Exercises 3-4 Anatomy Lab
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Ocular lenses
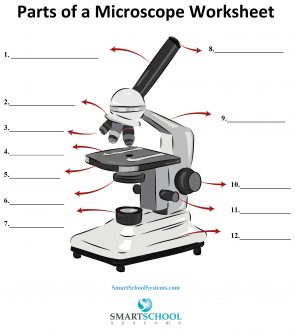
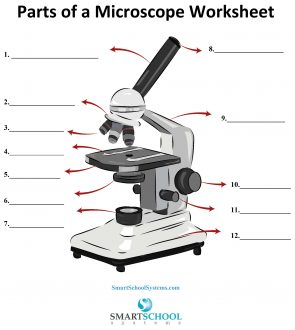
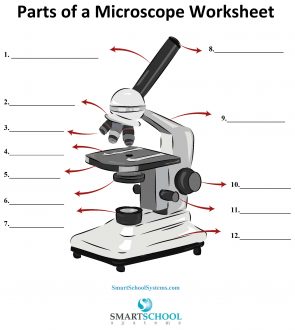
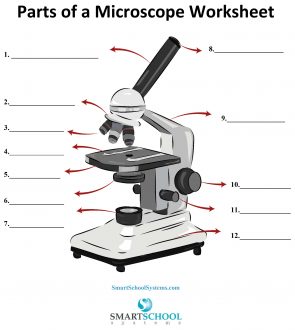
What part is #8 on the microscope?
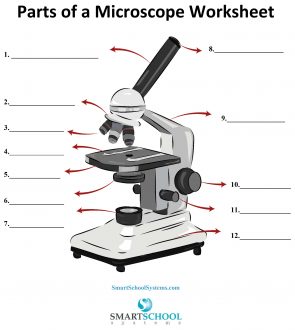
The arm
What part is #9 on the microscope?
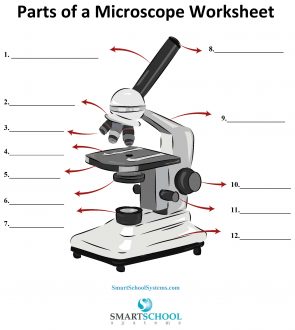
Rotating nosepiece
What part is #2 on the microscope?
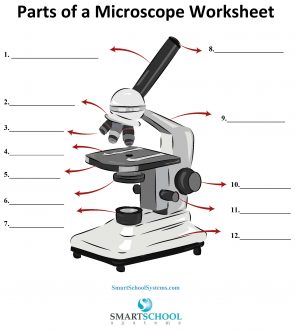
Objective lenses
What part is #3 on the microscope?
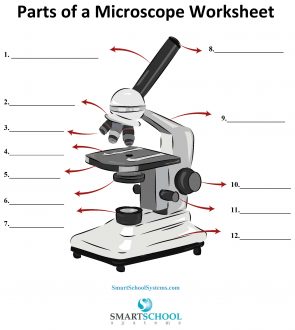
Mechanical stage
What part is #4 on the microscope?
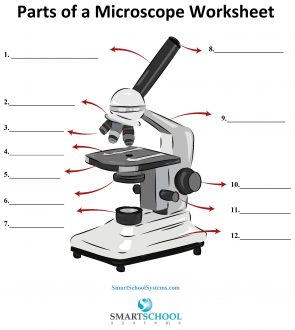
Stage
What part is #5 on the microscope?
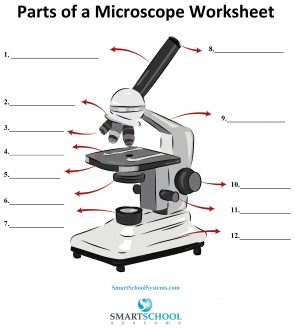
Condenser
What part is #6 on the microscope?
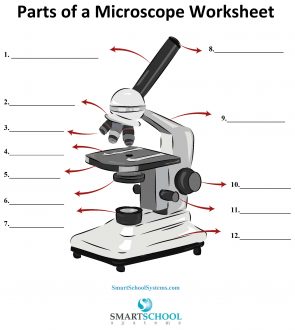
Condenser knob (regulates height of condenser)
What part is #11 on the microscope?
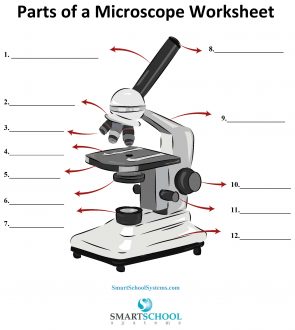
Coarse adjustment knob
What part is #10 on the microscope?
Fine adjustment knob
What part is #11 on the microscope?
Substage light
What part is #7 on the microscope?
Base
What part is #12 on the microscope?
Iris diaphragm lever (definition)
Adjusts size of aperture in condenser, controlling amount of light that passes through specimen
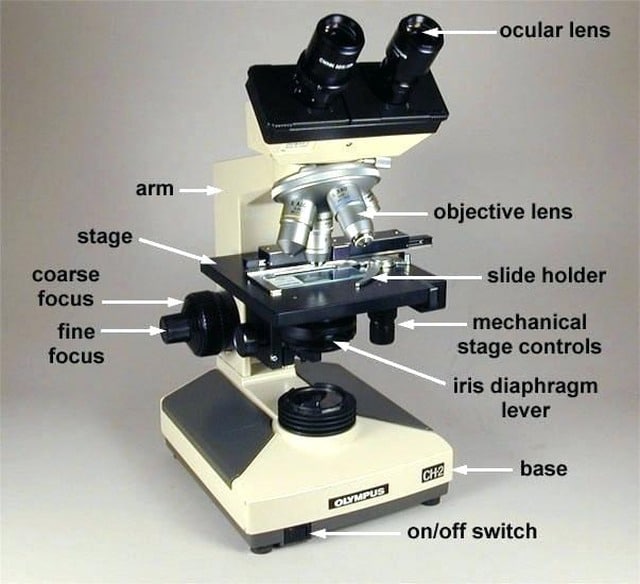
Mechanical stage controls (definition)
Moves specimen slide along x and y axis using two knobs
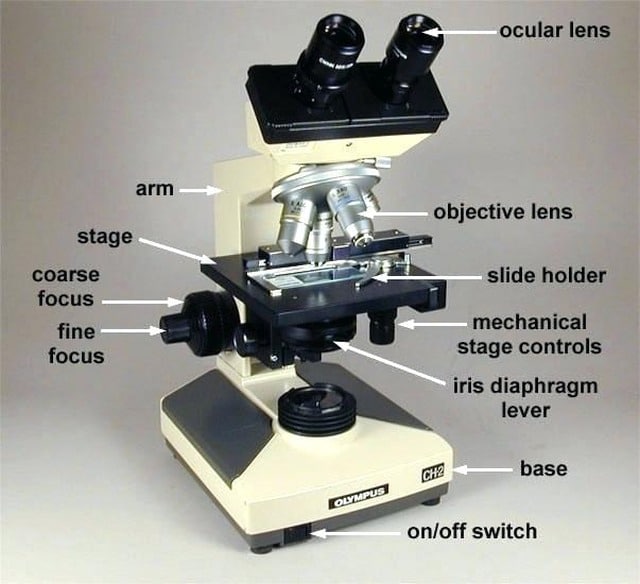
Total magnification (TM)
the power of the ocular lens multiplied by the power of the objective lens (ocular lens is always 10, objective lens change 4x, 10x, 40x, 100x) (10 x objective = TM)
Resolution
The ability to discriminate two close objects as separate in microscope
Base (definition)
The bottom of the microscope. Provides a sturdy flat surface to support and steady the microscope
Substage light (definition)
Located in the base. Light from the lamp passes directly upward through the microscope
Light control (definition)
Located on the base or arm. Dial allows you to adjust the intensity of the light passing through the specimen
Stage (definition)
The platform that the slide rests on while being viewed. Stage has a whole in it to allow light to pass through the stage through the specimen
Mechanical stage (definition)
Holds slide in position for viewing and has two adjustable knobs that control the precise movement of the slide
Condenser (definition)
Small non-magnifying lens located beneath the stage that concentrates the light on the specimen. May have a knob that lowers and raises condenser to vary light delivery. Best position is close to inferior surface of the stage
Coarse adjustment knob (definition)
Allows you to make large adjustments to the height of the stage to initially focus specimen
Fine adjustment knob (definition)
Used for precise focusing once the initial coarse focusing has been completed
Microscope head (definition)
Attaches to nosepiece to support the objective lens system. Provides for attachment of the eyepieces which house ocular lenses
Microscope arm (definition)
Vertical portion of the microscope that connects to the base and the head
Nosepiece (definition)
Rotating mechanism connected to head. Generally carries three or four objective lenses and permits positioning of the lens over the hole in the stage
Objective lenses (definition)
Lenses that are attached to the nosepiece. Usually has four objective lenses: scanning (4x), low-power (10x), high power (40x), and oil immersion (100x).
Ocular lens (definition)
two lenses located in eyepieces of microscope
Real Image
Formed when light rays converge and can be projected onto a screen. It is inverted and has the same or varying size compared to the object, depending on the distance from the lens or mirror
Virtual Image
A virtual image is formed when light rays appear to diverge from a point and cannot be projected onto a screen. It is upright and appears to be located behind the lens or mirror
Ribosomes
tiny spherical bodies composed of RNA and protein; floating free or attached to a membranous structure (the rough ER) in the cytoplasm. Actual sites of protein synthesis
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Membranous system of tubules that extends throughout the cytoplasm; two varieties (smooth and rough)
Rough ER
studded with ribosomes; tubules of the rough ER provide an area for storage and transport of the proteins made on the ribosomes to other cell areas
Smooth ER
a site of steroid and lipid synthesis, lipid metabolism, and drug detoxification. Does NOT have ribosomes for protein synthesis
Golgi Apparatus
stack of flattened sacs with bulbous ends and associated small vesicles; found close to the nucleus. Plays a role in packaging proteins or other substances for export from the cell or incorporation into the plasma membrane and in packaging lysosomal enzymes
Lysosomes
various-sized membranous sacs containing digestive enzymes including acid hydrolyses; function to digest worn-out cell organelles and foreign substances that enter the cell. Have the capacity of total cell destruction if ruptured and are for this reason referred to as “suicide sacs”
Peroxisomes
Small lysosome-like membranous sacs containing oxidase enzymes that detoxify alcohol, free radicals, and other harmful chemicals. They are particularly abundant in liver and kidney cells
Mitochondria
Generally rod-shaped bodies with a double-membrane wall; inner membrane is shaped into folds, or cristae; contain enzymes that oxidize foodstuffs to produce cellular energy (ATP); often referred to as the “powerhouse of the cell”
Centrioles
Paired, cylindrical bodies that lie at right angles to each other, close to the nucleus. Internally, each centriole is composed of nine triplets of microtubules. As part of the centrosome, they direct the formation of the mitotic spindle during cell division; form the bases of cilia and flagella and in that role are called basal bodies
Cytoskeleton
Provides cellular support; function in intracellular transport
Microfilaments
Formed largely of actin, a contractile protein, and are important in cell mobility, particularly in muscle cells
Intermediate filaments
stable elements composed of a variety of proteins and resists mechanical forces acting on cells
Microtubules
form the internal structure of the centrioles and helps determine cell shape
order of the cell cycle
G1 (growth), S (growth and DNA synthesizes), G2 (growth and final prep for division), M (mitotic phase)
Mitosis
product is two daughter nuclei that are genetically identical to the mother nucleus
Meiosis
product is four daughter nuclei that differ genetically from the mother nucleus and is used only for the production of gametes (egg and sperm) for sexual reproduction
order of mitosis
interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
Prophase
the centrioles separate releasing the spindle fibers. Chromosomes are formed within the nucleus. The nuclear envelope starts to disintegrate.
Metaphase
The Nuclear envelope and nucleolus disintegrate; the chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. The spindle fibers attach to the centromeres
Interphase
The centriole duplicates. The cell grows, performs normal cell functions, and DNA replicates. Then, the cell prepares for cell division
Anaphase
the cell elongates; the spindle fibers pull the chromosomes apart into sister chromatids
Cytokinesis
active cell divides and forms two separate cells that each start their own cell cycle
Telophase
The two nuclear envelopes form around the chromatids and the chromosomes uncoil; the spindle fibers disperse and the membrane starts to pull apart.
continuous
what type of process is mitosis