Anatomy of the Equine Gastrointestinal System (Part 1) - Dr. Masty
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Flank
topographic region of abdominal wall from ribs to ________
________ of the flank
skin and cutaneous trunci reflecting onto thigh
Paralumbar fossa
hollow area of the flank
Cranial boundary of the flank
Caudal boundary of the flank
Ventral boundary of the flank
Innervation of the flank
lateral cutaneous branches of __________ and branches of thoracic and lumbar spinal nerves
Five nerves of the flank:
1.) costoabdominal nerve
2.) iliohypogastric nerve
3.) ilioinguinal nerve
4.) genitofemoral nerve
5.) lateral cutaneous femoral nerve
costoabdominal nerve
thoracic nerve #
location of the costoabdominal nerve
costrochondral junction of rib 18
iliohypogastric nerve
L1
ilioinguinal nerve
L1
location of the ilioinguinal nerve
v
genitofemoral nerve
lumbar nerve #
lateral cutaneous femoral nerve
L4
location of the lateral cutaneous femoral nerve
subiliac lymph node with caudal branches of deep circumflex iliac artery
Skin of the abdominal wall
umbilicus located on ________
midline incision of the abdominal wall
cuts through _________
paramedian incision of the abdominal wall
cuts through _________
Five muscles of abdominal wall
1.) cutaneous trunci
2.) external abdominal oblique
3.) internal abdominal oblique
4.) transversus abdominis
5.) rectus abdominis
Cutaneous trunci muscle
sheet of muscle immediately deep to the skin
cutaneous omobrachialis
cutaneous muscle of the shoulder
External abdominal oblique muscle
muscle and aponeurosis; covered by abdominal tunica (aka tunica flava abdominus)
Three features of the external abdominal oblique muscle:
1.) caudo _________ fibers
2.) inguinal ligament
3.) __________ inguinal ring
4.) part of the ___________ sheath of the rectus abdominus muscle
inguinal ligament
________ edge of external abdominal oblique muscle
__________ inguinal ring
v
heave line
clinical condition known as "Heaves"; hypertrophy of muscular position of external abdominal oblique in emphysema
Two features of internal abdominal oblique muscle:
1.) cranio ___ fibers
2.) part of _______ sheath of the rectus abdominus msucle
Three features of transversus abdominus:
1.) all of _______ sheath of the rectus abdominus
2.) _________ fibers
3.) cranial branch of deep circumflex iliac artery
Three features of rectus abdominus:
1.) _________ tendon
2.) tendinous intersections, no aponeurosis
3.) covered by _________ and _________
Three ingional canal structures
1.) superfical inguinal ring
2.) deep inguinal ring
3.) vaginal ring
superfical inguinal ring
natural slit in apopneurosis of ____
deep inguinal ring
formed by edges of __________ abdominal oblique as it is positioned deep to the inguinal ligament
vaginal ring
peritoneal lining over _______ inguinal ring
Total path through the large intestine:
cecum --> ascending colon --> transverse colon --> small colon --> rectum --> anal canal --> anus
cecum
comma shaped, initial segment of the large intestine where fermentation occurs
The ascending colon is the _________ segment of the equine large intestine
longest
Model for the structure of the ascending colon
two "U"s on top of each other, connected on the left side of the body
The ascending colon is broken up into four segments:
1.) right ventral colon
2.) left ventral colon
3.) left dorsal colon
4.) right dorsal colon
Three flexures of the ascending colon:
1.) sternal flexure
2.) pelvic flexure
3.) diaphragmatic flexure
sternal flexure of the ascending colon
bend between the right ventral and left ventral quadrants (right to left)
pelvic flexure of the ascending colon
bend between the left ventral and left dorsal quadrants (ventral to dorsal)
diaphragmatic flexure of the ascending colon
bend between the left dorsal and right dorsal quadrants (left to right)
right ventral colon
1
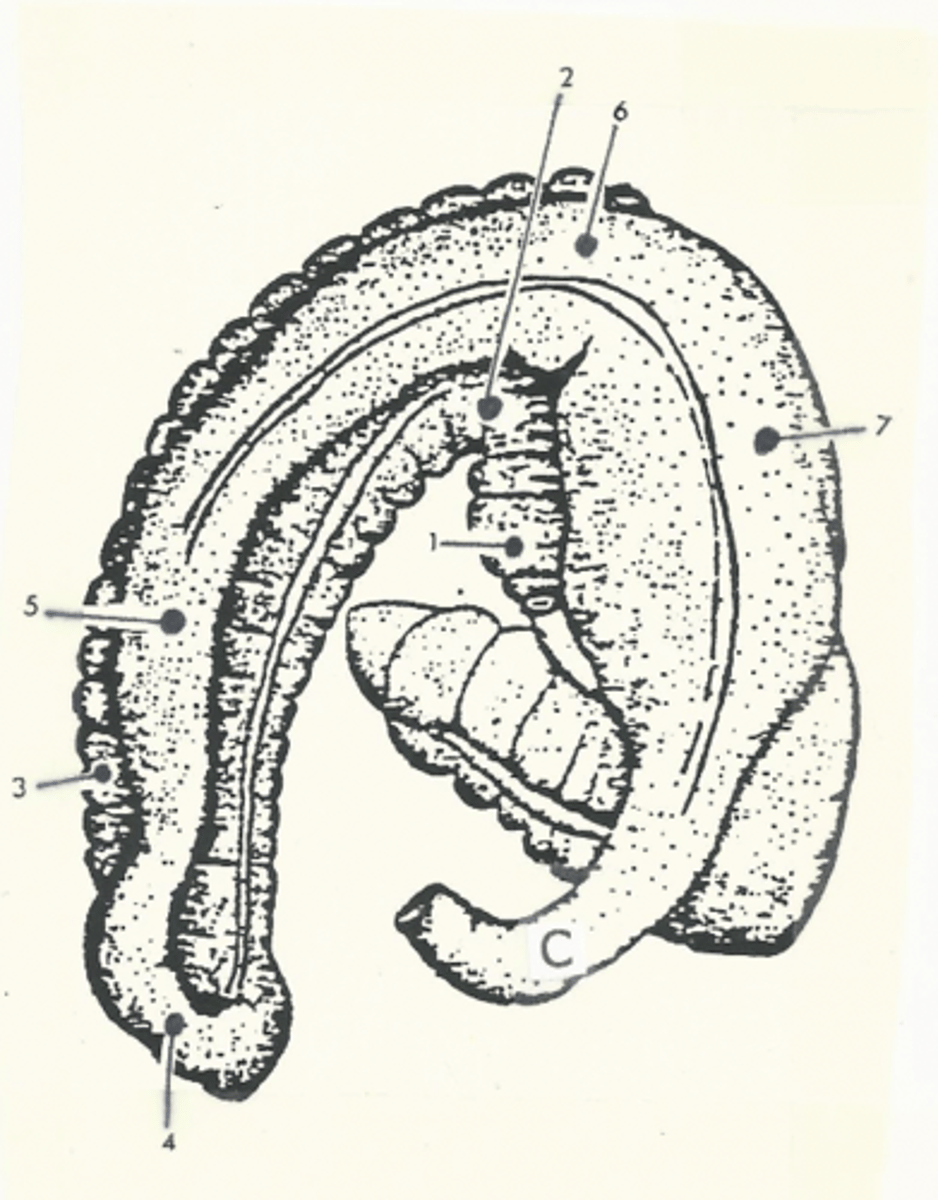
sternal flexure
2
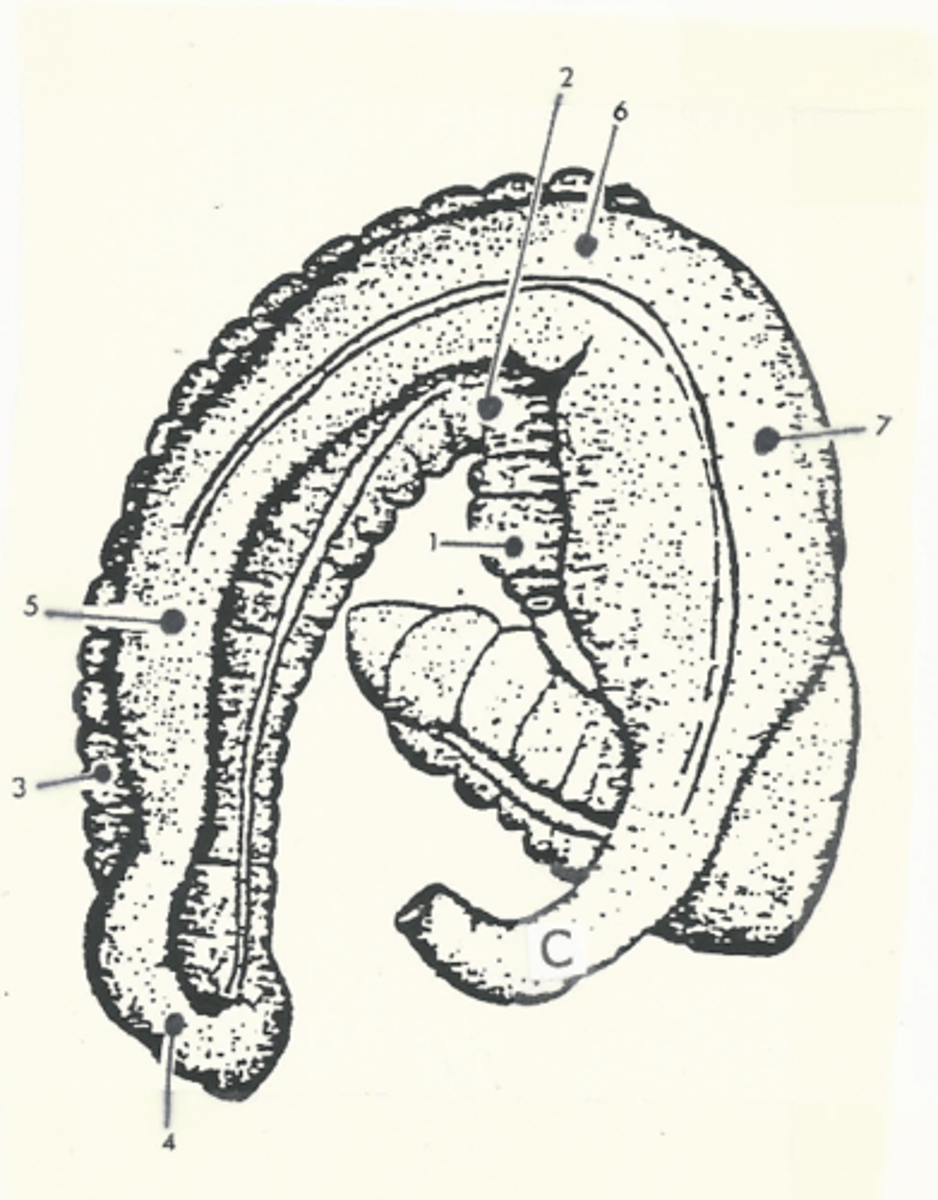
left ventral colon
3
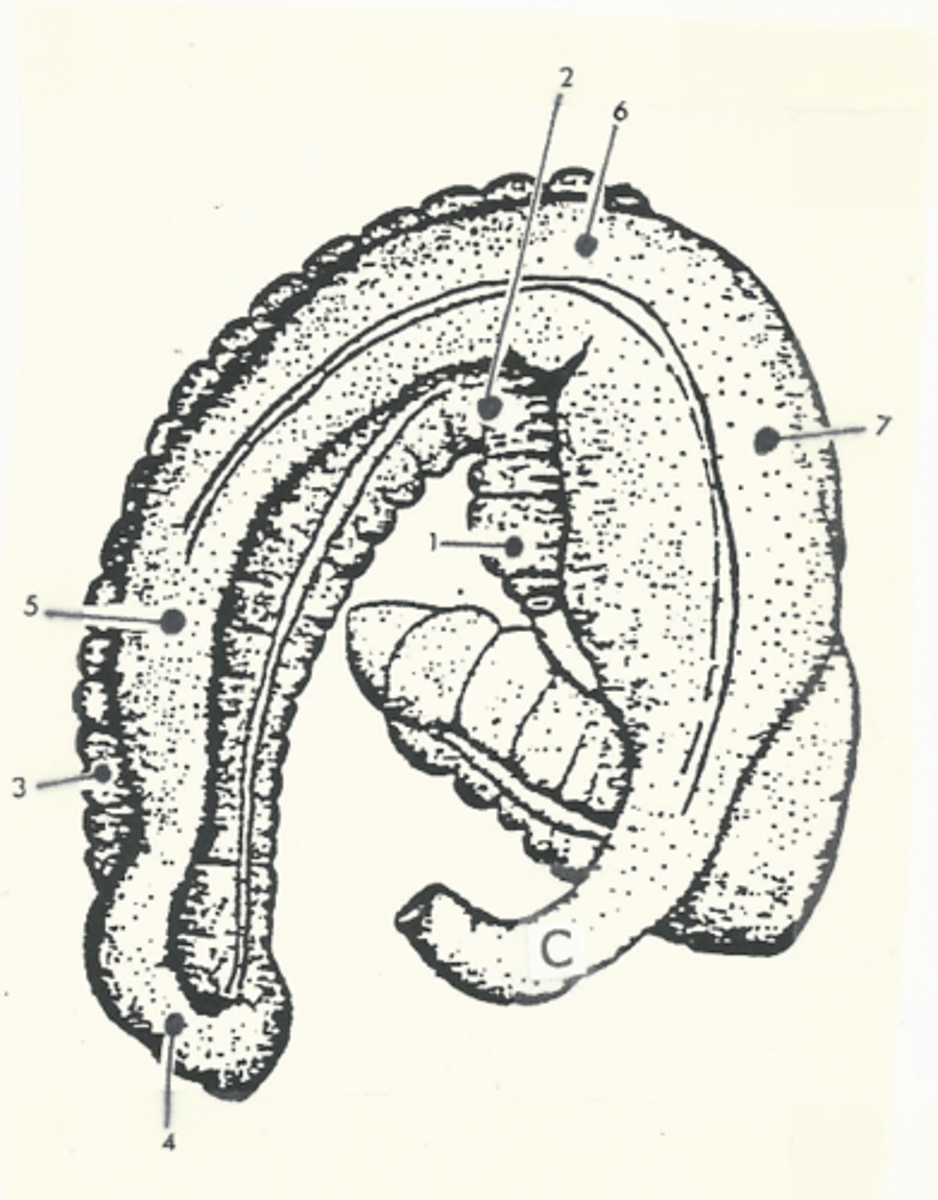
pelvic flexure
4
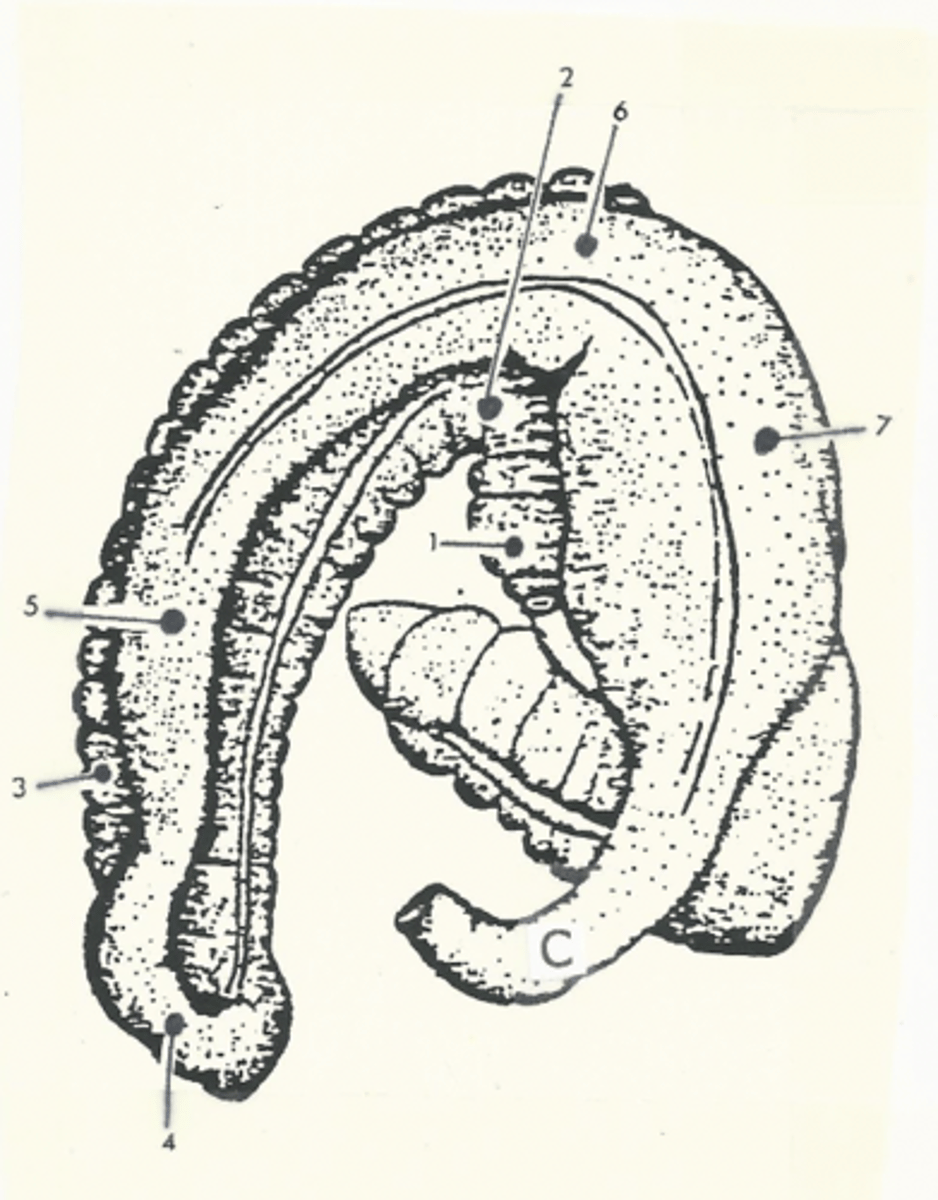
left dorsal colon
5
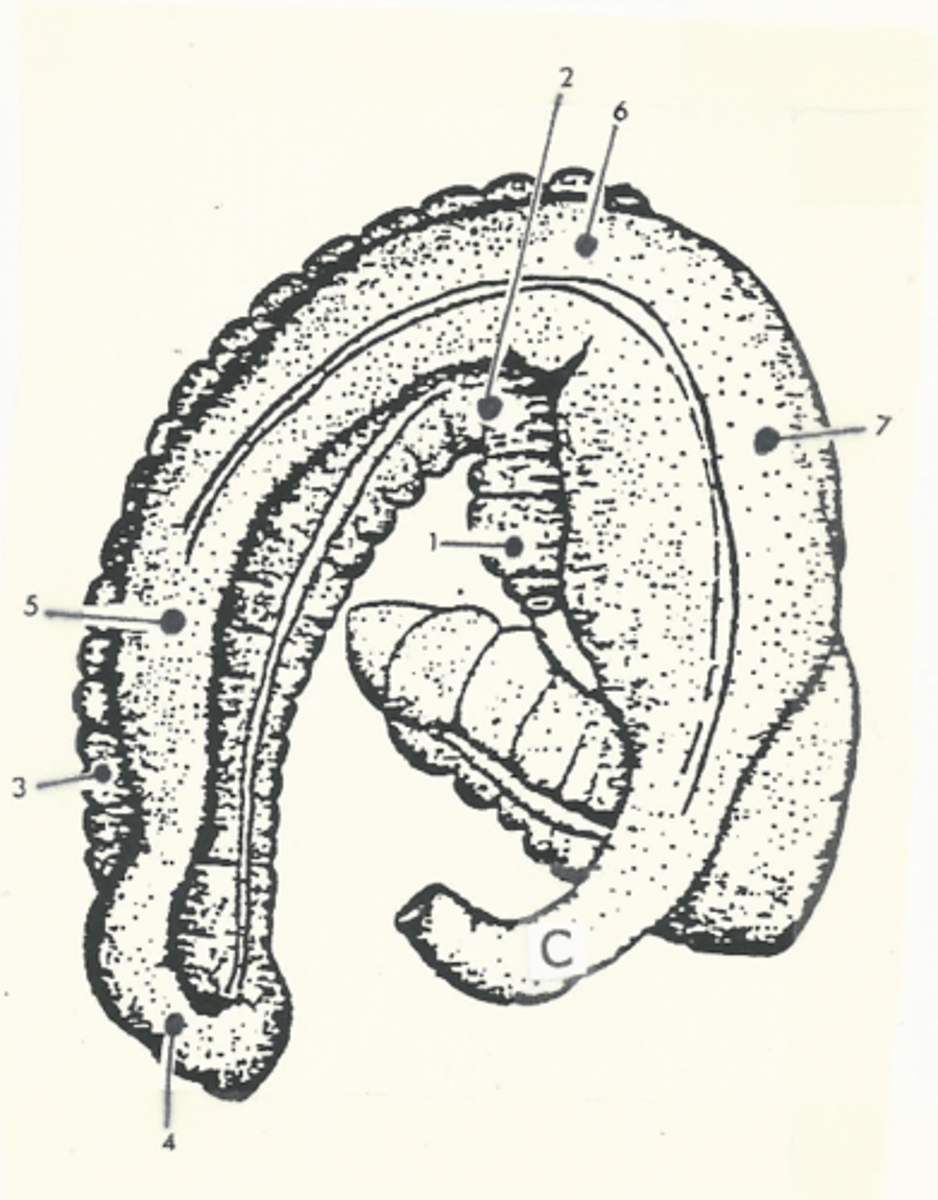
diaphragmatic flexure
6
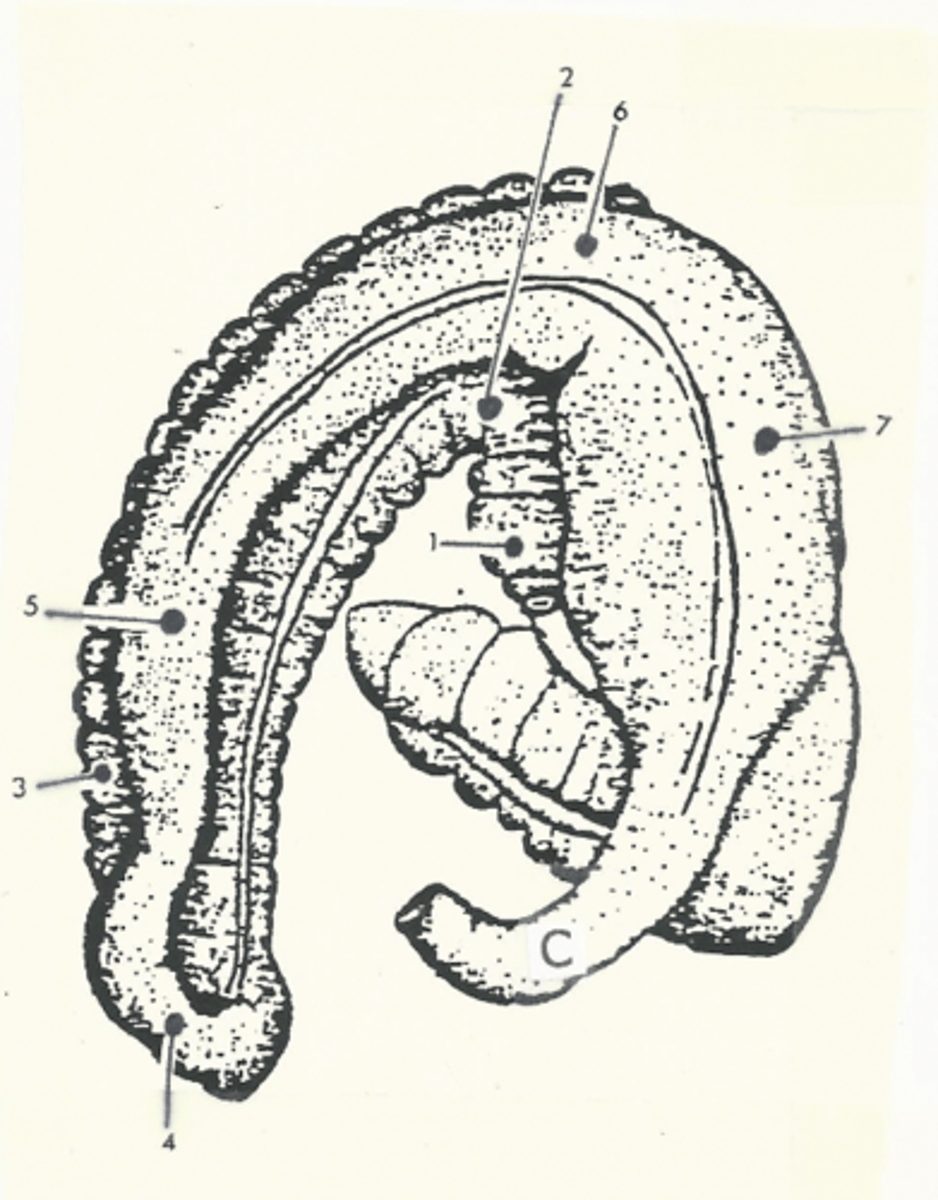
right dorsal colon
7
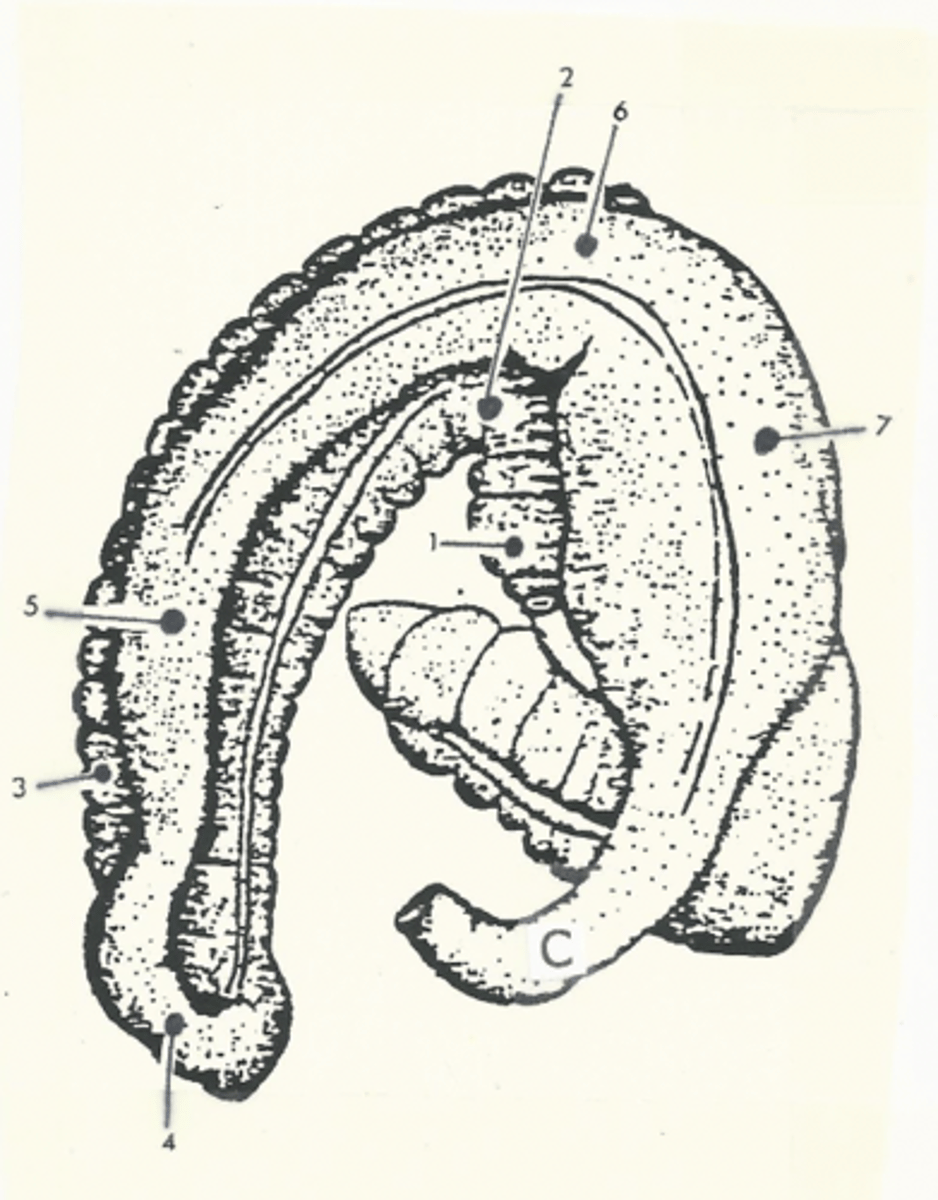
transverse colon
C
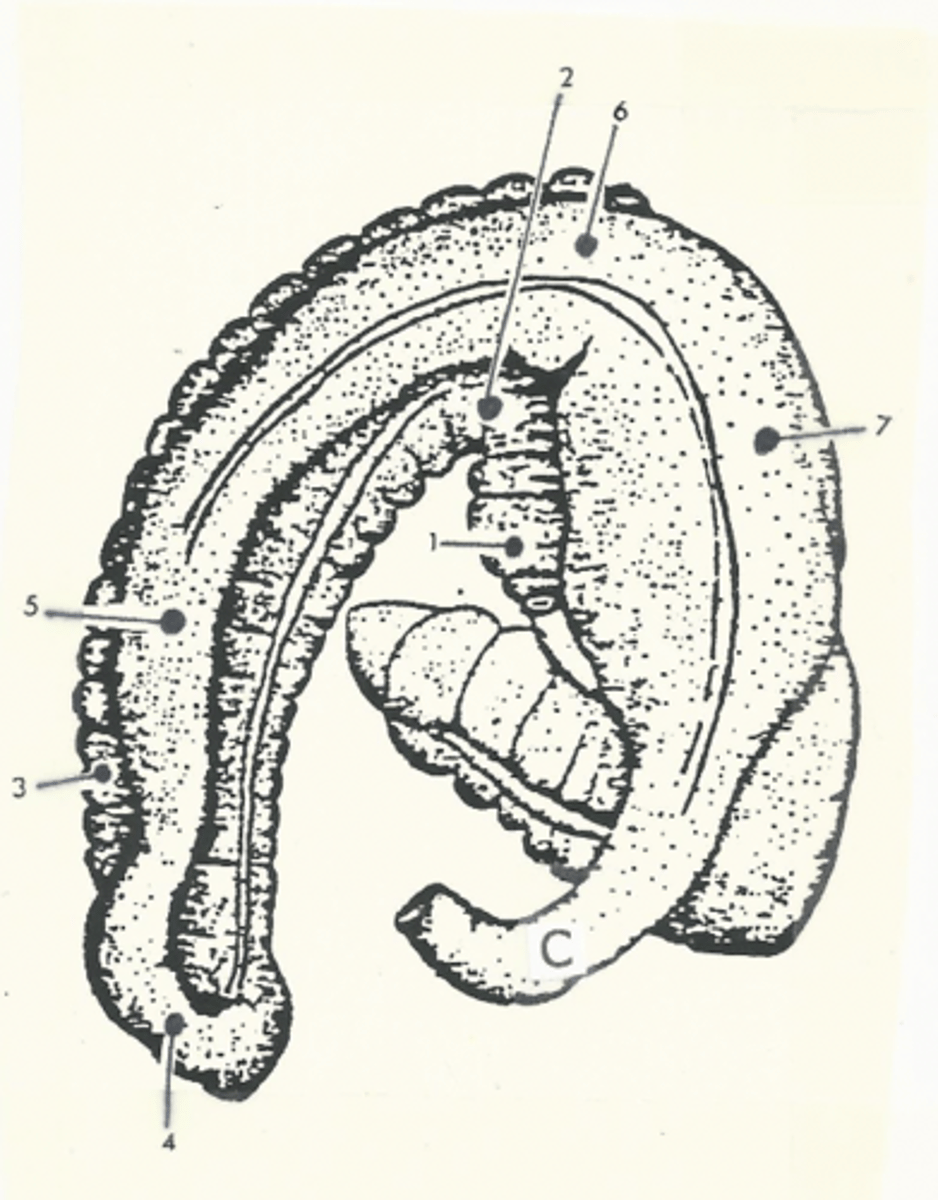
Transverse colon
shortest segment of the large intestine
The descending colon is aka...
the small colon
*due to its smaller diameter compared to the other segments of the large intestine
Two features of the small colon:
1.) bands
2.) sacs
bands of the small colon
strips of muscle along various segments of the small/descending colon
anatomic term for "bands"
tiniae coli
sacs of the small colon
pouches of the small/descending colon on the surface
anatomic term for "sacs"
haustra
The small colon changes names to the rectum at the level of the...
pelvic inlet
anal canal
terminal segment of the large intestine
anus
opening of the large intestine
The abdominal contents are located inside the _______ of the diaphragm
dome
The diaphragm bulges forward to the level of rib ____
rib 6
The abdominal cavity is divded into three compartments based on two lines spanning from...
1.) the tuber coxae to the elbow
2.) the tuber coxae to the umbilicus
Five abdominal organs located on the left side:
1.) liver
2.) stomach
3.) spleen
4.) left dorsal colon
5.) left ventral colon
liver topographic location on the left side
7-9 ribs, high compartment
stomach topographic location
9-15 ribs, high compartment
base of the spleen topographic location
15-18 ribs, high compartment
apex of the spleen topographic location
9-12 ribs, mid compartment
left dorsal colon topographic location
mid compartment, dorsal to the left ventral colon
What will be present located cranially on the left dorsal colon?
diaphragmatic flexure
left ventral colon topographic location
low compartment, ventral to the left dorsal colon and touching the ventral wall of the abdominal cavity
What will be present located cranially on the left ventral colon?
sternal flexure
Two abdominal organs in the middle of the abdominal cavity:
1.) small intestine
2.) descending/small colon
Which segments of the small intestine are in the middle of the abdominal cavity?
jejunum and ileum
Five abdominal organs located on the right side:
1.) liver
2.) descending duodenum
3.) right dorsal colon
4.) right ventral colon
5.) cecum
liver topographic location on the right side
between ribs 7-16, high compartment
descending duodenum topographic location
under the ribs, high compartment; does not go past the last rib into the paralumbar fossa!
right dorsal colon topographic location
dorsal to the right ventral colon, mid compartment
right ventral colon topographic location
ventral to the right dorsal colon, low compartment contacting the ventral body wall
The cecum is broken into three sections:
1.) base
2.) body
3.) apex
base of the cecum topographic location
right paralumbar fossa
body of the cecum topographic location
against flank
apex of the cecum topographic location
going craniomedially toward the midline (toward the left)
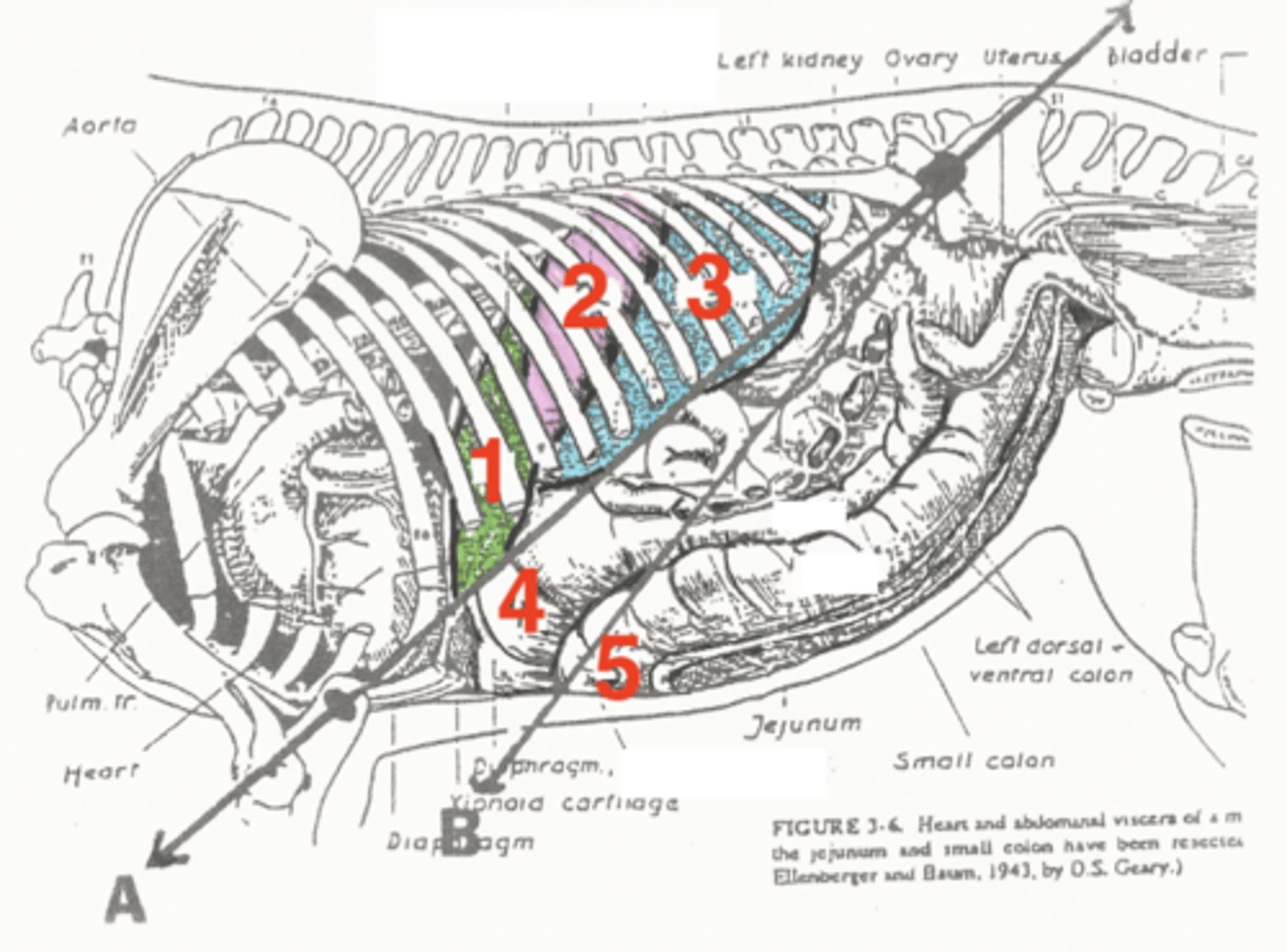
liver
1
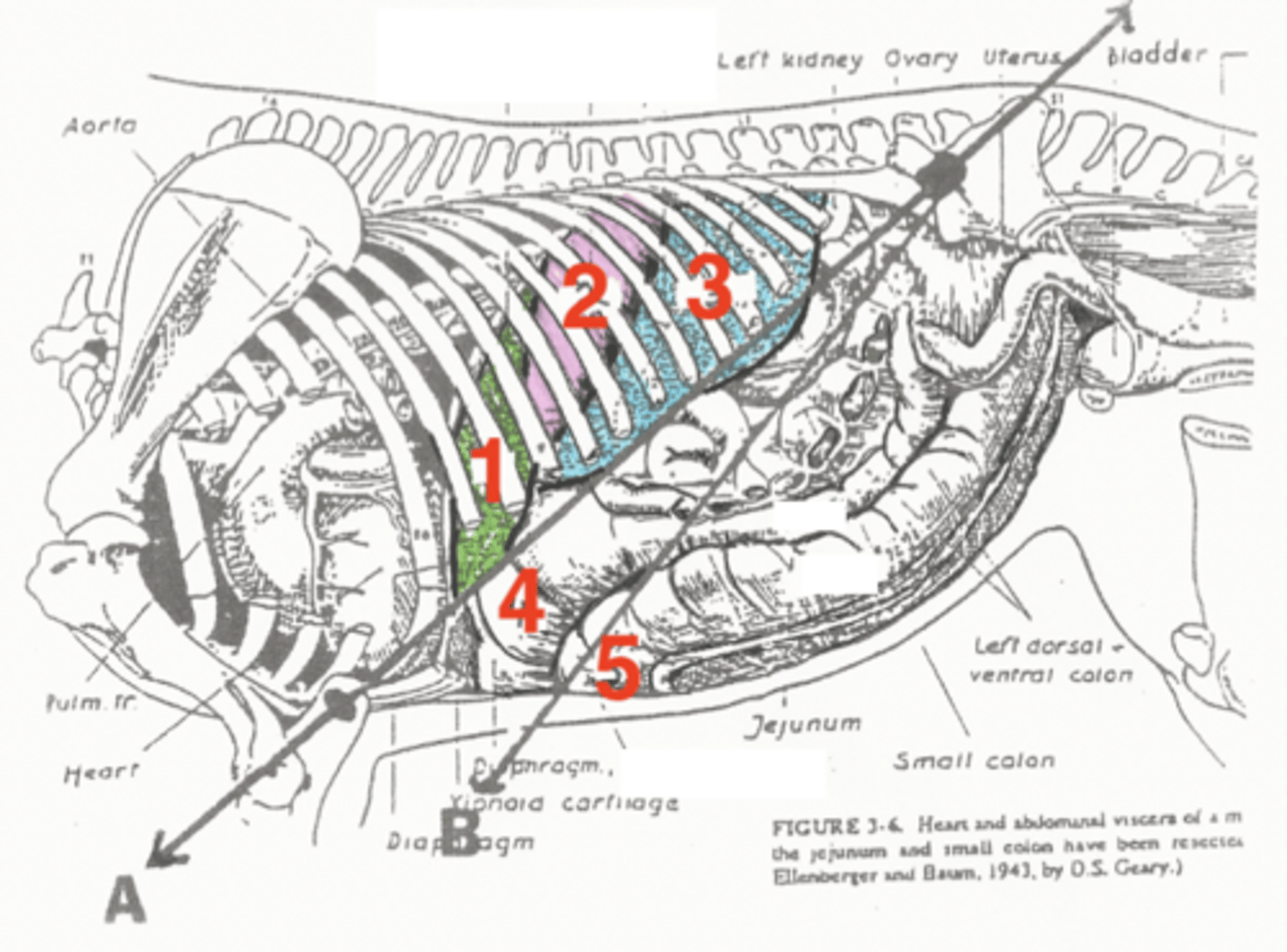
stomach
2
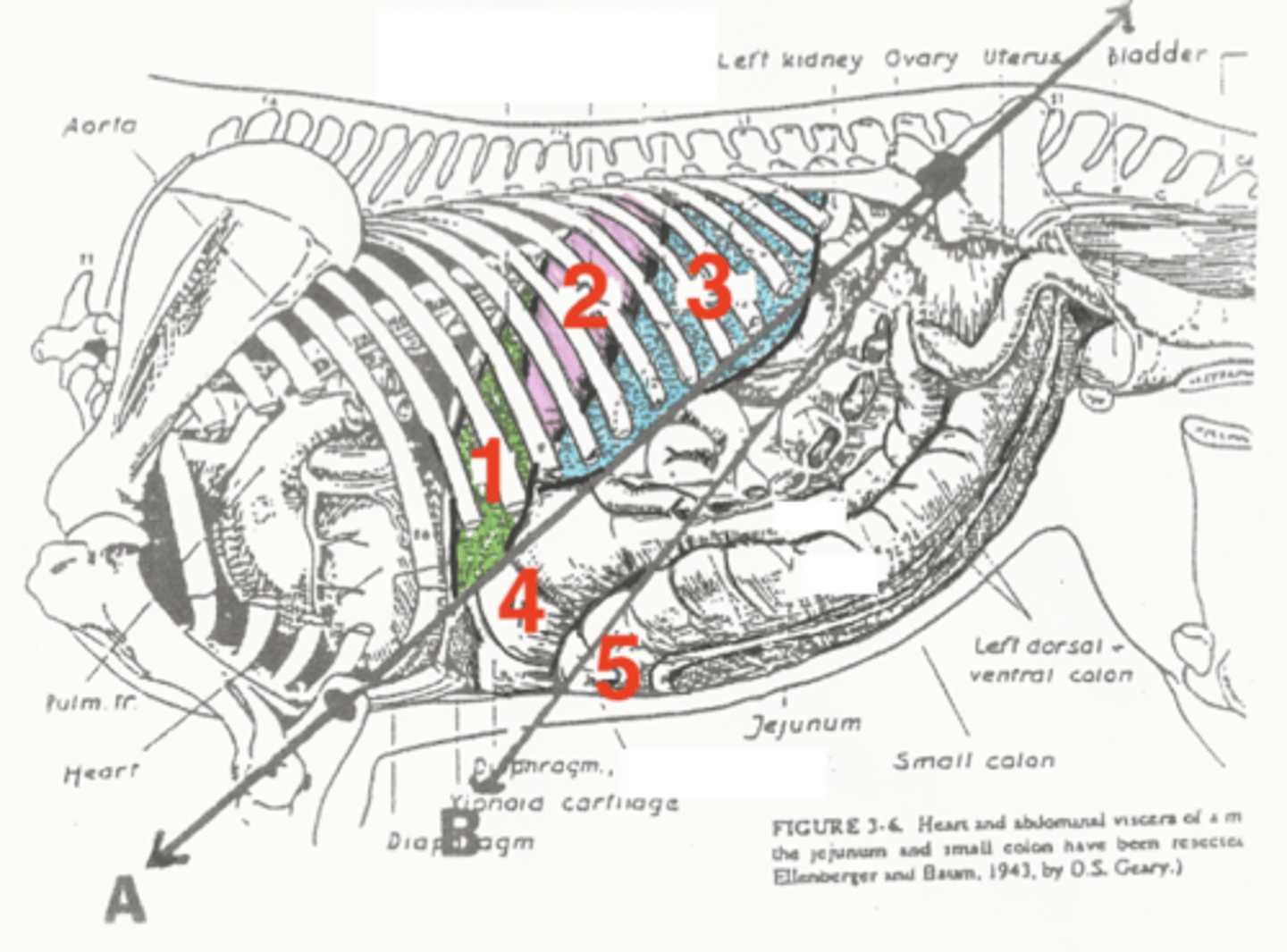
spleen
3
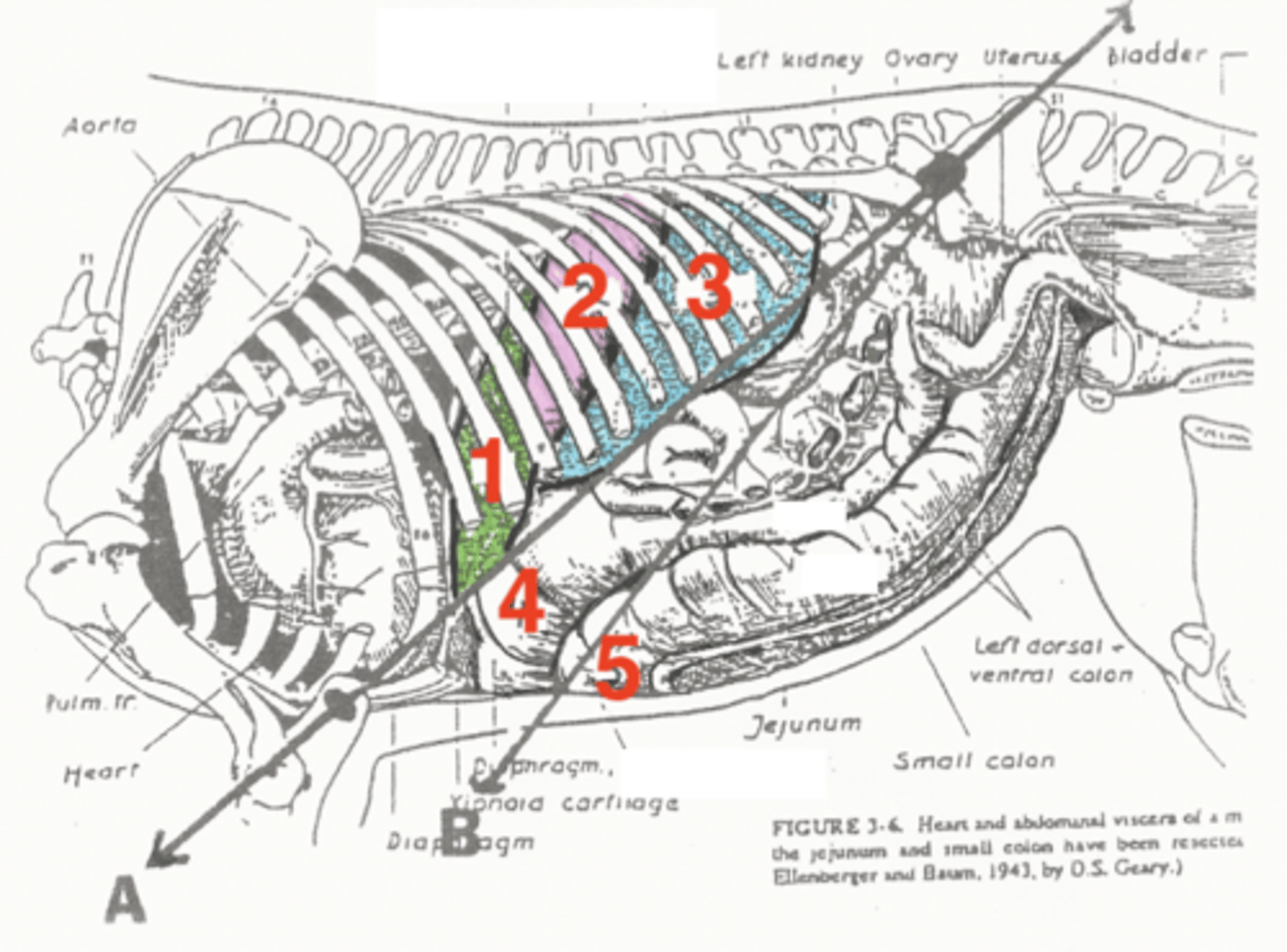
diaphragmatic flexure of left dorsal colon
4
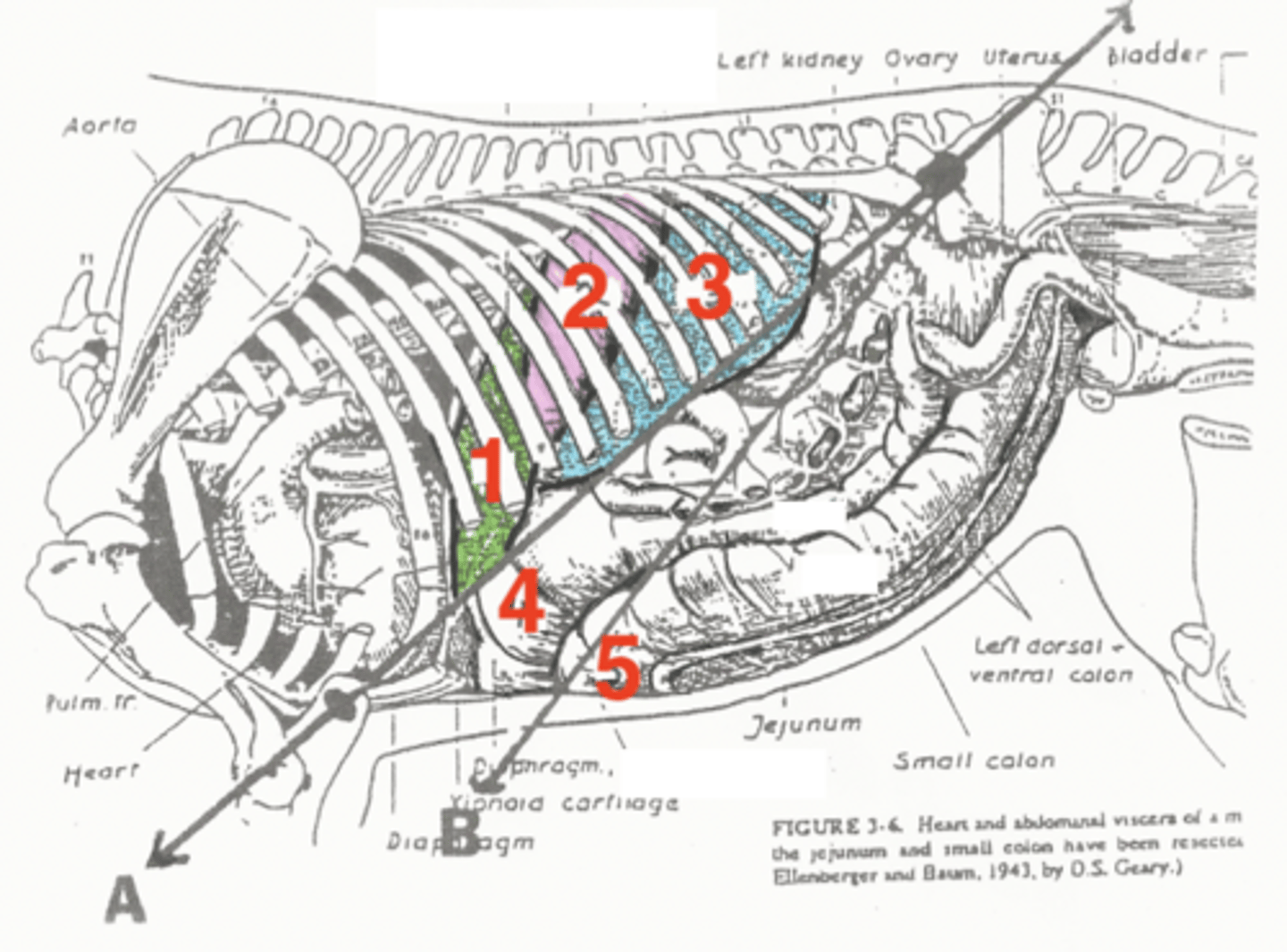
sternal flexure of left ventral colon
5
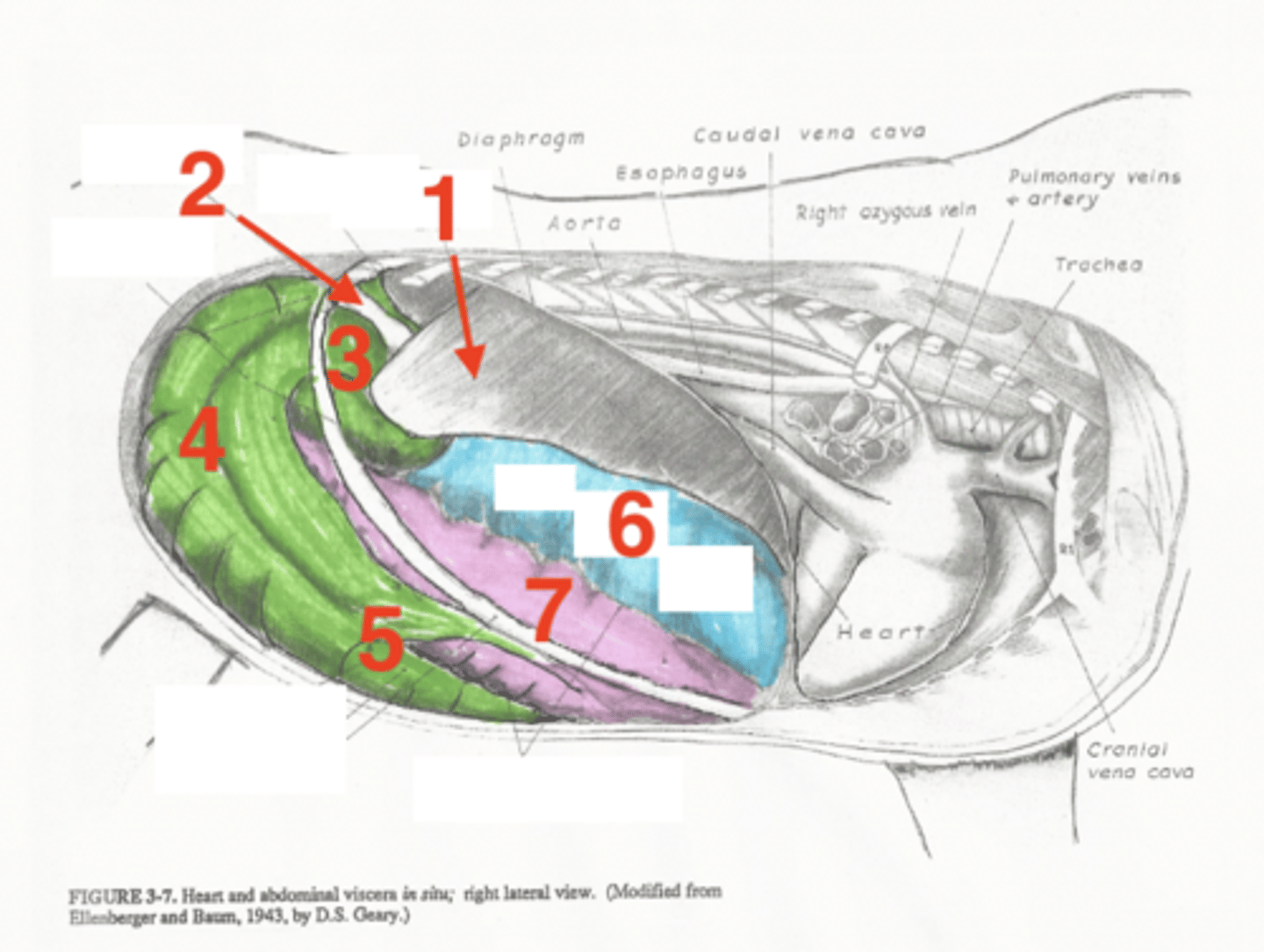
liver
1
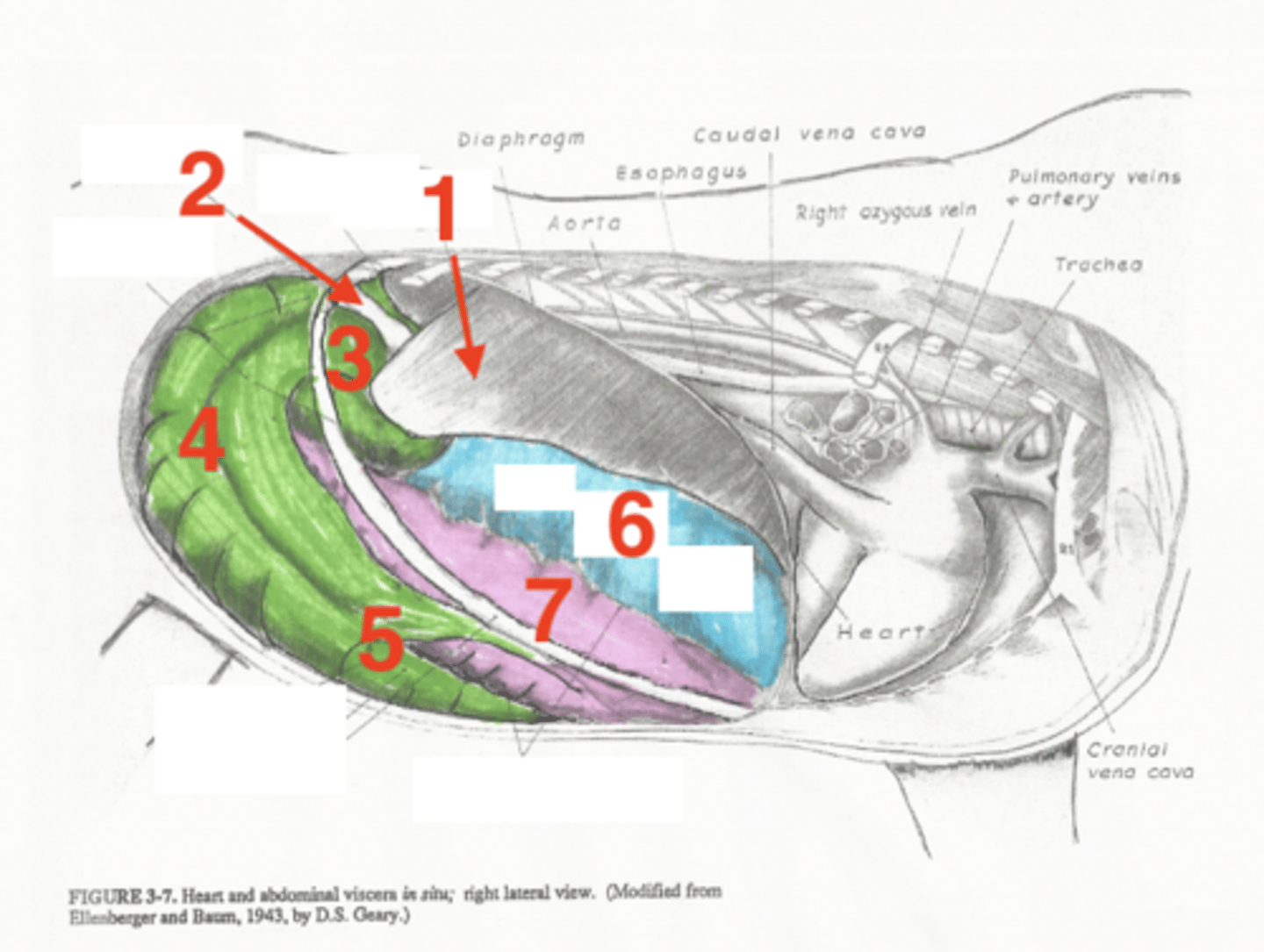
descending duodenum
2
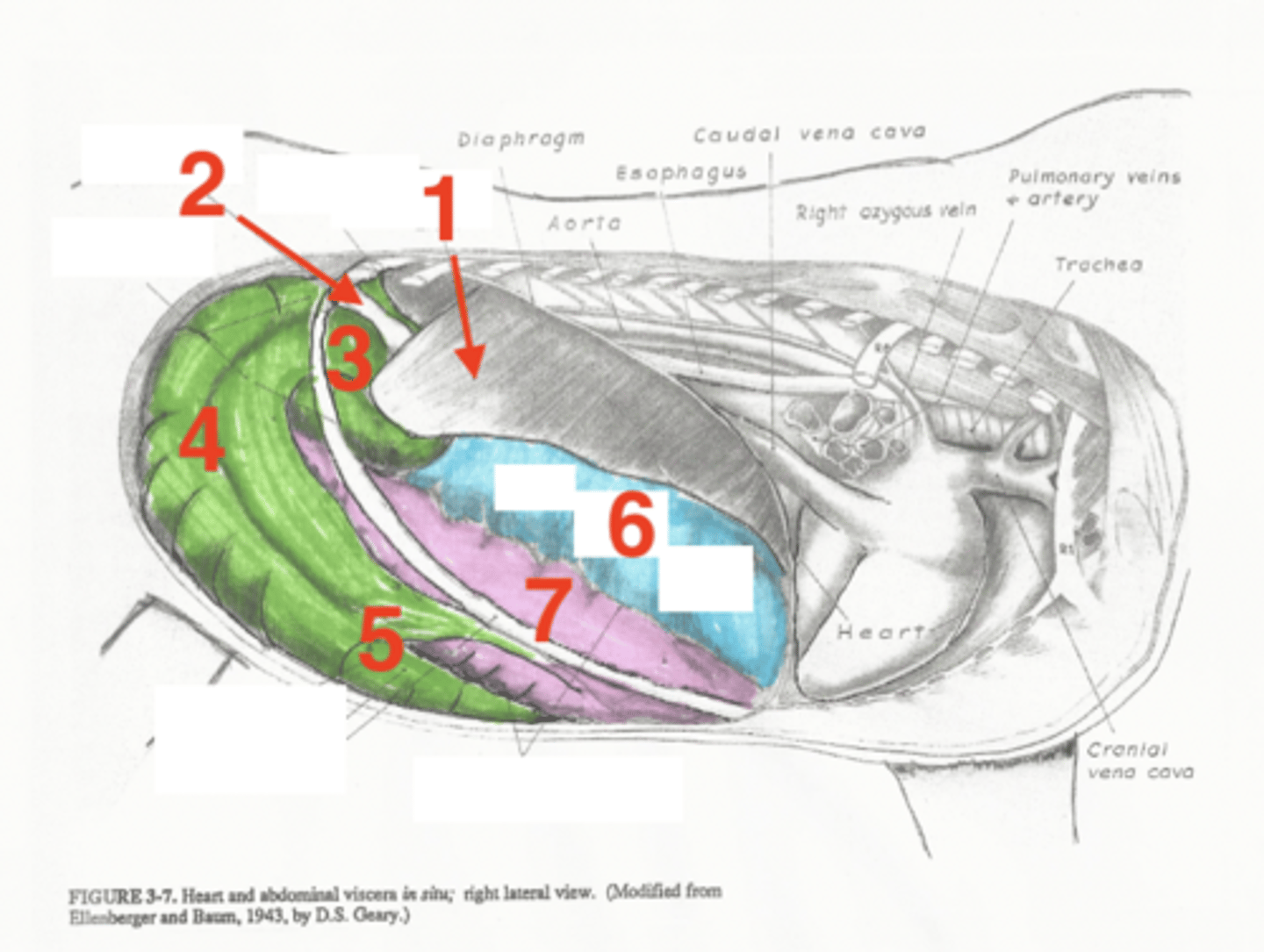
base of cecum
3
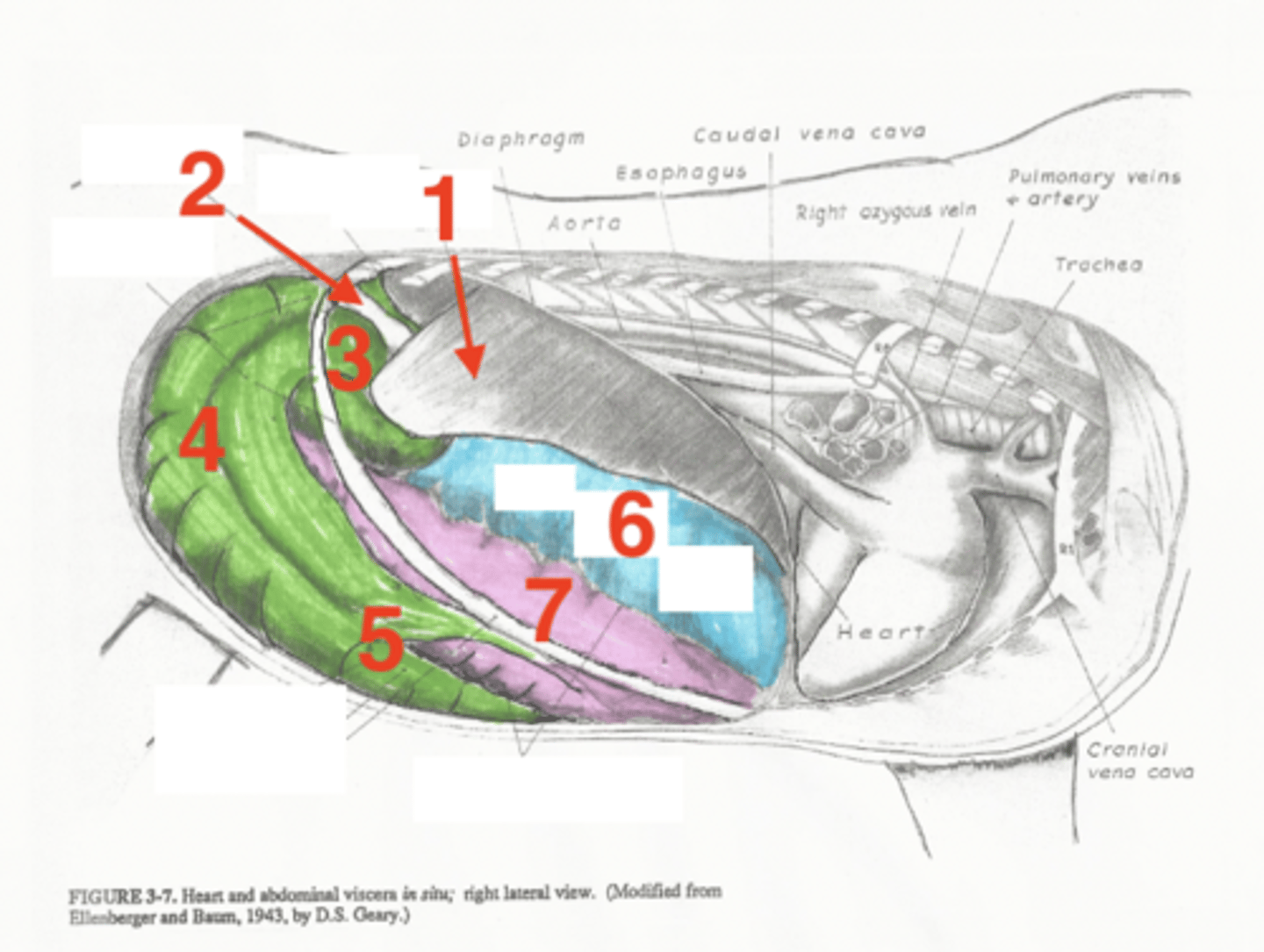
body of cecum
4
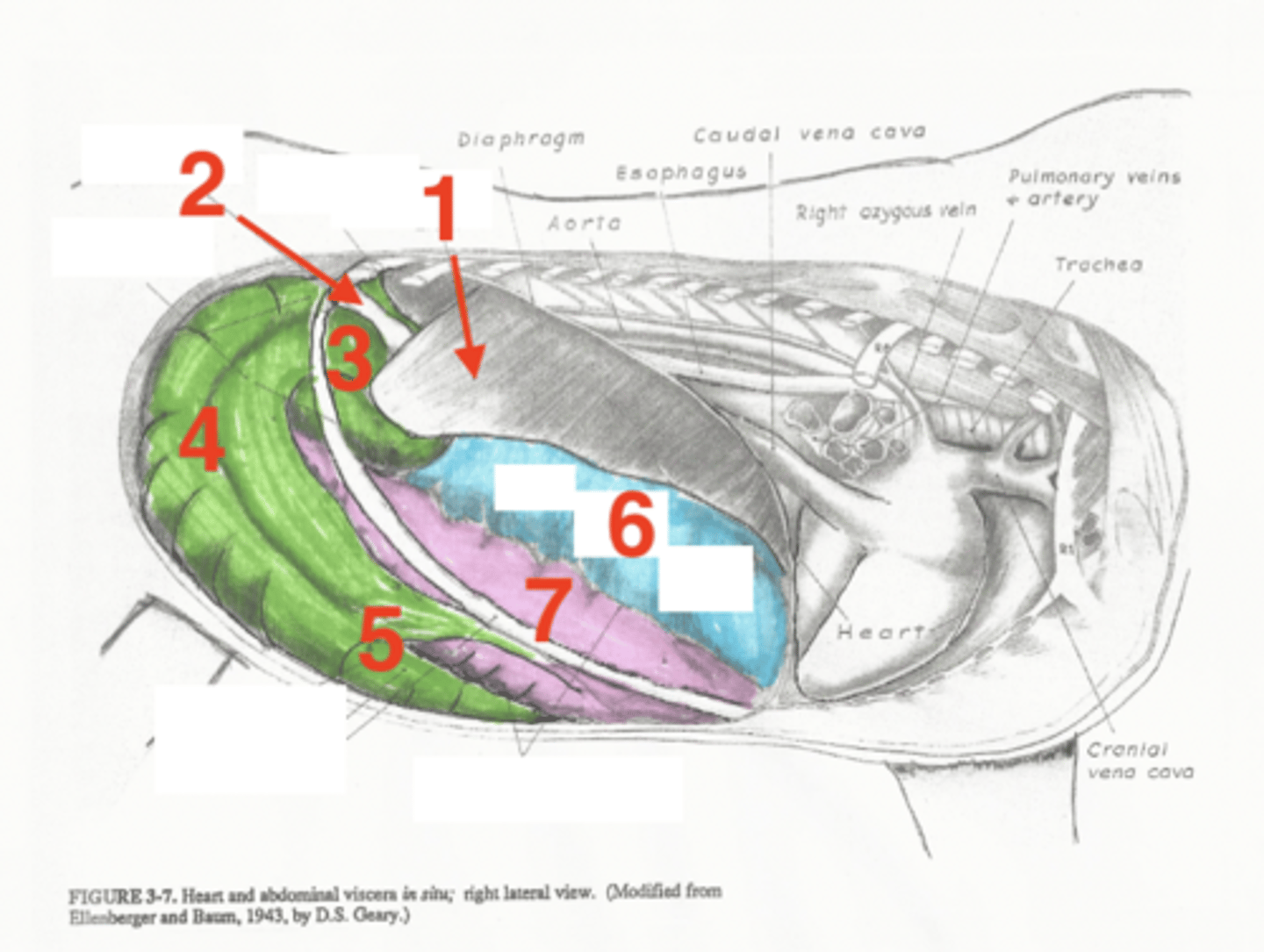
apex of cecum
5
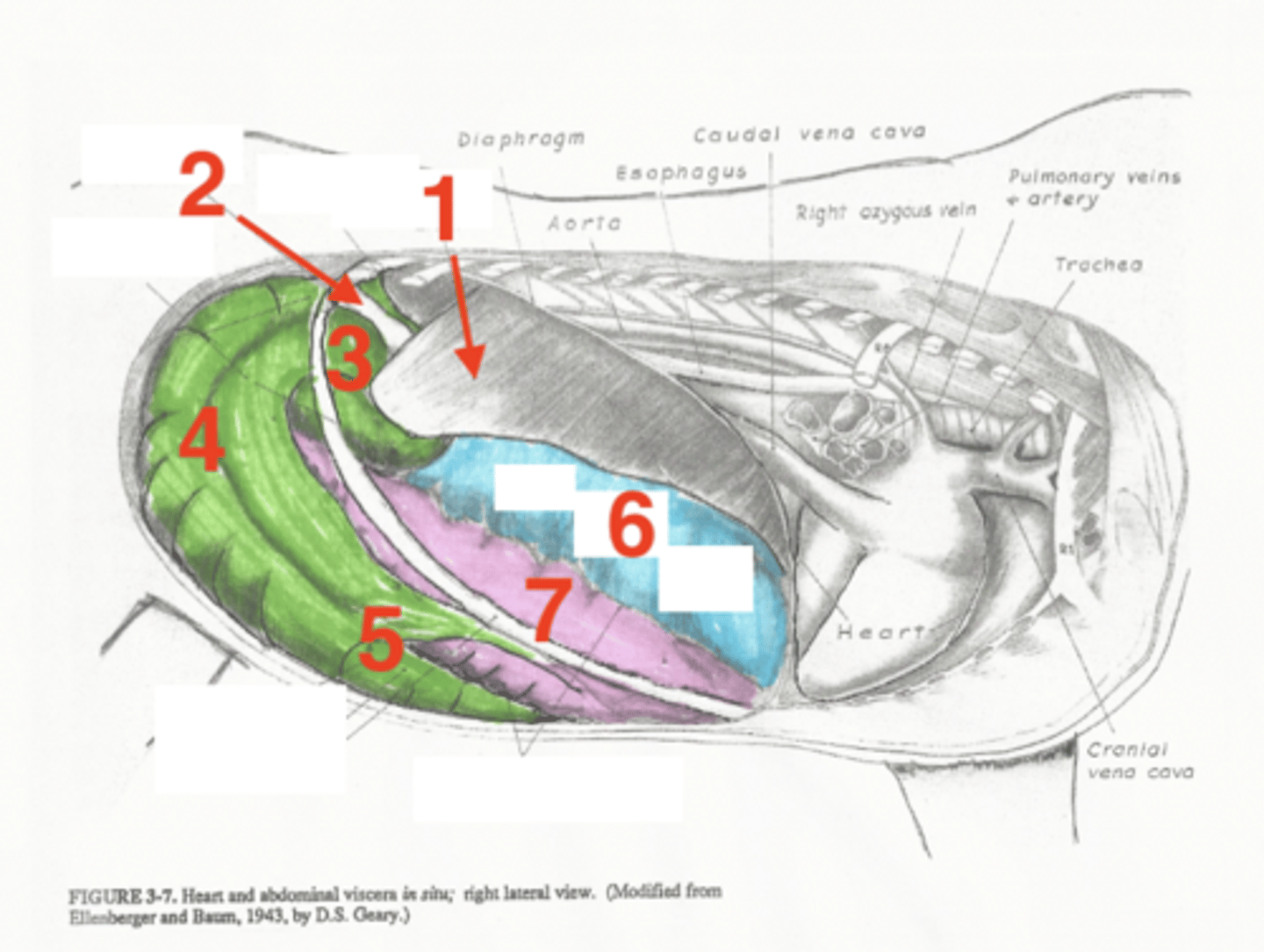
right dorsal colon
6
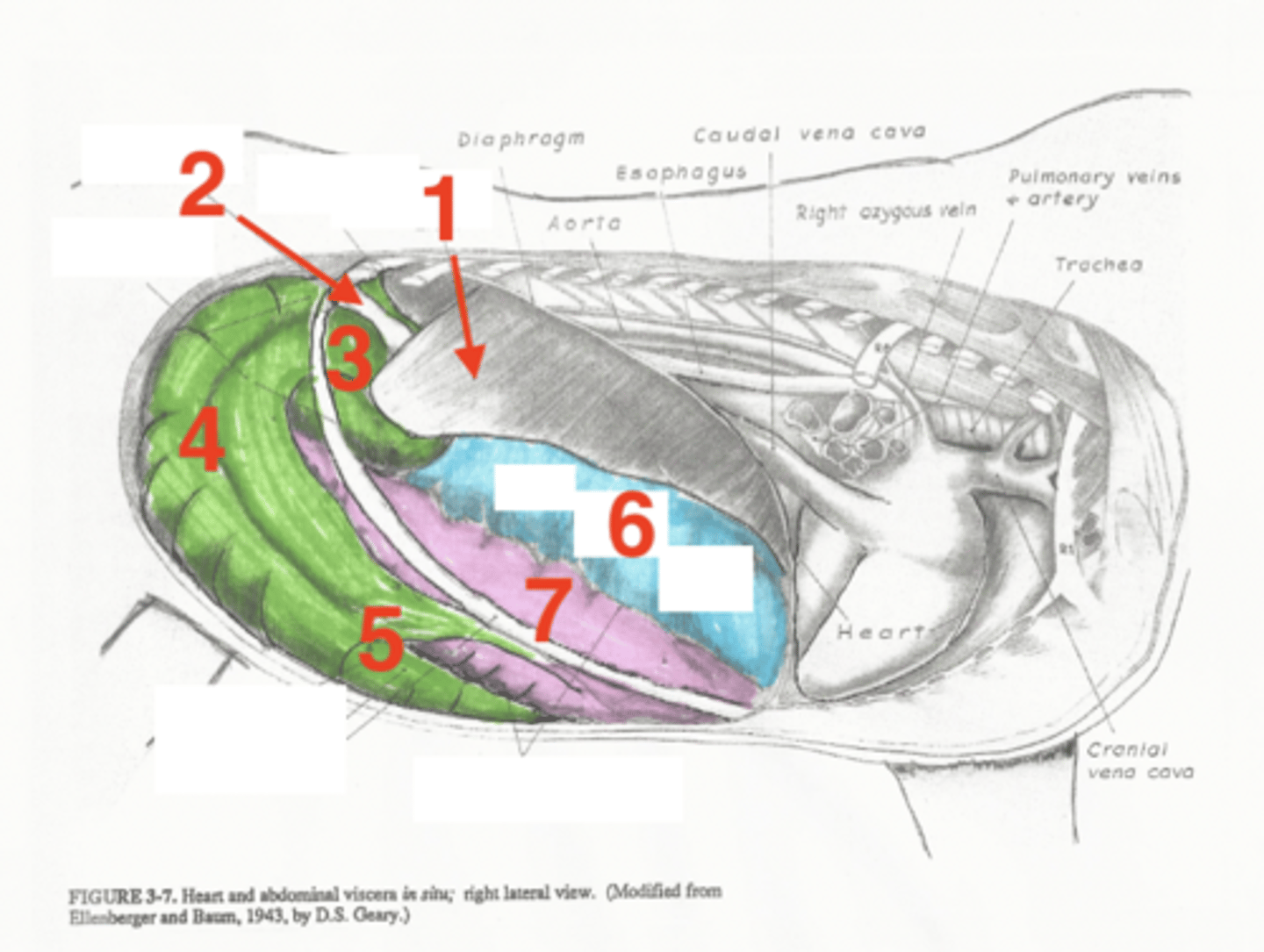
right ventral colon
7
The root of the mesentery is at the level of which vertebra in the horse?
L1
Topographic location of the right kidney
level of T16-18, L1
Topographic location of the left kidney
level of T18, L1-L3
Topographic location of the ovaries
half way between the tuber coxae and the last rib