Fields - Electric Fields
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
examples of applications of electric and magnetic fields
electrocardiogram
photocopiers
scrubbers that remove particulate matter
laws of electric charges
oppo charges attract
like charges repel
charged obj’s attract some neutral obj’s
what is elec charge
neutral atom
cation (# of protons > electrons)
anion (# of electrons > protons)
basic unit of elec charge
Coulomb (C)
1 C approx = amount of elec charge that passes through a 60 W light bulb in 2 s
watts (W)
methods of charging
friction (depends on force of attraction b/w nucleus and its outer elections)
induction (charged obj is brought close to a neutral obj WITHOUT contact)
contact (charged obj makes contact w neutral obj)
law of conservation of charges
Charge can be created or destroyed but the total charge (the difference between the amounts of positive and negative charge) within an isolated system is always conserved.
1 object gains e- while another loses the same amount
pt charges
vv small particles that carry a charge
coulomb’s law
see formula for electric force
coulomb’s law related to newton’s 3rd law
the elec force exerted on charge A by charge B is the same in mag and oppo in dir than the force exerted on charge B by charge A
comparing coulomb’s law to newton’s law of grav force
one is attractive and repulsive while the other is only attractive
both forces are non-contact
both forces act along a line joining the obj’s centers
both have constants but G is vv small while K is vv large but is cancelled out by the small charges
Fe is much _____ than Fg
greater
for more than two pt charges
you must calculate the vector sum of the elec forces and find the net force
when does the coulomb law apply
when the 2 charges are vv small compared to their dist
force
a push or pull on an obj
field of force
exists in a region of space when an appropriate object placed at any point in the field experiences a force.
properties of elec fields
a charge generates an elec field
an elec field causes an elec force and is the spetial region in which a force is exerted on any elec charge
field exerts attractive/repulsive forces on other charged obj’s
elec field is a vector (epselon symbol)
elec field
the elec force per unit POSITIVE CHARGE (N/C) this is why a pos charge always emits an elec field while a neg charge seems to accept it
elec fields (cont’d)
elec field lines always start on + charges and end on - charges
lines nvr cross
concentration of lines = strength of field
elec fields diagram
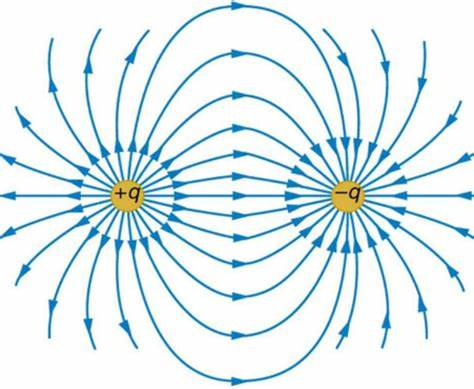
field theory
as r increases, field strength decreases and Fe also decreases
as r approaches infinity, field stren approaches 0 as well as Fe
Fe =
q (quantity affected by field) * epselon (field strength) (N/C)
Fg =
m (quantity affected by field) g (field stren) (N/kg)
epselon =
Fe/q OR kq/r² (the first works for charge distributions)
uniform elec fields
epselon does not depend on the separation of the plates
mag of elec field b/w 2 plates is directly proportional to the charge per unit area on the plates.
𝜀 is uniform everywhere in the space b/w the plates
when you pull or push a charge in the oppo dir of its tended path, you are
exerting a force over a distance thus doing work and thus converting kin to elec pot en
both grav and elec forces are
conservative
elec pot en is stored by
2 separated charges just as gravitational potential energy is stored by 2 separated masses but EE can be for charges that either attract or repel
see notes for formulas
when 2 charges are alike, work is done when
the charges are brought together, thus as r decreases, Ee increases and kin en decreases, so the Ee formula is positive
when 2 charges are opposite, work is done when
the charges are being separated, thus as r decreases, Ee decreases and Ek increases, if work is done to separate them, Ee becomes less negative as they are brought further apart
when work is done against the natural tendency of the charges
Ee increases since W = change in en
as r approaches infinity, Ee always approaches
0
what is Ee useful for
printers
tv’s and computer monitors
x-rays
radiation therapy
particle accelerators
charges moving from higher pot en to lower pot en =
useful en
no matter how much charge is moved, each C of charge will undergo the same
change in elec pot en
= elec potential
elec potential
Electric Potential Energy per unit positive test charge
elec potential cont’d
measured in J/C or volts (V)
denoted as V
V = 0 at infinity since Ee is 0 at infinity (ref pt)
elec pot diff
amount of work req per unit test charge to move a pos charge from oe pt to another pt in the presence of an elec field
if charge moves in dir of field, the elec potential
decreases and is converted to kin en and therm en
if charge moves in the dir against the field, the elec potential
increases as work is done against the force of the field which increases Ee
conservative forces
forces not grossly affected by Ff
difficult to analyze motion of particles using newton’s laws directly bc
Fe and a changes as r changes, so it’s better to use conservation of en and include kin en
for 2 like charges
as charges move farther apart, EE is converted into EK. −∆𝐸𝐸 = ∆𝐸K
∆𝐸𝐸 = -∆𝐸K if they are brought together
for two oppo charges
as charges move farther apart, EK is converted into EE. ∆𝐸𝐸 = -∆𝐸K
-∆𝐸𝐸 = ∆𝐸K if they are brought together
for parallel plates, the dist b/w plates is
directly proportional to the elec potential difference
in parallel plates, the electric force is
constant, therefore the acceleration of a particle would be constant
elementary charge
the charge of an electron or proton aka 1.602 × 10^-19
the milikan oil drop experiment
an experiment to det the elementary charge
set-up involves two electrically charged plates, one pos and one neg
a source of ionizing radiation
and an atomizer spraying oil onto the top plate
excess number of electrons means the charge is
neg
deficit number of electrons means the charge is
pos
limitations of milikan’s experiment
accurately calculated the elementary charge
but could not adequately describe the motion of charged particles due to the presence of charged particles
findings of milikan’s experiment
each charge was either the elem charge or a multiple of the elem charge
each charge was never less than 1.602 × 10^-19
the a of particles calculated using newton’s 2nd law is
instantaneous
where is the reference level
at infinity
potential difference
the difference in electric potential in at two different points in a field
volts measure
change in energy per unit charge as batteries and such do work to move the electrons
at infinity, Ee =
0
parallel plate special equations
see notes
accelerating electrons vs protons
electrons start on the side of the negative plate and is propelled through a hole on the opposite plate, aka the positive plate → accelerating protons is the same concept but starts on the pos plate and propelled thru hole in neg plate
no _____ exists outside plates
electric field stren