BIO 201 Exam 1
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Cytology
The study of large structures and features of the body visible to the naked eye, often referred to as macroscopic anatomy
histology
the study of microscopic structures and tissues of organisms
afferent
toward the control center
homeostasis
keeping stable internal environment
Normal rage
limits for condition allowing normal function
Set point
typical or optimal value in the normal range
negative feedback loop
a process that counteracts a change in a regulated variable, helping to maintain homeostasis within an organism.
stimulus
change in condition that is controlled and monitored
receptor
makes the measurements (could be organs, cells, proteins)
afferent signal
Carries measureent sto decision center
control center
compares stimulus signal to desired condition
efferent signal
Conveys decision from control center to responding unit
effector
NOUN; structure, a thing that reverses the change (NOT an action)
Response
VERB; the action of the effector reversing the stimulus
result
change in condition opposition of stimulus, consequence of effectors action
anatomical position
Standard reference for describing locations in the body
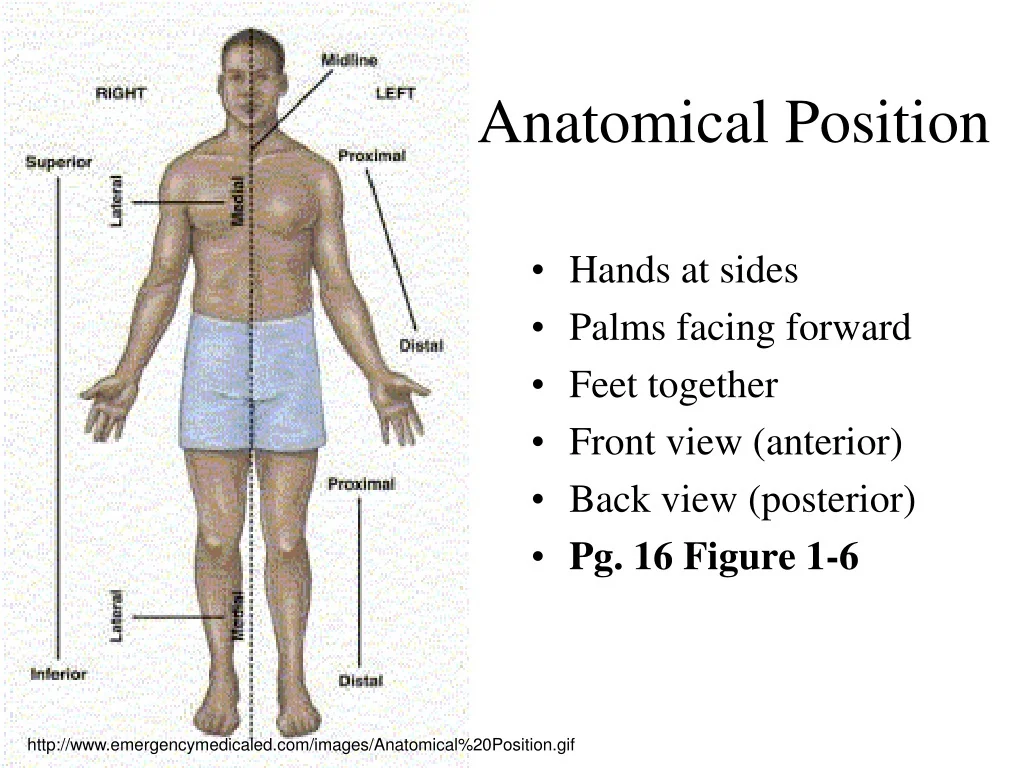
Superior/ cranial
Up, toward top, not for limbs
Inferior/caudal
down, toward groin, not for limbs
proximal
toward the origin of limbs
distal
away from origin of limbs
anterior/ventral
front, toward belly
posterior/dorsal
Back
medial
Toward he midline of the body
lateral
Away from midline
superficial
Near body surface
Deep
far from body surface (internal)
cross-section/transverse
divide top and bottom
frontal/coronal
divide front from back
saggital
divides right from left
midsagittal
Median plane (down the midline)
parasagittal
off center from median plane
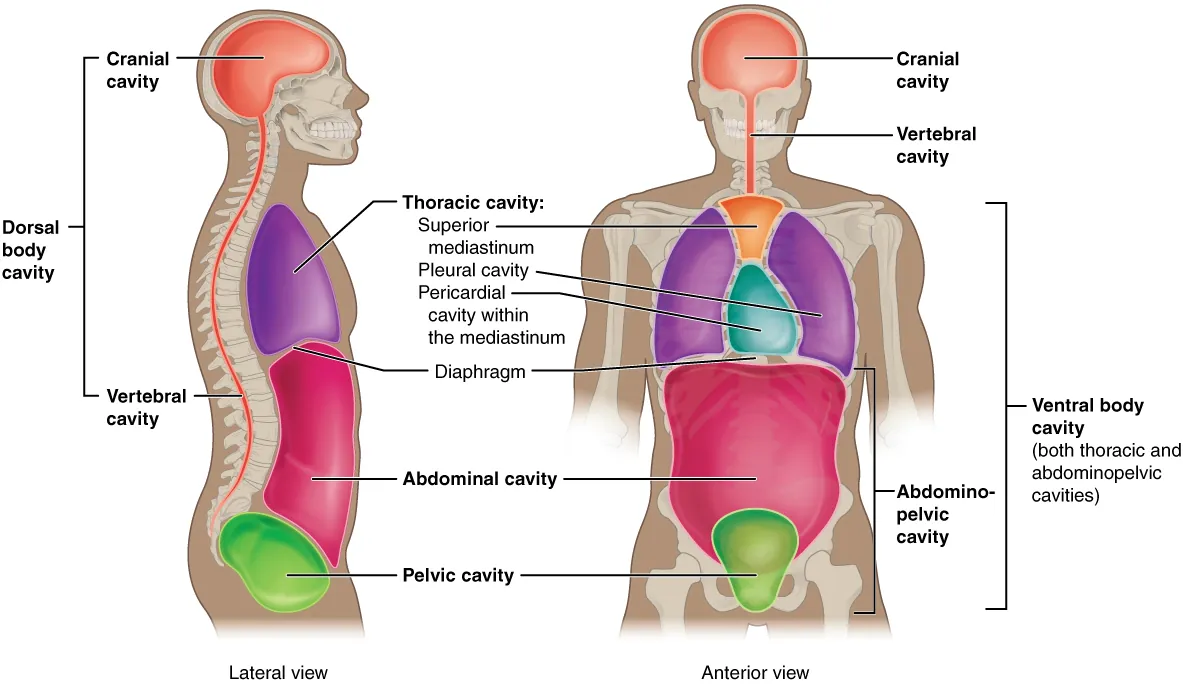
thoracic cavities
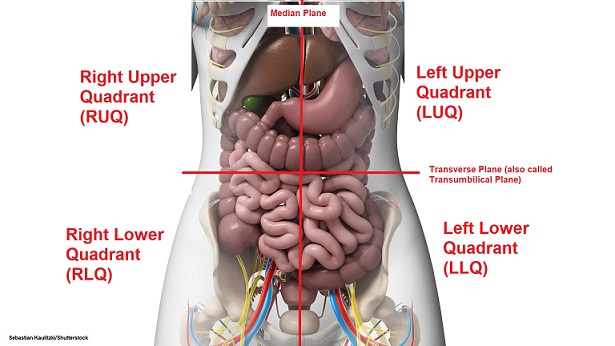
Abdominal quadrants
Abdominal regions
Apical
Top
basal
bottom
lateral
sides
avascular
without blood vessels
epithelia roles
protection, filtration, absorption, secretion
basement membrane
basal ECM fibers woven into a sheet; binds epithelium to CT below
squamous
Flat and thin
cuboidal
equally tall and wide
columnar
tallest
simple squamous
Location: air sacs of lungs and the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
Function: allows materials to pass through by diffusion and filtration and secretes lubricating substances
simple cuboidal
location: in ducts and secretory portions of small glands and in the kidney tubules
Function: secretes and absorbs
simple columnar
location: ciliated tissues are in larger bronchioles, uterine tubes and uterus; smooth are in the digestive tract, bladder
Function: absorbs; it also secrets mucus and enzymes
pseudostratified columnar
Location: ciliated tissue lines the bronchi, trachea, and much of the upper respiratory tract
Function: secrets mucus; ciliated tissue moves mucus
stratified squamous
Location: lines the vagina, esophagus, and mouth
Function: protects against absorption
Stratified cuboidal
location: sweat glands, salivary glands, and the mammary glands
Function: pierced against abraison
stratified columnar
Location: the male and female urethrae and the ducts of some glands
Function: secrets and protects
transitional
location: lines the bladder, urethra and the ureters
Function: allows the urinary organs to expand and stretch
exocrine
secrete onto body surfaces through ducts
endocrine
secrete hormones into blood
hormones
a chemical secreted by 1 tissue/organ into the blood to affect another tissue/organ
merocrine
cell remains intact
apocrine
secretes from top, cell cap pinches off
holocrine
the whole thing, cell bursts
collagen
flexible, tensile strength, unbranched, inelastic
elastic fibers
thin, wavy, branched, stretch & spring back
reticular fibers
thin, branched, delicate
proteoglycan
forms a gel
Mensenchymal cell
stem cell for many different CT cell types
fibroblast
Secretes glycoproteins and proteoglycans in fibrous tissue
adipocyte
stores fat for energy, padding, thermoregulation
white blood cells
manage inflammation and infection
Areolar tissue
unspecialized filler tissue with vessels and nerves
white adipose
Adipocytes, little ECM, lipid for ATP, padding
brown adipose
adipocytes, little ECM, lipid for creating heat
Reticular tissue
more reticular fibers, liver, and lymphoid
Regular CT
parallel fiber
irregular CT
has fibers, not parallel
chondrocytes
secrete ECM from inside lacunae
perichondrium
dense irregular fibrous CT capsule
Avascular
nutrients from perichondrium, slow healing
Hyaline cartilage
ribs, nose, joints, growth plates
fibrocartilage
more collagen, resists tears
Elastic cartilage
more elastin for recoil
periosteum
dense irregular fibrous CT capsule
Cancellous
deep, trabeculae with bone marrow between
plasma
h2o, nutrients, ions, wastes, proteins
Erythrocyte (RBC)
aculeate when mature, carry o2
platelet
call fragment that triggers clotting
leukocyte
Nucleated, inflammation, immunity
lymphatic vessels
Return excess tissue fluid to veins
lymph
fluid, solutes, WBCs, no RBCs or platelets
contractile
Cells gotten to move bones, face and organs
myofilaments
cytoskeleton filaments increase overlap to contract
Voluntary
Conscious and reflexive movements, body position
Multinucleate
Many peripheral nuclei
striated
myofilaments overlap gives microscopic bands
involuntary
No direct, conscious control
autorhythmic
contracts on its own with nervous system oversight only
mononucleate
Centra, single nucleus