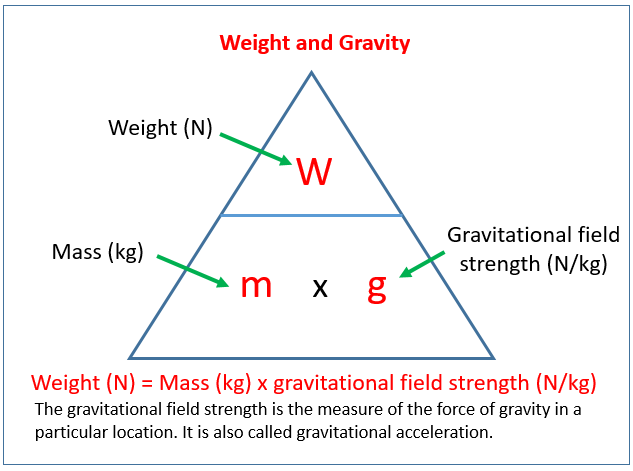
g =
gravitational field strength, force per unit mass (N/kg). At earth’s surface, g = 9.8 N/kg
w=
w=mg

what does a balance measure?
weight but displays mass (because g is known)
density (ρ)
mass per unit volume, units kg/m3
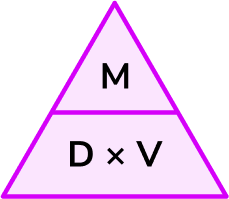
density=
mass/volume
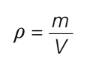
scalar quantity has
vector quantity
magnitude and direction
scalar examples
distance, speed, time, mass, energy and temperature
vector examples
distance, speed, time, mass, energy and temperature
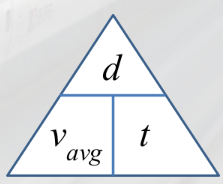
speed
distance travelled per unit time
speed =
v = s/t
average speed=
total distance travelled/total time taken
velocity
speed in a given direction
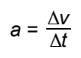
acceleration
change in velocity per unit time
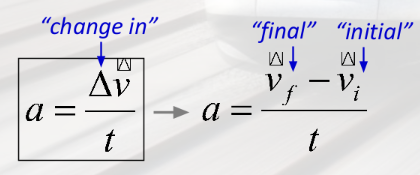
an object moving with increasing speed is…
accelerating
an object moving with decreasing speed is
decelerating
deceleration
a negative acceleration
that the acceleration of free fall g for an object near to the surface of the Earth is approximately constant and is approximately…
9.8 m/ s^2
gravitational field strength is equivalent to
the acceleration of free fall
friction
force that resists sliding between two surfaces; results in heating
air resistance
force that resists an object’s motion through air (friction in gas)
elastic
force that restores an object to its original shape
Hooke’s Law of springs
the extension of a spring is proportional to the force applied
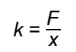
F=
kx
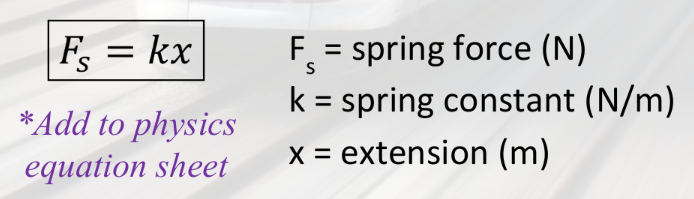
Newton's second law of motion states
F = ma, or when there is a resultant force on an object it will accelerate in the direction of the force.
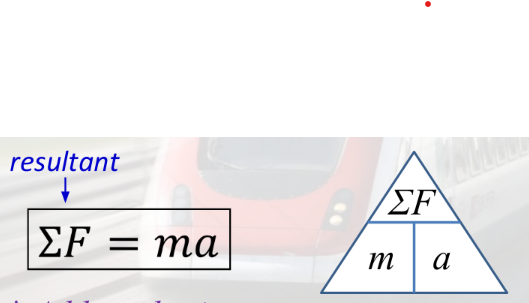
the resultant force and the acceleration
are in the same direction
resultant force
the sum of two or more forces acting on an
object
Forces in the same direction
are added
Forces in opposite directions
are subtracted
force (F)
a push or pull between two objects, units Newtons
Forces can change the
size, shape or motion of an object
moment =
force × perpendicular distance from the pivot
when there is no resultant force and no resultant moment…
an object is in equilibrium
Pressure (p) =
force/area
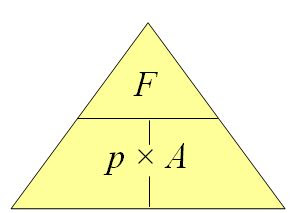
state that energy may be stored as
kinetic, gravitational potential, chemical, elastic (strain), nuclear, electrostatic and internal (thermal)
equilibrium
no resultant force and no resultant moment; motion does not change
principle of moments
If a system is in equilibrium, the sum of the anticlockwise moments about a turning point equals the sum of the clockwise moments
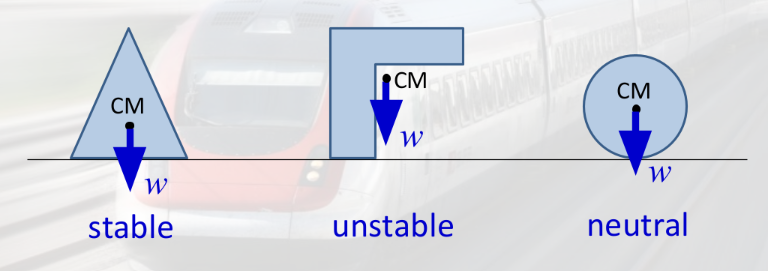
Centre of Mass (CM)
the centre of an object’s mass distribution
An object acts as if its entire weight acts at the centre of mass
A system is stable when its CM is directly above or below the base
equation for kinetic energy
Ek= 1/2 mv^2
the equation for the change in gravitational potential energy
change in x Ep = mg x change in h
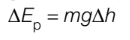
mechanical or electrical work done is equal to
the energy transferred
radiation from the Sun is the main source of energy for all our energy resources
except geothermal, nuclear and tidal
efficiency
efficiency = useful energy output/total energy input
× 100%
efficiency = useful power output/total power input
× 100%
energy is released by nuclear fusion in the Sun
energy is released by nuclear fission in nuclear reactors
power (p)
work done per unit time and also as energy transferred per unit time
power (p) equation
P = W/t
P = change in E/t