Physics B.5 terminology
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Define electric current + what is it measured in
The rate of flow of charge measure in amperes (A)
Define charge + what is it measured in
Can be either positive or negative measured in coulombs (C)
Define conventional current?
The flow of positive charge from the positive terminal to the negative terminal
What is the direction of conventional current?
From positive to negative
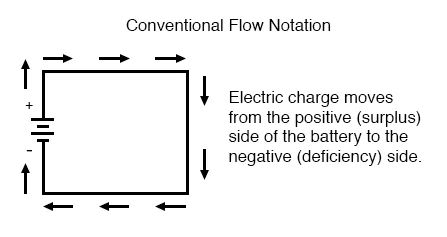
What is the direction of electrons in a current?
From negative to positive

Define potential difference (p.d.)
The work done per unit charge on moving a positive charge between two points along the path of the current
Define electronvolt (eV)
The amount of energy needed to move an electron through a potential difference of one volt
What are electronvolts measured in?
Joules (J)
What are conductors made up of? (on the atomic scale)
They are made up of positively charged metal ions within a sea of delocalised electrons
What are insulators?
It is a material that has no free charges, hence it does not allow the flow of charge through them very easily
What type of electricity can insulators conduct?
static electricity
When does electric resistance happen?
When free electrons collide with metal ions which resist their flow
Define resistance
The ratio of the potential difference across the component to the current flowing through it
Name three things resistance of a sample depends on
the material it is
the length of the sample
the cross-sectional area of the sample
What is the relationship between resistance and length of a wire/cross-sectional area?
Resistance of a wire is
Directly proportional to its length
Inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area
What is the constant of proportionality for resistance?
resistivity
Define resistivity
The resistivity of a material is equal to the resistance per unit length of a material with unit cross-sectional area
State Ohm’s law
For a component at constant temperature, the current through it is proportional to the potential difference across it
Give an example of an ohmic and non-ohmic component
fixed resistor - ohmic component
filament lamp - non-ohmic component
Give three examples of non-ohmic devices
lamps
LEDs
thermistors
When making a current-voltage graph, what would be on the y and x axis?
x-axis —>potential difference
y-axis —> current
What is a light-dependent resistor?
An LDR is a resistor whose resistance depends on the light intensity
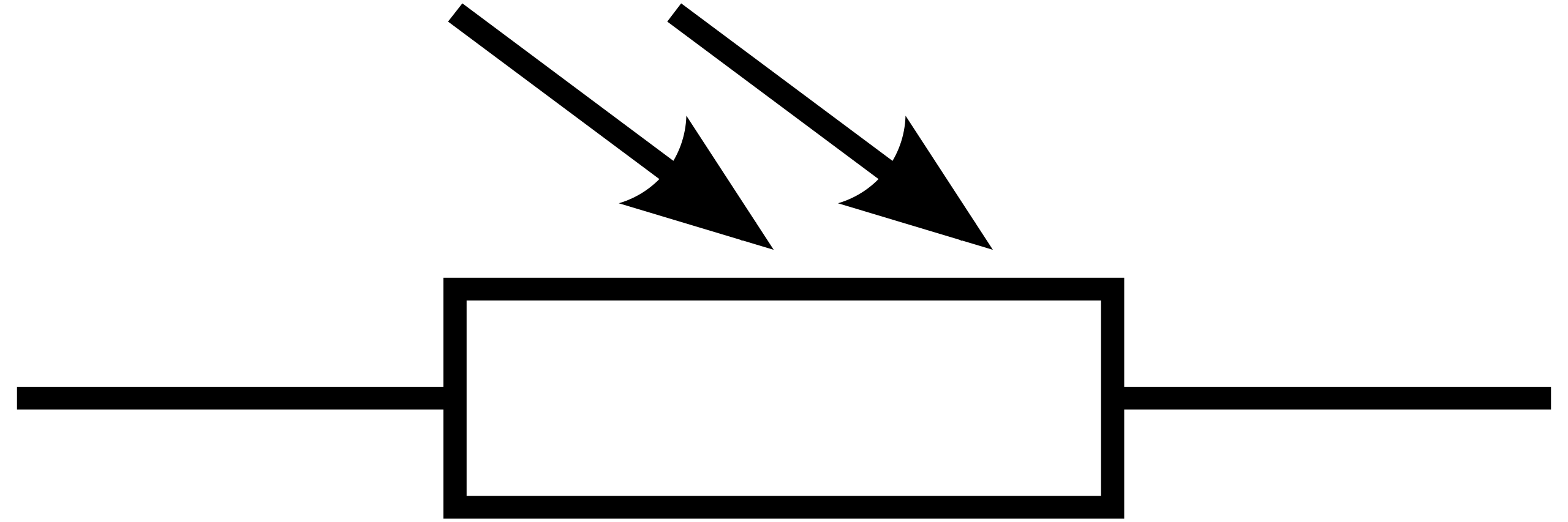
What happens to the resistance of an LDR when light intensity increases?
The resistance decreases
What happens to the resistance of a thermistor when the temperature it receives increases?
The resistance decreases
What is a potentiometer?
A resistor with a sliding contact to form an adjustable voltage divider
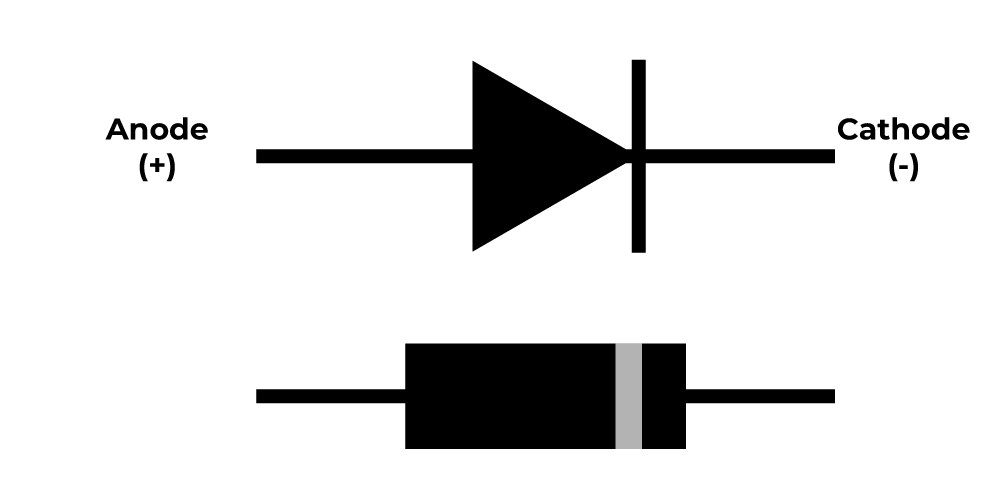
What is a diode?
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts electricity primarily in one direction . It has high resistance on one end and low resistance on the other end
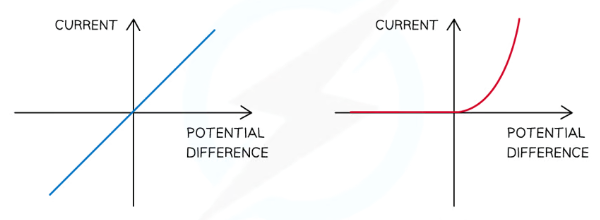
Which graph (blue or red) represents the resistance in either a semiconductor diode or a resistor?
blue → resistor
red → semiconductor diode
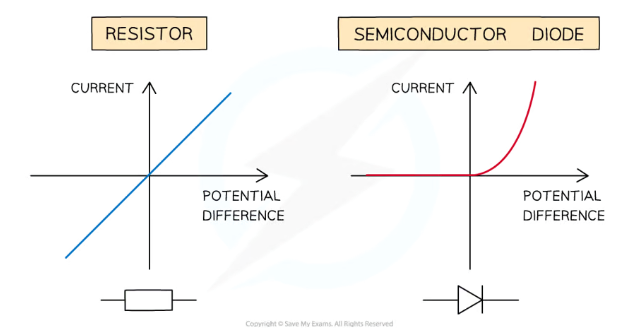
What happens to the current if a diode is reverse biased?
The current through the diode is zero
What component has these I-V characteristics and produces this graph?
A filament lamp
Under what circumstances can a filament lamp behave as an ohmic component and why?
When it has very small voltages going through it (it doesn’t heat up)
Define direct current
Direct current is current that only flows in one direction and has one value
Explain resistance on an atomic level
Free electrons collide with metal ions which resist their flow
This transfer of energy results in an increase in the kinetic energy of the atoms in the lattice
This raises the overall internal energy of the metal
The macroscopic result of this transfer is the heating up of the wire which causes resistance
What is the resistance of an ideal voltmeter?
It is infinite and no current passes through it
What is the resistance of an ideal ammeter?
It is zero and all the current passes through it
The combined resistance of resistors connected in parallel is (more/less) than the resistance of any of the individual components
less
Define electrical power
Electrical power is the rate of change of work done
Name 6 main sources of electrical energy
Electric cells
Chemical cells / batteries
Solar cells
Mains electricity
Wind generators
What do chemical cells (batteries) do?
They utilise chemical reactions to provide a potential difference
(can be rechargeable or non-rechargeable)
What do photovoltaic (solar) cells in solar panels do?
They convert electromagnetic radiation (photons) from the Sun into electrical energy
What happens when photons from the Sun are incident on the solar heating panels?
The light energy is transferred into thermal energy
The solar photons are absorbed by electrons on the surface of the photovoltaic cells, giving them enough energy to move and be released from the surface
These electrons transfer the thermal energy into electric energy which is then transferred to the external circuit
Name 3 advantages and 3 disadvantages of single-use batteries
Advantages:
High energy density
Portable source of electrical energy
Potential to join many is series to increase p.d.
Disadvantages:
Non-rechargeable/limited power supply
High internal resistance
Made from non-renewable materials
Name 3 advantages and 2 disadvantages of mobile phone batteries
Advantages:
High electrical efficiency
Rechargeable, long lifetime
Fast charging time
Disadvantages:
Capacity of the cell degrades over time
Internal resistance increases over time
Name 2 advantages and 3 disadvantages of car batteries
Advantages:
Rechargeable
Delivers high currents in a short time
Disadvantages:
Low energy density - very heavy compared to power output
Internal resistance increases as battery degrades
Made from non-renewable materials
Name 3 advantages and 3 disadvantages of a solar cell
Advantages:
Unlimited supply of energy - renewable
Cheap maintenance
No fuel required
Disadvantages:
Variable output - highly weather dependent
Only available during the day
Requires large areas
Name 2 advantages and 3 disadvantages of a wind generator
Advantages:
Unlimited supply of energy - renewable
High set-up cost but becomes economical
Disadvantages:
Variable output - highly weather dependent
Requires favourable local conditions to be placed in windy locations
Noise/visual pollution
Name 3 advantages and 2 disadvantages of a mains electricity
Advantages:
High energy density of fuel
Reliable/available energy at any time
Well-known and developed technology
Disadvantages:
Produces greenhouse gases
Unsustainable (non-renewable)
Define electromotive force (e.m.f.)
EMF is the amount of chemical energy converted to electrical energy per coulomb of charge (C) when charge passes through a power supply
Name two sources of EMF
Cells and batteries