Regulation of Renal Blood Flow and Glomerular Filtration
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is Renal Plasma Flow and how is it calculated?
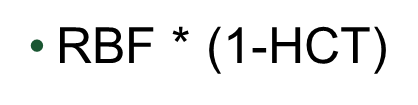
Renal Plasma Flow is the amount of plasma passing through the kidneys over time
→ calculated by multiplying renal blood flow with (1-hematocrit)
What is the Filtration Fraction

The fraction of the plasma that is filtered through the glomerular capillary into ultrafiltrate
→ dividing glomerular filtration rate by the renal plasma flow
What factors influence the glomerular filtration rate?
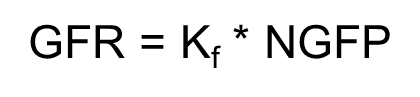
1) Net Glomerular Filtration Pressure (NGFP)
→ pressure that is applied to the filtration barrier (sum of hydrostatic pressures and oncotic pressures)
→ NGFP can be changed by glomerular hydrostatic pressure
→ Bowman capsule pressure and glomerular colloid oncotic pressure are not modified in physiological conditions
2) Capillary Filtration Coefficient (Kf)
→ takes into account number and size of pores (surface area) as well as the pores ability to allow for water movement
→ KF will remain relatively constant
What three things control glomerular hydrostatic pressure
1) Arterial Pressure
2) Afferent Arteriolar Resistance
3) Efferent Arteriolar Resistance
How does the sympathetic nervous system modify renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate?
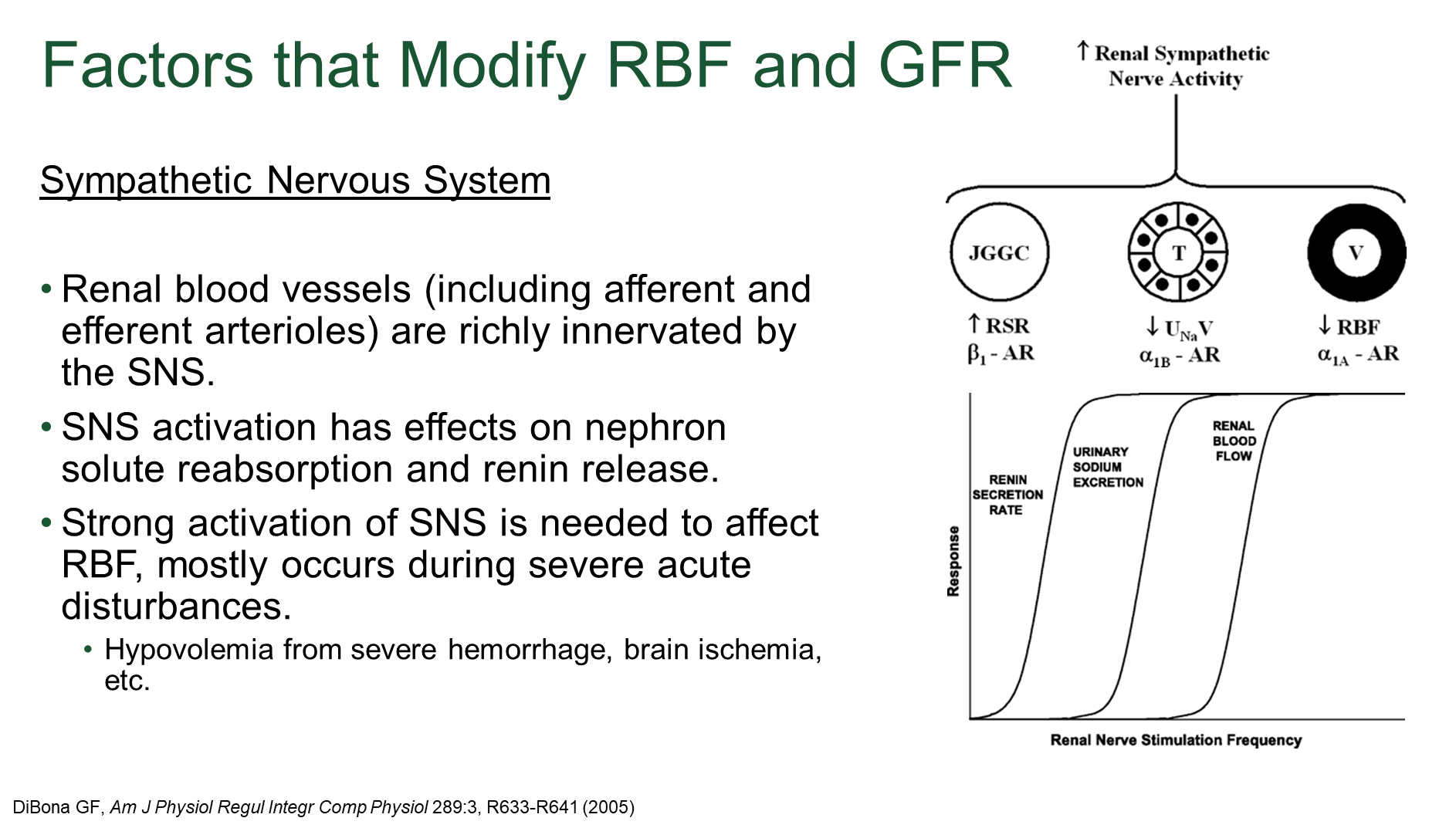
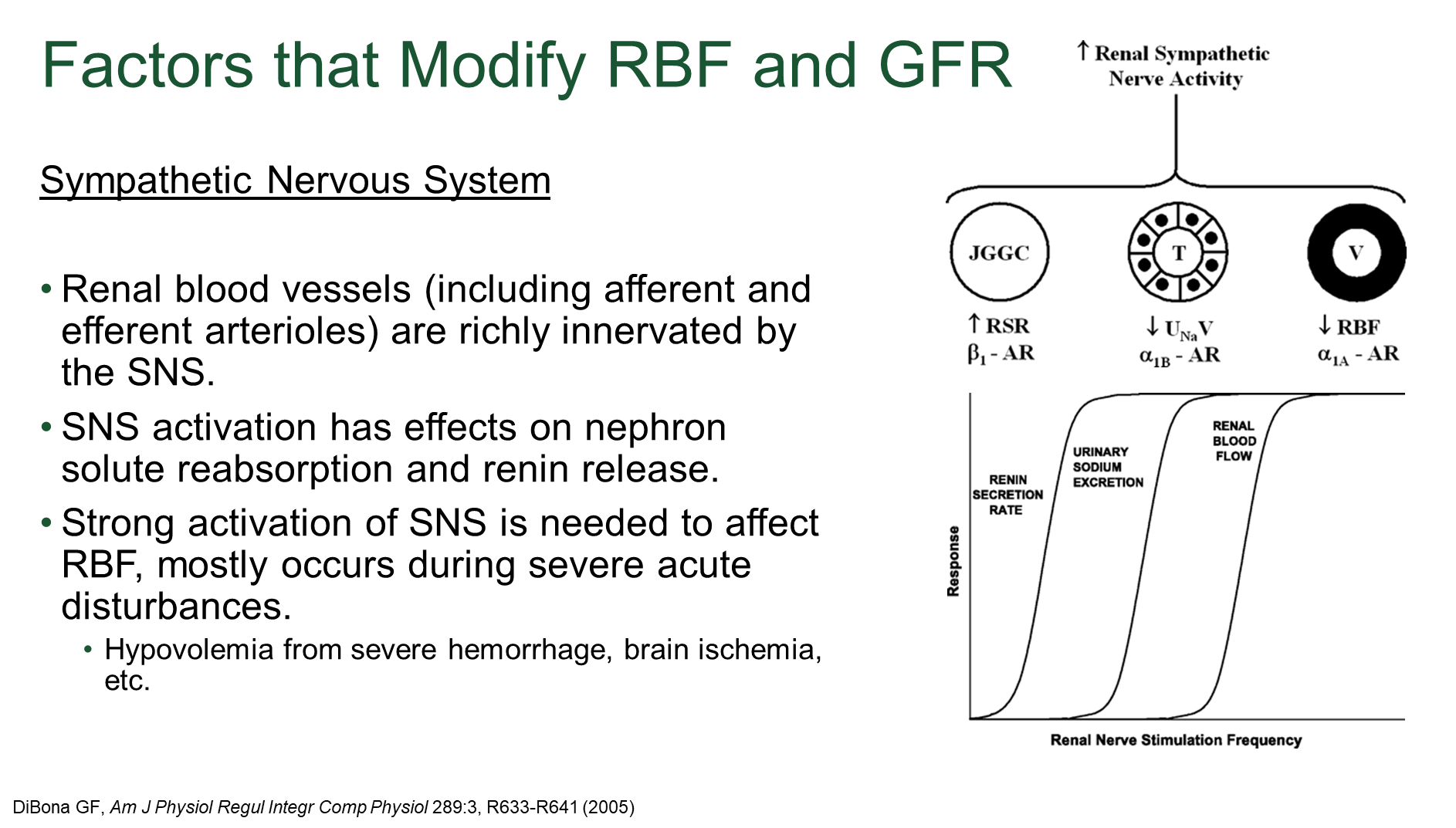
The sympathetic nervous system activation at high/strong levels causes vasoconstriction of the renal blood vessels
→ SNS can also promote solute reabsorption and renin release
What is the effect of Angiotensin II on modifying renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate
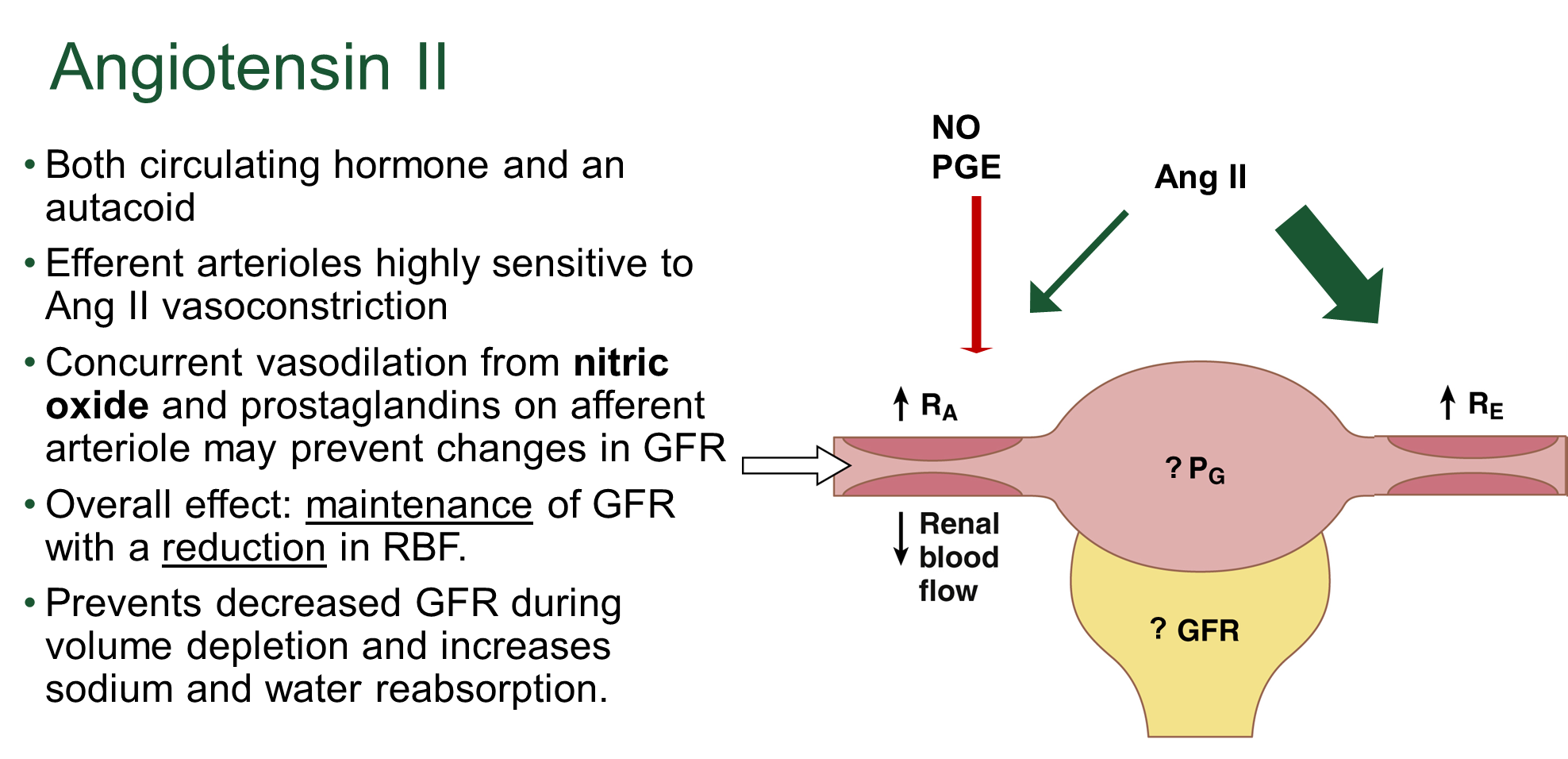
Angiotensin II is a circulating hormone and autacoid that favors efferent arteriole vasoconstriction relative to afferent arteriole vasoconstriction
→ this leads to an increase in GFR and a reduction in renal blood flow due to vasoconstriction of the efferent arteriole
What is the effect of Nitric Oxide and Prostaglandins on GFR and RBF
Nitric Oxide and Prostaglandins are vasodilatory molecules
1) NO - derived from endothelial cells and promotes both vascular dilation and sodium excretion
→ inhibiting NO or damaging endothelium will lead to increased resistance and subsequent decreased GFR
→ preferentially at the afferent arterioles
2) Prostaglandins cause vasodilation at the arterioles as well
→ not a main mediating factor at the kidney, but may used to dampen the effect of constricting effects of the SNS and Angiotensin II
Why does our body autoregulate GFR and RBF
GFR and RBF remain stable over a wide range of arterial blood pressures by autoregulation
→ without regulation, the GFR and RBF would rapidly increase with increase mean arterial pressure
What is Myogenic Autoregulation?

Myogenic Autoregulation - Intrinsic capability of blood vessels to respond to blood pressure
→ stretch on vessels causes calcium influx and responsive vasoconstriction
→ this leads to decreased pressure downstream and decreased renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate as a result
minor method of control
What is Tubuloglomerular Feedback and Autoregulation?
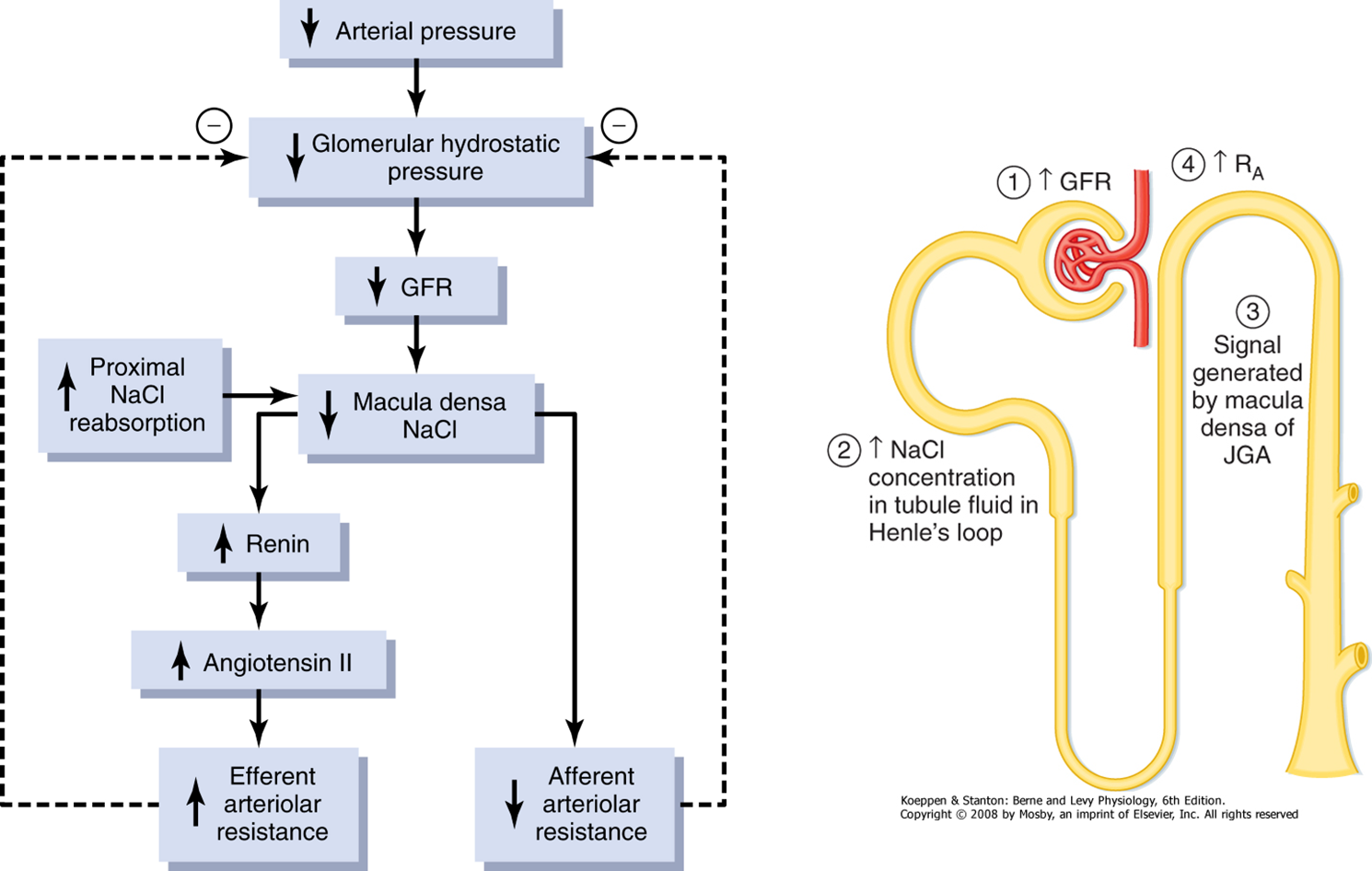
Tubuloglomerular Feedback is the process where the tubules and nephron communicate with the glomerulus in a feedback loop
1) Distal tubule interacts with the afferent and efferent arteriole via the macula densa which senses changes in NaCl in the distal tubule
→ based on salt levels, the macula densa can trigger changes in resistance in the afferent and efferent arterioles
2) In response to low sodium, indicating decreased GFR, macula densa cells will trigger increased afferent arteriole constriction
3) In response to reduction in sodium, macula densa will trigger activation of the juxtaglomerular cells to secrete renin
→ renin will eventually become angiotensin II leading to increased efferent arteriole resistance
What factors stimulate and decrease renin release?
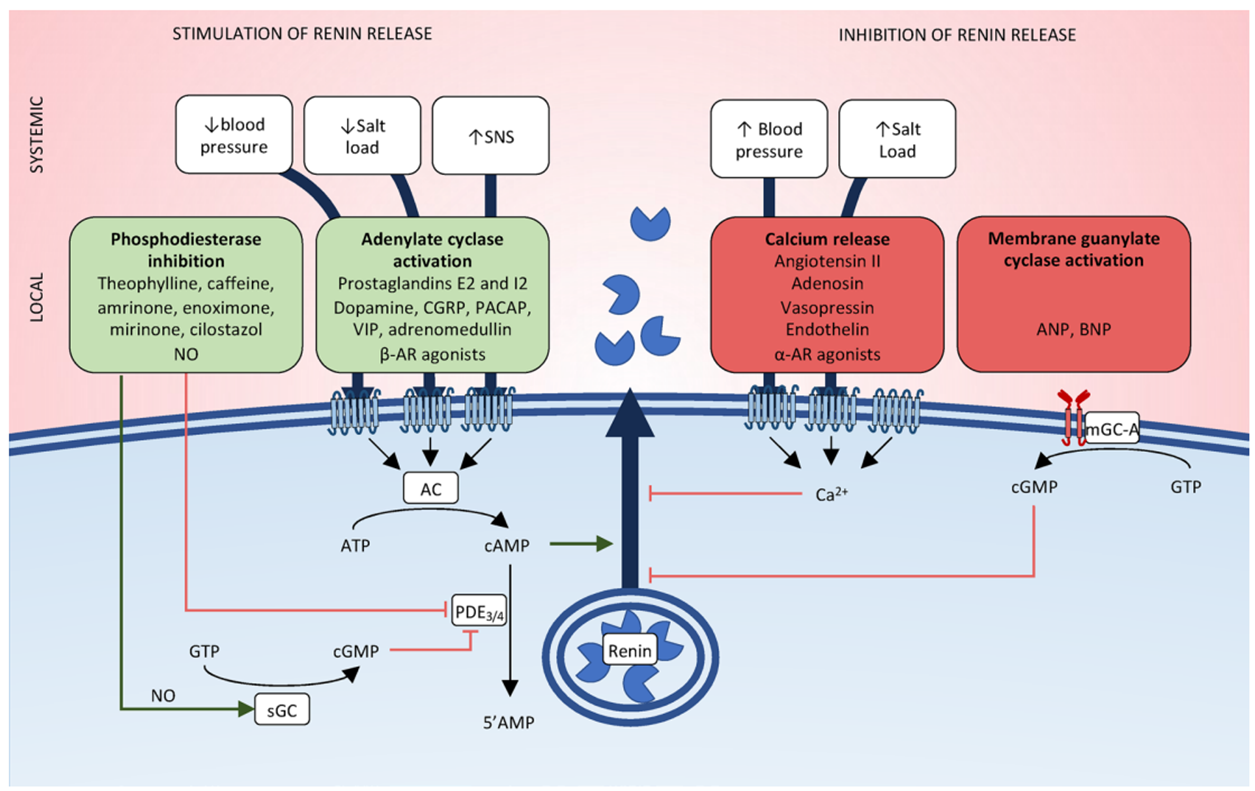
1) Stimulation
→ decreased blood pressure
→ decreased NaCl delivery to the macula densa
→ increased SNS activity
2) Decrease
→ Increased blood pressure
→ increased salt load
What is Glomerulotubular Balance
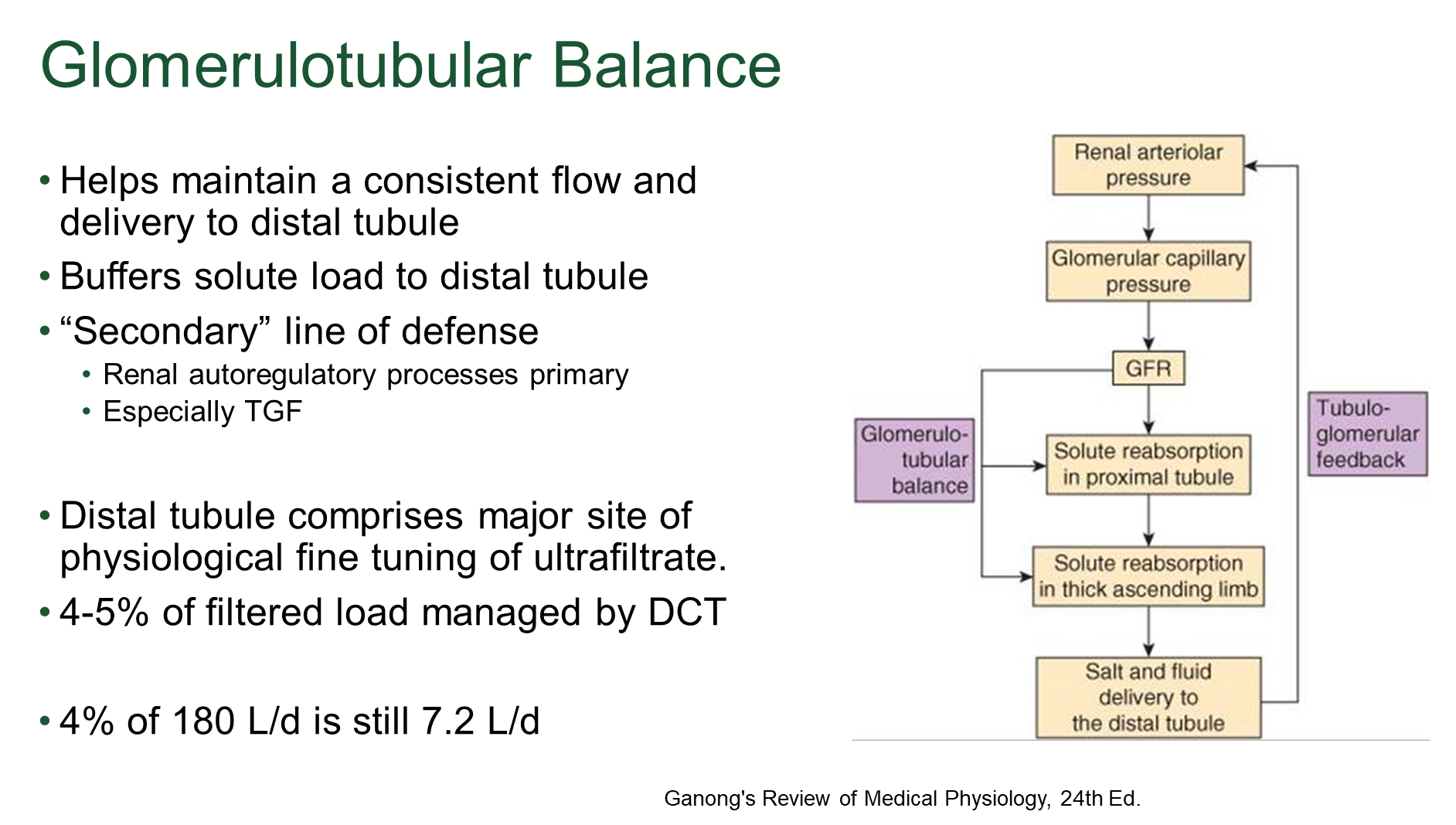
Physiological mechanism that ensures a constant proportion of glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed by the tubules
→ when filtered load goes up, tubular reabsorption will increase at a constant rate relative to the increased filtered load
→ buffers the amount of solute delivered to the distal tubule