Anatomy & Physiology: Cancer and Cell Cycle Learning Targets
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Contains learning targets from Cancer and Cell Cycle (mitosis, mutations, cancer) for the final
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1
New cards
Top risk factor for cancer
Age
2
New cards
Why is age the top risk for cancer?
More time for genetic mutations to develop
3
New cards
How cancer develops
Mutations in DNA cause cells to grow out of control
4
New cards
Tumor suppressor genes
* Slow down cell division
* Repair DNA mistakes
* Apoptosis (cell suicide)
* Repair DNA mistakes
* Apoptosis (cell suicide)
5
New cards
Proto-oncogenes
Control the speed of the cell cycle
6
New cards
Benign Tumor
Non-cancerous tumor
7
New cards
Malignant Tumor
Cancerous tumor
8
New cards
Types of Mutations
* Substitution
* Deletion
* Insertion
* Deletion
* Insertion
9
New cards
Substitution (mutation)
* Point mutations
* one nucleotide is replaced by a different nucleotide
* causes incorrect amino acid to be formed, not the worst unless stop codon is formed early
* one nucleotide is replaced by a different nucleotide
* causes incorrect amino acid to be formed, not the worst unless stop codon is formed early
10
New cards
Original: TAC GAG CAT CAC TGT ATC
Mutation: TAC GA**T** CAT CAC TGT ATC
Mutation: TAC GA**T** CAT CAC TGT ATC
Substitution
11
New cards
Deletion (mutation)
* Frameshift mutation
* one(or more) nucleotide is deleted all together
* causes incorrect amino acids to be formed and last codon doesn’t have 3 bases, not good
* one(or more) nucleotide is deleted all together
* causes incorrect amino acids to be formed and last codon doesn’t have 3 bases, not good
12
New cards
Original: TAC GAG CAT CAC TGT ATC
Mutation: TAC GA**C** ATC ACT GTA TC
Mutation: TAC GA**C** ATC ACT GTA TC
Deletion
13
New cards
Insertion (mutation)
* Frameshift mutation
* the addition of one or more nucleotides into a segment of DNA
* causes incorrect amino acids to be formed because there is a extra base added causing the last codon to not have 3 bases , not good
* the addition of one or more nucleotides into a segment of DNA
* causes incorrect amino acids to be formed because there is a extra base added causing the last codon to not have 3 bases , not good
14
New cards
Original: TAC GAG CAT CAC TGT ATC
Mutation: TAC GAG CAT **T**CA CTG TAT C
Mutation: TAC GAG CAT **T**CA CTG TAT C
Insertion
15
New cards
Point Mutations (3)
* Nonsense
* Missense
* Silent
* Missense
* Silent
16
New cards
Nonsense (point mutation)
occurs when one nucleotide is substituted and this leads to the formation of a **stop codon** instead of a codon that codes for an amino acid (substitution)
17
New cards
Original: Met-Leu-Val-Val-Thr-STOP
Mutation: Met-Leu-**STOP**- - -
Mutation: Met-Leu-**STOP**- - -
Nonsense
18
New cards
Missense (point mutation)
occurs when one nucleotide is substituted and the codon produces a **different amino acid** in the sequence of amino acids (Frameshift)
19
New cards
Original: Met-Leu-Val-Val-Thr-STOP
Mutation: Met-Leu-**Pro**-Val-Thr-STOP
Mutation: Met-Leu-**Pro**-Val-Thr-STOP
Missense
20
New cards
Silent (point mutation)
a nucleotide is substituted but the **same amino acid** is produced anyway
21
New cards
Original: Met-Leu-Val-Val-Thr-STOP
Mutation: Met-Leu-Val-Val-Thr-STOP
Mutation: Met-Leu-Val-Val-Thr-STOP
Silent
22
New cards
Carcinogen
Anything that can cause cancer
ex. tobacco, alcohol, sunlight
ex. tobacco, alcohol, sunlight
23
New cards
Amount of individuals who will get cancer
22\.92%
24
New cards
Inherited Mutations
* Gene defects that are passed from parent → child
* mutation exists in all cells
* mutation exists in all cells
25
New cards
Acquired Mutations
DNA changes that are acquired during a person’s life
26
New cards
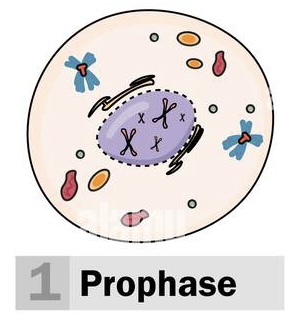
Prophase (1)
* Longest phase (50%-60% spent there)
* Chromosomes become visible
* Centrioles separate to opposite sides of cell (form spindles)
* Nucleolus disappears and nuclear envelope breaks down
* Chromosomes become visible
* Centrioles separate to opposite sides of cell (form spindles)
* Nucleolus disappears and nuclear envelope breaks down
27
New cards
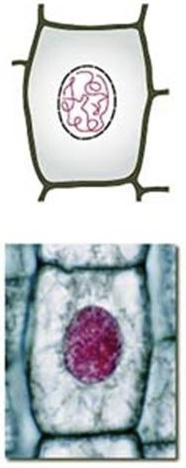
Identify the phase of mitosis
Prophase
28
New cards
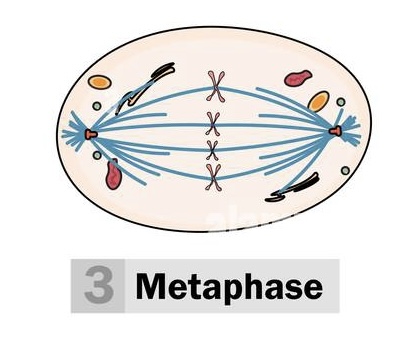
Metaphase (2)
chromosomes line up in center of cell
29
New cards

Identify the phase of mitosis
Metaphase
30
New cards
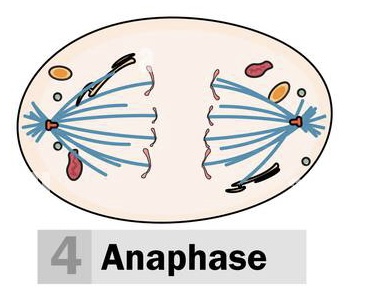
Anaphase (3)
sister chromatids split up apart into individual chromosomes and move apart
31
New cards
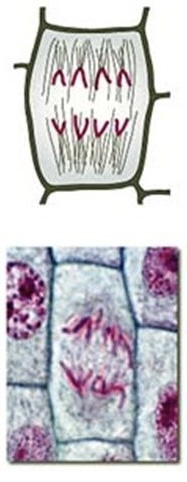
Identify the phase of mitosis
Anaphase
32
New cards
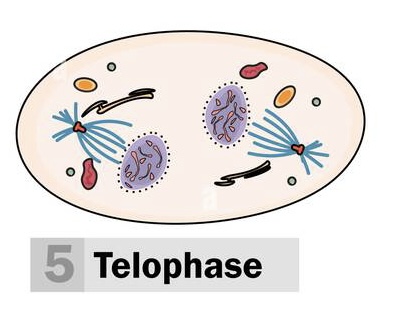
Telophase (4)
* Chromosomes turn back into chromatin
* Centrioles go back into pairs (spindles disappear)
* Nucleolus appears and nuclear envelope forms again
* Final step
* Centrioles go back into pairs (spindles disappear)
* Nucleolus appears and nuclear envelope forms again
* Final step
33
New cards

Identify the phase of mitosis
Telophase
34
New cards
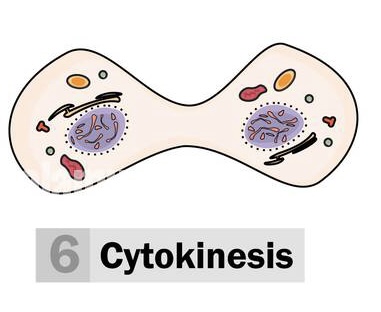
Cytokinesis
* NOT part of mitosis
* Cell division
* Cell plate (line forms and makes 2)
* Cleavage furrow pinches them apart
* Cell division
* Cell plate (line forms and makes 2)
* Cleavage furrow pinches them apart
35
New cards
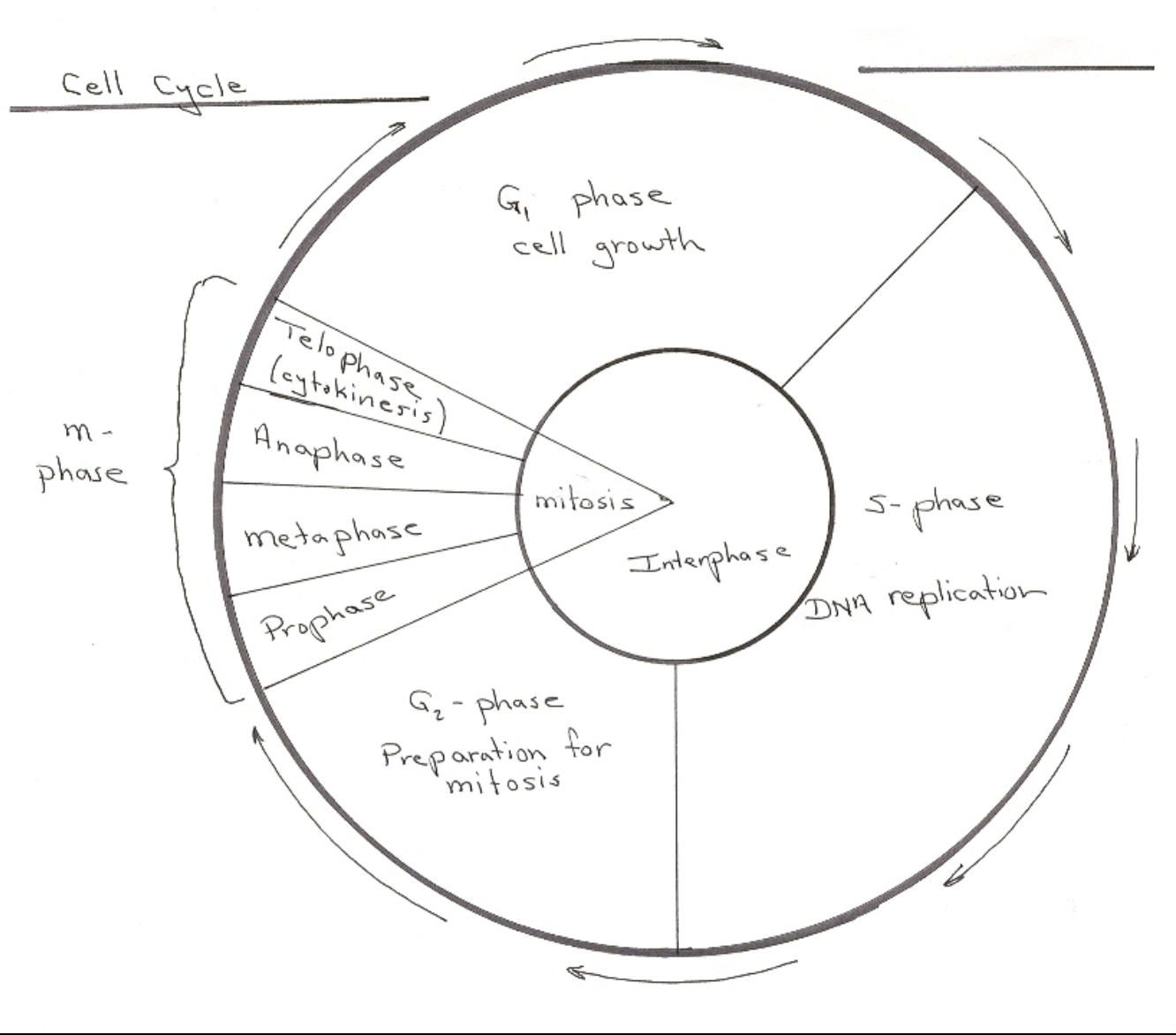
Interphase
* Cell is performing everyday tasks (metabolic)
* 90% spent in this stage
* G1, S, G2
* 90% spent in this stage
* G1, S, G2
36
New cards
G1 (interphase)
Cell growth
37
New cards
S (interphase)
DNA replication (make/copy chromosomes)
38
New cards
G2 (interphase)
Prepare for mitosis