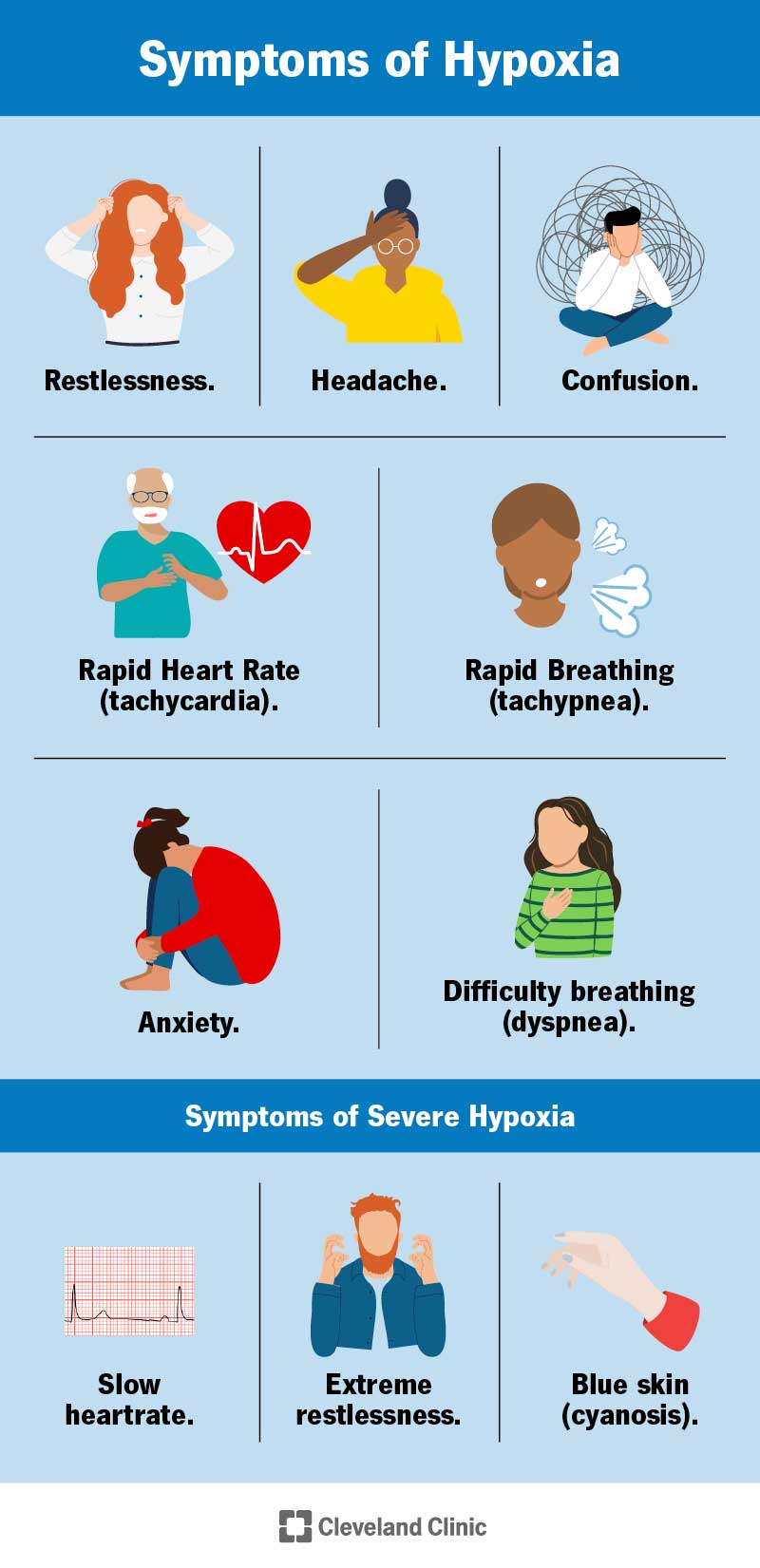
🥼 Chapter 13: Respiratory System & The Skin
1/158
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
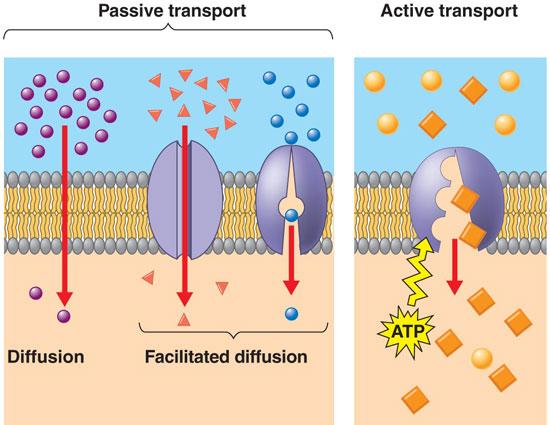
What diffusion do single-cell eukaryotes and simple multicellular organisms acquire oxygen through?
Define this term.
Simple diffusion. A process in which a substance moves through a semipermeable membrane without any help from transport proteins
What is ventilation? What zone is it a part of?
Movement of air into and out of lungs. It is the conduction zone

What is respiration? What zone is it a part of?
Gas exchange between lungs & blood + blood & tissues. It is called the respiratory zone

pH is regulated by the conversion of?
CO2 into carbonic acid into bicarbonate and H+ ions
What ion concentration measures the pH?
hydrogen ion
When CO2 increases, what occurs?
It leads to more carbonic acid and more H+ ions that decreases the pH. It causes the substance to be more acidic.
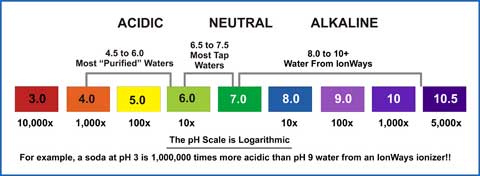
What is alkaline?
What is acidic?
What is neutral?
Alkaline solutions have a pH greater than 7 with more hydroxide ions than hydrogen ions
Acidic solutions have a pH less than 7 and have more hydrogen ions
Neutral solutions have a pH of 7 and a balance of hydrogen/hydroxide ions
What is hyperventilation? What does it cause?
Too much breathing, + O2 than CO2
Alkalization of blood — Respiratory alkalosis

What is hypoventilation? What does it cause?
Too little breathing, + CO2 than O2
Acidification of blood — Respiratory acidosis

What organ regulates pH over several hours to days? How does it do so?
Kidneys
They control bicarbonate and hydrogen ions in blood by excretion or retention of ions through urine production
Breathing results in heat loss. How does this occur and what is the term called?
Thermoregulation
Occurs through sweating — liquid water absorbs heat when in water vapor
Breathing through mouth as panting during exercise to increase heat loss
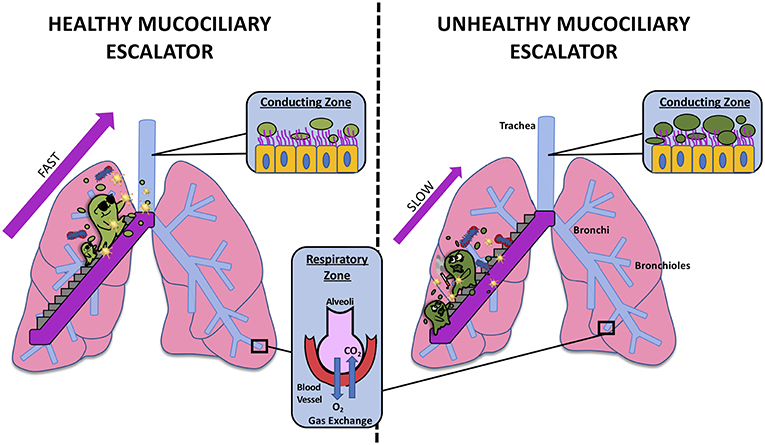
The respiratory system protects from diseases. How does it do this? Explain.
Mucociliary escalator: defense mechanism with layer of mucus and cilia that moves mucus with trapped particles upwards throat to be expelled
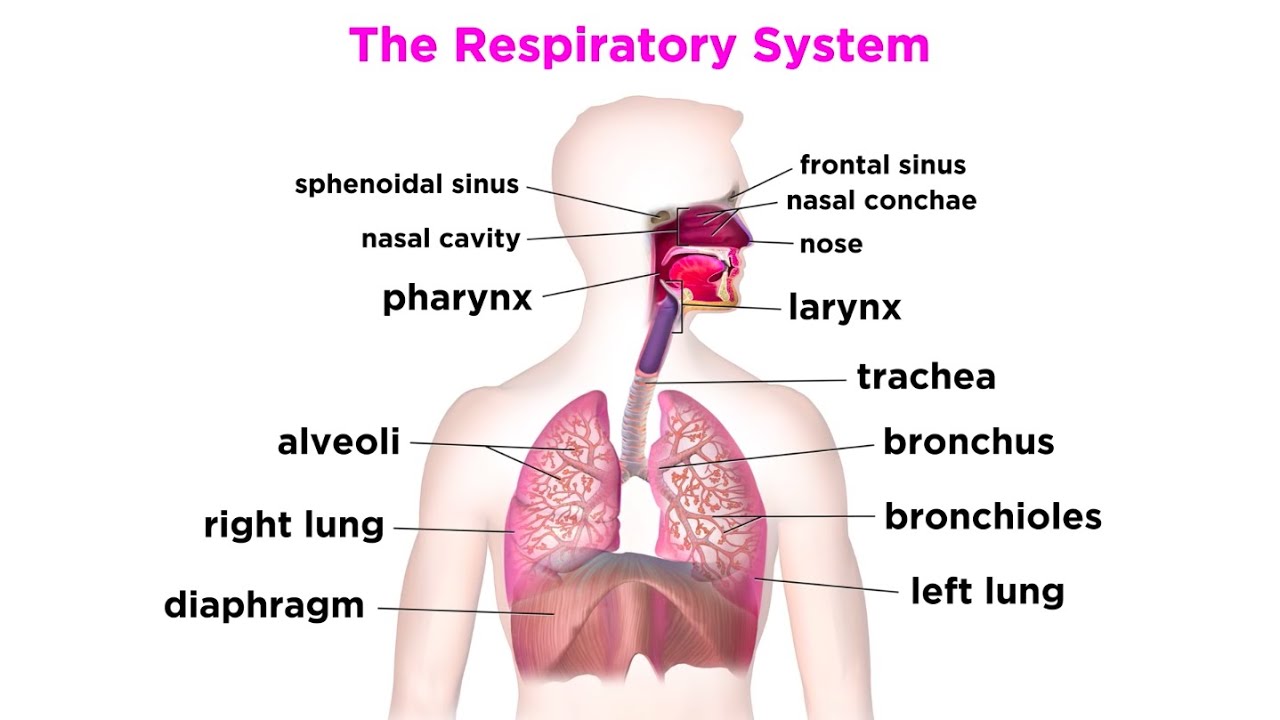
What is the pathway of air?
Nose
Nasal cavity
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
Terminal bronchioles
Respiratory bronchioles
Alveolar ducts
Alveoli
What is the pharynx?
Throat area
Separated for air and food

What is the larynx?
Has epiglottis
2 vocal cords
Made of skeletal muscle/cartilage (voluntary)

What happens to the epiglottis when you swallow?
It closes to prevent food and liquid from entering your lungs

What is the trachea?
Rings of cartilage to prevent collapse

The trachea is split into two _______. One for each lung
Bronchi
What cells line the trachea and bronchi?
Cilitated epithelial cells
Bronchi split into _______ that are made of _____ muscle to help ____________
bronchioles
smooth
adjust air flow
Why is smooth muscle beneficial to bronchioles and trachea?
It allows for voluntary and involuntary contractions
The conduction zone begins at the ______ and ends at the ______
nose
terminal bronchioles

Terminal bronchioles are the smallest branches where no ___ ___ occurs
gas exchange

State the anatomy that is part of the conduction zone
State the anatomy that is part of the respiratory zone
Conduction: trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, terminal bronchioles
Respiratory: respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs

What are alveoli ducts?
Lead to alveoli and made of them
Branches into respiratory bronchiole

What are alveoli?
Tiny sacs with thin walls in charge of gas exchange with blood
One cell thin except where capillaries are

Epithelial cells are _____ _____ cells that serve as a pathway for air. they are too thick for _______ _______
Tall columnar
Gas exchange

What are goblet cells?
Specialized cells that secrete sticky mucus to trap pathogens and particles
Located in the epithelial cells of the digestive and respiratory tract in the stomach, small intestine, trachea bronchi and larger bronchioles and are glandular simple columnar cells.

What does the upper tract have to remove pathogens? How does it do this?
Cilia that sweeps mucus through swallowing and coughing aka the mucocilliary escalator

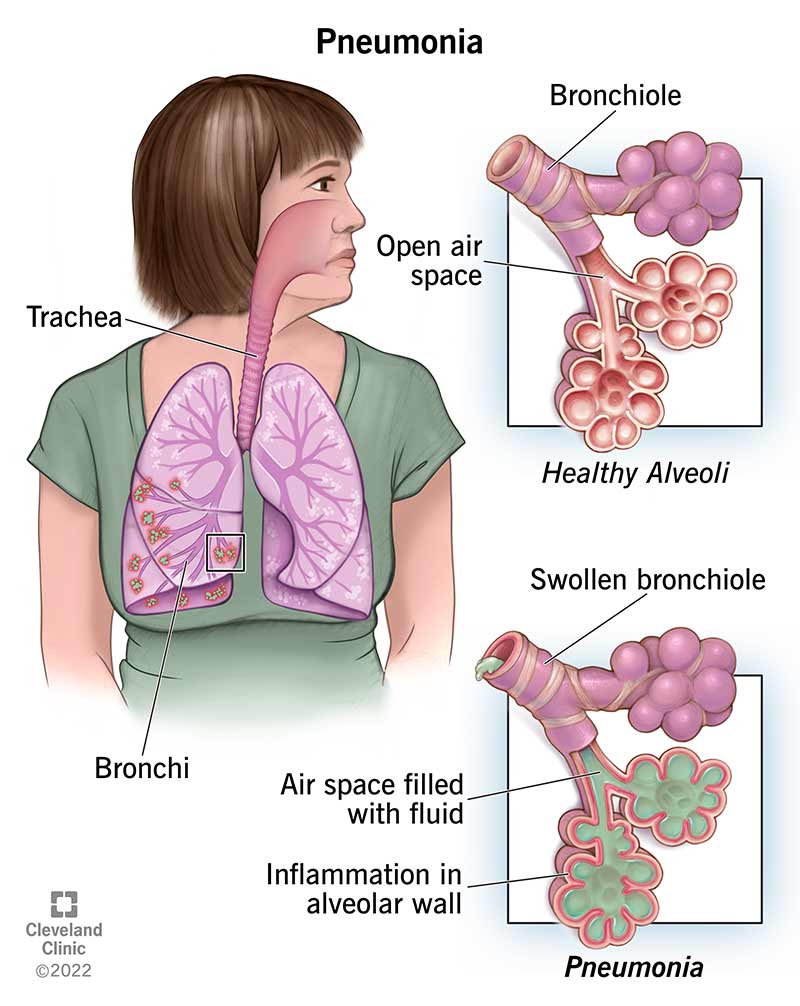
What is pneumonia? What are the symptoms?
Bacterial/viral infection of lungs that cause damage to epithelial cell lining of lungs and paralyzes the cilia — causes coughing and inability to clear lungs
Oxygen (O₂) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) must diffuse across epithelial cells to pass through the blood because epithelial cells form the barrier between the external environment and the bloodstream. Tall columnar cells are less ideal for rapid diffusion because
Their elongated shape makes a longer distance for gases to diffuse through, slowing the process down

Since the tall columnar cells are too thick for gas exchange, gas-exchanging surfaces are lined with _______ cells. Why?
Squamous epithelial cells. They are flatter and are simple with one layer of cells. Reduces distance for gases to diffuse and allow for exchange of gases

To protect the gas exchange surfaces without mucus, ________ patrol the alveoli
Alveolar macrophages
Vibrissae help
Filter air and trap matter
What is lysozyme?
Where are they located?
Nasal cavity/saliva
Attacks peptidoglycan cell walls of gram positive bacteria (staph/strep)
What are macrophages?
A type of white blood cell that surrounds and kills microorganisms, removes dead cells, and stimulates the action of other immune system cells
How do mucosal surfaces help the immune system?
Secretory IgA (sIgA) is a polymeric IgA that's found on the mucosal surfaces of the respiratory, intestinal, and reproductive tracts of humans and other mammals. sIgA has several functions that help prevent infection by stopping bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens from attaching to epithelial cells
What are mast cells?
Mast cells are immune cells that play a role in many physiological and pathological conditions.
They are found in connective tissues throughout the body and are part of the immune and neuroimmune systems.
Mast cells are best known for their role in allergies and anaphylaxis, but they also have many protective functions
Immune response: Mast cells help the immune system respond to bacteria and parasites, and control other types of immune responses. They contain receptors that recognize bacterial pathogens, and can release mediators to kill pathogens and promote bacterial clearance.
Wound healing: Mast cells are involved in wound healing and angiogenesis.
Vascular permeability: When activated, mast cells release histamine and other vasoactive mediators that increase vascular permeability and local blood flow. This can help expel mucosal parasites and increase mucus production in epithelial cells, which may help immobilize pathogens.
Venom detoxification
What is surfactant?
A soapy substance that coats alveoli and reduces surface tension, preventing collapse and facilitating efficient gas exchange.

What is surface tension?
Cohesive forces between molecules at the surface of a liquid, causing the surface to behave like a stretched elastic membrane

Why is surface tension relevant in the lungs?
Because it can cause alveoli to collapse, making it difficult to inflate them during inhalation and impairing gas exchange
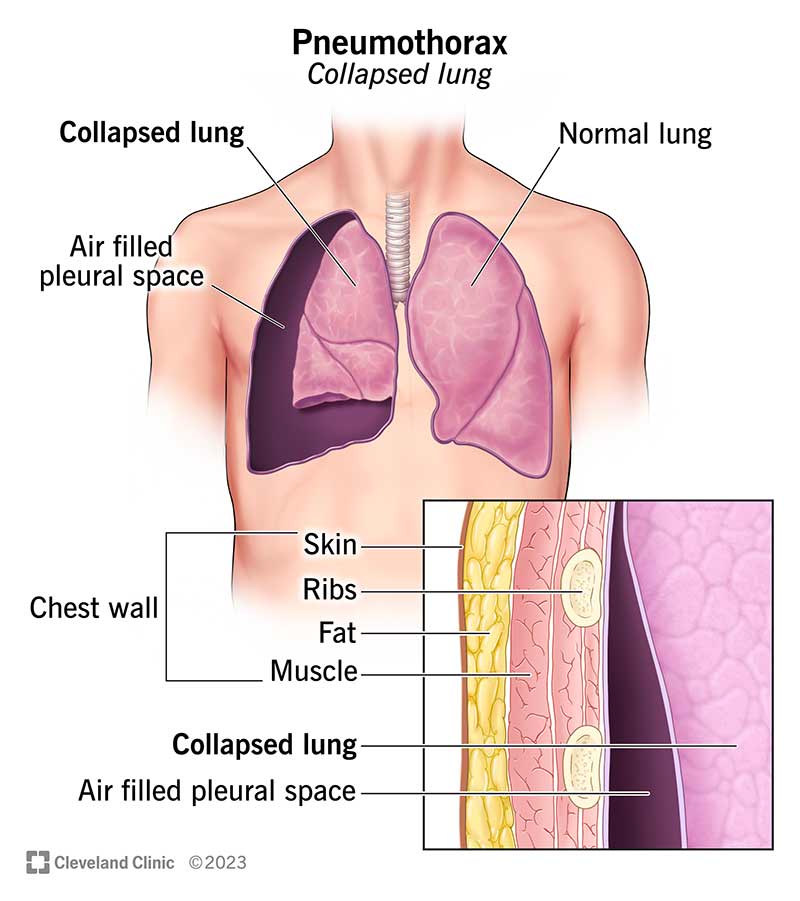
What is meant by a collapsed lung? What causes it?
Typically refers to a condition known as a pneumothorax, which can occur when one or more alveoli within the lung fail to inflate properly
Caused by:
obstruction
compression by buildup of air or fluid in pleural space
loss of surfactant
What is surfactant made of?
Lipids and proteins, phospholipids
Surfactant is secreted by specialized cells in the
Alveoli
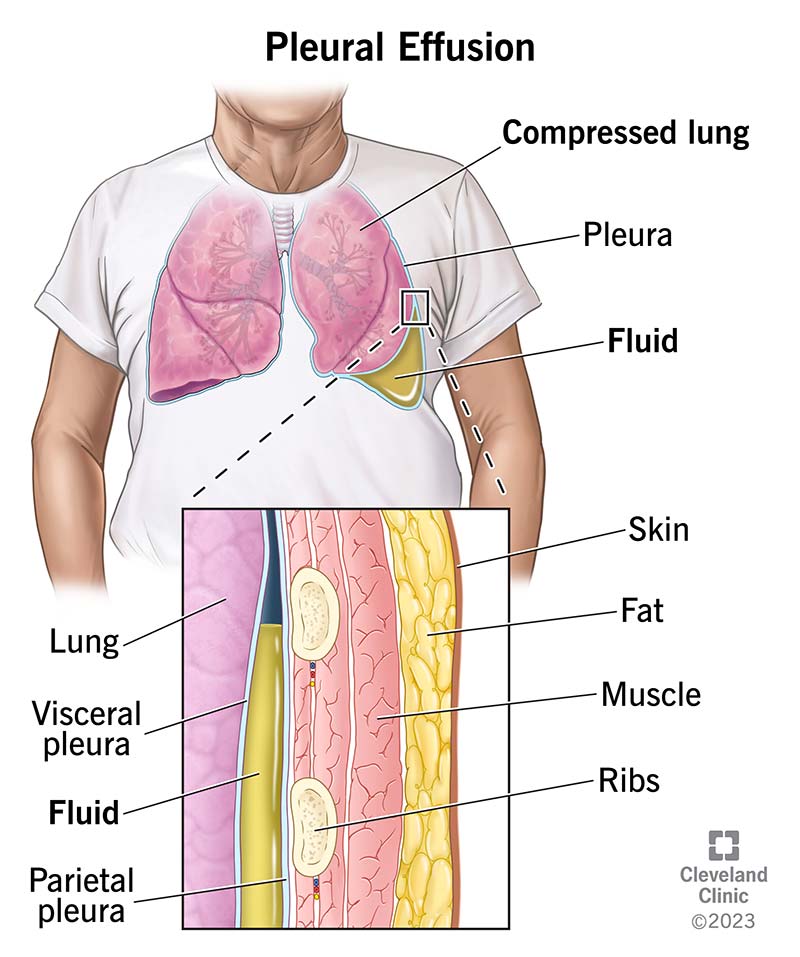
What is the pleural space? What is it composed of?
Membrane that surrounds the lungs composed of:
visceral pleura
pleural space
parietal pleura
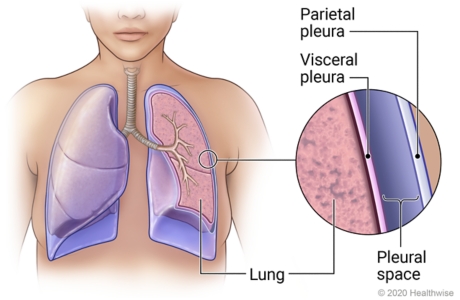
What is the pressure in the pleural space compared to atmospheric pressure?
The pressure in the pleural space is typically lower than atmospheric pressure

How does the lower pressure in the pleural space help keep the lungs expanded?
The lower pressure in the pleural space creates a negative pressure, which helps keep the lungs expanded by pulling them outward

What happens if fluid leaks into the pleural space?
It causes pleural effusion
It disrupts the negative pressure and can cause the lung to partially or completely collapse
During inspiration, what occurs to the lungs, diaphragm and muscles?
Lungs expand outward
Diaphragm contracts
External intercostal muscles contract
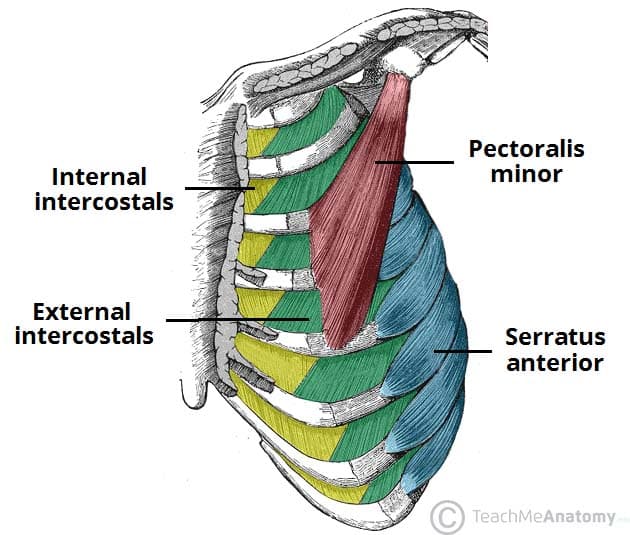
During FORCED expiration, what occurs to the lungs, diaphragm and muscles? What is forced expiration called?
Diaphragm relaxes
Internal intercostal muscles + abdominal muscles contract
Exertion
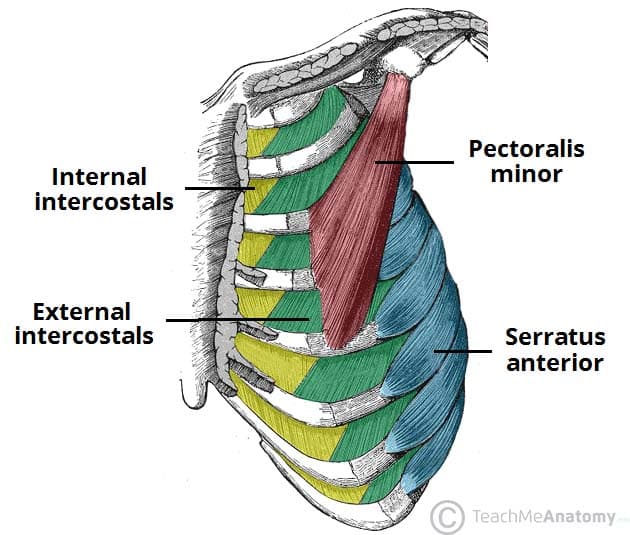
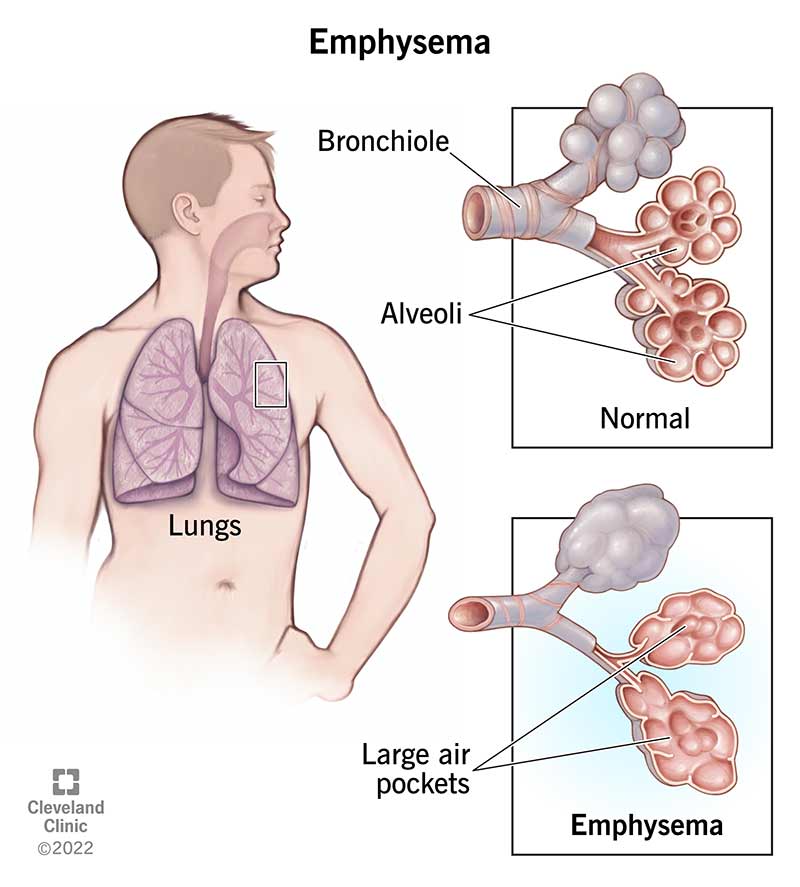
What is emphysema?
Disease in alveolar walls
Reduces elasticity = exhalation relies on this
Makes exhalation difficult
Usually effects of cigarettes
What is Boyle’s law?
increased volume = decreased pressure
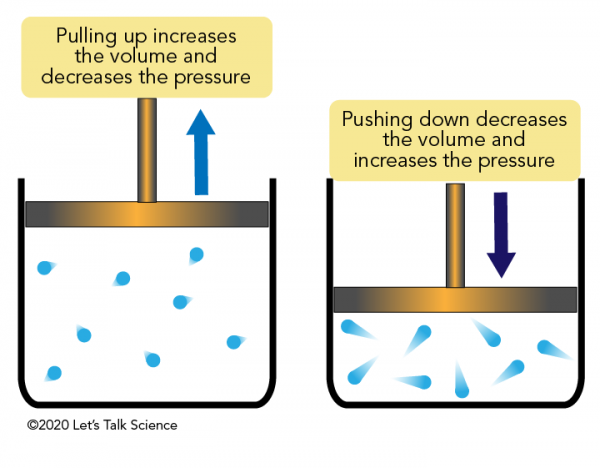
Expiration is usually a _____ process so no muscle contraction is needed
passive
Exertion is usually a _____ process
active
What is the shape of the diaphragm during rest vs contraction?
Rest: dome shaped, bulge upward
Contraction: flattens and pulls cavity downward

What is spirometry?
Measurement of air volume entering or exiting lungs during ventilation, calculated through a spirometer
What is tidal volume (TV)?
Amount of air that moves in and out of lungs during normal relaxed breathing

What is expiratory reserve volume (ERV)?
Extra amount of air you can forcefully exhale after you have exhaled normally

What is inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)?
Extra amount of air you can inhale after you have inhaled normally

What is functional residual capacity (FRC)?
The amount of air remaining in your lungs after a normal relaxed exhalation

What is the inspiratory capacity (IC)?
The maximum amount of air you can breathe in after a normal exhalation

what is residual volume (RV)?
The amount of air that remains in your lungs after you exhale as much as possible

What is vital capacity?
The maximum amount of air you can exhale after taking the deepest breath you can
Ex: If you take the deepest breath possible and then blow out all the air you can, the total air exhaled is your vital capacity

What is the total lung capacity (TLC)? How do you measure it?
The total amount of air your lungs can hold
Sum of vital capacity and residual volume
TLC = VC + RV aka all the air you can exhale after the deepest breath plus the air that remains in your lugs after exhalation

What is the purpose of pulmonary arteries?
Carry deoxygenated blood towards lungs away from heart
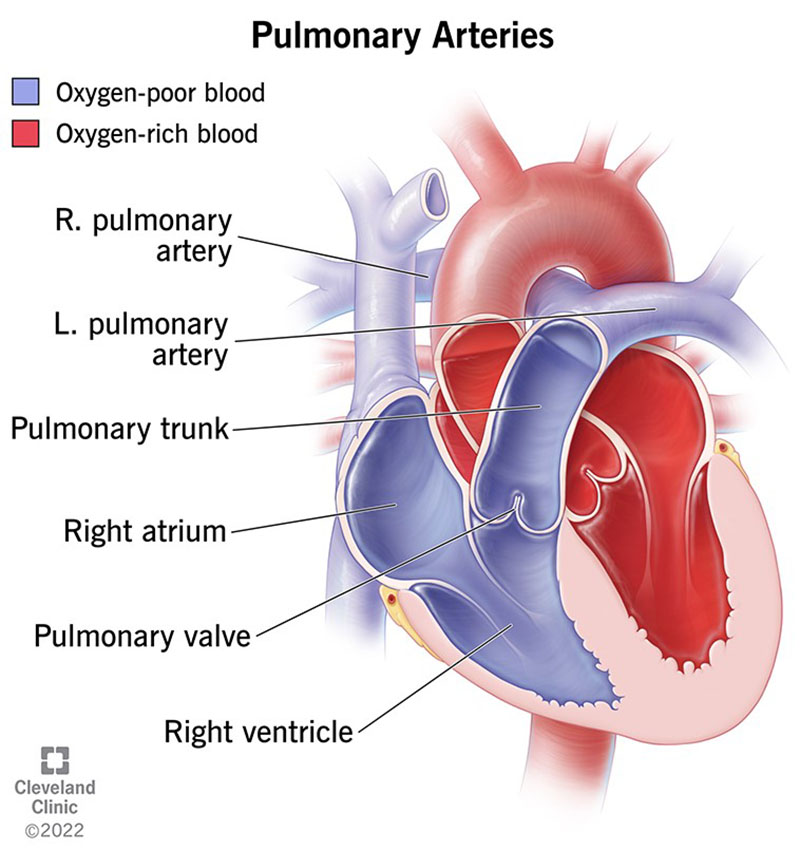
Pulmonary arteries have low levels of ____ and high levels of ____
O2
CO2
What surrounds the lungs and allows for passage of RBCs?
Capillaries
Capillaries drain into _____ that drain into ______
venules
veins
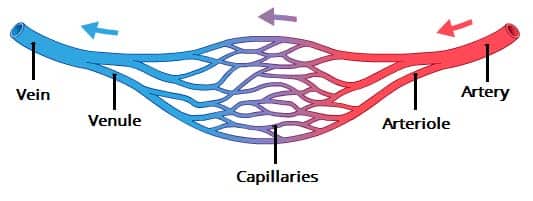
Why is the lymphatic system in the lungs so beneficial?
Aids removal of excess fluid from lungs
Maintains healthy pulmonary circulation
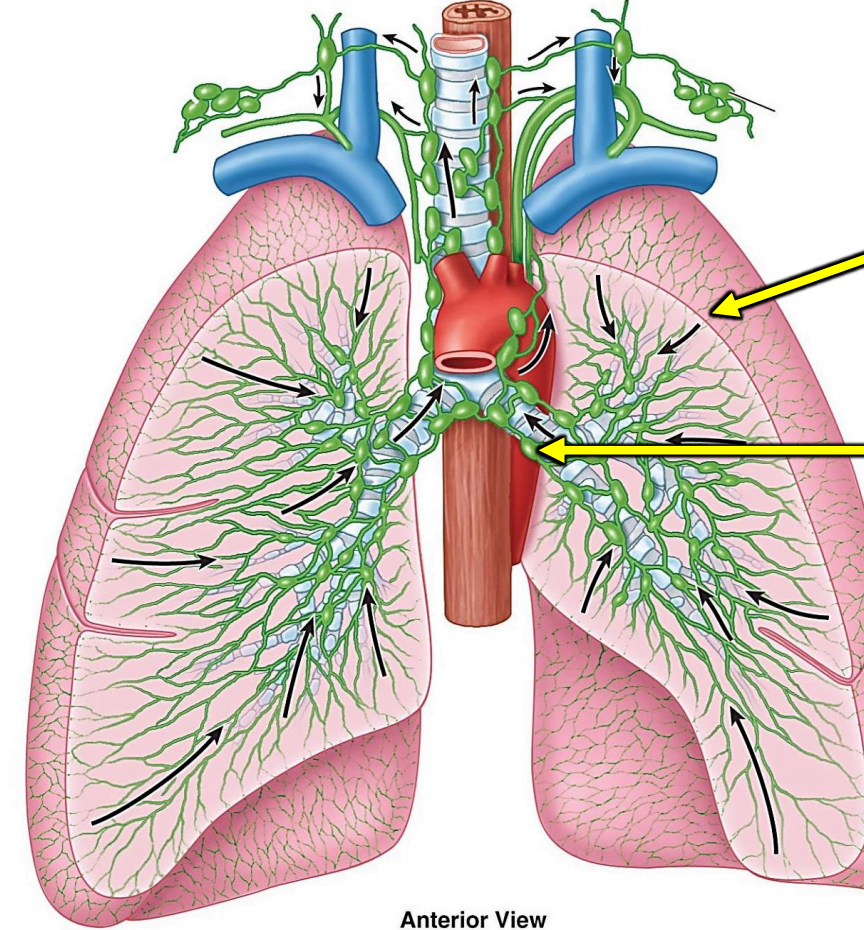
What is the condition name for fluid buildup in the lungs?
Pulmonary edema
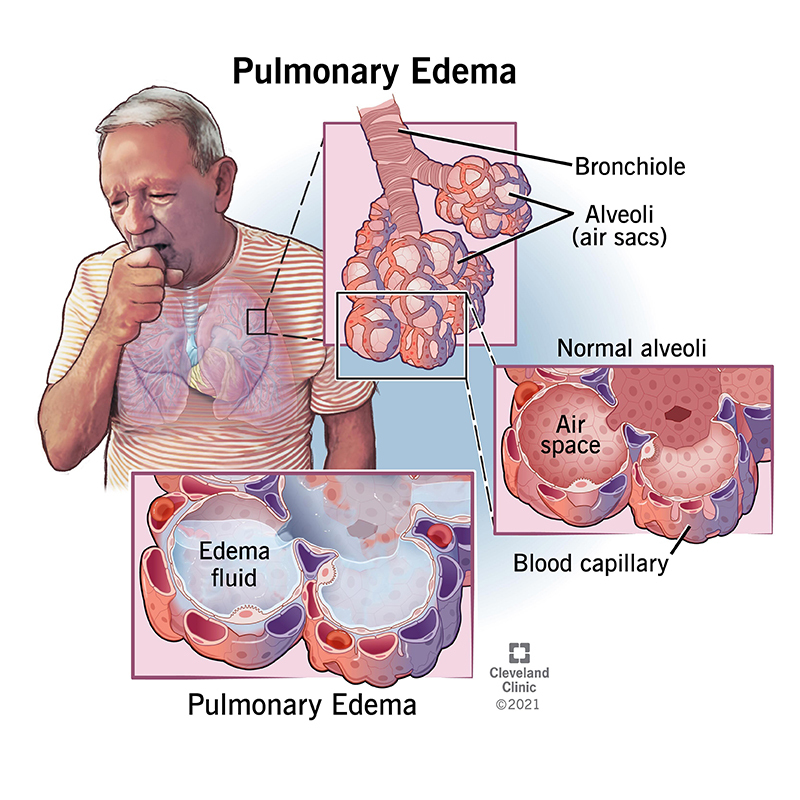
If pressure is too high, what occurs to the fluid?
It can leak into the lung tissue from the capillaries
What is hemoglobin? What is it made of?
Protein that acts as a oxygen carrier
Contains heme an iron containing molecule
Heme binds with globin protein
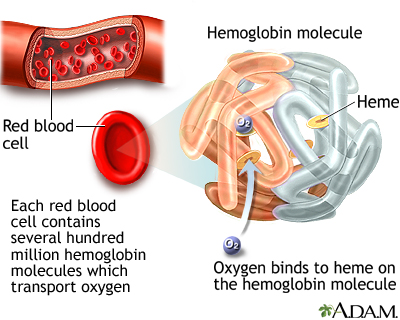
Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) has a _____ affinity for oxygen than adult hemoglobin. Why?
Higher
Fetuses need oxygen for their development to support growth/metabolism

What is an erythrocyte?
Red blood cell
What are the different ways CO2 is carried in the blood?
dissolved in plasma
bound to hemoglobin at different site than O2
as bicarbonate ions in RBCs that go into the plasma
What elements make up air?
Nitrogen 78%
Oxygen 21%
What is hypoxemia?
Low levels of oxygen in the blood
What is Henry’s law?
Amount of gas that gets into liquid depends on partial pressure of gas and how much gas is around
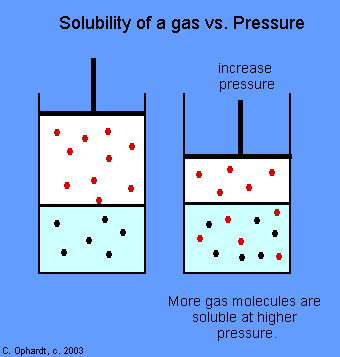
How does Henry’s law affect the lungs and breathing?
When you breathe in, your lungs fill with air and has a lot of oxygen
The oxygen from the air goes into your blood because it has a high concentration of oxygen in the air
The oxygen in your blood gets carried all over your body to your cells and carbon dioxide heads back to the lungs
Since there is more CO2 in your blood than in the air in the lungs, the CO2 moves from blood to your lungs
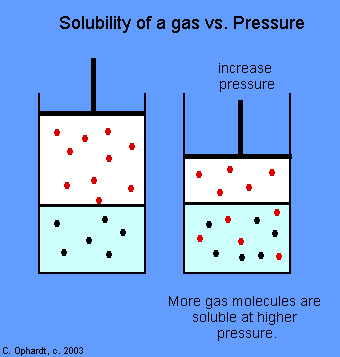
Amount of gas dissolved into a liquid depends on two things:
Partial pressure and solubility
Oxygen passes through 3 layers to get from alveoli to blood:
Alveolar epithelium
Interstitial liquid basement membrane
Capillary endothelium
Which part of the brain regulates involuntary breathing?
Medulla oblongata (brain stem)

___ and ___ are primary factors that influence breathing, ___ is secondary
CO2
pH
O2
Where/What are peripheral chemoreceptors found? Where do they send their signals?
Sensory cells in aorta and carotid arteries
Monitor levels of CO2, pH and O2
Send signals to medulla to adjust
![16) Locations of peripheral chemoreceptors [22]. | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/306097538/figure/fig12/AS:394992129462286@1471184870906/Fig-216-Locations-of-peripheral-chemoreceptors-22.png)
Where are central chemoreceptors found? What are they? What do they do?
Found in sensory cells in medulla oblongata of brainstem
They monitor levels of CO2 and pH in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
If CO2 increases due to hypoventilation or metabolic processes, sends message to brainstem to increase breathing rate — expels carbon dioxide and restore pH balance
What is hypercarbia?
Condition where there is abnormally high levels of carbon dioxide in the blood
what is the carbonic buffer system? Why is it important?
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 → H+ + HCO3-
Regulate pH of blood and ensure it remains in narrow range for physiological functions
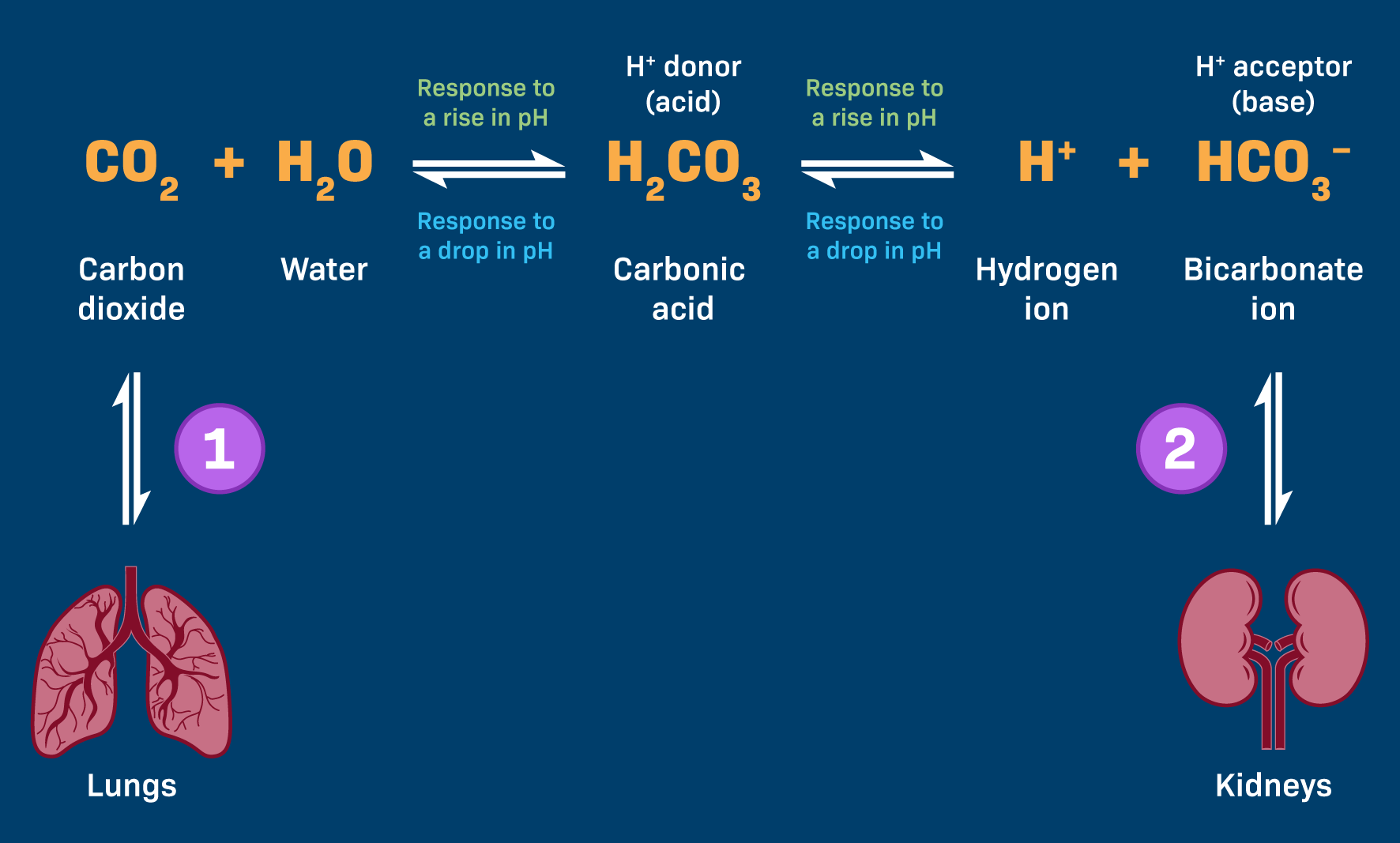
If blood pH increases, there is a _____ shift to the buffer equation as ______ of hydrogen ions
Left, reduction

If blood pH decreases, there is a _____ shift to the buffer equation as ______ of hydrogen ions
Right, increase

What is metabolic acidemia?
Too much acid/CO2 in blood

What is metabolic alkalemia?
Too little acid/CO2 in blood

Proper breathing regulation is crucial for maintaining ________
Homeostasis
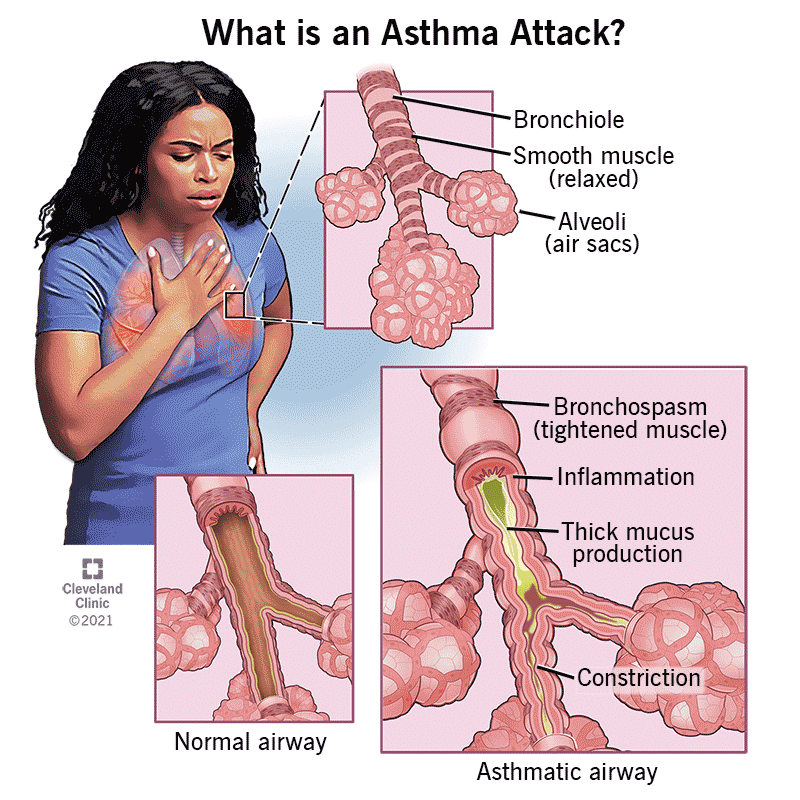
Asthma treatment often involves bronchodilators to alleviate symptoms caused by bronchoconstriction. What is asthma? What do bronchodilators do?
Asthma is the spasm/constriction of the airway smooth muscles
Medications used to expand and relax the airway muscles
What are the types of bronchodialators?
Beta 2 agonists: a class of drugs that relax smooth muscles by acting on the beta2 adrenergic receptor
They are commonly used to treat breathing conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).

What is bronchodialation? What neurotransmitter/hormone is involved?
Smooth muscle relaxation, increases ventilation
Mediated by epinephrine counteracts bronchoconstriction

What is bronchoconstriction? What neurotransmitter/hormone is involved?
Smooth muscle contraction in bronchi and bronchioles triggered by irritants
Regulated by parasympathetic nerves that release acetylcholine (ACh)
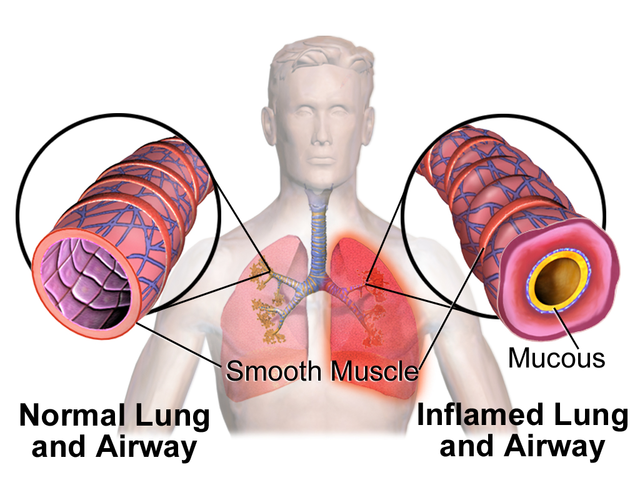
What are stretch receptors? What are irritant receptors?
Stretch receptors: inhibit inspiratory signals to prevent over inflation
Irritant receptors: trigger broncho-constriction to prevent irritants from entering
What is diabetic ketoacidosis?
A life-threatening complication of diabetes that occurs when the body doesn't have enough insulin to allow blood sugar into cells for energy. Instead, the liver breaks down fat for fuel, producing acids called ketones that can build up to dangerous levels in the blood.
what are the effects of hyperventilation?
Respiratory alkalosis
What’s the difference between acidosis vs alkalosis?
Acidosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal decrease in the pH level of the blood, making it more acidic
Alkalosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal increase in the pH level of the blood, making it more alkaline or basic