Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Reflexes
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Spinal Cord
Information highway connecting brain and lower body.
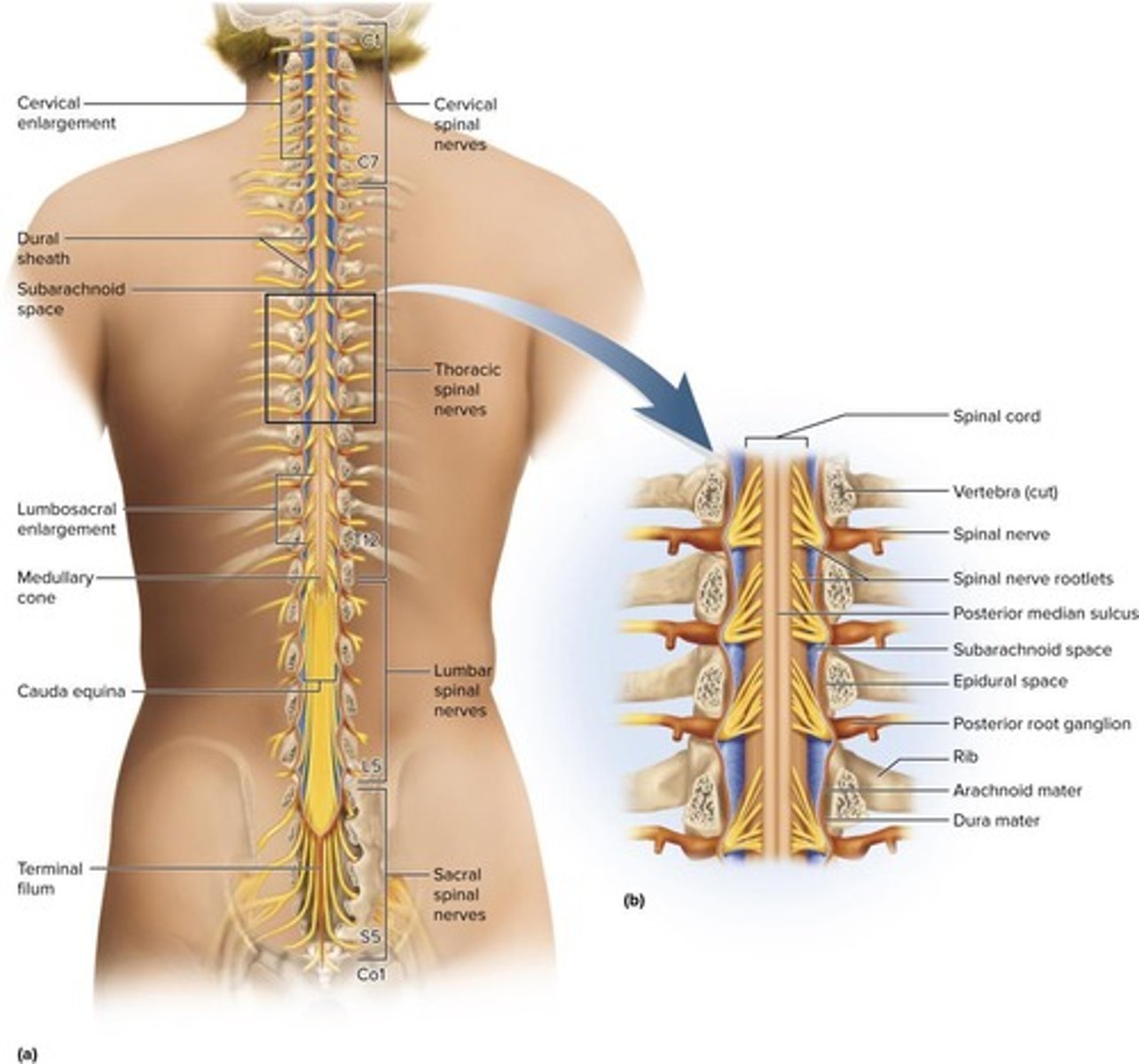
Spinal Nerves
31 pairs of nerves arising from the spinal cord.
Conduction
Nerve fibers transmit sensory and motor information.
Neural Integration
Spinal neurons process multiple inputs for output.
Locomotion
Central pattern generators coordinate walking movements.
Reflexes
Involuntary responses vital for posture and protection.
Cervical Enlargement
Thicker spinal cord area for upper limb nerves.
Lumbosacral Enlargement
Thicker area for pelvic and lower limb nerves.
Medullary Cone
Tapered end of the spinal cord.
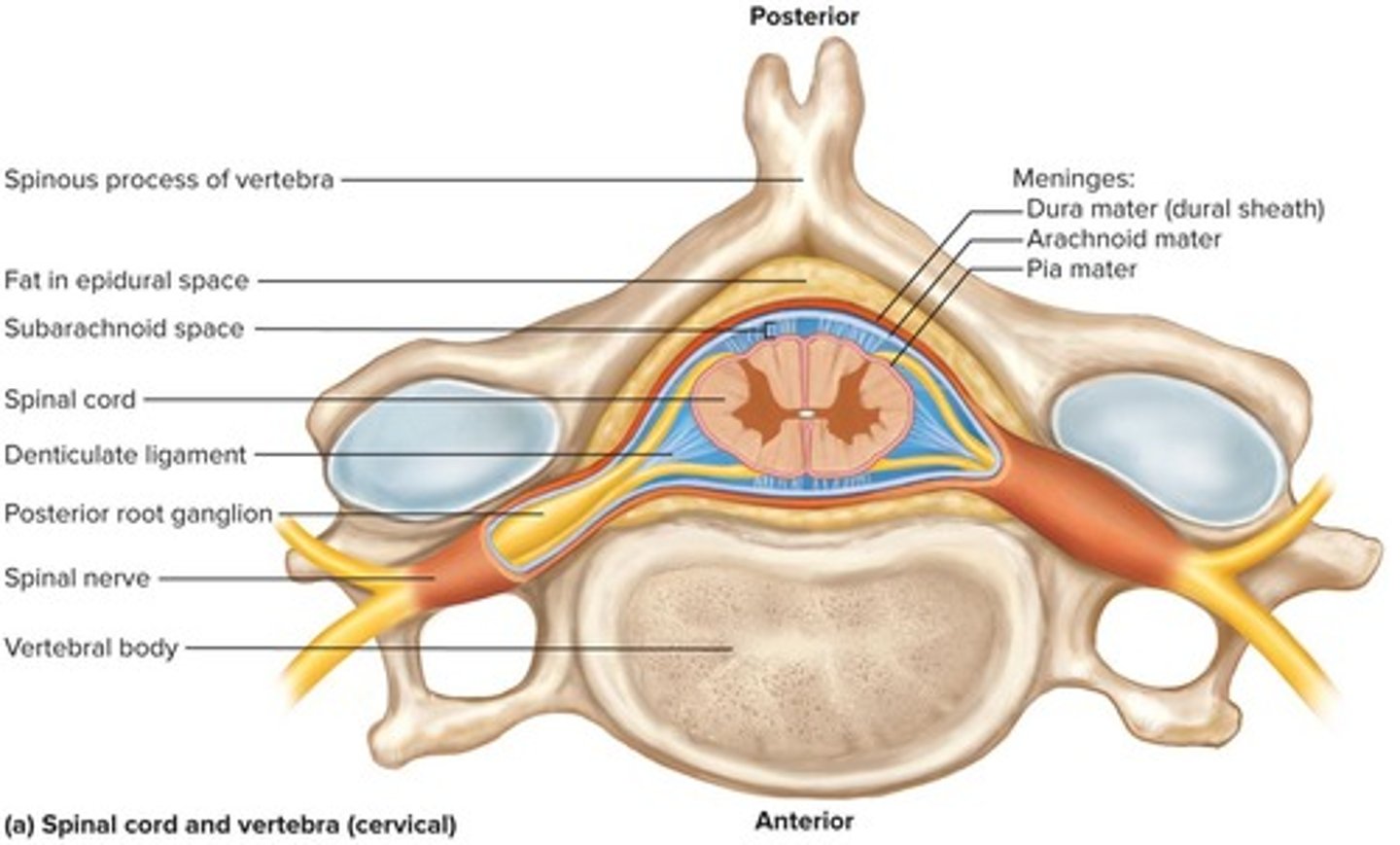
Meninges
Three membranes enclosing the brain and spinal cord.
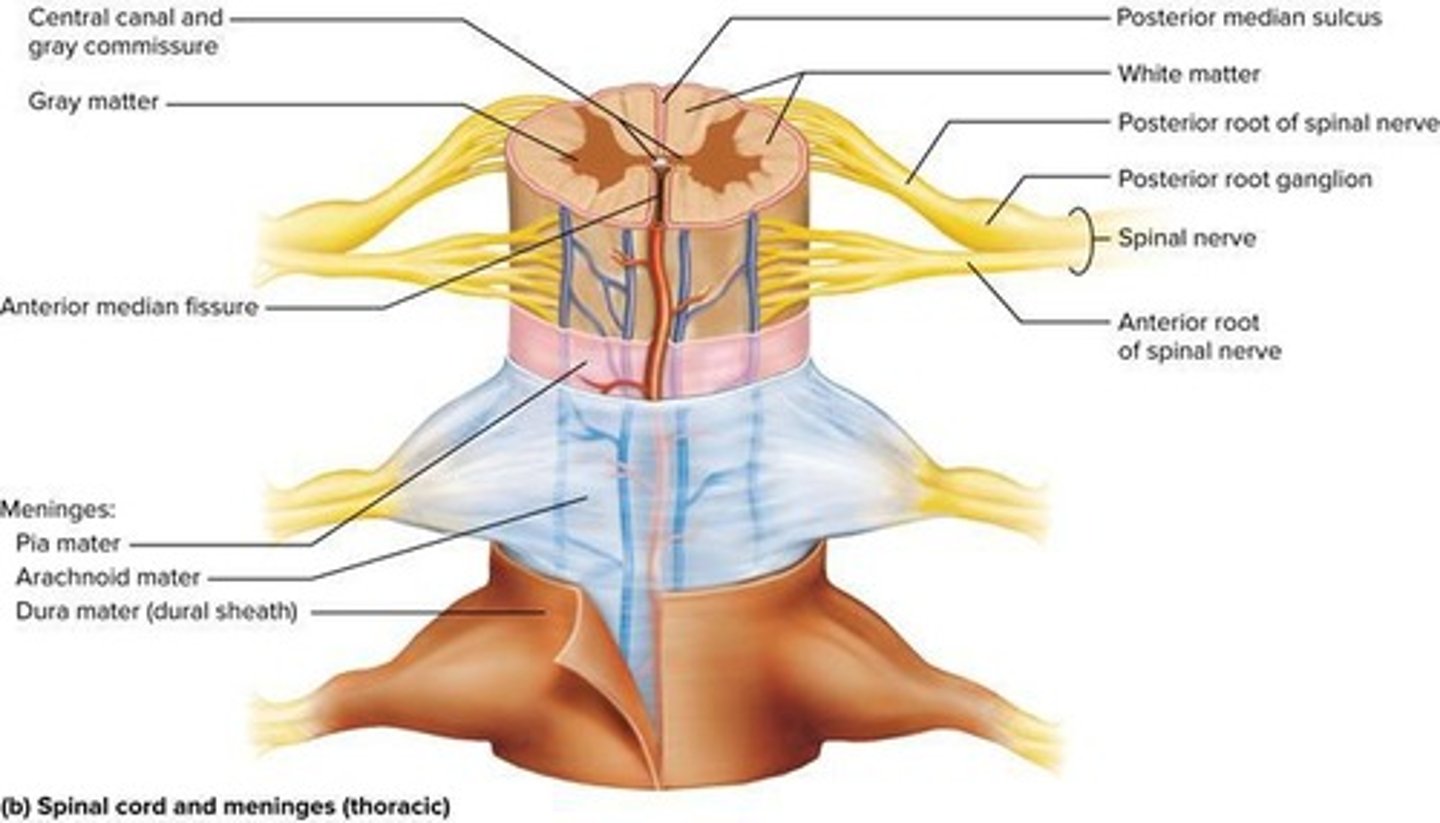
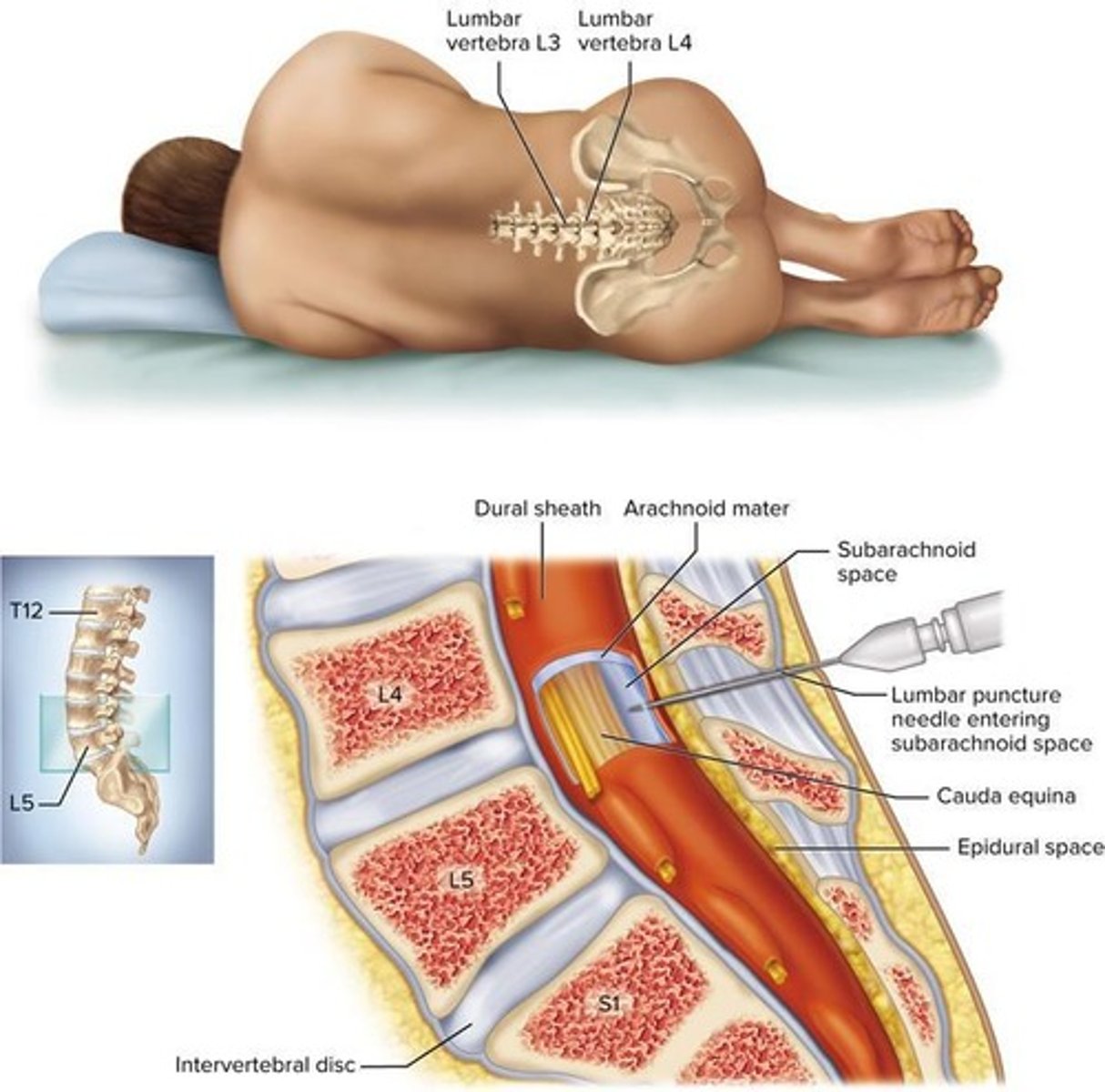
Dura Mater
Outer layer of the meninges, tough and protective.
Arachnoid Mater
Middle layer, adheres to dura and contains CSF.
Pia Mater
Delicate inner layer following spinal cord contours.
Epidural Space
Space between dura mater and vertebrae.
Subarachnoid Space
Contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) between arachnoid and pia.
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Fluid cushioning the brain and spinal cord.
Lumbar Puncture
Procedure to sample CSF from the spinal canal.
White Matter
Myelinated axons carrying signals in CNS; surrounds gray matter
Gray Matter
Central core of spinal cord, butterfly-shaped.
Dorsal Horns
Pair of posterior horns in gray matter.
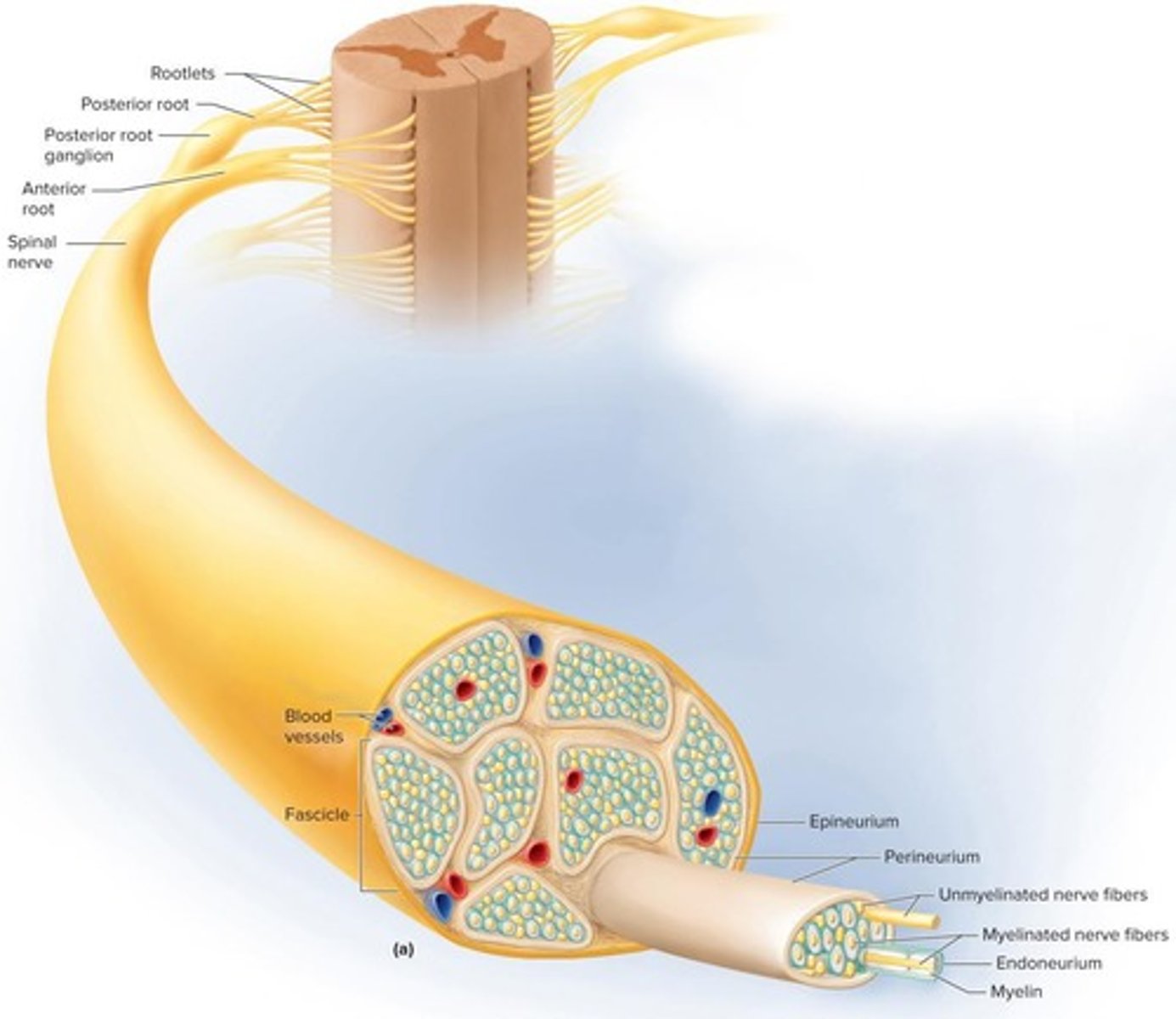
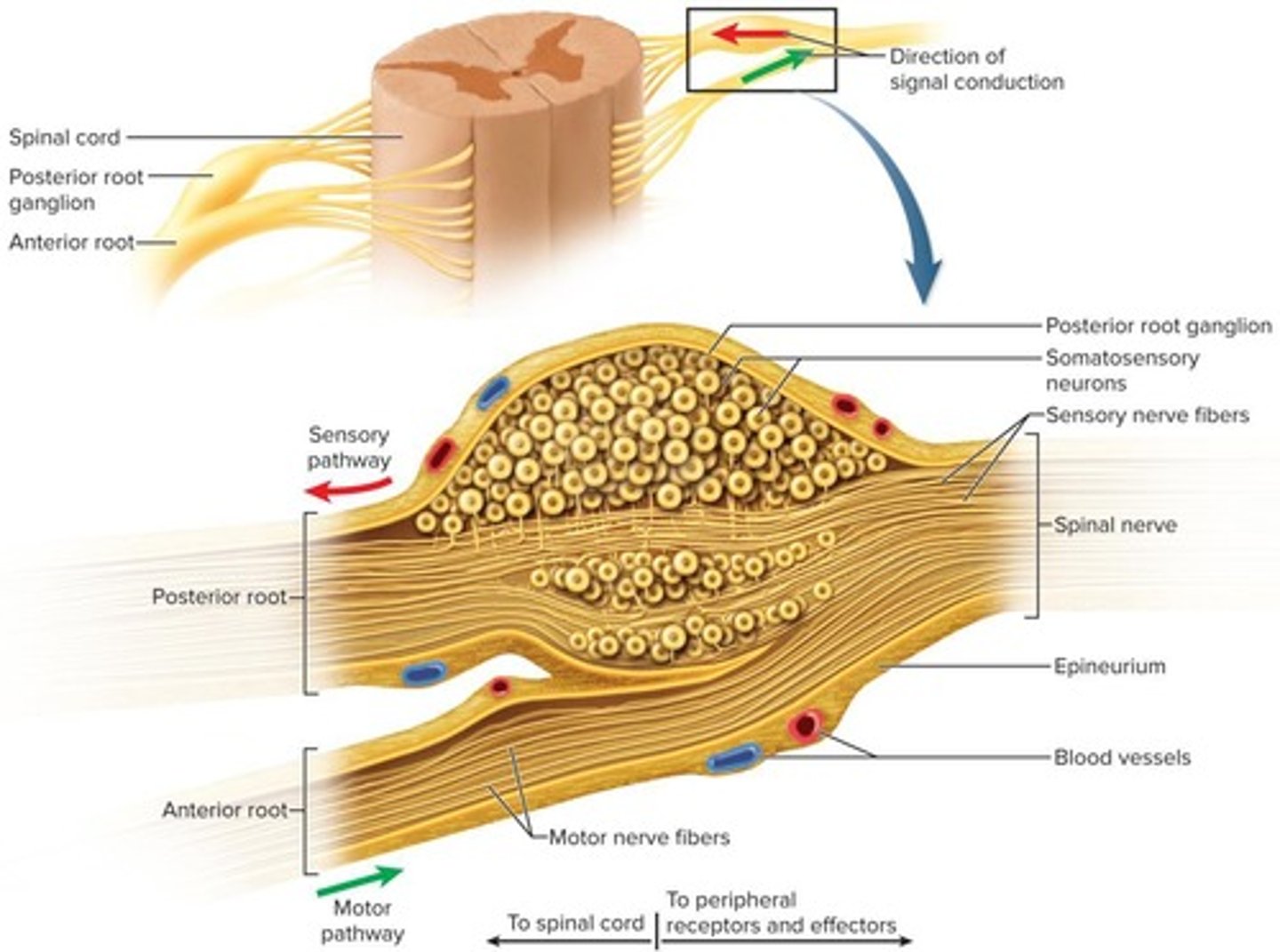
Dorsal Root
Carries sensory fibers to spinal cord.
Ventral Horns
Pair of thicker anterior horns in gray matter.
Ventral Root
Carries motor fibers from spinal cord.
Gray Commissure
Connects right and left gray matter sides.
Central Canal
Contains CSF, lined with ependymal cells.
Lateral Horn
Contains sympathetic neurons, visible from T2 to L1.
Funiculi
Three regions of white matter in the spinal cord. Contains neuron cell bodies, processes information.
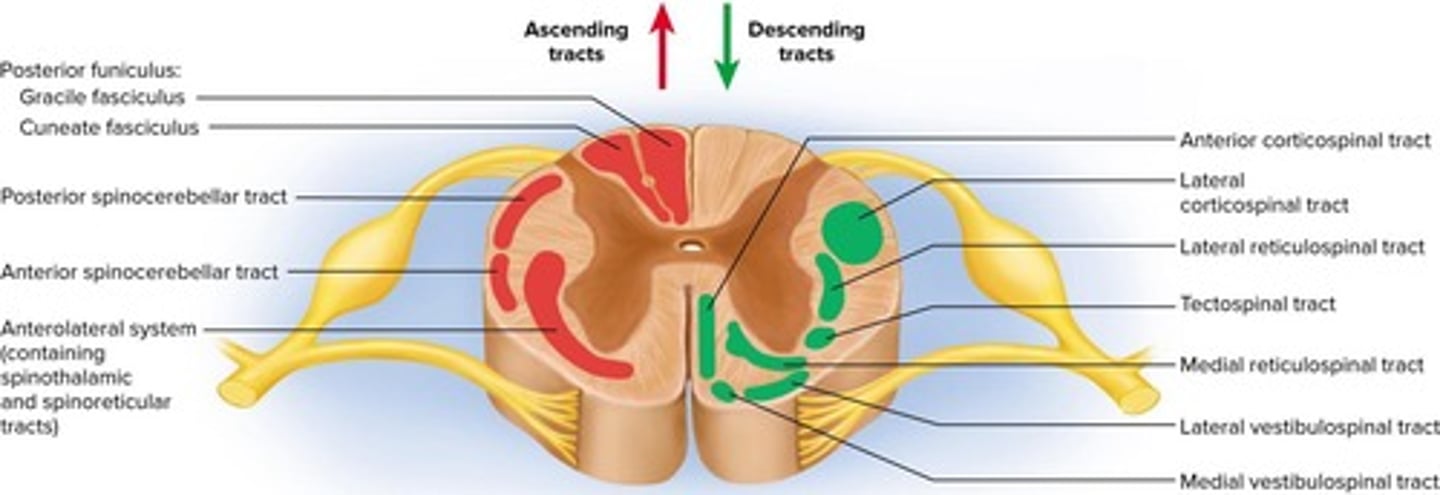
Ascending Tracts
Carry sensory information up spinal cord.
Descending Tracts
Carry motor information down spinal cord.
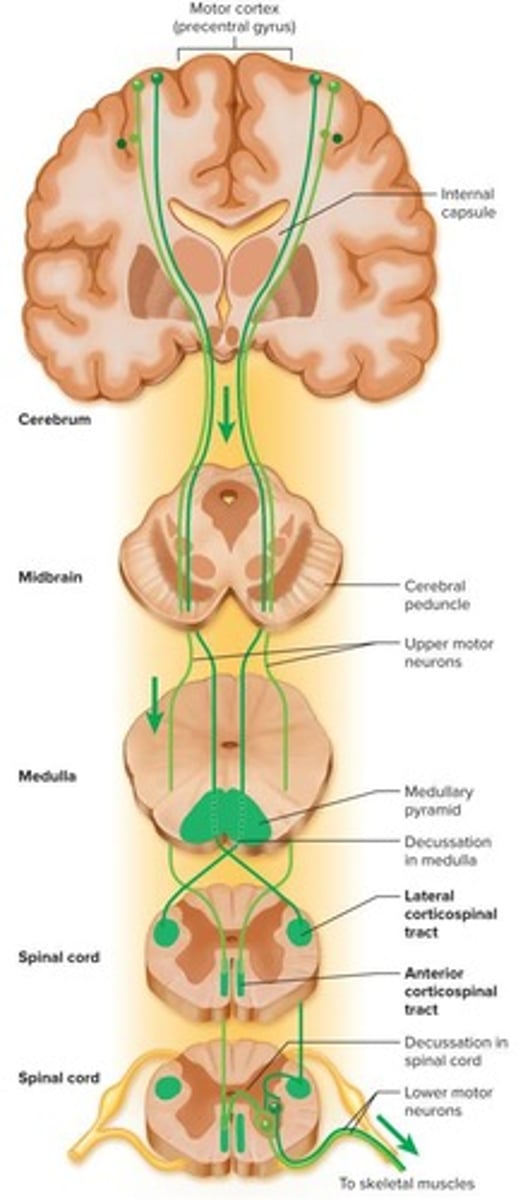
Decussation
Crossing of midline in many tracts.
Contralateral
Origin and destination on opposite body sides.
Ipsilateral
Origin and destination on the same body side.
Gracile Fasciculus
Carries signals from lower body to brain.
Cuneate Fasciculus
Carries signals from upper body to brain.
Spinothalamic Tract
Carries pain and temperature signals to brain.
Spinoreticular Tract
Carries pain signals from tissue injury.
Spinocerebellar Tracts
Carry proprioceptive signals to cerebellum.
Upper Motor Neuron
Originates in cortex, controls lower motor neuron.
Lower Motor Neuron
Neuromuscular junction leads to muscle contraction.
Corticospinal Tracts
Control precise, coordinated movements from cortex.
Tectospinal Tract
Reflex turning of head to sights and sounds.
Reticulospinal Tracts
Control posture and balance muscles.
Poliomyelitis
Caused by poliovirus, destroys motor neurons.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Destroys motor neurons, causes muscle atrophy.
Nerve
Cord-like organ of bundled nerve fibers.
Mixed Nerves
Contain both afferent and efferent fibers.
Schwann Cells
Surround nerve fibers, forming myelin sheath.
Endoneurium
Loose connective tissue around individual nerve fibers.
Perineurium
Wraps bundles of nerve fibers into fascicles.
Epineurium
Dense tissue wrapping entire nerve.
Ganglion
Cluster of neurosomas outside the CNS.
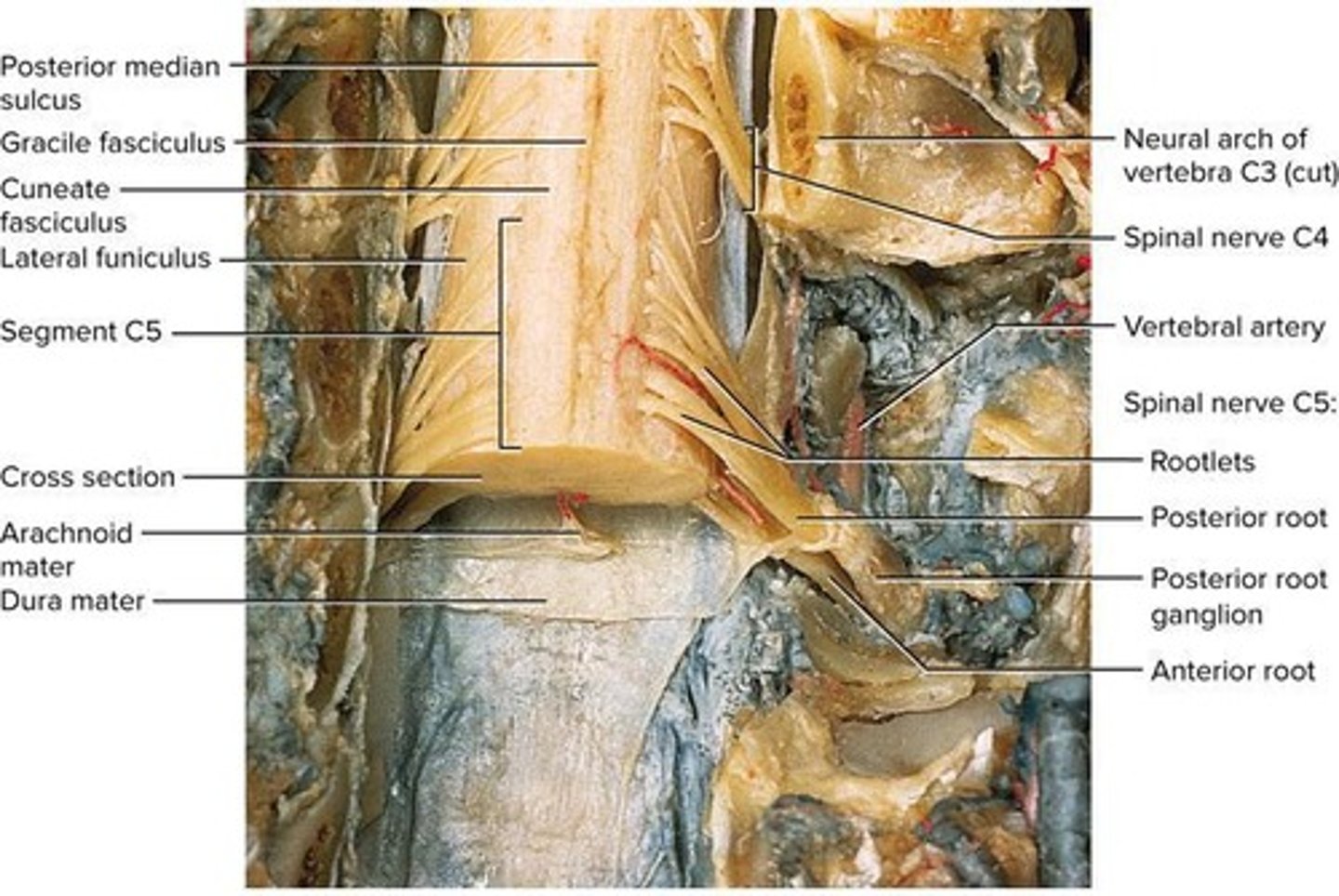
Dorsal Root Ganglion
Contains sensory neuron cell bodies.
Cauda Equina
Bundle of nerve roots from L2 to S5.
Anterior Ramus
Innervates limbs and forms plexuses.
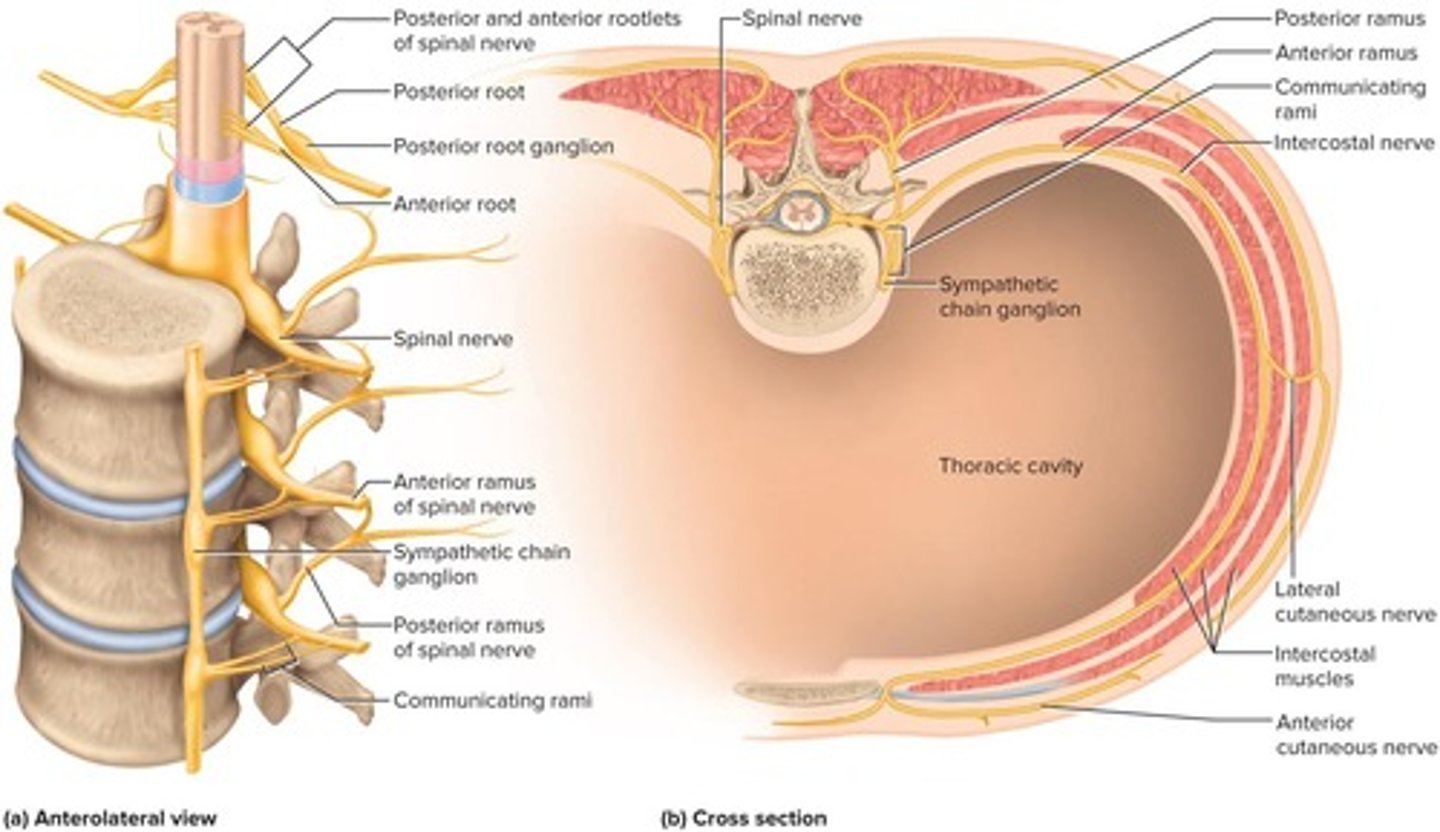
Posterior Ramus
Innervates skin and muscles of back.
Meningeal Branch
Innervates meninges and spinal ligaments.
Shingles
Localized disease from varicella-zoster virus reactivation.
Chickenpox
Common childhood disease caused by varicella-zoster virus.
Posterior root ganglia
Location where varicella-zoster virus remains dormant.
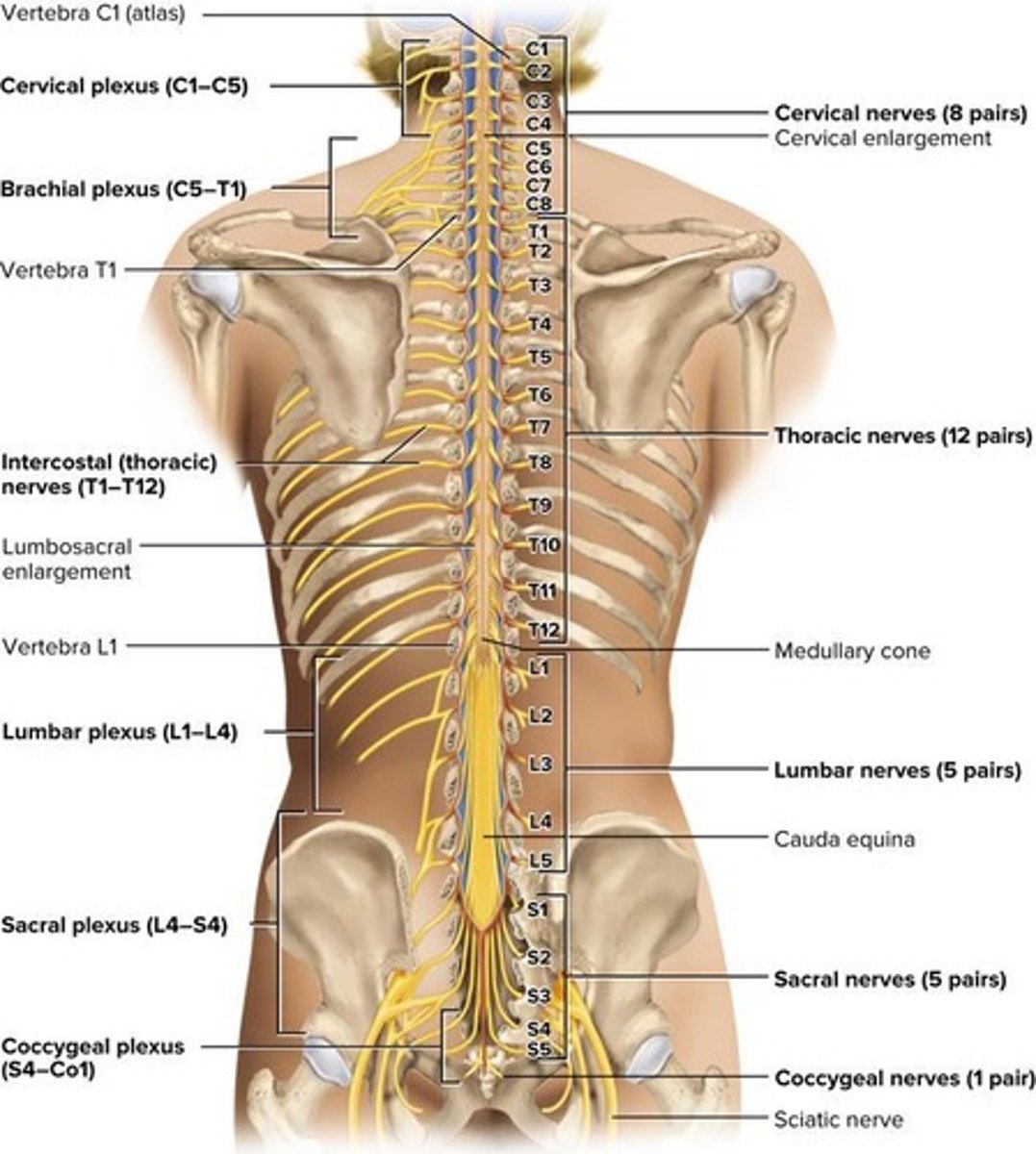
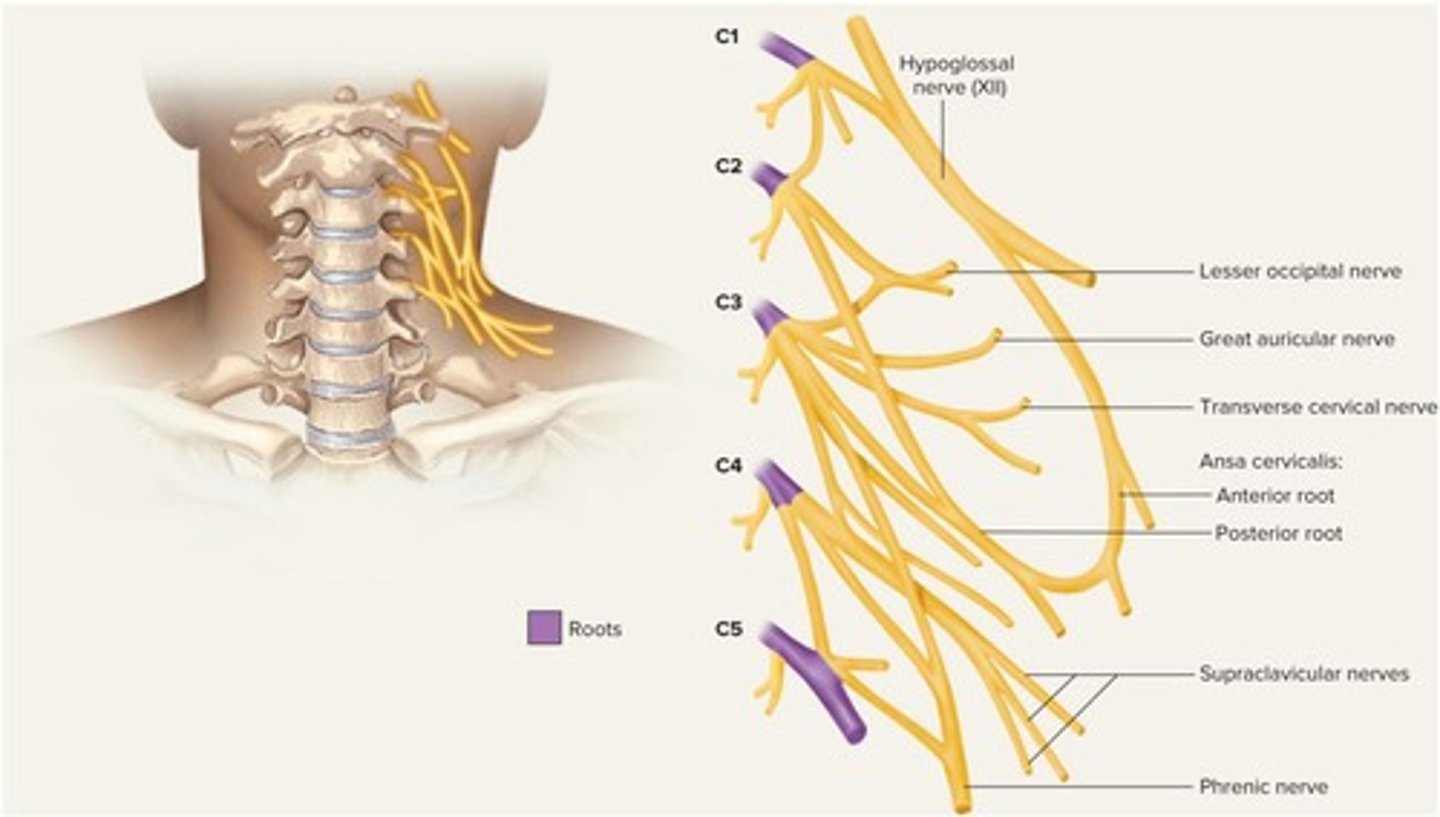
Cervical plexus
Nerve plexus supplying neck and diaphragm.
Brachial plexus
Nerve plexus supplying upper limb and shoulder.
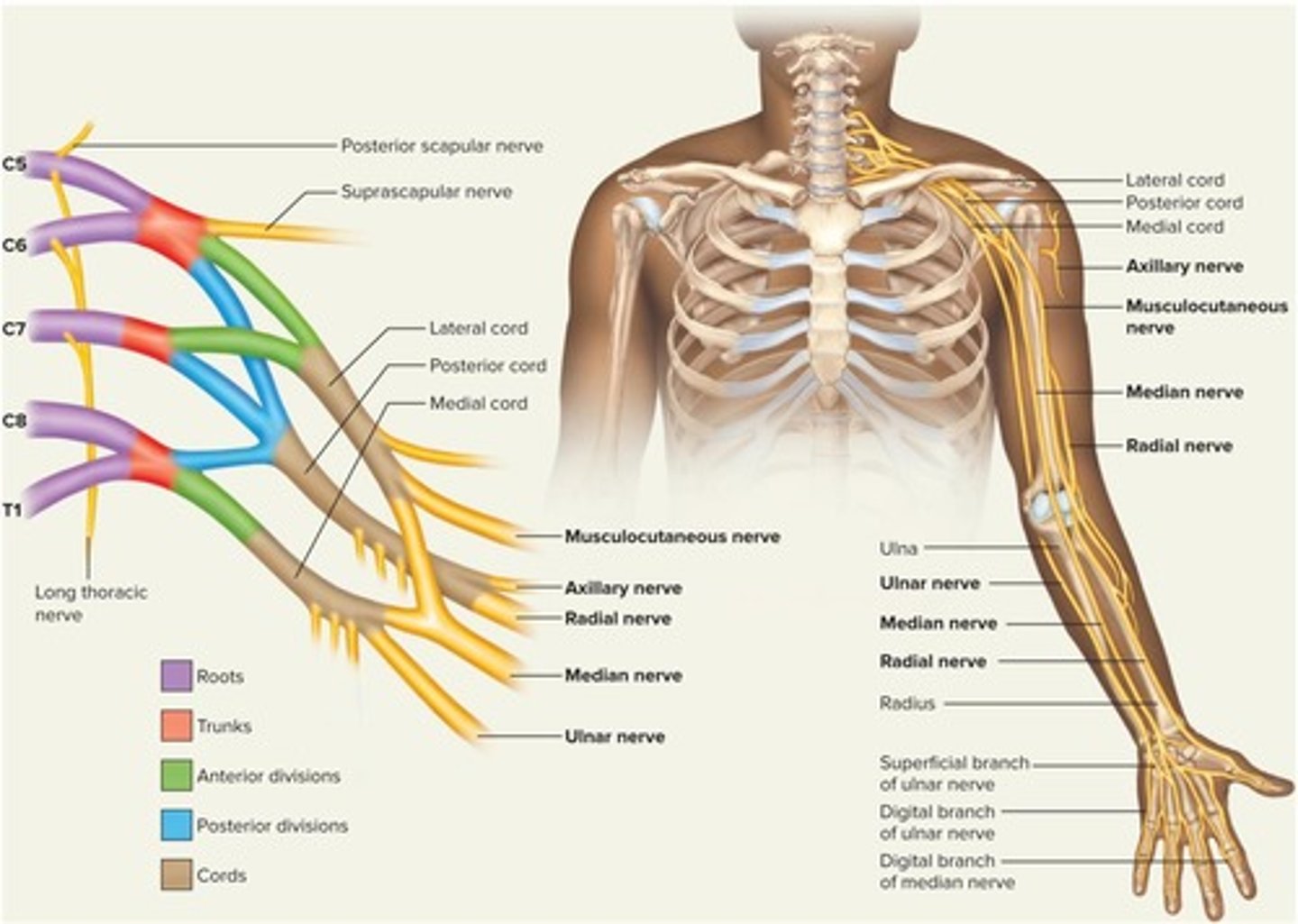
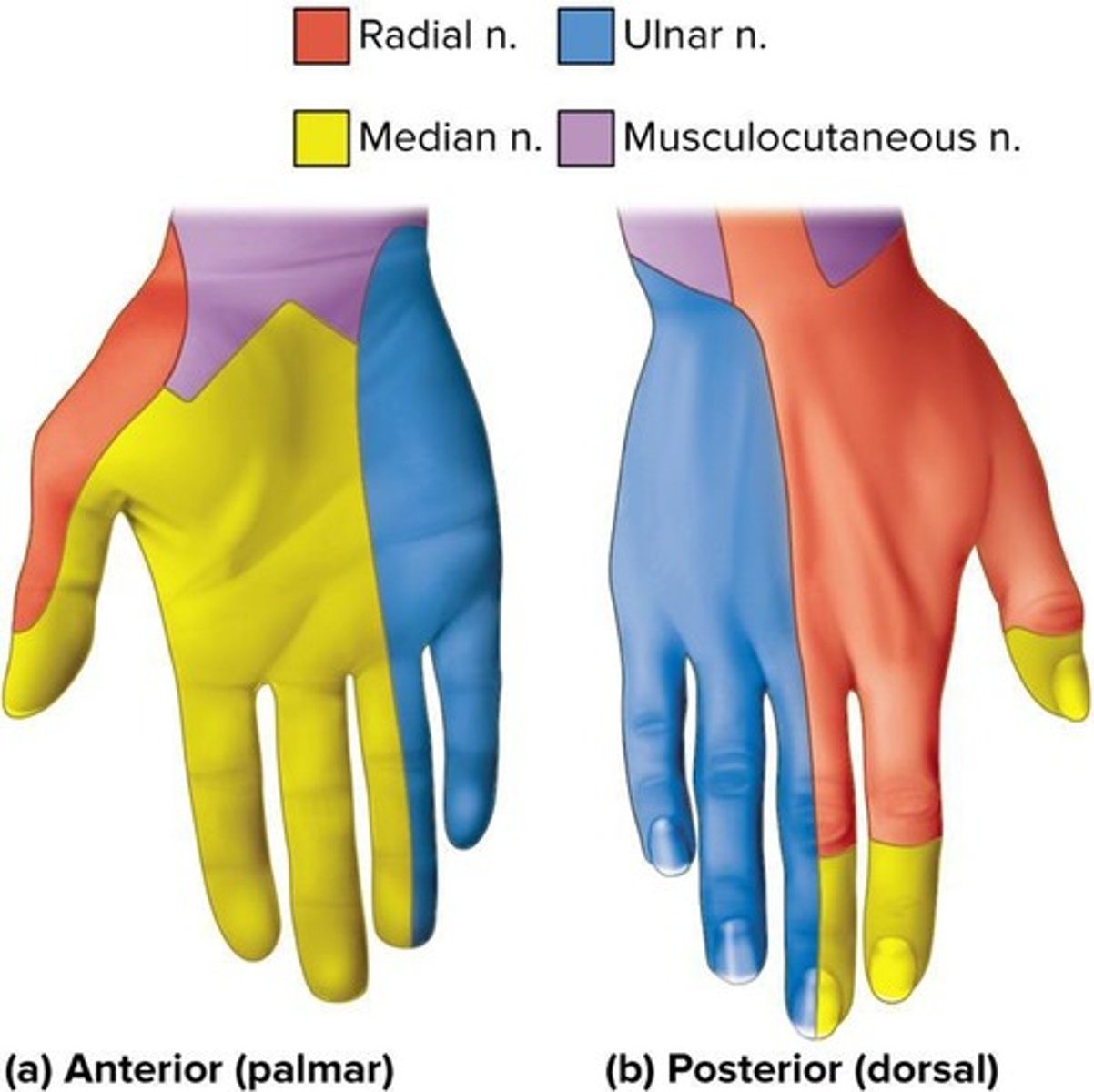
Median nerve
Nerve associated with carpal tunnel syndrome.
Lumbar plexus
Nerve plexus supplying lower back and genitalia.
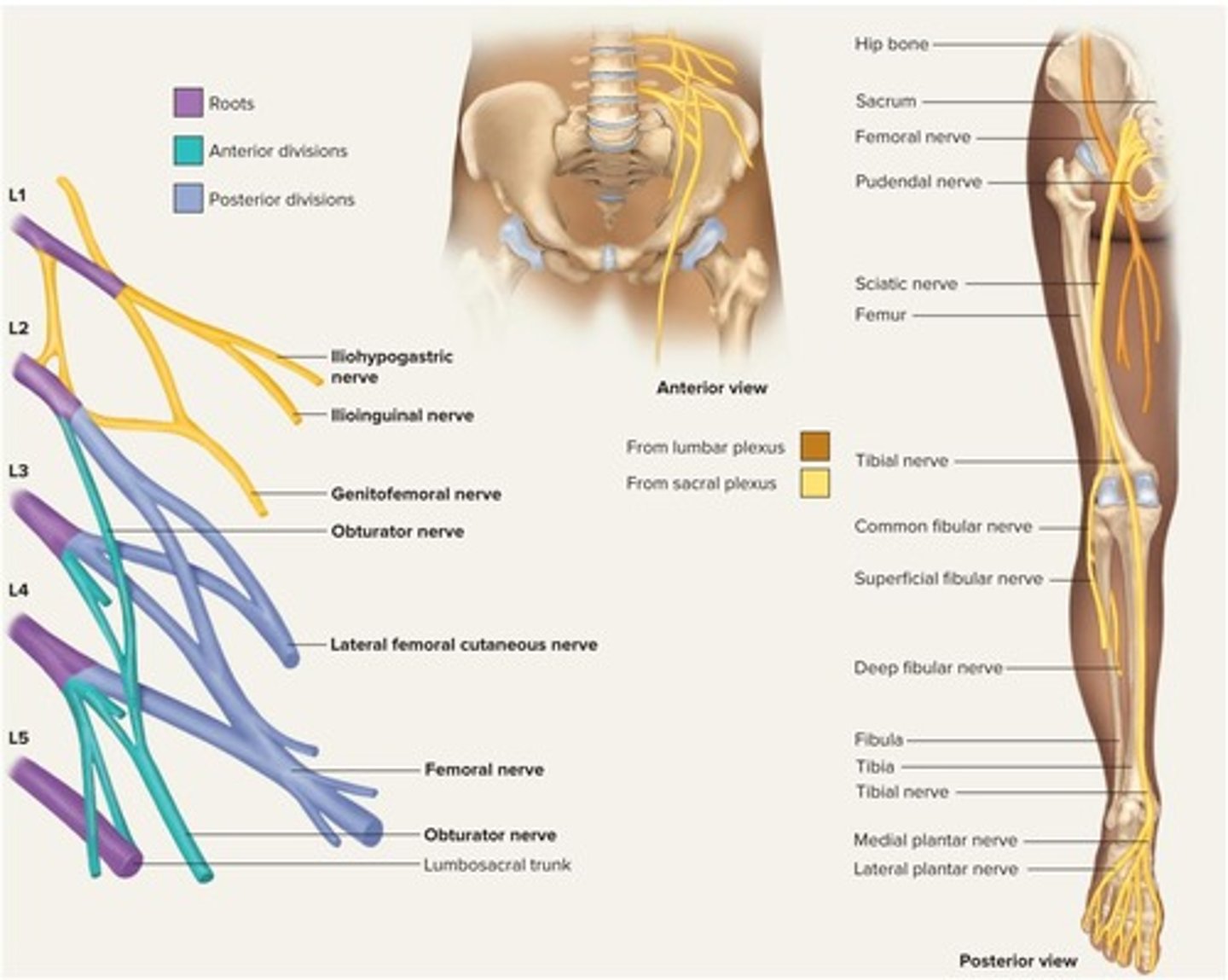
Sacral plexus
Nerve plexus supplying lower trunk and limbs.
Coccygeal plexus
Nerve plexus at the base of the spine.
Proprioception
Body position and movement information to the brain.
Somatic reflexes
Reflexes involving skeletal muscle contraction.
Dermatome
Skin area conveying sensory input to a spinal nerve.
Dermatome map
Diagram showing skin regions innervated by spinal nerves.
Somatic receptors
Receptors in skin, muscles, or tendons for reflexes.
Afferent nerve fibers
Carry sensory information to the spinal cord.
Integrating center
Synaptic contact point in spinal cord gray matter.
Efferent nerve fibers
Carry motor impulses to muscles from spinal cord.
Effectors
Muscles that execute the reflex response.
Muscle spindle
Stretch receptor in skeletal muscles monitoring length.
Extrafusal fibers
Muscle fibers generating force for movement.
Gamma motor neuron
Innervates intrafusal fibers to maintain muscle spindle tension.
Stretch reflex
Muscle contraction in response to stretching.
Knee-jerk reflex
Monosynaptic reflex tested by tapping the patellar tendon.
Reciprocal inhibition
Prevents antagonist muscles from opposing agonist contraction.
Flexor reflex
Withdrawal of limb from injurious stimulus.
Polysynaptic reflex arc
Pathway involving multiple synapses to reach muscle.
Crossed extension reflex
Extensor contraction in opposite limb during withdrawal.
Intersegmental reflex
Reflex input and output occur at different spinal levels.
Tendon organs
Proprioceptors in tendons monitoring tension.
Golgi tendon organ
1 mm long, monitors tension in tendons.
Complete transection
Total severance of spinal cord causing loss of function.
Paraplegia
Paralysis of both lower limbs.
Quadriplegia
Paralysis of all four limbs.
Paresis
Partial paralysis or weakness of limbs.