MCAT 2023
1/702
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
703 Terms
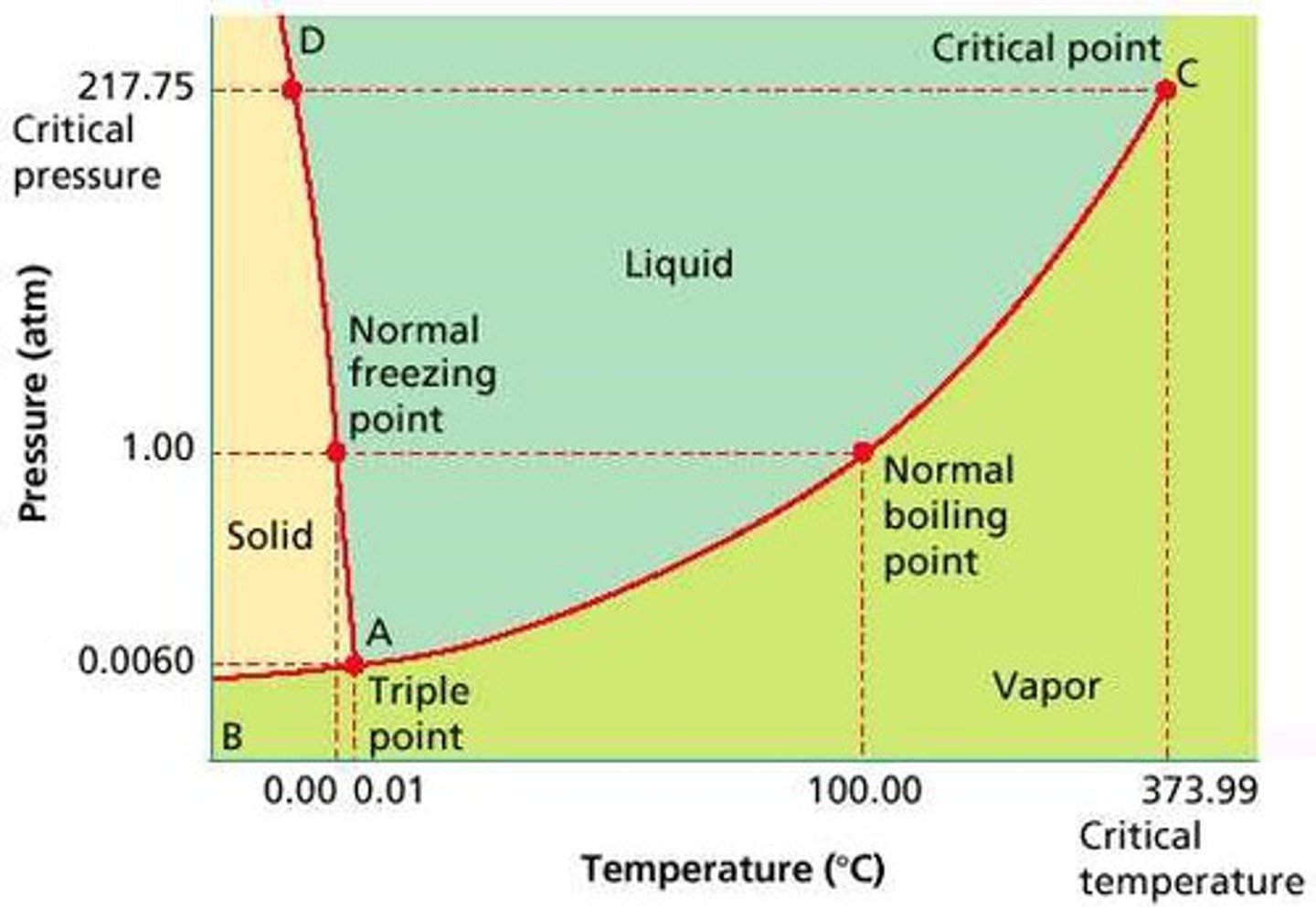
Phase Diagram
a graph showing the conditions at which a substance exists as a solid, liquid, or vapor
a line separates the regions that correspond to the solid and liquid phases. For most substances, since the solid phase is denser than the liquid, this line has a positive slope. This indicates that it is possible to convert the liquid substance into solid by increasing pressure. Since the opposite is true for water, however, the line between these regions has a negative - or downward-tilting - slope. This hallmark is one easy way to distinguish the phase diagram of water from that of most other compounds.
social facilitation
stronger responses on simple or well-learned tasks in the presence of others
bystander effect
the tendency for any given bystander to be less likely to give aid if other bystanders are present
bystander effect factors
individuals do not intervene to help victims when others are present
-less likely to notice danger in crowds
-take cues from others
-degree of responsibility is decreased
-cohesiveness of group
Deindividuation
when an individual seems to lose himself or herself in the group's identity
social loafing
the tendency for people in a group to exert less effort when pooling their efforts toward attaining a common goal than when individually accountable
group polarization
the enhancement of a group's prevailing inclinations through discussion within the group. doesn't have to be irrational.
normative social influence
behavior that is motivated by the desire to gain social acceptance and approval
informational social influence
influence resulting from one's willingness to accept others' opinions about reality
Groupthink
the mode of thinking that occurs when the desire for harmony in a decision-making group overrides a realistic appraisal of alternatives. leads to irrational decisions by a group.
characteristics of group think
invulnerability, rationalization, lack of introspection, stereotyping, pressure, lack of disagreement, self-deception, insularity
Irving Janis and groupthink
members of a group are so driven to reach unanimous decisions that they no longer truly evaluate the consequences of their decisions
occurs when the groups making decision are isolated and homogeneous, there is a lack of impartial leadership inside or outside the gorup, when there is a high level of pressure for a decision to be made
Conformity
when someone's behavior, beliefs, or thinking changes to line up with the perspective of others
compliance
when the person conforms but internally dissents
Conversion
genuine change in someone's beliefs
Asch Experiment
experimented how people would rather conform than state their own individual answer even though they know the group's answer is wrong, length of lines
compliance (requests)
responses to requests from someone with no power to enforce that request.
foot-in-the-door technique
asking for a small commitment and, after gaining compliance, asking for a bigger commitment
door-in-the-face technique
asking for a large commitment and being refused and then asking for a smaller commitment
low-ball technique
persuasive technique in which the seller of a product starts by quoting a low sales price and then mentions all of the add-on costs once the customer has agreed to purchase the product
obidience
changing one's behavior at the command of an authority figure
Milgram Experiment
an experiment devised in 1961 by Stanley Milgram, a psychologist at Yale University, to see how far ordinary people would go to obey a scientific authority figure with giving electric shocks
Stanford Prison Experiment (Zimbardo)
classic "experiment" where individuals were assigned to be guards / prisoners. w/in days they took on their roles and went too far. Highly unethical
social norms
rules, spoken or unspoken, that regulate behavior, beliefs, attitudes, and values of members of society
social control
the way norms are taught, enforced, and perpetuated
deviance
when someone doesn't follow a norm
formal vs informal norms
Formal:
-generally written down, like laws
-precisely defined, publicly presented and have strict penalties for violators
informal: generally understood but less precise and carry no specific punishment
Folkways
insignificant informal norms that involve small details, violating them does not cause too much of a problem, example: fashion, wearing socks with sandals
mores
informal norms, which incur severe disapproval when violated. ex: cheating on romantic partner
taboos
even more restrictive norms that generate extreme disapproval. Ex: cannabalism, incest. Driven by culture. Some are forbidden by law and some aren't.
Anomie
Refers to situation where there is a poor match between society's stated norms and the norms that an individual responds to
sanctions
punishment or negative consequences for violating a social norm. Rewards for following social norm.
adding a solute to water will ----- bp and ----- mp,
increase; lower
differential association theory
theory that individuals learn deviance in proportion to number of deviant acts they are exposed to, and deviance is learned socially, draws from symbolic interactionism
labeling approach
focuses on how behavior is affected by being labeled as a deviant.
Primary Deviance (Labeling Theory)
the initial act or attitude that causes one to be labeled deviant
secondary deviance (labeling theory)
subsequent acts of rule breaking that occur after primary deviance and as a result of your new, deviant label, the stigma attached to it and people's expectations of you
strain theory
focuses on the role of social and economic pressures towards deviance. Says that some people would commit crime under straining conditions.
Socialization
how we learn informal and formal norms by interacting with other people and insitutions
agents of socialization
family, education system, mass media, peers, workplace
Fads
a new behavior that suddenly becomes extremely popular, then fades
mass hysteria
irrational fear of a perceived threat, verging on the point of a collective delusion
riots
characterized by large # of people who engage in dangerous behavior, such as vandalism, violence, or other crimes. Deindividation, loss of self identity, occurs. Often violent and targeted against an established institution or authority figure.
peer pressure
influence from members of one's peer group.
Anaerobic
Process that does not require oxygen
Halophiles
"salt-loving" archaea that live in environments that have very high salt concentrations
What to the numbers on the bottom of the Element on MCAT Periodic table mean?
the molar mass of the element in grams/mol
How many grams are in a kilogram?
1000
What is molarity?
mol/L
A mole
a number of items equal to Avogadro's number (6.02 × 1023)
a 1 M solution of glucose contains
6.02 × 1023 molecules of glucose in each liter of solution.
millimolar (mM)
10^-3 M
micromolar (µM)
10^-6 M
nanomolar (nM)
10^-9 M
If a person drank a large quantity of hypersaline ocean water, the person could die because absorption of salt into the blood will cause it to become:
hypertonic compared with the cytosol of the body's cells, causing osmosis of water out of the cells.
Does NaCl readily diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer? What does and why?
No, but water does, through osmosis which establishes isotonic solution on both side of the membrane
simple diffusion
movement of a solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
what molecules can simply diffuse across the cell membrane?
small or nonpolar, examples including gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide. Water is small enough to some extent such as when water can diffuse through the membrane but other solutes cannot
Aquaporins
A transport protein in the plasma membrane of a plant or animal cell that specifically facilitates the diffusion of water across the membrane
What organ has a lot of aquaporins?
Kidneys, collecting ducts of nephrons
Hypertonic
when comparing two solutions, the solution with the greater concentration of solutes
A cell in a hypertonic solution will
shrink and lose water
a cell in a hypotonic solution
-Gains water, water travels from environment into cell
-Ruptures or lyse (hemolysis of red blood cells)
colligative properties
properties that depend on the concentration of solute particles but not on their identity
4 colligative properties of solutions
vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, osmotic pressure
vapor pressure
the pressure exerted by a vapor over a liquid
A higher vapor pressure indicates
that a larger number of solvent particles were able to escape the liquid and enter the gas phase
boiling point
-temperature at which the vapor pressure of a solution equals the atmospheric pressue
-The temperature at which a liquid changes to a gas
Water is an unusual substance in that the solid is less dense than the liquid at the freezing point, resulting in a solid form that floats on top of the liquid. Which of the following best explains this phenomenon?
the bent structure of the water molecule and ratio of covalently bonded hydrogens to lone pairs of e-'s on the oxygen atom maximizes the hydrogen bonding interactions that occur in the solid phase, producing a hexagonal structure with large empty spaces
what is the chemical formula for gypsym?
CaSO4 (Ca has 2+ charge, and SO4 has a 2- charge, so ratio has to be 1:1 to be neutral)
ionic compound
a compound composed of positive and negative ions but has no net charge overall
beta decay
-radioactive decay in which an electron is emitted (a neutron is converted to a proton and an electron is emitted)
-Mass Number stays the same and atomic number increases by 1
-faster than alpha particles and penetrate further, can pass through paper, but not an aluminum sheet. Negatively charged
gamma decay
radioactive decay by emission of a gamma ray, no change in mass number or atomic number
chiral
sp3 hybridized, attached to 4 different groups
formula for number of sterioisomers
2^n
chemical extractions
used to separate compounds based on different solubilities
Distillation
A process that separates the substances in a solution based on their boiling points
Recrystallization
Used to purify chemicals. By dissolving both impurities and a compound in an appropriate solvent, either the desired compound or impurities can be coaxed out of solution, leaving the other behind.
Chromatography
A technique that is used to separate the components of a mixture based on the tendency of each component to travel or be drawn across the surface of another material. Based on the affinity to the column.
Centrifugation
Separates components by density using high speed spinning. more dense particles travel to the bottom.
At the end of a distillation, the compound remaining in the original flask will be
the one with higher boiling point
boiling points of aldehyde
300 C
boiling points of carboxylic acids
170 C
Boiling points & melting pts of alkanes and alkenes
low
Due to hydrogen bonding, alcohols and carboxylic acids have ___ melting/boiling points than aldehydes and ketones and can function as organic weak ___.
higher; acids
A mass of 10 kg is dropped from a height of 20 m. Ignoring air resistance, what is the maximum speed it achieves?
What formulas would you use to solve this?
PE = mgh
KE = 1/2(m)v^2
A mass of 10 kg is dropped from a height of 20 m. Ignoring air resistance, what is the maximum speed it achieves?
PE = mgh
PE = 10kg 10 m/s^2 20 m
PE = 2000 kg/s^2 = 2000 J
KE = 1/2*10kg v^2 = 2000 J
v = sqrt(400) = 20 m/s
stereocenter
sp3, bonded to 4 different substituents
The preferred ion configuration of many elements on the periodic table is determined by:
the tendency of elements to gain or lose electrons until they have the same electron configuration as the nearest noble gas
equation for torque
τ = F∙d∙sin(θ)
-F is the force applied
-d is the distance that the force is applied from the fulcrum
-θ is the angle between the lever arm and the force that is applied
sin 90°
1
For an anterior force of 98 N and a torque of 13 Nm, what is the distance from which force was applied? Given force was applied perpendicular to rotation
T = r F sin(theta)
Perpendicular so theta = 90 degrees, sin theta = 1
13 Nm = r (98N) (1)
r = 13 Nm/98N
r = 0.133 m
or r = 133 mm
What unit is torque measured in?
Nm (Newtons * meters)
how many mm are in 1 meter?
1000
torque is caused by
force applied to a lever arm at a certain distance from an object capable of rotating, known as a fulcrum
three ways to increase the torque applied to an object
(1) increasing the force, (2) increasing the distance at which the force is applied from the fulcrum, and (3) adjusting the angle at which the force is applied to make it as close as possible to perpendicular to the lever arm.
velocity
distance/time (m/s)
If a 90-kg man undergoes a turning acceleration of 5 m/s2 during a running turn, what is the magnitude of force experienced by the foot due to the ground?
990 N
To turn while running, the foot must push off the ground, which applies a shearing force while simultaneously supporting the weight of the body.
We must account for the normal force exerted by the ground on the foot. This is a verticle force which occurs as a result of the runner's weight. We must also consider the acceleration force since direction is changing. This force is horizontal. These two force vectors are perpendicular and will form a right triangle.
Fnormal = mg = 90 kg(10) = 900 N
Fturning = 90(5) = 450
a^2 + b^2 = c^2
c = sqrt(900^2 + 450^2)
c = 90(10^2 + 5^2)^1/2
c = 90(125)^1/2
c = 90*11 = 990 N
equivalence point of a titration
on a graph, it is the point with vertical line
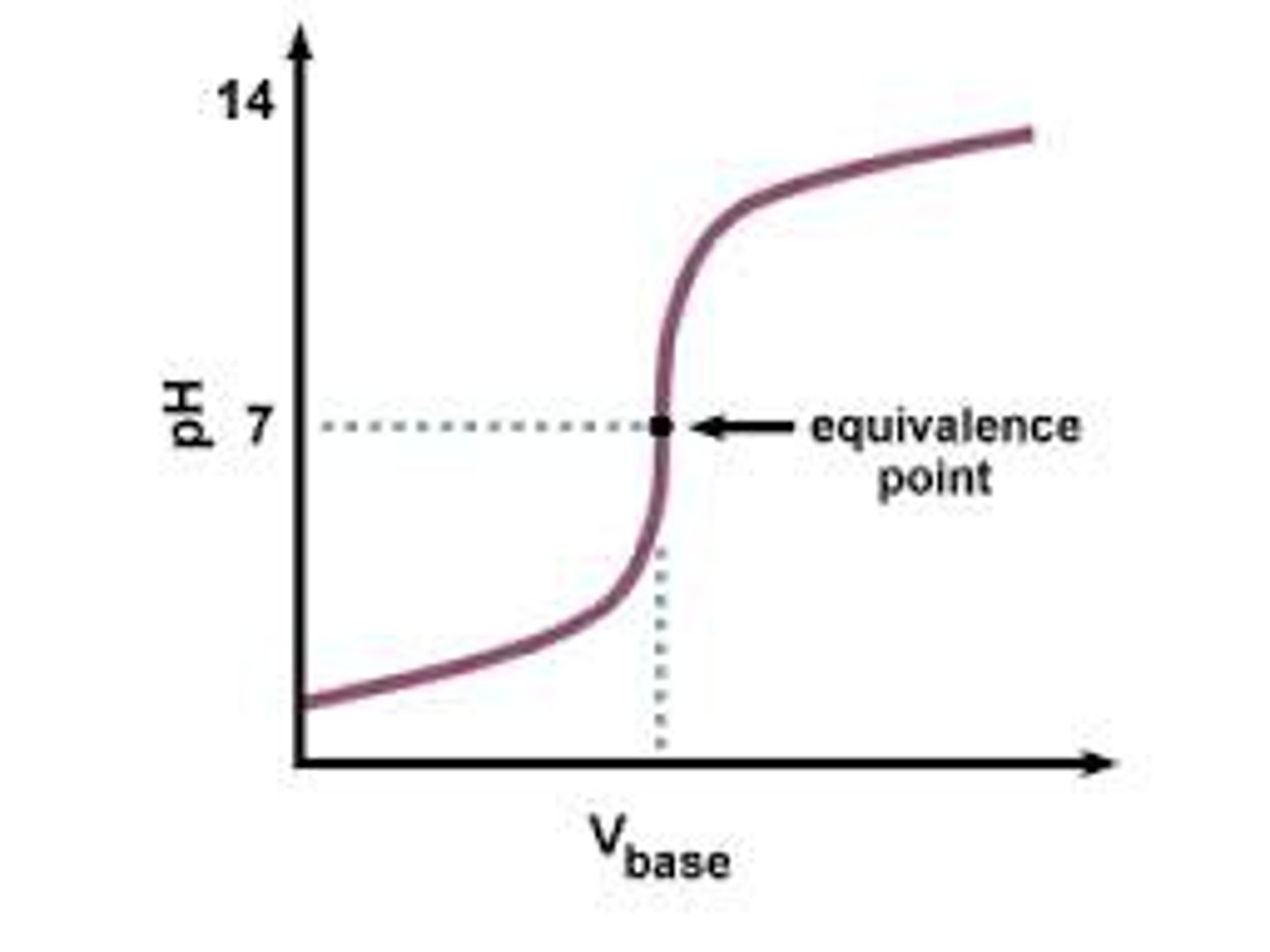
If the equivalence point of a titration with catopril is when 7.5 mL of 2*10^-2 M of NaOH is a added, How many moles of captopril were present in the original analyte solution tested?
# moles = M V = 210^-2 mol/liter 7.5mL /1000mL = 1.510^-4 mol NaOH
since this is equivalence point, the mols NaOH will equal mols Catopril, so answer is 1.510^-4 mol 1000 mmol/1mol = 0.15 mmol