Gravitational Potential Energy, Kinetic Energy, and Elastic Potential Energy Plus Their Formulas
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:15 PM on 8/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
GPE
________ can be found by multiplying the mass and height of an object by "g.
2
New cards
EPE
________ can be found by @ @* multiplying half of the spring constant* @ @ by how much the object has been stretched or compressed.
3
New cards
KE
________ is the product of half the objects mass and its velocity squared.
4
New cards
Note
"g"- is the most common value of GPE for an object near the Earths surface where gravitational acceleration is estimated at a constant of 9.8 meters/second^2
5
New cards
*Note
A **joule *is the amount of energy exerted when a force of one newton is applied over a displacement of one meter
6
New cards
SI Units
Newtons/meters (N/m)
7
New cards
SI Units
Meters (m)
8
New cards
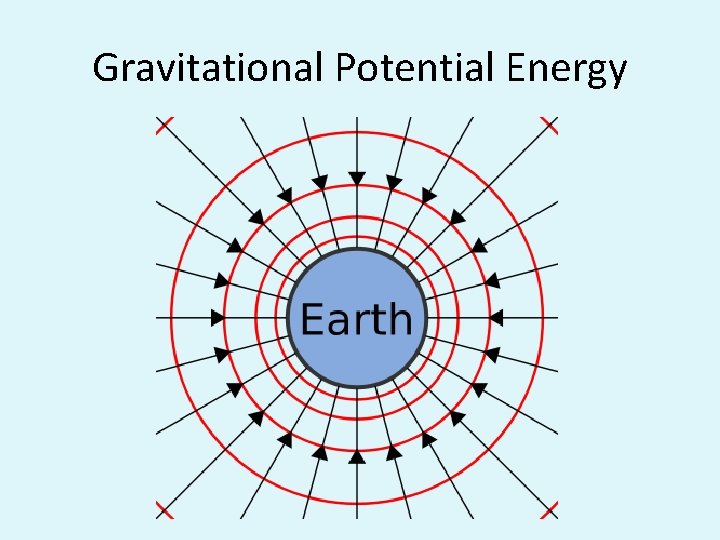
Gravitation Potential Energy
The energy an object posses due to its position in a gravitational field
9
New cards
GPE can be found by multiplying?
The mass and height of an object by “g”
10
New cards
GPE Formula
GPE= mass * g * height
11
New cards
SI Unit for Mass?
Kilograms (kg)
12
New cards
SI Unit for g?
Meters/Second^2
13
New cards
SI Unit for Height?
Meters (m)
14
New cards
What unit is GPE measured in?
Joules (J)
15
New cards
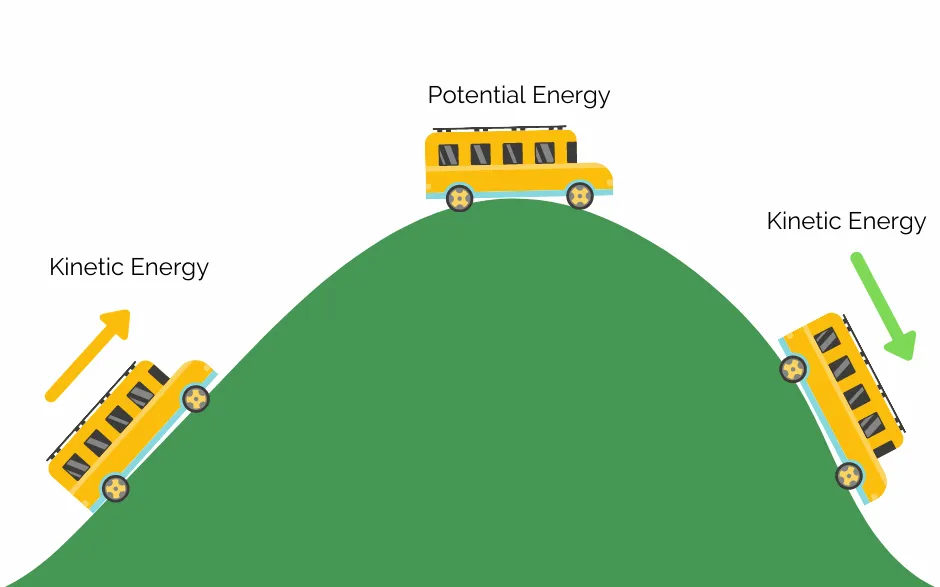
Kinetic Energy
An object's energy due to being in motion
16
New cards
KE can be found by multiplying?
Half of the object's mass by its velocity squared
17
New cards
KE Formula
KE=1/2m * v^2
18
New cards
Velocity
The speed of an object in a given direction
19
New cards
What unit is KE measured in?
Joules (J)
20
New cards
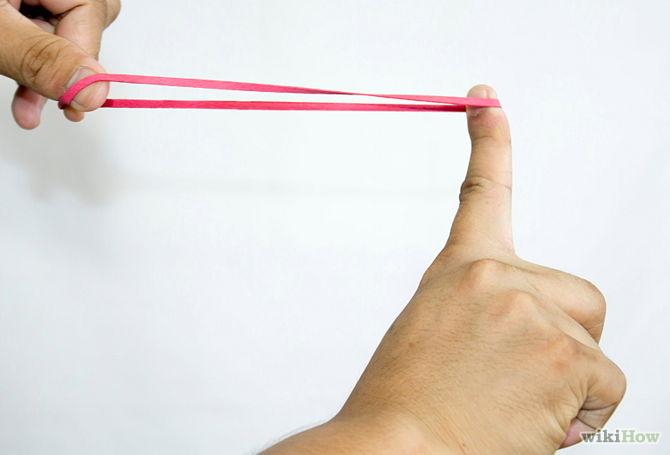
Elastic Potential Energy
Energy stored as a result of applying a force onto an elastic object by stretching. --- It’s the energy stored in a spring

21
New cards
EPE can be found by multiplying?
Half of the spring constant by how much the object has been stretched or compressed
22
New cards
EPE Formula
EPE= 1/2k (spring constant) * x (displacement)^2
23
New cards
k (the spring constant)
How stiff the spring really is
24
New cards
x (displacement)
How much the spring has been stretched or compressed.
25
New cards
What SI units are k measured in?
Newtons/meters (N/m)
26
New cards
What SI unit is x measured in?
Meters (m)
27
New cards
What unit is EPE measured in?
Joules (J)