language science & theory
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
theory
descriptive statements or principles devised to explain a group of facts or a phenomena
repeated, tested w/ scientific method
science
generating & testing theories
theories of child development
behaviorist theory
nativist / universal grammar
social - interactionist theory
cognitive theory
nativist/universal grammar
noam chomsky
existence of an innate language module, a Language Acquisition Device
children are born with Universal Grammar
children are born with linguistic competence, they don’t have to acquire a certain level of cognition to be able to talk
children use input to discover parameters of their language and then slowly figure out how to satisfy the general grammatical rules of their native language
narrow down universal, innate languages to their specific language
universal grammar
a basic set of grammatical rules, universal across languages
Chomsky believes children are born with this
Language Acquisition Device
an innate language model Chomsky thought children were born with
behaviorist theory
B.F. Skinner
learning through operant conditioning and reinforcement
reinforced behaviors are strengthened and punished behaviors are suppressed
language, like all other behaviors, is learned through operant conditioning
child is positively reinforced after making a sound, leading to a desire to continue that behavior
Skinner believes language is NOT innate - nothing in the brain makes us predisposed to learn language
children learn language through environmental stimuli and adult reinforcement of their vocalizations
social-interactionist theory
Lev Vygotsky
used in classrooms and by SLPs to provide language support & help children achieve skills
children learn through their experiences and social interactions
learning takes place in the zone of proximal development
thought and speech develop independently
speech helps development of cognition, as those thoughts can then be expressed through speech
learning is innately a social phenomenon
scaffolding is structured support
zone of proximal development
difference between a children’s actual and potential development - the difference between what a learner can learn independently and what they gain / learn through guidance with the help of adults or peers & appropriate scaffolding
cognitive theory
Jean Piaget
language development is the product of the child’s experiences with the physical environment and their cognitive development
acquiring more cognitive skills means children need more language skills to express their thoughts
children construct their knowledge of the world through schemas
children have an active role in constructing schemas
achievements in cognition lead to achievements in language development (interaction)
language is acquired through imitation
schemas
children’s views, their cognitive thought process on how things happen
4 stages of cognitive development
sensorimotor (0-2 years) - object permanence, developing some cognitive skills
preoperational (2-7 years) - lacks conservation, classification, theory of mind understanding; egocentric speech, gaining understanding of world & language
concrete operations (7-11 years) - less egocentric, conservation, classification skills effective
formal operations (11 years+) - perform higher level cognitive skills through hypotheticals, verbal reasoning
behaviorist theory main points
Skinner
operant conditioning & reinforcement
language is NOT innate
adult reinforcement of child vocalizations
nativist/universal grammar main points
Chomsky
Language Acquisition Device (LAD)
Universal Grammar
cognitive theory main points
Piaget
4 stages of cognitive development
schemas
cognition precedes language, language supports higher-level thought
social constructivist theory main points
Vygotsky
zone of proximal development
scaffolding
language learning through social interaction, supports cognitive abilities
linkage of theory to practice
people let their experience about phenomena guide their practices - depending on what you believe, it will fuel the way you practice
“practitioners must make every effort to understand the theories that guide particular practices”
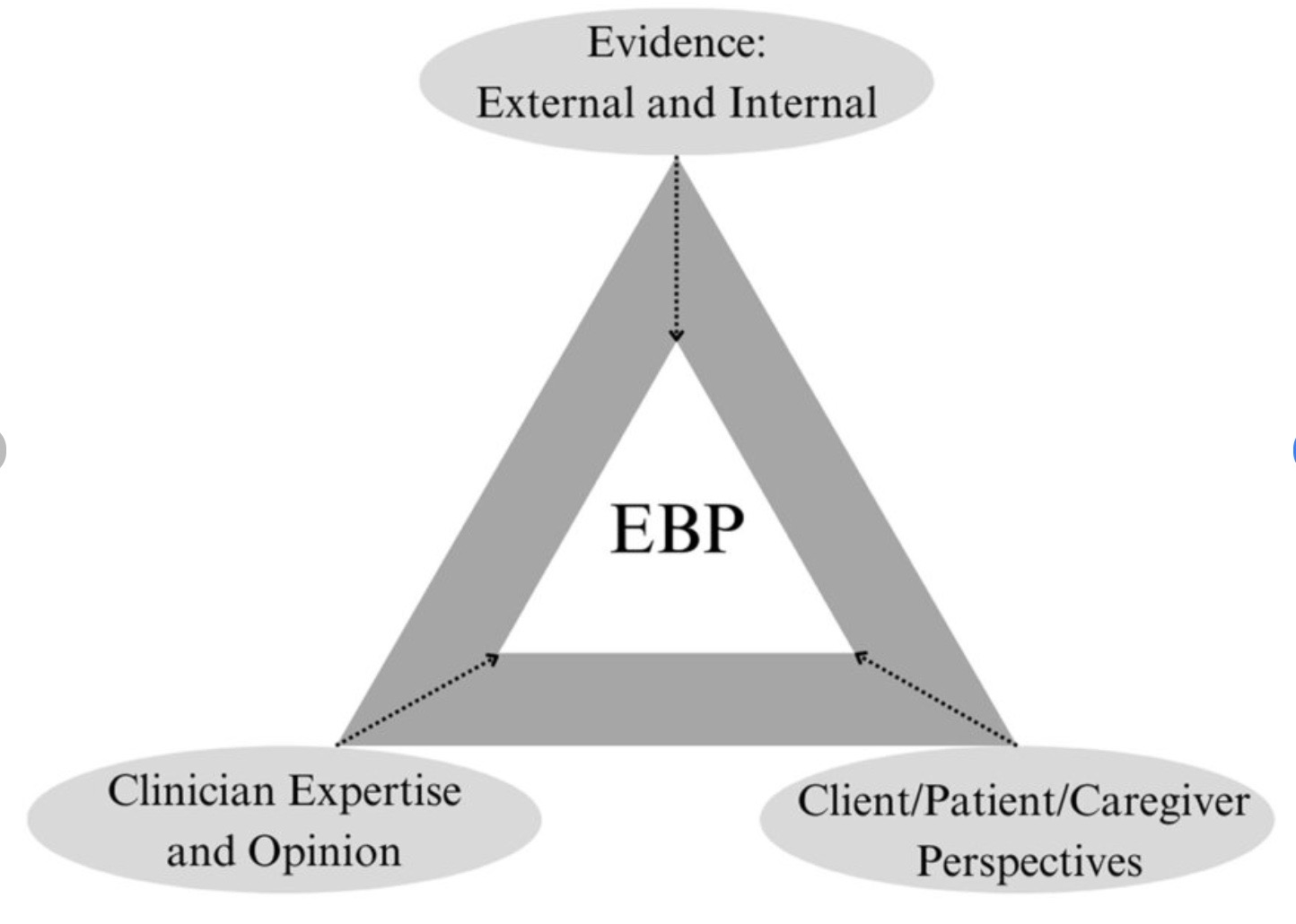
evidence based practice
new ideas are driven by theory, which support science
research and treatment methods must be supported with research
ASHA says to integrate: high quality research, client preference, and their own experience as practitioners
how do we use theories?
prevention: attempt to keep language difficulties from arising
particularly important for children who are considered at-risk
intervention & remediation: creation and use of treatment programs to help individuals with language difficulties
applicable to providing services to individuals across the lifespan
enrichment: provision of enriching language-learning experiences to improve and learn new skills
educating teachers on ways to promote children’s language in the pre-k classroom
interdisciplinary
the study of language is an _______ science
SLPs, speech language scientists, developmental & cognitive psychologists, linguists, anthropologists, sociologists, educators all involved
types of research
basic (theoretical): generating or refining existing knowledge base
ways children learn word meanings, acquire grammatical structures, ages at which they produce certain sounds
applied: testing different approaches or practices relevant to real-world knowledge
experimental research design to examine the relationship of an approach and the outcome (test certain therapy treatments and how it helped the patient)