structure of crystals and diffraction exam 3
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
interstitial
in metals, the self-_______ concentrations is negligible in metals regardless of temperature
disordered
in a ____ solid solution, the probability of a site being occupied is proportional to the at% alloying composition
anti-site
can consider chemical disordering as an increase in _____ defects
decreases
a decrease in chemical ordering ____ the intensity of superlattice peaks
schottky defect
Charge-compensating cation and anion vacancies.
frenkel defect
Charge neutral vacancy-interstitial pair
opposite
When point defects have _____ charges, their electrostatic attraction will favor them being in neighboring sites.
T
a dislocation characterized by b and t can only move in slip planes containing both b and t (T/F)
burgers vector
Describes the magnitude and direction of displacement of the crystal lattice across the dislocation, remains constant
tangent vector
unit vector that varies along curvilinear dislocations and is tangent to every point along the dislocation line; it is constant for straight (segments of ) dislocations
perpendicular
in an edge dislocation, b is ____ to t (their dot product=0 and cross product = glide plane normal)
parallel
in a screw dislocation, b is ____ to t (their dot product=|b|l)
positive
is this a positive or negative edge dislocation?
conservative
GLIDE or SLIP of dislocations is a ______ motion, there is a conservation of lattice sites
non-conservative
CLIMB of dislocations is a ____ motion, requires destruction or creation of lattice sites for motion to occur.
positive
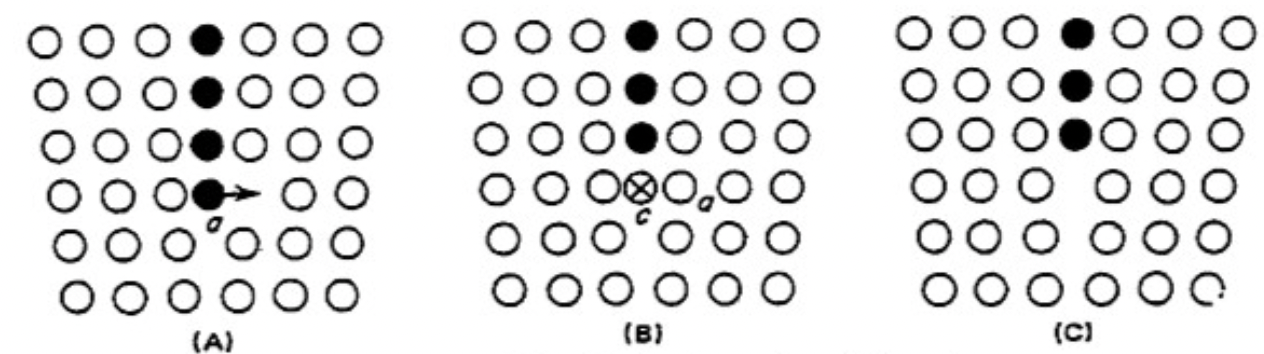
is this a positive or negative climb?
negative

is this a positive or negative climb?
T
only dislocations with edge character (edge and mixed) can climb, not screw (T/F)
F
slip planes with low planar atomic density is preferred (T/F)
<111>
what is the likely burgers vector in a BCC crystal?
<100>
what is the likely burgers vector in a primitive cubic crystal?
<110>
what is the likely burgers vector in an FCC crystal?
is not
partial/imperfect dislocation has a burgers vector that ___ a lattice translation
shortest
in an alloy, the likely burgers vector is the ____ distance between two lattice sites of same element
shockley
Planar Dissociation reaction of unit dislocations produce a ribbon of stacking fault (SF) bound by pairs of _____ partials that are favorable regarding elastic line energy reduction
F
high stacking fault energy makes it difficult to cross-slip (T/F)
vacancy
A _____ can be described as a vacant lattice site that normally is occupied by an atom when the perfect reference state is considered
lower
vacancies have ___ mobility than self-interstitials
independent
enthalpy of formation for vacancies is (independent/dependent) of temperature
increases
Does the enthalpy for vacancy formation increase or decrease with an increase in the melting temperature?
smaller
the enthalpy of migration for self interstitials is typically much _____ than that for vacancies
dislocation, disclination
_____ line defects involve translation of one part of a crystal with respect to another, _____ line defects involve rotation of one part of a crystal with respect to another
glissile, sessile
dislocations that can move easily by slip are _____ and those that have difficulty are ____ (they cannot move by slip)
parallel, perpendicular
an edge dislocation moves _____ in the direction of shear, a screw dislocation moves _____ in the direction of shear
frank, sessile
The ____ loop is a planar dislocation that results from a condensation of point defects in a close-packed crystal, which is a partial dislocation and is ______ (glissile/sessile) because it cannot move by slip.
paralell
The direction of dislocation motion, or slip direction, is _____ to b
T
Preferred slip systems are in close-packed directions on close-packed planes (T/F)
cross-slip, screw
_______ is a mechanism that occurs when a dislocation encounters an obstacle and switches slip plane, only ____(screw/edge) dislocations can do this.
highest
Dislocations lying in a slip system with the ____ Schmid factor will be the first to move when a force is applied
raises
The effect of interactions between the elastic fields of several dislocations within vicinity of each other ___ the external stress needed to move a dislocation.
forest, decreases
One dislocation “threads through” the slip plane of another dislocation, what type of dislocation is this? Once it has been cut by another moving dislocation, the mobility of both dislocations ______
frank-read source
A mechanism that requires a glissile dislocation to be pinned at two ends that bows into an arc under applied stress, increasing curvature as stress increases, until it reaches a critical point and simply generates a new loop surrounding the pinned points.
arrhenius
Law that describes how the number of vacancies in equilibrium is exponentially related to an increase in temperature, independent of enthalpy of formation
dot, cross
when determining alternative slip plane for a cross slip, you find another plane normal for a close packed plane for which its ___ product with b = 0. to find the subsequent tangent vector, you take the ____ product of b and plane normal.
cross
given b and t, you take the ___ product to find the slip plane
plane normal, b

Cos1= cosine between loading direction and ____
cos2= cosine between loading direction and ____
F
Glide motion of the screw dislocation causes displacement by its Burgers vector for specific regions of a crystal, while edge dislocation climb motion does not cause any displacements in crystals (T/F)
F
A dislocation is a line defect that is always straight and typically aligned along crystallographic directions associated with a low value of the elastic modulus (T/F)
a/6
if a burgers vector direction is multiplied by a/2, what would its subsequent shockley partial be multiplied by?
burgers
elastic line energy or self-energy is proportional to the square of the magnitude of the ____ vector for dislocations
‘
in kroger-vink notation, how do you show charge relative to normal ion charge on site if its negative?
^o
in kroger-vink notation, how do you show charge relative to normal ion charge on site if its positive?
charge and mass
in a kroger-vink notation equation, what two things must be balanced?