parasit lab: nematodes
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:10 AM on 2/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
1
New cards
nemathelminthes
phylum of round worms
2
New cards
egg
can be classified as fertilized or unfertilized
3
New cards
ova
can be classified as embryonated or unembryonated
4
New cards
ascaris lumbricoides
most common human helminthic infection globally
5
New cards
giant intestinal roundworm
common name of ascaris lumbricoides
6
New cards
small intestine
habitat of ascaris lumbricoides
7
New cards
humans
final host of ascaris lumbricoides
8
New cards
embryonated egg
infective stage of ascaris lumbricoides
9
New cards
egg
diagnostic stage of ascaris lumbricoides
10
New cards
ingestion of embryonated egg (soil)
mode of transmission of ascaris lumbricoides
11
New cards
200,000
Female worm produces approximately ____ eggs per day.
12
New cards
moist, warm, shaded soil
optimum environmental conditions for the larvae to develop
13
New cards
male
curved posterior tail
14
New cards
female
long pointed tail
15
New cards
cuticle
a tough layer of protection in the outermost layer
16
New cards
genital girdle
responsible for the contractions for the releasing of the ova in females
17
New cards
trilobated lips
Ascaris lumbricoides has also been called a “good kisser” because it has ____ for both females and males
18
New cards
albuminoid coat or mammilary coat
outer layer of unfertilized ovas
19
New cards
glycogen layer
middle layer of unfertilized ovas
20
New cards
inner lipoidal and vitelline
unfertilized eggs lack the _____ layer
21
New cards
corticated
when albuminoid/mammilary coat is prominent
22
New cards
decorticated
egg is smooth and the mamillary coat is not present or extremely minimal
23
New cards
loeffler's syndrome
ascaris lumbricoides causes
24
New cards
Albendazole & Mebendazole
ascaris lumbricoides drug treatment
25
New cards
intestinal obstruction
if a large amount of eggs ingested of about 200,000 eggs per day overtime if chronically progressed may lead to ____.
26
New cards
trichuris trichiura
Also called Trichocephalus triciura
● Soil Transmitted Helminth (STH)
● Soil Transmitted Helminth (STH)
27
New cards
whipworm
common name of trichuris trichiura
28
New cards
large intestine
habitat of trichuris trichiura
29
New cards
humans
final host of trichuris trichiura
30
New cards
embryonated egg
infective stage of trichuris trichiura
31
New cards
egg
diagnostic stage of trichuris trichiura
32
New cards
ingestion of infective stage
mode of transmission of trichuris trichiura
33
New cards
4-8 years
trichuris trichiura lifespan
34
New cards
single lanceolate specule
male end of the posterior has a ___
35
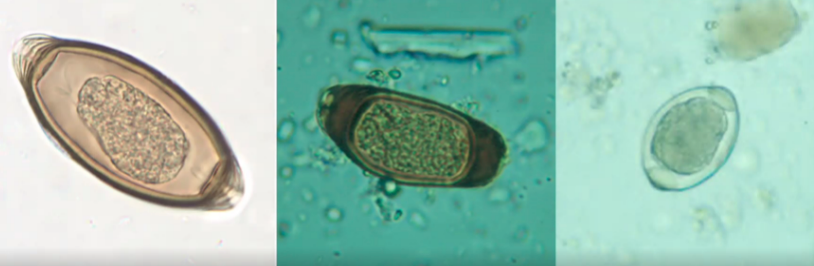
New cards
barrel, football, japanese lantern, lemon
trichuris trichiura resembles __
36
New cards
bipolar
has ___ mucus plugs
37
New cards
Capillary philippinensis ova
trichuris trichiura is confused with __
38
New cards
pin-fashion
adult attaches and burrows its anterior end into the intestinal mucosa in a ___ manner
39
New cards
enterobius vermicularis
originally called the Oxyuris vermicularis
40
New cards
pinworm, seatworm (tiwa), worm of society
common names of enterobius vermicularis
41
New cards
large intestine
habitat of enterobius vermicularis
42
New cards
humans
final host of enterobius vermicularis
43
New cards
embryonated egg
infective stage of enterobius vermicularis
44
New cards
egg
diagnostic stage of enterobius vermicularis
45
New cards
inhalation; autoinfection, retroinfection
mode of transmission of enterobius vermicularis
46
New cards
autoinfection
you infect yourself such as through ingestion of self-contaminated foods
47
New cards
retroinfection
migration of newly hatched larvae from the anal skin back into the rectum
48
New cards
oviposition
females die after __
49
New cards
copulation
males die after ___
50
New cards
2 months
adult life span of enterobius vermicularis
51
New cards
Gravid females
____ migrate nocturnally outside the anus and oviposit while crawling on the skin of the perianal area
52
New cards
cephalic alae/lateral
adult enterobius vermicularis possess ____ wings
53
New cards
esophageal
adult enterobius vermicularis possess ____ bulb that is flask shaped
54
New cards
male
shorter and thinner; curved posterior talk
55
New cards
females
longer and wider; pointed posterior tail
56
New cards
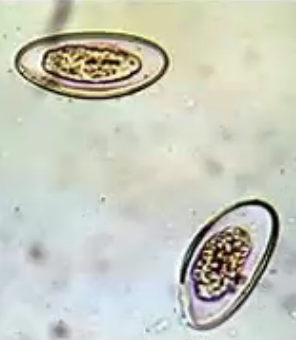
plano convex/lopsided/D-shaped egg
enterobius vermicularis egg shape
one side is flat while the other is curved
one side is flat while the other is curved
57
New cards
perianal swab
diagnosis of enterobius vermicularis
58
New cards
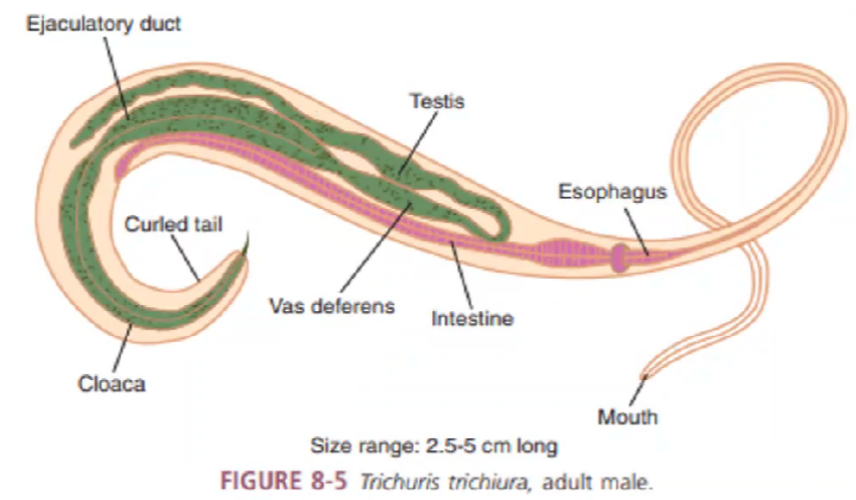
male trichuris trichiura
identify

59
New cards
enterobius vermicularis egg
identify
60
New cards
cephalic alae or lateral wings
identify

61
New cards
true
T/F: Cephaluc alae is found in the anterior end of adult Enterobius vermicularis
62
New cards
false
T/F: Male pinworm can be recovered in scotch tape swab