Chapter 1 Vocabulary: Morphology and Maturation of Human Blood Cells (Hematopoiesis)
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of vocabulary flashcards covering key concepts, cell types, and stages of hematopoiesis and blood cell morphology from Chapter 1 notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Hematopoiesis
The dynamic process of production and development of all blood and marrow cells; all blood cells derive from hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs).
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs)
Pluripotent stem cells that continuously self-renew and differentiate into every blood cell lineage; reside in specialized bone marrow niches.
Stem cell niche
A specialized microenvironment in bone marrow that provides signals supporting HSC self-renewal and multilineage repopulation.
Extramedullary hematopoiesis
Blood cell production outside the bone marrow, a compensatory mechanism when marrow cannot meet demand.
Buffy coat
The layer containing white blood cells and platelets after centrifugation of blood.
Plasma
The liquid component of blood (about 55% of blood) composed mainly of water with proteins and other solutes.
Albumin
Major plasma protein (about 55% of plasma proteins) that contributes to oncotic pressure.
Globulins
Plasma proteins making up about 38% of plasma proteins; involved in immune function and transport.
Fibrinogen
Plasma protein essential for coagulation; accounts for about 7% of plasma proteins.
RBCs (erythrocytes)
Mature red blood cells responsible for oxygen transport; biconcave discs 7–8 μm in diameter with no nucleus.
WBCs (leukocytes)
Nucleated cells of the immune system that defend against infection; include neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes.
Platelets (thrombocytes)
Anucleate cytoplasmic fragments (~1–4 μm) essential for hemostasis; contain granules and are found in the buffy coat.
Segemented neutrophil
Neutrophil with a multilobed nucleus (2–5 lobes) connected by filaments; cytoplasm pink; secondary granules contain alkaline phosphatase.
Band neutrophil
Immature neutrophil with a horseshoe-shaped nucleus; edges nearly parallel; normally 2–6% of neutrophils.
Eosinophil
Granulocyte with large orange-red granules; 0–4% of WBCs; granules 0.2–1.0 μm; cytoplasm pink to orange.
Basophil
Granulocyte with large violet-blue granules; 0–2% of WBCs; granules coarse and variable in size.
Lymphocyte
Mononuclear leukocyte (20–44% of WBCs); small with round nucleus and clumped chromatin; pale blue cytoplasm.
Monocyte
Largest WBC; gray-blue cytoplasm with fine granules; nucleus with folds/convolutions; 2–9% of WBCs.
Plasmacyte (plasma cell)
Mature B cell that produces antibodies; eccentrically placed nucleus and deep blue cytoplasm with perinuclear clearing.
Pronormoblast (rubriblast, proerythroblast)
Earliest recognizable erythroid precursor; round nucleus with nucleoli; distinct dispersed chromatin.
Basophilic normoblast (prorubricyte, basophilic erythroblast)
erythroid precursor with basophilic cytoplasm and coarsened chromatin pattern.
Polychromatophilic normoblast (rubricyte, polychromatophilic erythroblast)
Smaller erythroblast with pink (Hb) and blue (RNA) cytoplasm; late stage where pink often dominates.
Orthochromatic normoblast (metarubricyte, orthochromatic erythroblast)
Nucleated erythroblast with pyknotic nucleus; cytoplasm largely polychromatic; final nucleated erythroid stage.
Reticulocyte
Anucleate erythrocyte with residual RNA; polychromatic cytoplasm; visualized with special stains (e.g., methylene blue).
Erythrocyte (discocyte)
Mature red blood cell; nucleus- and organelle-free; flexible disc important for microcirculation passage.
Myelopoiesis (granulocytopoiesis)
Production and maturation of granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils) and monocytes.
Myeloblast
Earliest recognizable granulocytic precursor; round reddish-blue nucleus; delicate chromatin; minimal cytoplasm; no granules.
Promyelocyte
Granulocytic precursor with prominent primary granules and a large nucleus with nucleoli.
Neutrophilic myelocyte
Granulocytic precursor with round/oval nucleus and secondary pinkish granules.
Neutrophilic metamyelocyte
Granulocytic precursor with bean-shaped nucleus; indentation and abundant pink secondary granules.
Megakaryocyte
Largest bone marrow cell; multilobulated nucleus; cytoplasm fragments to form platelets.
Megakaryocytopoiesis
Process by which megakaryocytes proliferate and fragment to form platelets.
Monopoiesis
Monoblasts → promonocytes → monocytes → macrophages.
Lymphopoiesis
Development of lymphoid cells (T, B, NK) from HSCs; occurs in thymus and bone marrow for maturation; secondary organs coordinate immune responses.
Lymphoblast
Large lymphoid precursor with a large nucleus, thin chromatin, and nucleoli.
Prolymphocyte
Intermediate chromatin pattern in lymphoid development; clumped chromatin; characteristic paranuclear chromatin features.
Plasmablast
Early antibody-secreting B-cell precursor with large nucleus and fine chromatin; plasmacytic differentiation begins.
Proplasmacyte
Precursor to plasmacyte with blue cytoplasm and prominent juxtanuclear area; nucleus often eccentric.
Diapedesis
Movement of leukocytes across endothelium into tissues during immune response.
Cytokines
Soluble glycoprotein mediators secreted by cells to promote proliferation, differentiation, growth, or apoptosis of target cells.
G-CSF
Growth factor that stimulates neutrophil production; used clinically to treat neutropenia.
GM-CSF
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; stimulates multiple lineages including granulocytes and macrophages.
EPO
Erythropoietin; growth factor that stimulates erythroid precursor proliferation and differentiation.
Myeloid:Erythroid (M:E) ratio
Ratio of myeloid to erythroid precursors in bone marrow; about 4:1 in healthy adults.
Osteoclast
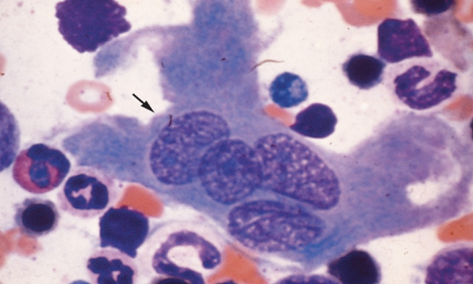
Giant (>100 µm) multinucleated, irregularly shaped marrow phagocytes responsible for bone resorption. Derived from monocyte macrophage hematopoietic lineage.
Osteoblasts
Large cell that can measure up to 30 um and are responsible for bone formation by synthesizing and secreting bone matrix.