oocyte maturation
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
immature vs mature oocytes
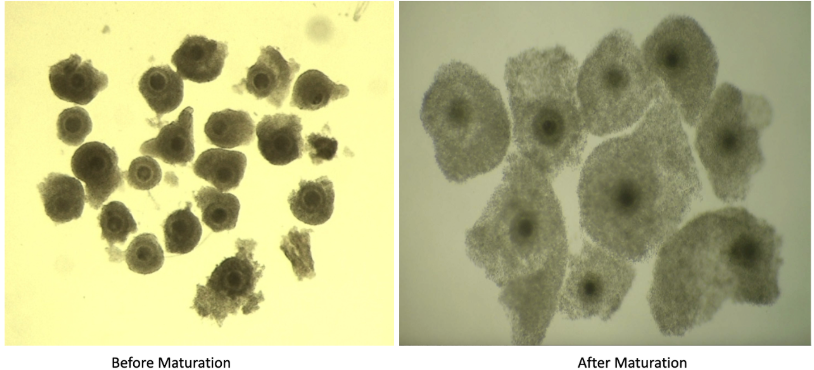
oocyte maturation
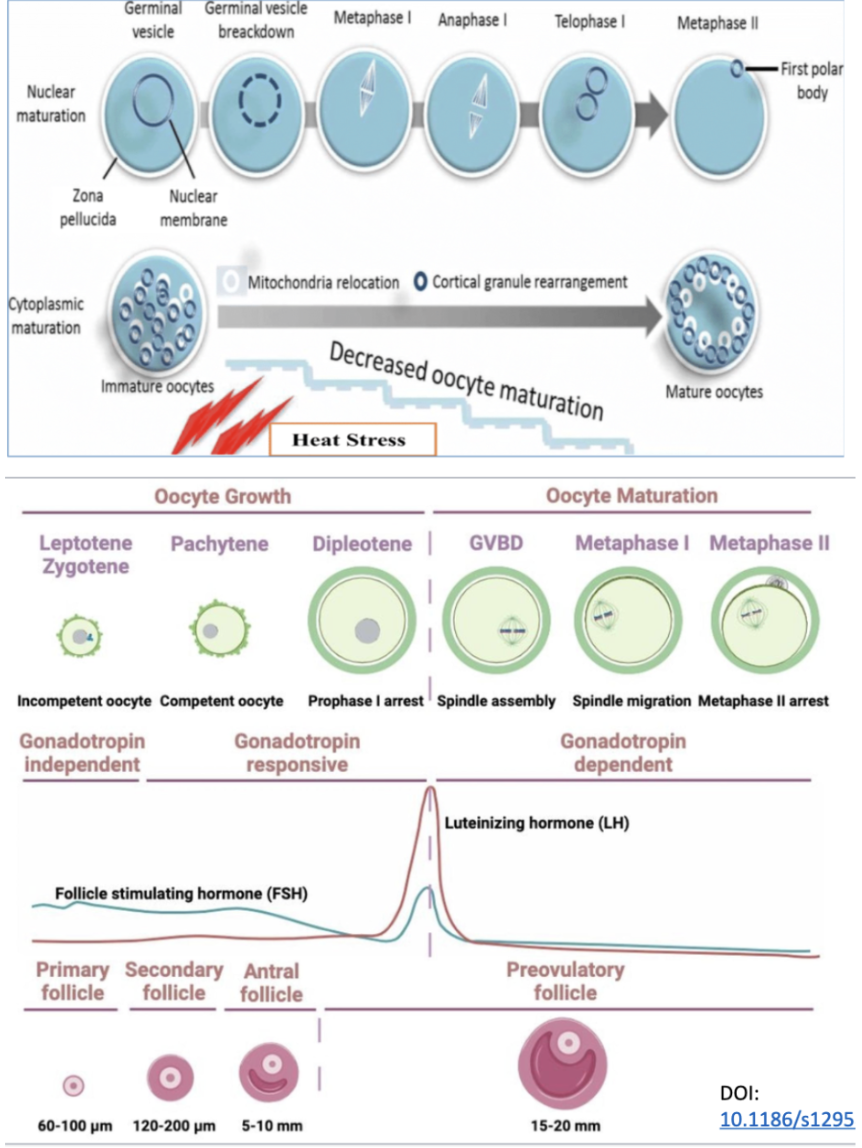
nuclear maturation
before LH surge
after LH surge
cytoplasmic maturation
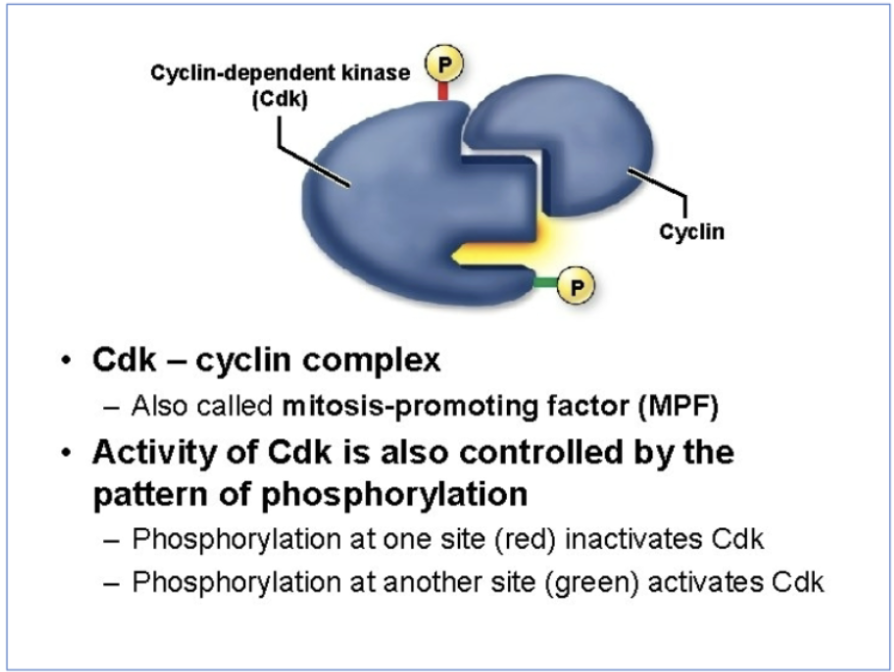
MPF
M-phase promoting factor
mitosis promoting factor
maturation promoting factor
CDZ-cyclin complex
CDK
Cyclin B
activity of CDK is also controlled by the pattern of phosphorylation
phosphorylation at one site (red) inactivates CDK
phosphorylation at another site (green) activates CDK
timeline of MPF activity
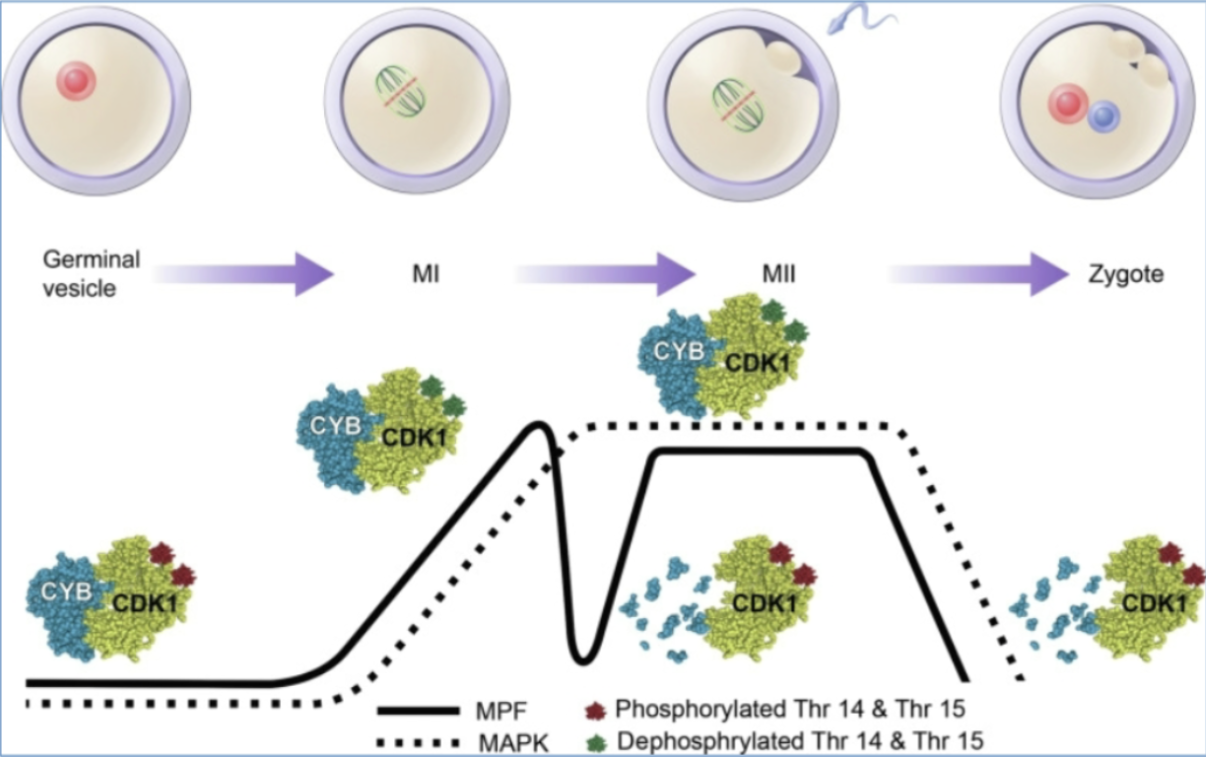
MPF
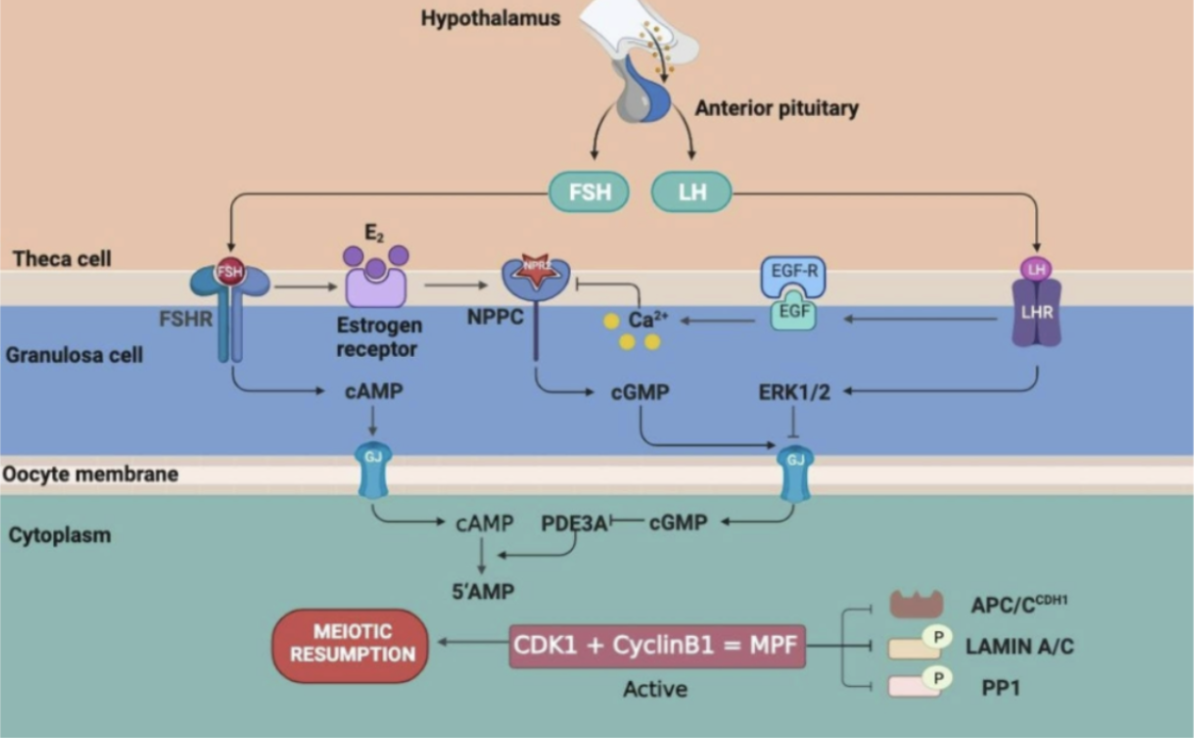
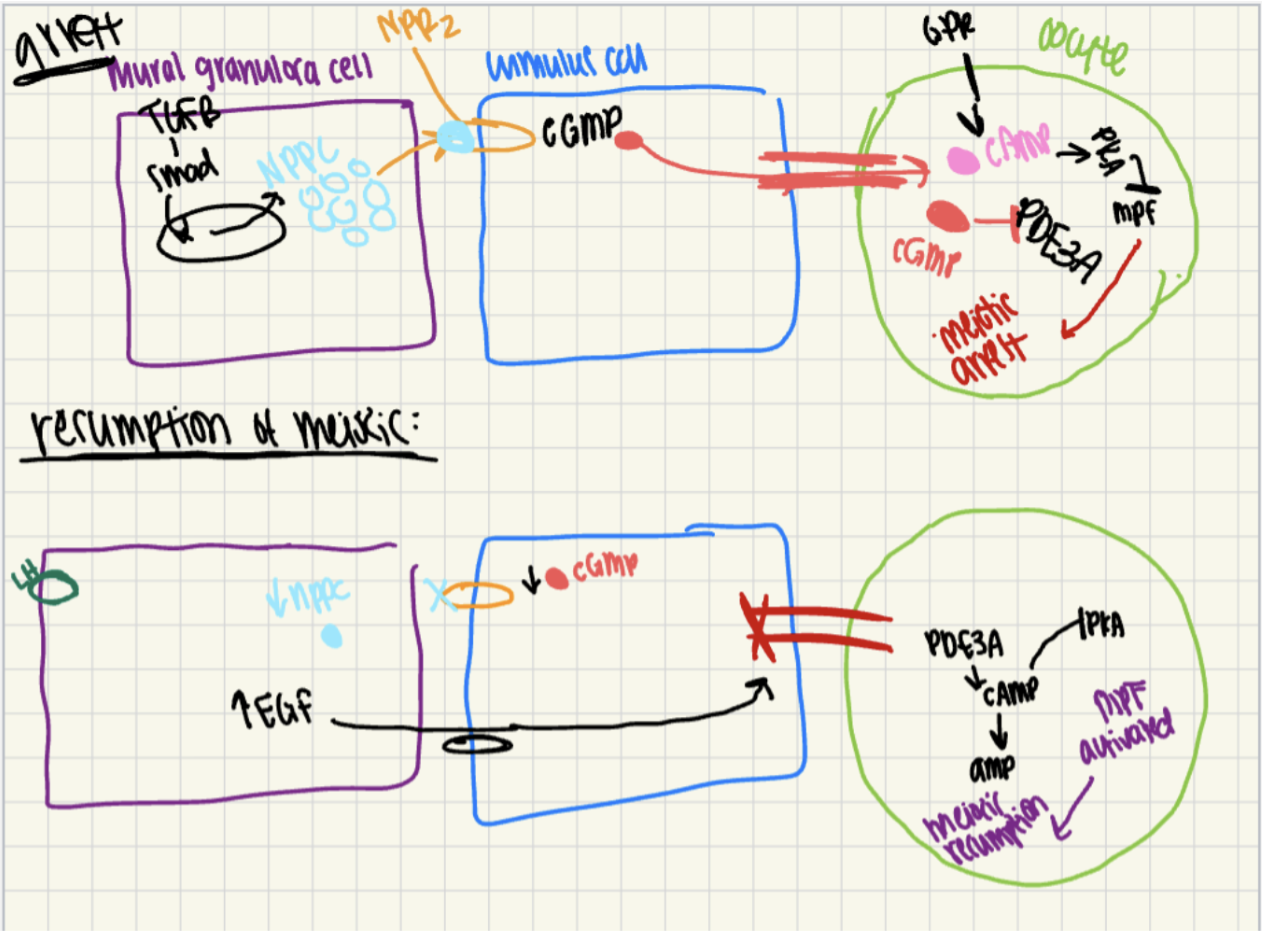
cAMP-mediated meiotic arrest
what maintains elevated cAMP concentrations?
granulosa/cumulus-derived cGMP
granulosa-derived factor stimulation of adenylate cyclase (AC)
binding to G-protein receptor 3 (GPR3)
FSH
other hormones
phosphodiesterase 3A (PDE3A) block
resumption of meiosis
decreased g-coupled protein kinase receptor 3 (GPR3) signaling
increased PDE3A
decreased granulosa/cumulus cGMP
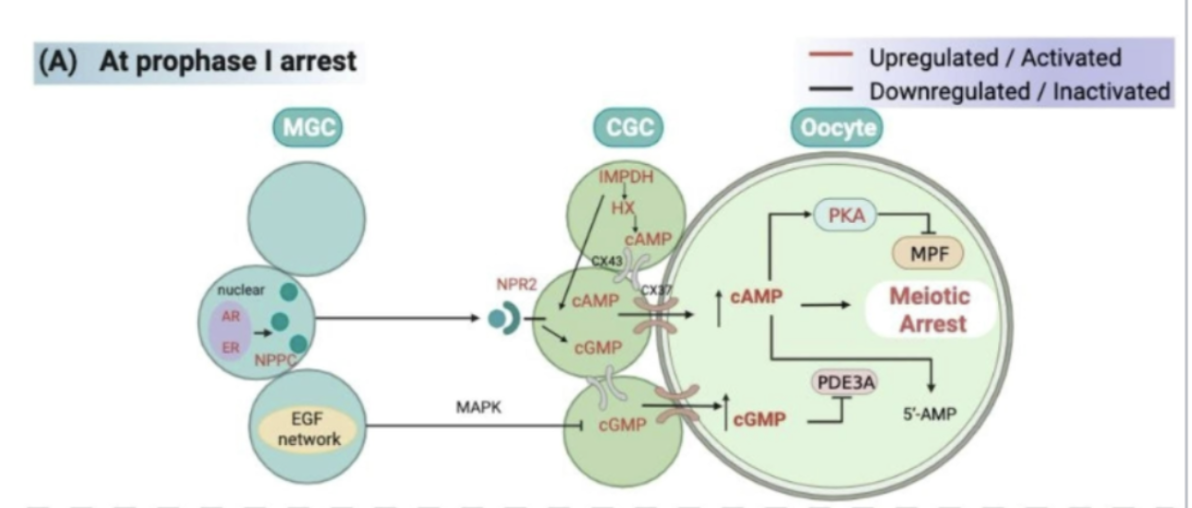
granulosa-cumulus cell maintenance of elevated cAMP levels
NEED TO KNOW:
species differences exist
cumulus cell-derived cGMP
gap junctions
phosphodiesterase (PDE3A)
natriuretic peptide receptor 2 (NPR2)
receptor activity controlled by natriuretic peptides (NPP), and the expression of NPPs are influenced by various cumulus-granulosa factors
paracrine system
so, elevated cGMP, blocks PDE3A, and this maintains elevated cAMP levels
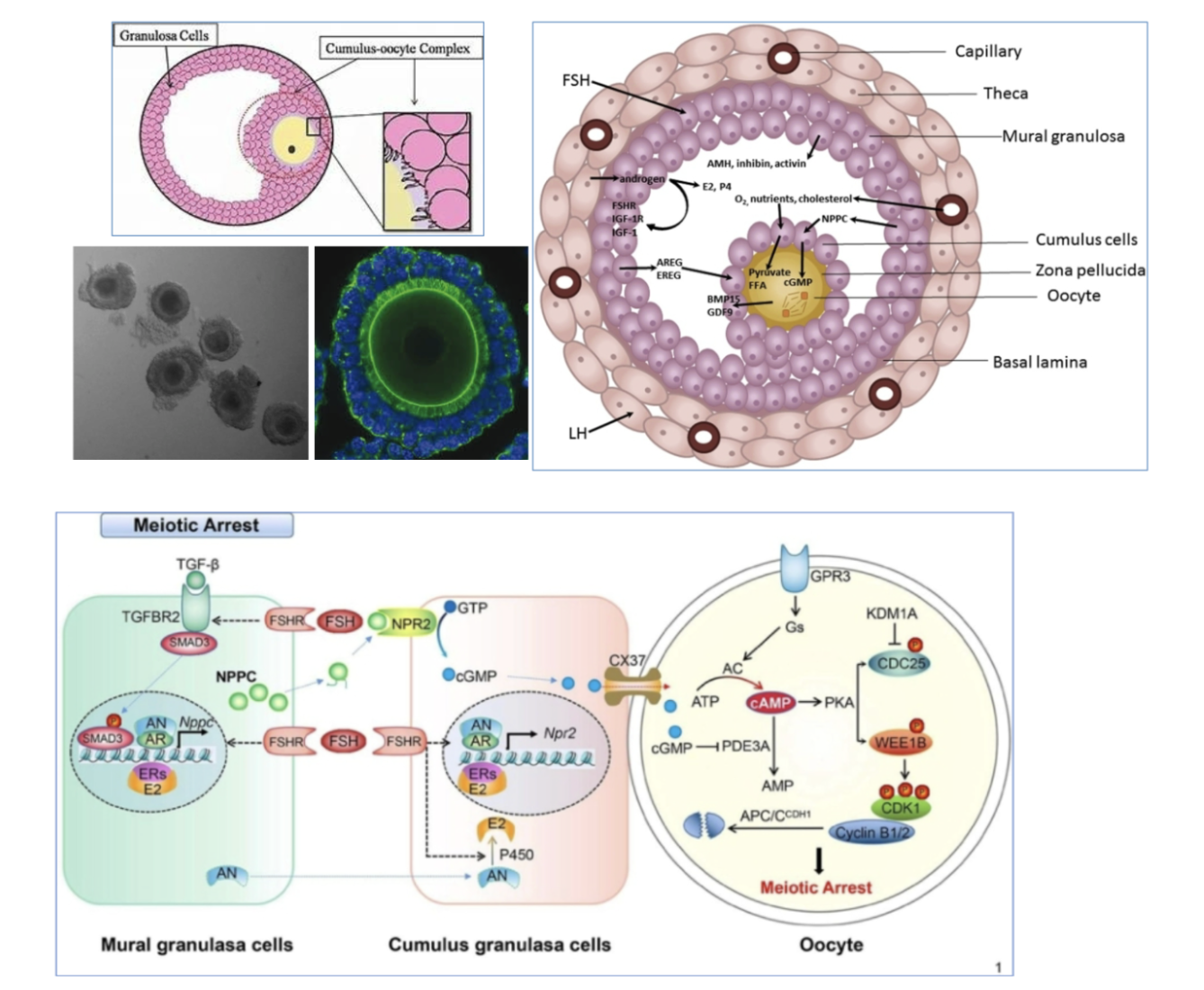
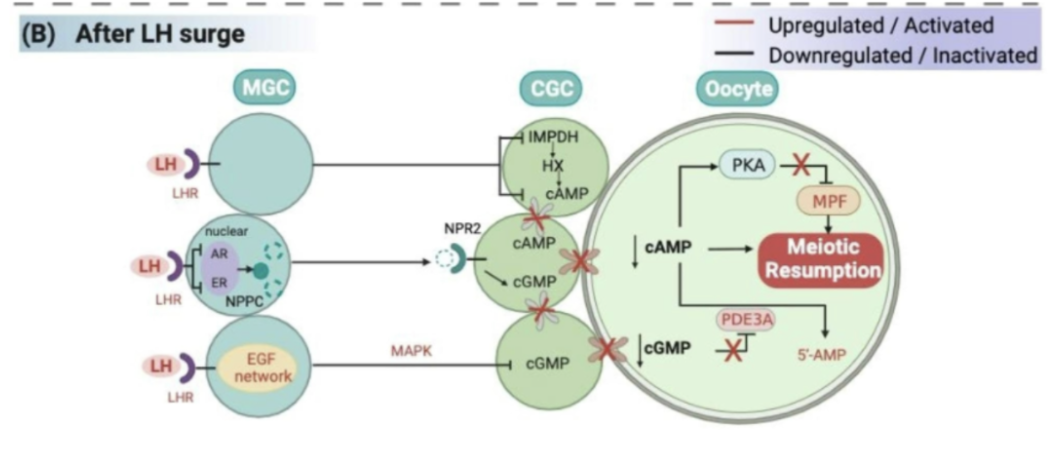
granulosa-cumulus cell mediation of meiosis resumption
LH-induced reduction in oocyte cAMP
NO LH RECEPTORS ON OOCYTE — ACTS ON GRANULOSA CELLS
LH increases granulosa cell cAMP
increases PDE1 and PDE5
decreases cGMP
PDE3A block is released in oocyte
conversion of cAMP to AMP
LH-mediated stimulation in EGF-like molecules (EGF-LP)
A-Reg, E-Reg act through EGF receptor (EGFR) in granulosa/cumulus cell to reduce cGMP transport through the oocyte
block NPR2
blocks cGMP production
block gap junctions
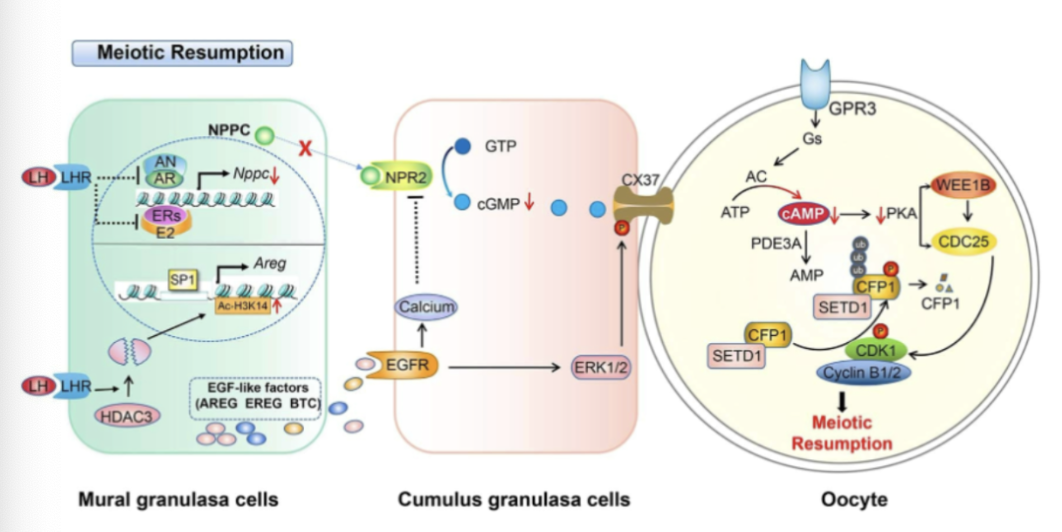
resumption of meiosis during in vitro fertilization (IVF)
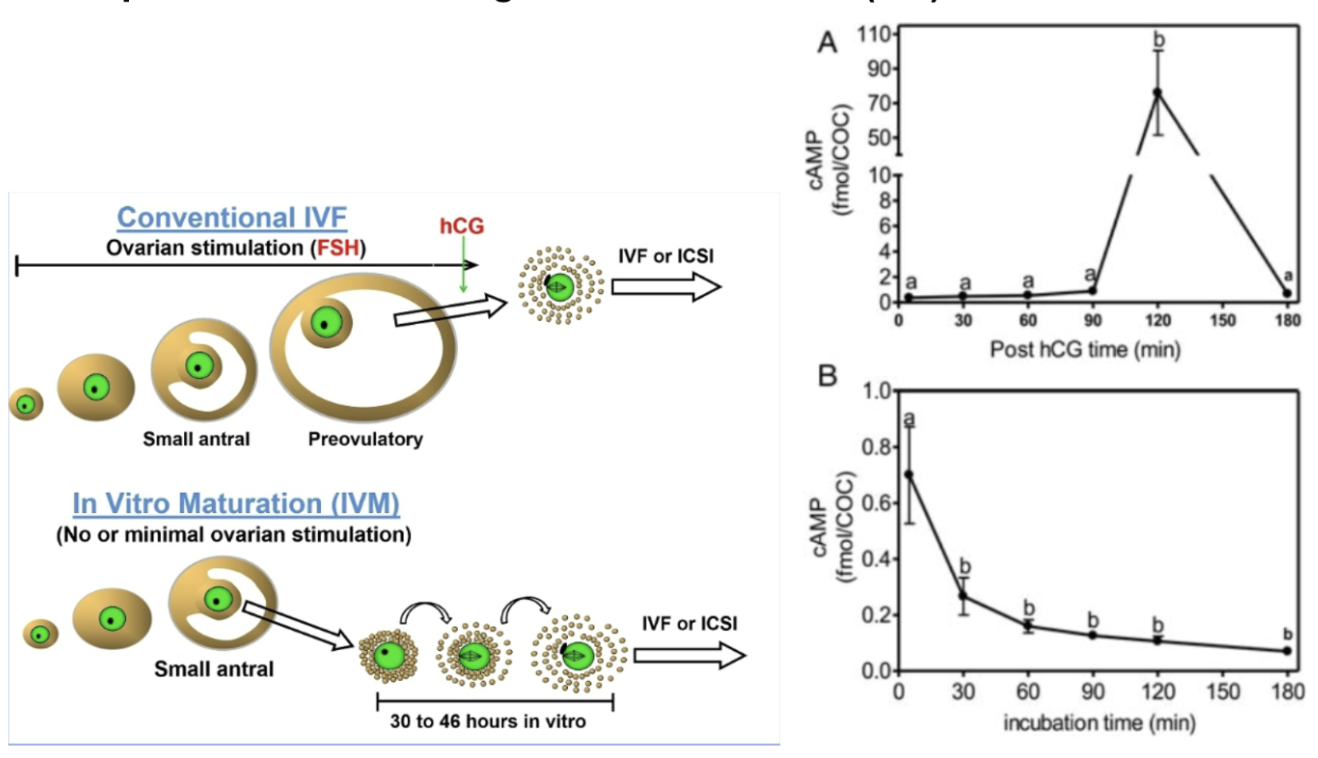
simulated physiological oocyte maturation (SPOM)
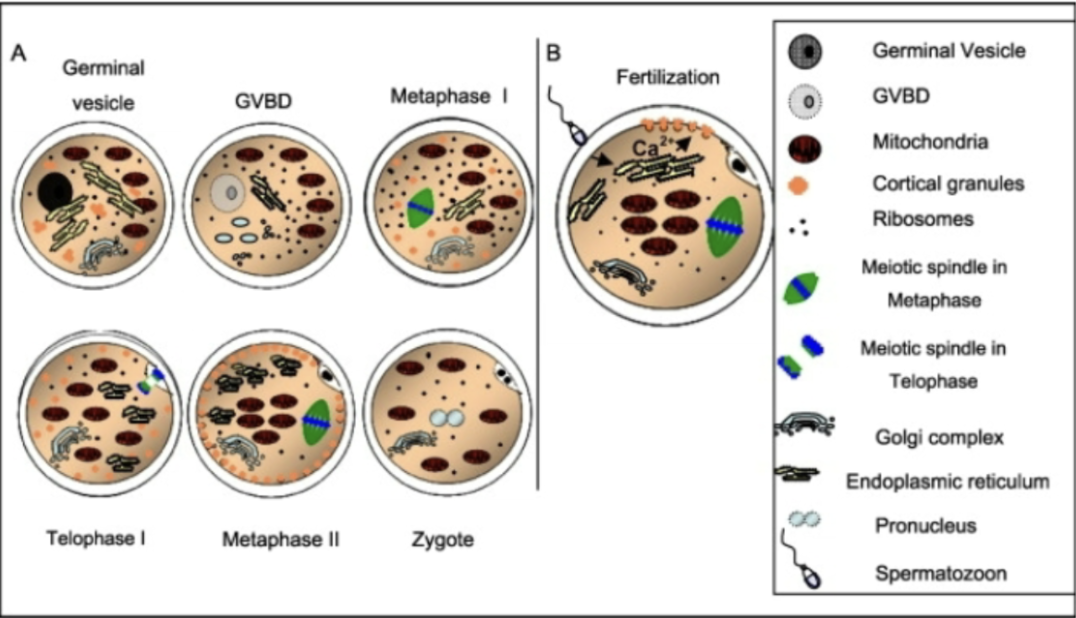
cytoplasmic (ooplasmic) maturation
cortical granule expansion and redistribution
mitochondria expansion and cellular redistribution
protein and mRNA packaging
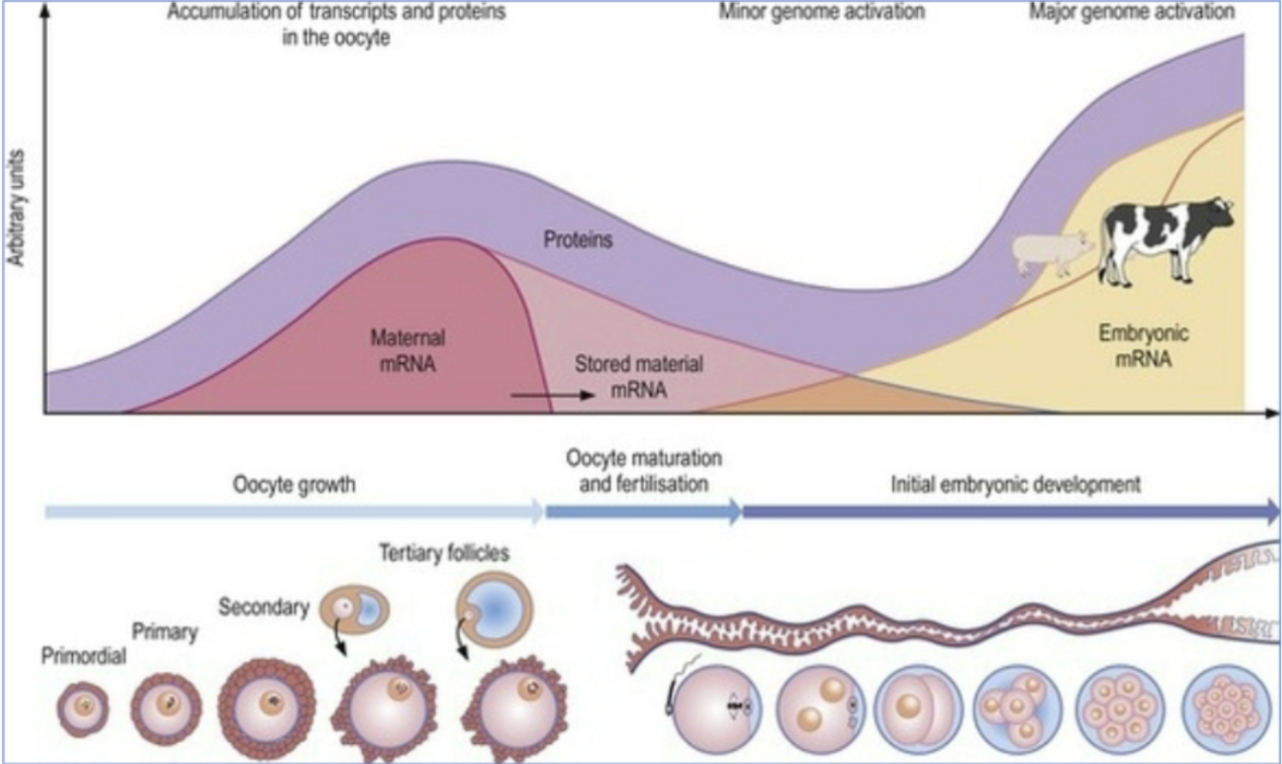
maternal mRNA storage
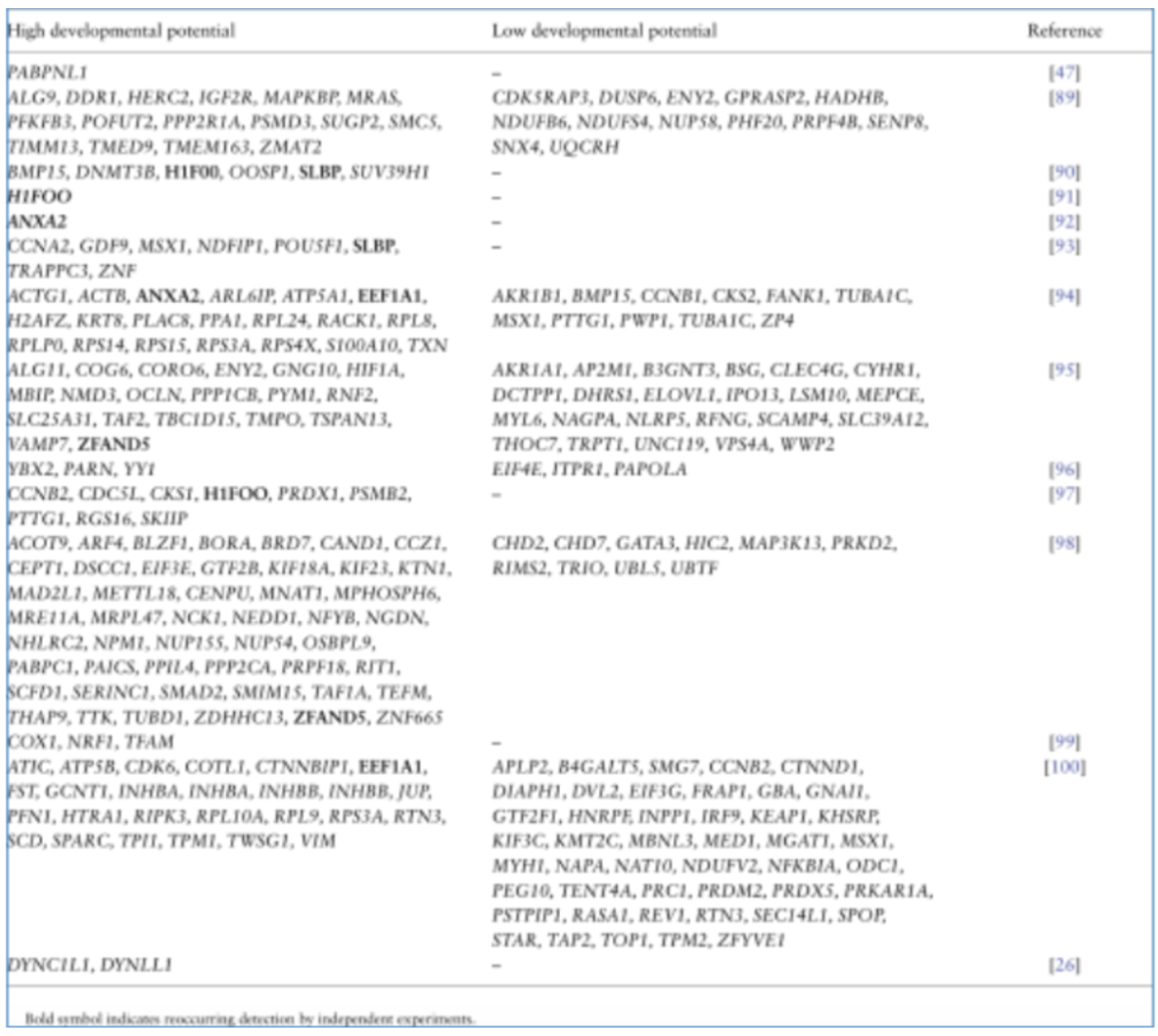
bovine transcripts associated with oocyte competency
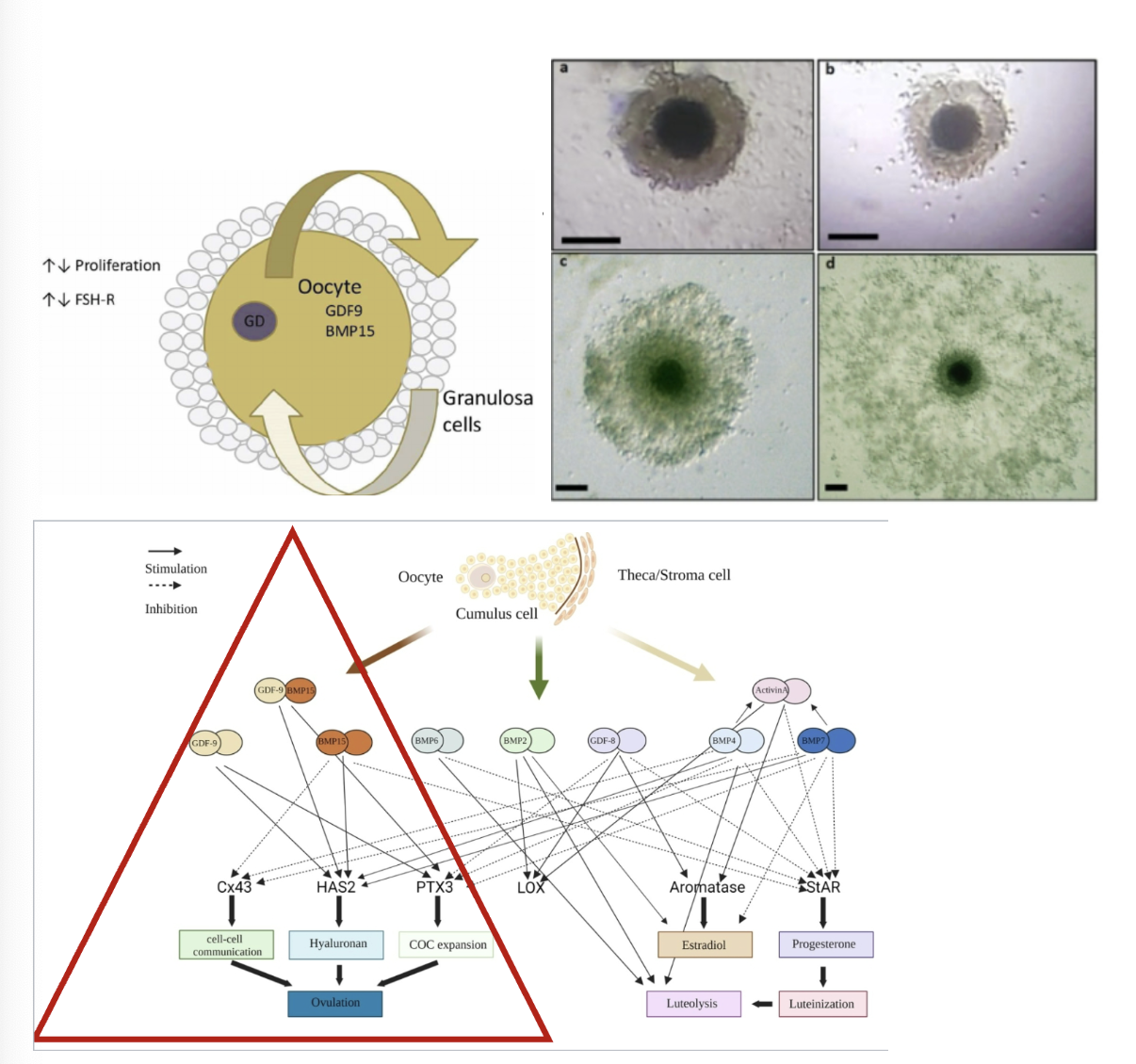
oocyte-secreted factors
soluble growth factors
growth-differentiation factor 9
bone morphogenetic protein 15
modulate various cumulus and granulosa cell activities
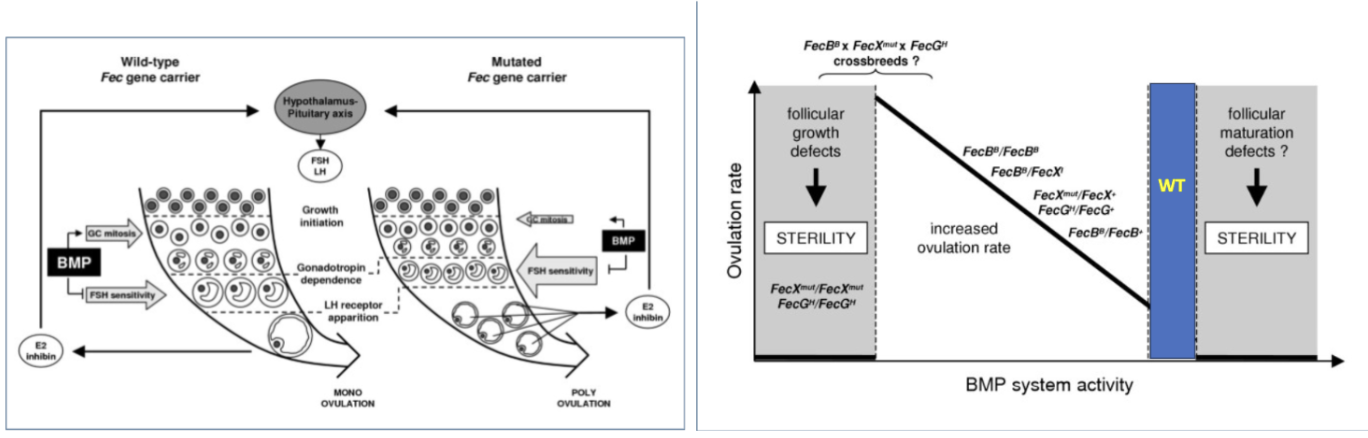
fecundity genes in sheep
inverdale sheep
romney breed
FecX mutation:
BMP15
single allele mutation = increased lamb #
increased twinning, triplets
double allele mutation = sterile
several other Fec mutations have been discovered
all of them target BMP15 of GDF9
Booroola Merino
FecB mutation:
BMPR-1B
wildtype: 1-2 lambs/ewe
monoallelic FecB: 3-4 lambs/ewe
biallelic FecB: 5+ lambs/ewe
terminology
fertility:
actual reproductive performance
number of offspring produced
fecundity:
the potential for an individual to reproduce
the capacity to produce offspring
number of gametes
health
environment
evolutionary

fecundity genes in sheep: mechanism
picture…