The Female Reproductive System Overview
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
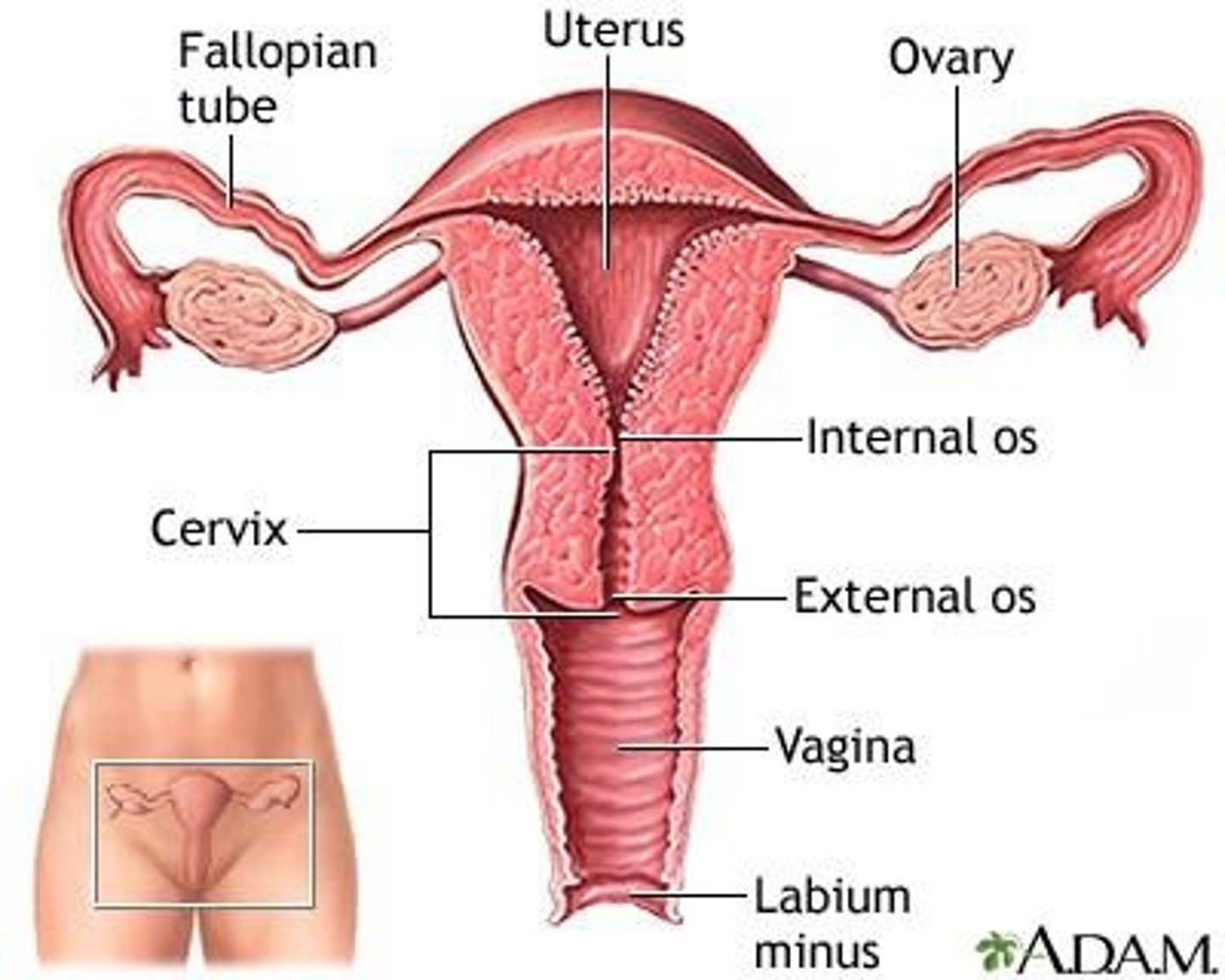
What are the internal genitalia of the female reproductive system?
Ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina.
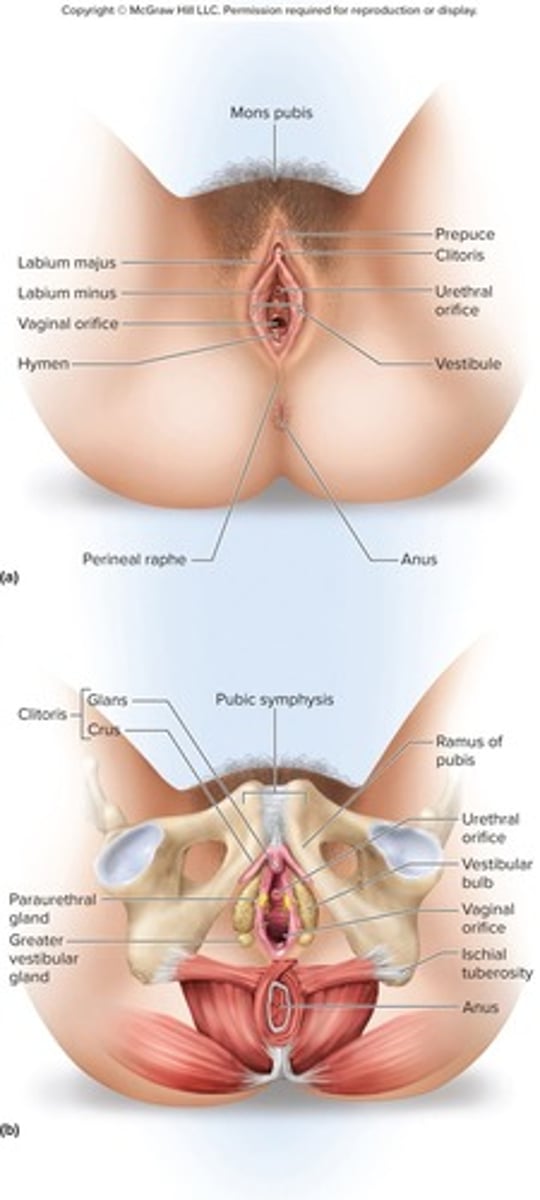
What are the external genitalia of the female reproductive system?
Clitoris, labia minora, labia majora, associated subcutaneous glands, and erectile tissues.
What are the primary sex organs in the female reproductive system?
The ovaries.
What are the secondary sex organs in the female reproductive system?
The other internal and external genitalia.
What is the function of the ovaries?
To produce egg cells (ova) and sex hormones.
Describe the shape and location of the ovaries.
Almond-shaped and nestled in the ovarian fossa of the posterior pelvic wall.
What is the tunica albuginea?
A capsule surrounding the ovaries, similar to that of the testes.
What are the two main regions of the ovaries?
Outer cortex where germ cells develop and inner medulla occupied by major arteries and veins.
What occurs during ovulation?
The bursting of the follicle and the release of the egg.
What ligaments attach the ovaries to other structures?
Ovarian ligament (to uterus), suspensory ligament (to pelvic wall), and mesovarium (to broad ligament).
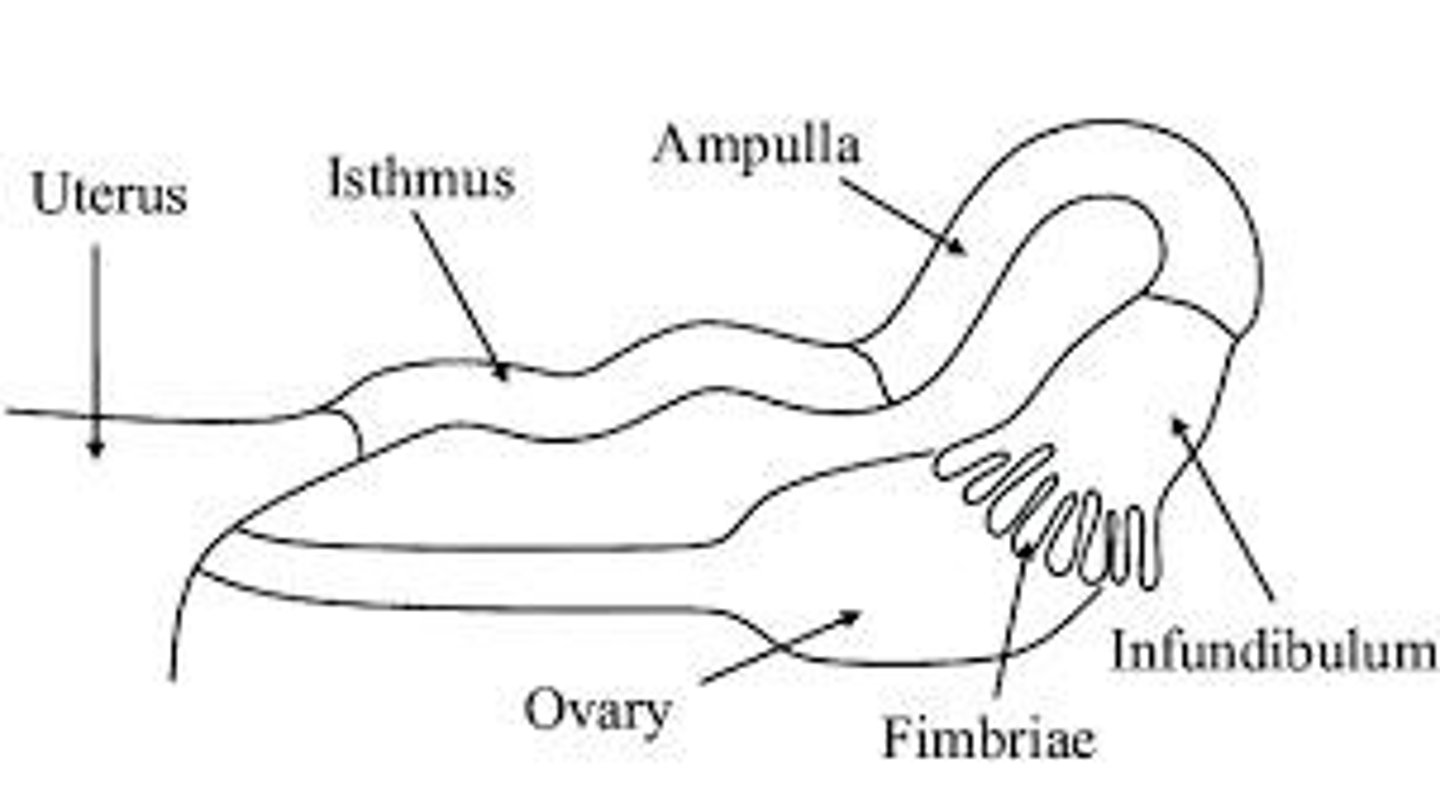
What are the uterine tubes also known as?
Oviducts or fallopian tubes.
What are the three regions of the uterine tubes?
Infundibulum, ampulla, and isthmus.
What is the function of the cilia in the uterine tubes?
To help move the egg toward the uterus.
What is the primary function of the uterus?
To harbor the fetus, provide nutrition, and expel the fetus at the end of its development.
What are the three regions of the uterus?
Fundus, body, and cervix.
What is the cervical canal?
The passage that connects the lumen of the uterus to the vagina.
What is the role of cervical glands?
To secrete mucus that prevents the spread of microorganisms from the vagina to the uterus.
What is a Pap smear?
A test for early detection of cervical cancer, involving the removal and microscopic examination of loose cells from the cervix and vagina.
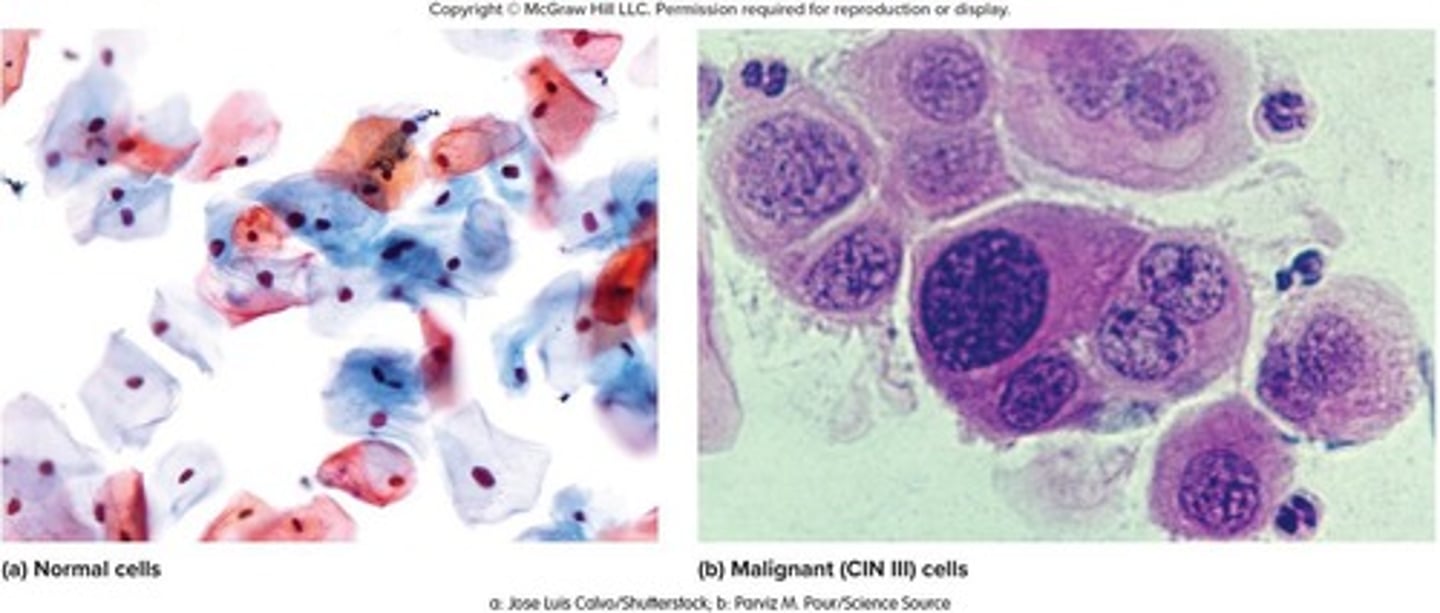
What is the most common cause of cervical cancer?
Human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted pathogen.
What are the three grades of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia?
Class 1 (mild dysplasia), Class 2 (calls for a biopsy), Class 3 (may require radiation therapy or hysterectomy).
What are the three layers of the uterine wall?
Perimetrium, myometrium, and endometrium.
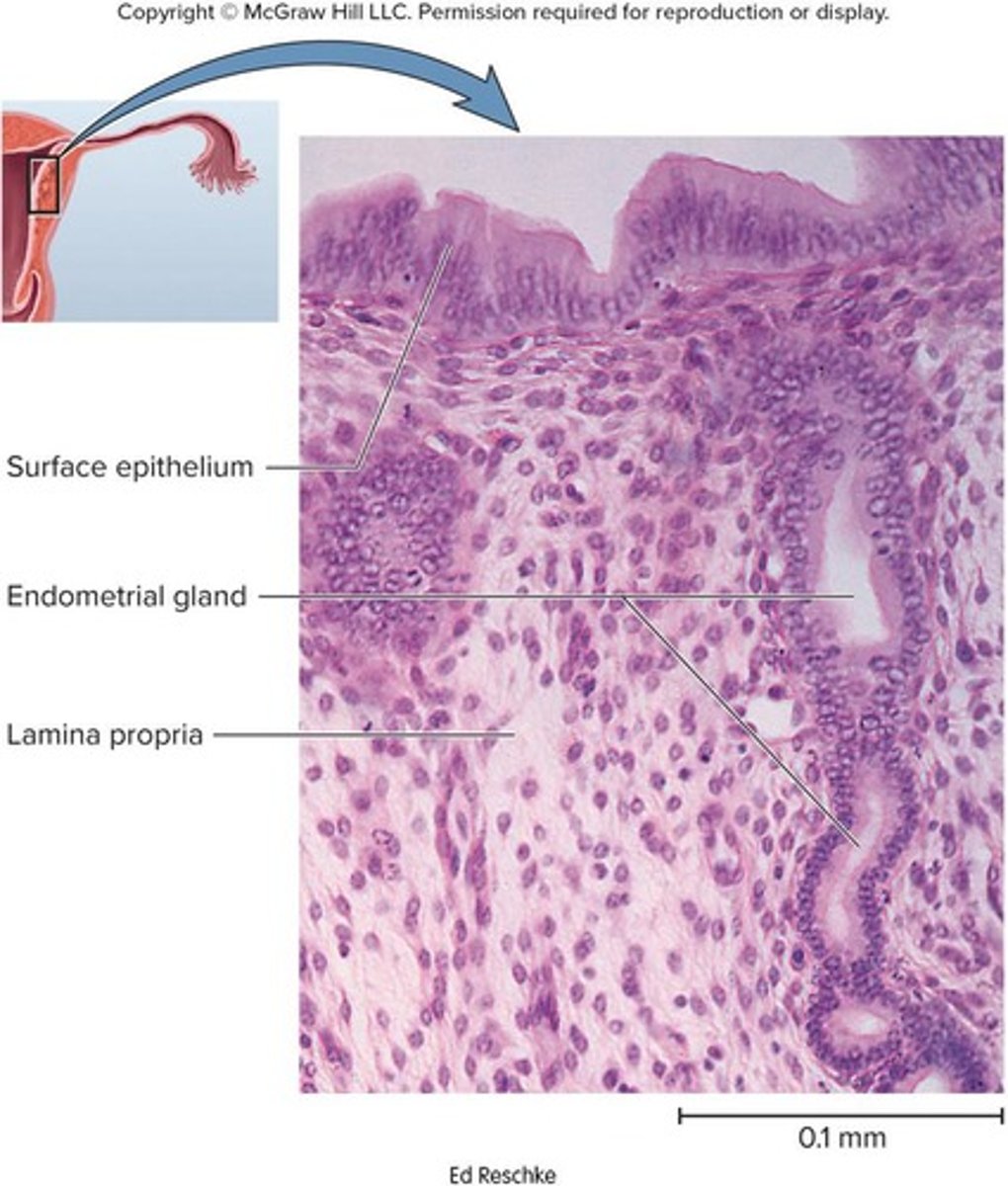
What is the function of the myometrium?
To produce labor contractions and expel the fetus.
What is the endometrium?
The inner mucosa of the uterus, consisting of simple columnar epithelium, compound tubular glands, and a stroma with leukocytes and macrophages.
What are the two layers of the endometrium?
The functional layer (stratum functionalis) which is shed during menstruation, and the basal layer (stratum basalis) which regenerates the functional layer.
What role does the endometrium play during pregnancy?
It serves as the site of attachment for the embryo and forms the maternal part of the placenta.
What is the vagina and its primary functions?
A distensible muscular tube 8 to 10 cm long that allows for discharge of menstrual fluid, receipt of penis and semen, and birth of a baby.
What are the three layers of the vaginal wall?
Outer adventitia, middle muscularis, and inner mucosa.
How is the vagina positioned in relation to other structures?
It is tilted posteriorly between the rectum and urethra.
What are vaginal rugae?
Transverse friction ridges at the lower end of the vagina.
What is the hymen?
Mucosal folds that cover the vaginal opening.
How does the vaginal epithelium change from childhood to puberty?
It changes from simple cuboidal to stratified squamous epithelium.
What is the role of bacteria in the vagina?
They ferment glycogen to lactic acid, producing an acidic pH that inhibits the growth of pathogens.
What is the vulva?
The collective term for the external genitalia.
What is the mons pubis?
A mound of fat over the pubic symphysis that bears most of the pubic hair.
What are the labia majora?
Thick folds of skin and adipose tissue inferior to the mons pubis, with the pudendal cleft between them.
What are the labia minora?
Thin, hairless folds of skin medial to the labia majora.
What is the vestibule in female anatomy?
The space between the labia minora that contains the urethral and vaginal openings.
What is the clitoris and its function?
An erectile, sensory organ that is the primary center for sexual stimulation.
What are vestibular bulbs?
Erectile tissues located deep to the labia majora.
What are the greater and lesser vestibular glands?
Glands that open into the vestibule to keep the vulva moist and provide lubrication.
What are paraurethral glands?
Glands (female prostate) that open into the vestibule near the external urethral orifice.
What is the structure of the female breast?
A mound of tissue overlying the pectoralis major, consisting of a body, axillary tail, areola, and nipple.
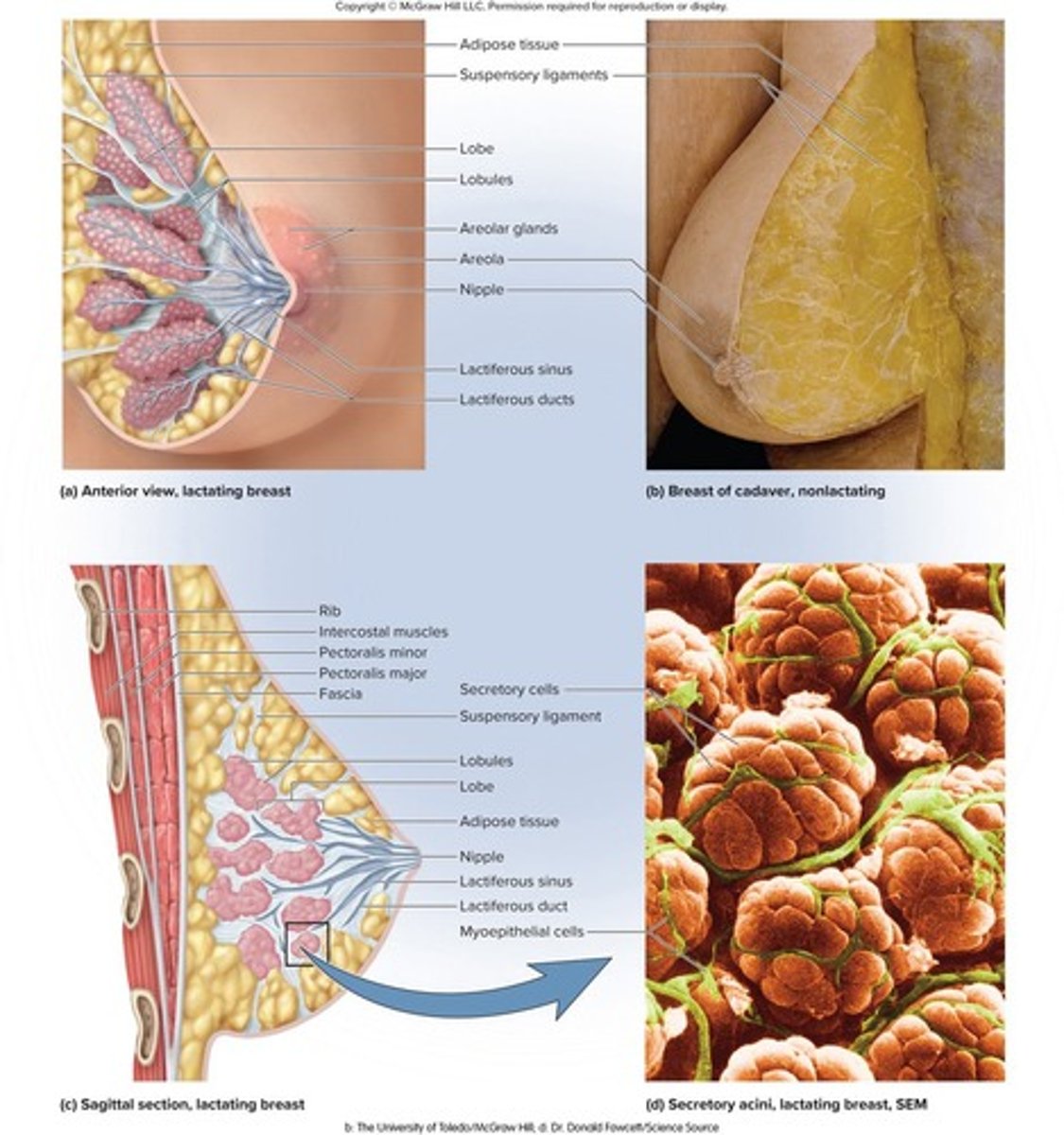
What happens to the mammary glands during pregnancy?
They develop within the breast and remain active during lactation.
What are the signs of breast cancer?
Signs may include a lump, skin puckering, changes in skin texture, and drainage from the nipple.
What are some risk factors for breast cancer?
Aging, exposure to ionizing radiation, carcinogenic chemicals, excessive alcohol and fat intake, and smoking.
What percentage of breast cancer cases lack identifiable risk factors?
Over 70%
How are tumors typically discovered in breast cancer detection?
Through breast self-examination (BSE) and mammograms.
What is a lumpectomy?
A surgical procedure that involves the removal of the tumor only.
What does a simple mastectomy entail?
Removal of breast tissue only or breast tissue and some axillary lymph nodes.
What is involved in a radical mastectomy?
Removal of the breast, underlying muscle, fascia, and lymph nodes.
What treatments follow surgery for breast cancer?
Radiation or chemotherapy.
What is breast reconstruction?
A surgical procedure that uses skin, fat, and muscle from other parts of the body to reconstruct the breast.
At what age does puberty typically begin for well-nourished girls in affluent countries?
Between ages 8 to 10.
What hormone triggers the onset of puberty?
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
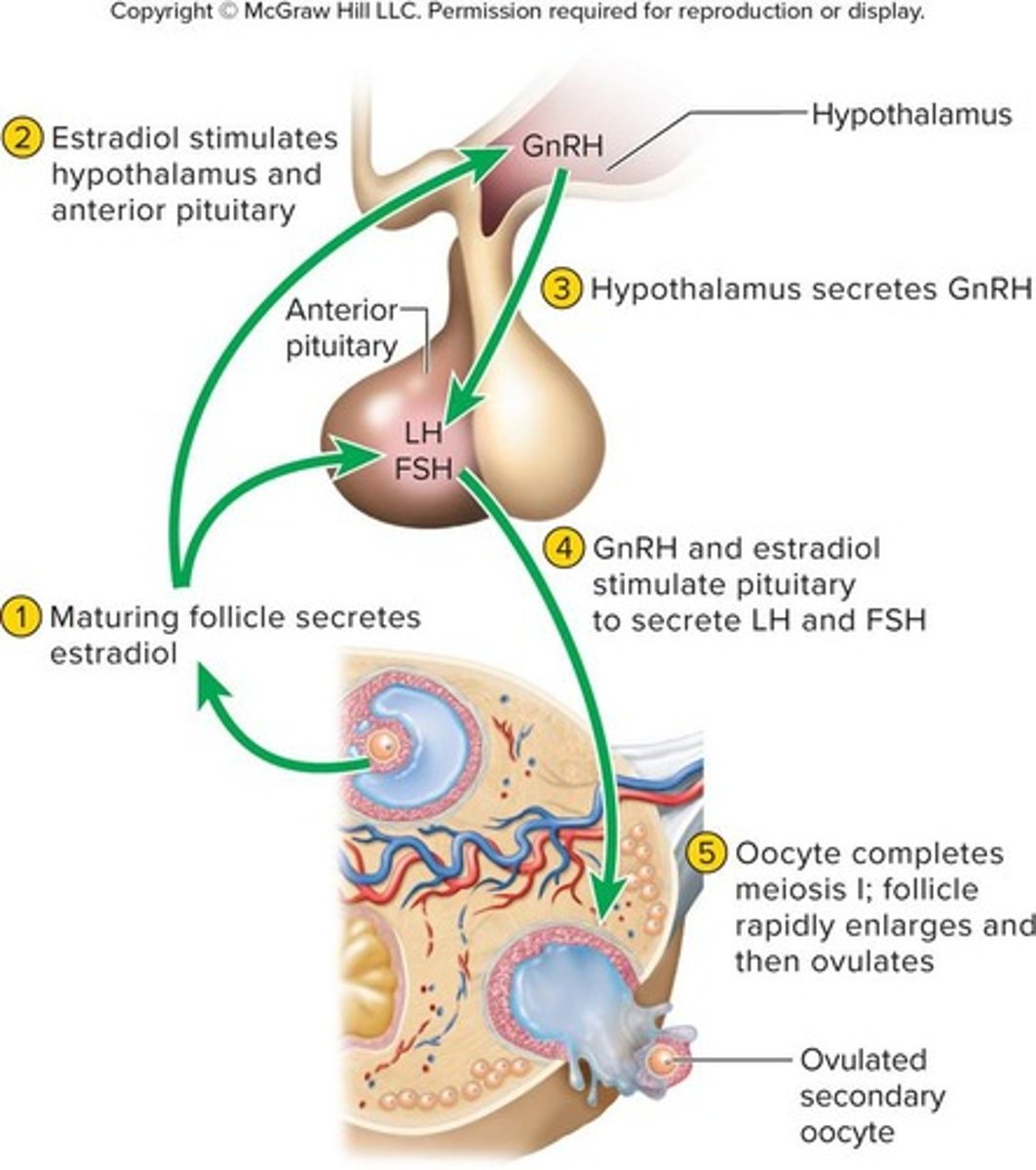
What role does FSH play in female puberty?
FSH stimulates ovarian follicles to secrete estrogen, progesterone, inhibin, and a small amount of androgen.
What is thelarche?
The onset of breast development and the earliest noticeable sign of puberty.
What is pubarche?
The appearance of pubic and axillary hair, sebaceous glands, and axillary glands.
What is menarche?
The first menstrual period.
What is the average age of onset for menarche due to improved nutrition?
12.5 years.
What is climacteric?
The midlife change in hormone secretion accompanied by menopause.
What happens to the uterus, vagina, and breast during menopause?
They atrophy.
What are common effects of menopause on the body?
Increased vaginal infections, thinner skin, rising cholesterol levels, and declining bone mass.
What is the reproductive cycle?
The sequence of events from fertilization to giving birth and returning to fertility.
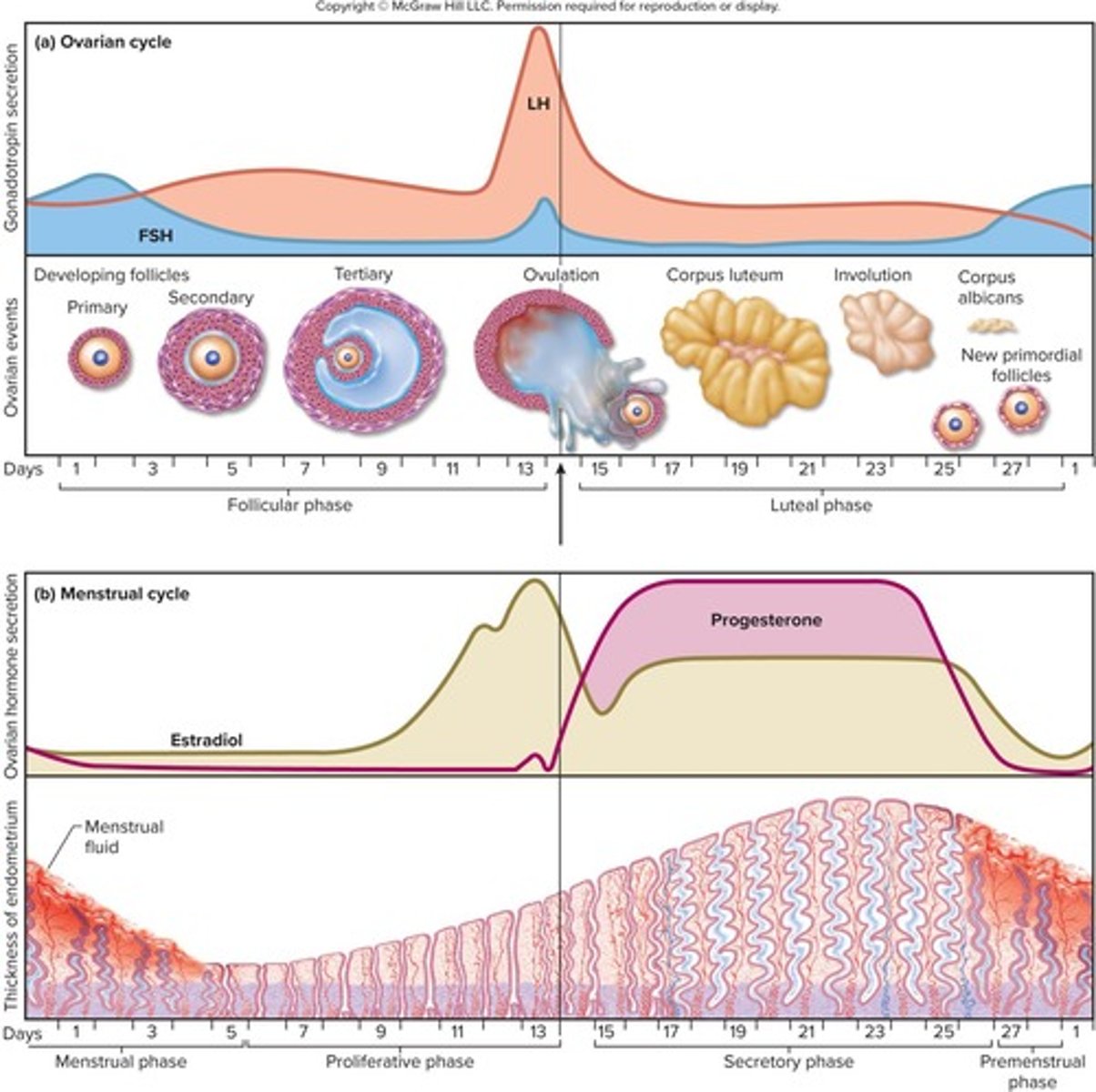
What are the two interrelated cycles of the sexual cycle?
The ovarian cycle and the menstrual cycle.
What is the average duration of the sexual cycle?
28 days, but it can vary from 20 to 45 days.
What is the basic hierarchy of hormonal control in the sexual cycle?
Hypothalamo-pituitary-ovarian axis.
What occurs during the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle?
FSH stimulates follicles to grow and secrete estradiol, leading to ovulation.
What happens during ovulation?
The mature follicle ruptures and releases the egg.
What is the duration of the luteal (postovulatory) phase?
From day 15 to day 28, from just after ovulation to the onset of menstruation.
What happens to the follicle after ovulation if pregnancy does not occur?
The follicle ruptures, collapses, bleeds into the antrum, and the follicular cells multiply to fill the antrum.
What is the corpus luteum and what does it secrete?
The corpus luteum is the ovulated follicle that secretes estrogen and progesterone.
How do estrogen and progesterone affect the pituitary gland during the luteal phase?
They inhibit LH and FSH secretion by the pituitary via negative feedback.
What occurs to the corpus luteum around day 22 if pregnancy does not occur?
The corpus luteum begins involution (shrinkage) and by day 26, it is completely involuted, leaving a scar called corpus albicans.
What happens to estrogen and progesterone levels as the corpus luteum degenerates?
Estrogen and progesterone secretion drops.
What initiates the rise of FSH levels again after the luteal phase?
The pituitary is no longer inhibited, allowing FSH levels to rise and stimulate a new cohort of follicles.
What is the purpose of the proliferative phase in the uterine cycle?
It involves rebuilding the functional layer of the endometrium lost during menstruation.
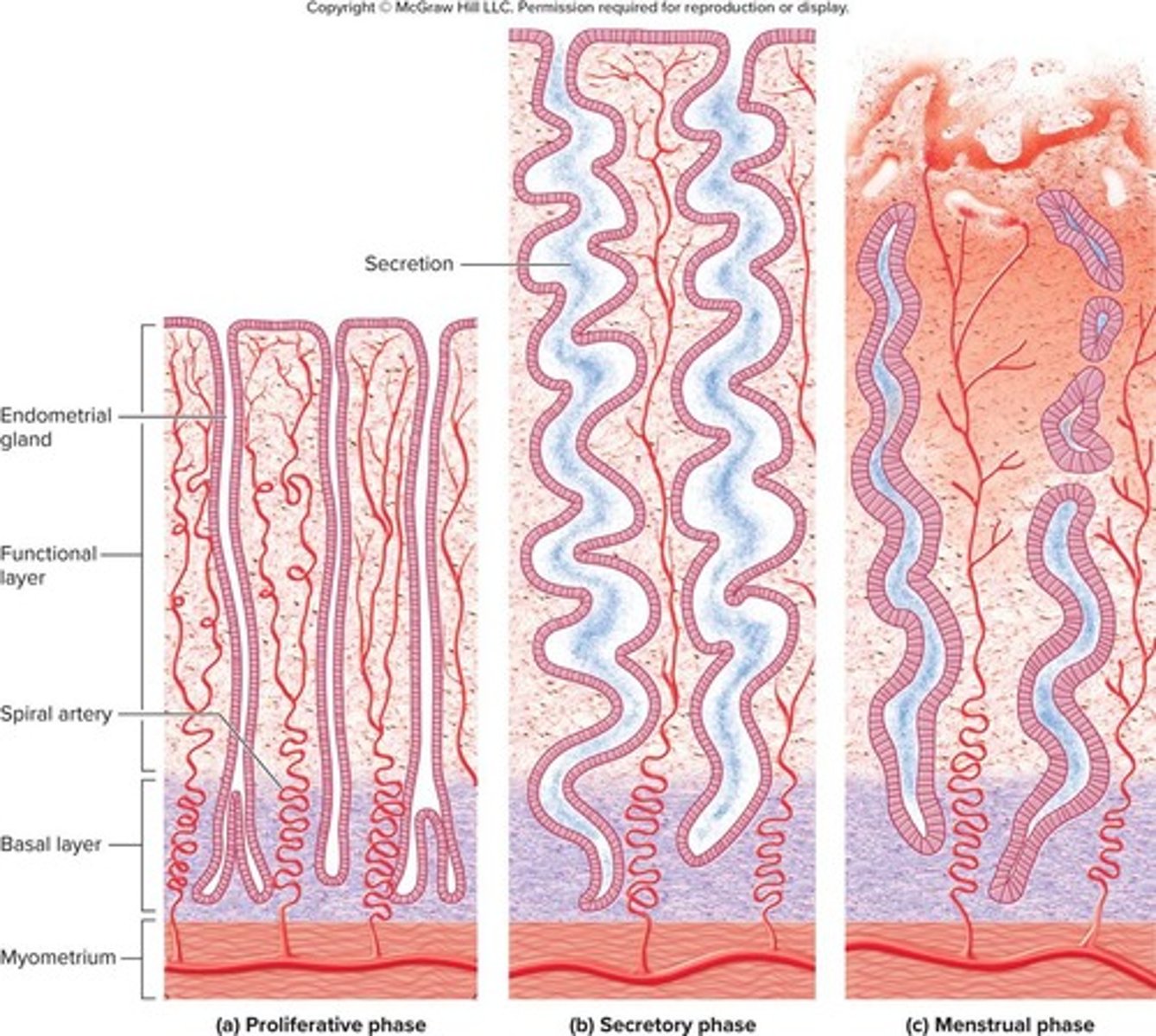
What role does estrogen play during the proliferative phase?
Estrogen stimulates mitosis in the basal layer and regrowth of blood vessels in the endometrium.
How thick is the endometrium by day 14 of the uterine cycle?
The endometrium is 2 to 3 mm thick.
What occurs during the secretory phase of the uterine cycle?
The endometrium thickens due to secretion and fluid accumulation, and glands secrete glycogen.
What is the thickness of the endometrium by the end of the secretory phase?
The endometrium is 5 to 6 mm thick.
What triggers the premenstrual phase?
The atrophy of the corpus luteum and the fall of progesterone levels.
What is endometrial ischemia and when does it occur?
Endometrial ischemia is interrupted blood flow that occurs during the premenstrual phase.
What is the menstrual phase?
The period where menstrual fluid is discharged from the vagina, marking the first day of the new cycle.
How much fluid does the average woman expel during menstruation?
About 40 mL of blood and 35 mL of serous fluid over a 5-day period.
What are behavioral methods of contraception?
Methods include abstinence, fertility awareness-based methods, and withdrawal (coitus interruptus).

What are barrier and spermicidal methods of contraception?
Methods include male and female condoms, diaphragms, sponges, and spermicides like foams, creams, and jellies.
What is the primary function of hormonal methods of contraception?
Most hormonal methods prevent ovulation by inhibiting FSH and LH.
What are morning after pills and how do they work?
Emergency contraceptive pills that induce menstruation if implantation has not occurred and inhibit ovulation, sperm movement, and implantation.
What is the intrauterine device (IUD) and its function?
A springy device left in the uterus that irritates the uterine lining to destroy sperm or inhibit their motility.
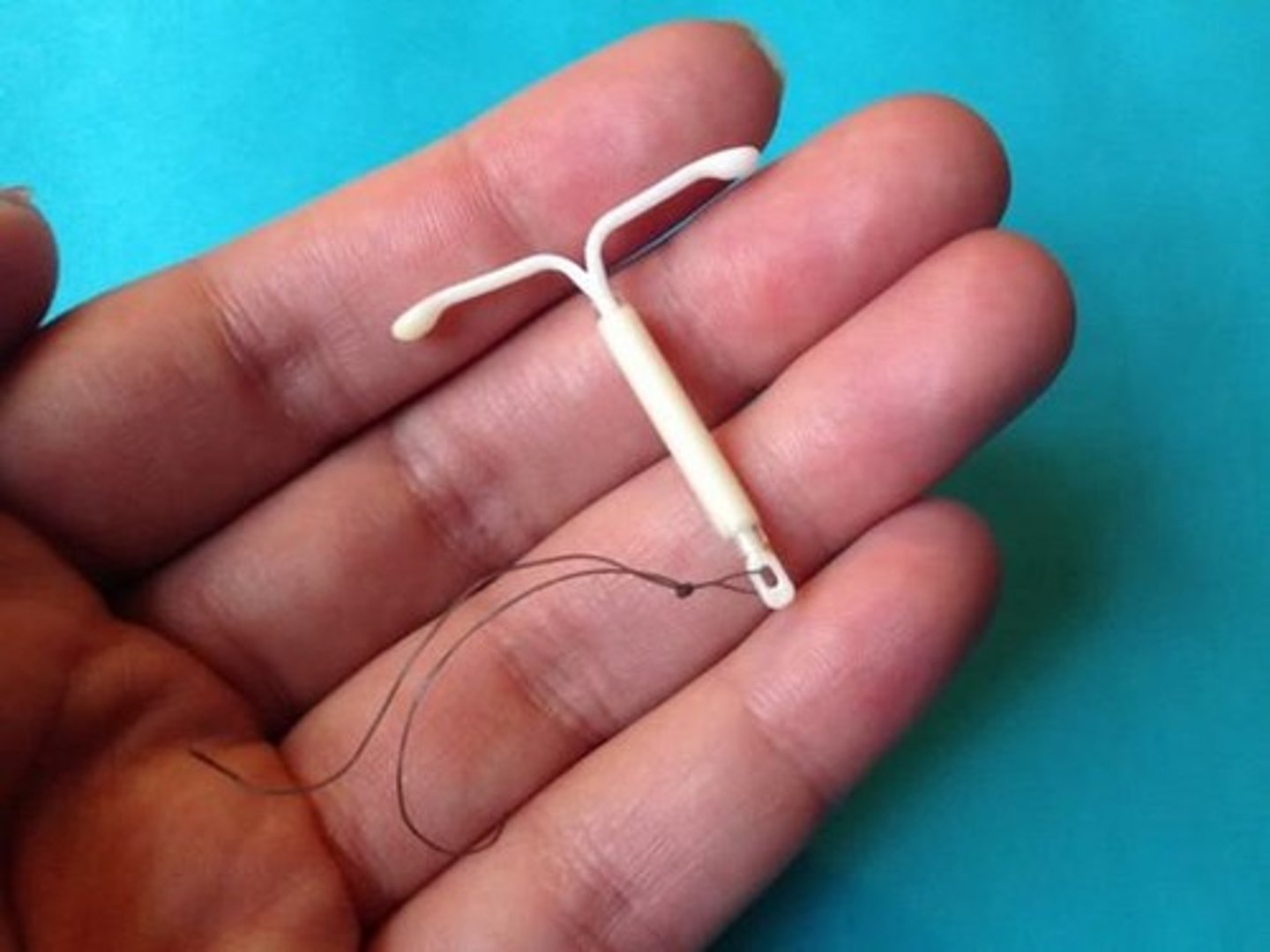
What is surgical sterilization in the context of contraception?
Clamping or cutting the genital ducts, such as vasectomy for males and tubal ligation for females.