Unit 5 AP Chemistry
1/27
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Zeroth order integrated rate law
[A]t-[A]0=-kt
A plot of [A]t vs. t produces a straight line for zero order reactions only(slope=-k)
![<p>[A]t-[A]0=-kt</p><p>A plot of [A]t vs. t produces a straight line for zero order reactions only(slope=-k)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ef3ba241-4aed-4805-9003-9f333341f169.jpg)
First Order Integrated Rate Law
Ln[A]t-ln[A]0=-kt
Ln[A]t vs. t produces a straight line(with a negative k slope) for first order reactions only.
![<p>Ln[A]t-ln[A]0=-kt</p><p>Ln[A]t vs. t produces a straight line(with a negative k slope) for first order reactions only.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b76ac646-a724-48d5-b8b4-63193a567a9b.jpg)
what order relates to the half-life being constant(same amount of time passes as the concentration of the reactant halves-independent of concentration)?
First order
Half-life equation for first order processes
T1/2=0.693/k
T1/2=half-life
This equation can be used for any half life problem, as these processes are always first order(radioactive decay processes).
Relationship between half life and k
Inversely proportional. If k is small, the half life is long(slow rate)
Second Order Integrated rate law
1/[A]t-1/[A]0=kt
A plot of 1/[A]t vs. t produces a straight line for second order reactions only. Has a positive linear slope of k.
![<p>1/[A]t-1/[A]0=kt</p><p>A plot of 1/[A]t vs. t produces a straight line for second order reactions only. Has a positive linear slope of k. </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ceac328a-c54b-405e-881b-672dddca8fb8.jpg)
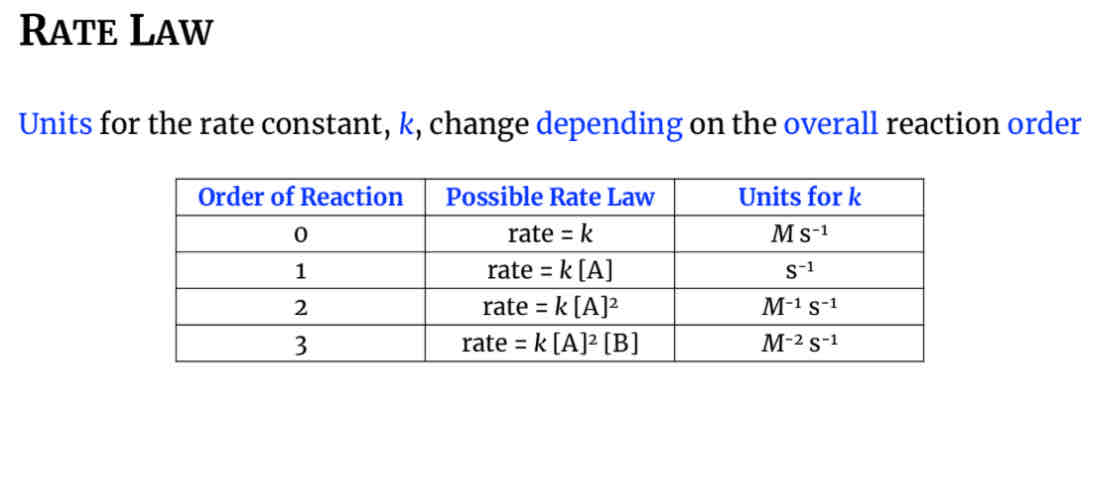
Units for zeroth rate law
M x s-1
First order rate law units
S-1
Second order rate law units
M-1 x s-1
Half life
The time it takes for the concentration of a reactant to halve.
Kinetics
The study of reaction rates(speeds)
How can the rate of a reaction be viewed? what do all reaction rates compare?
1.The rate of disappearance of a single reactant
2.The rate of appearance of a single product
3.The rate at which the overall reaction proceeds
All reaction rates compare the change in concentration over a unit of time.
Reaction rates of a single reactant
A—>B
Rate of disappearance of a single reactant. rates=-change in concentration of A/change in time.
Change in concentration is always final-initial so rates are ALWAYS POSITIVE VALUES!
Rate of Appearance of a single product
Rates=change in concentration of B/change in time. rates are always positive. These are average rates.
The rate at which one species appears or disappears…
Can be used to find the rates for other species
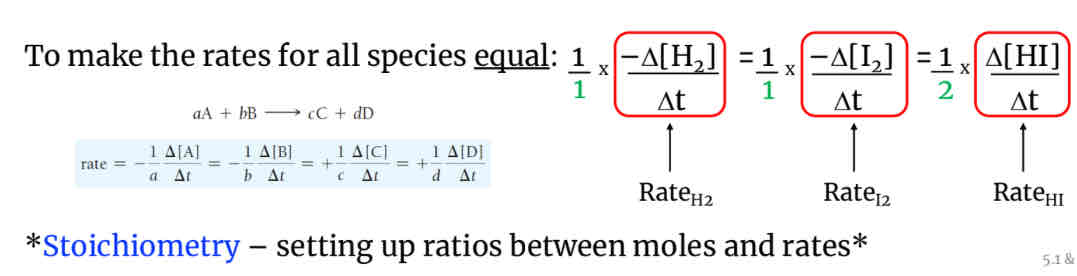
Ex: In H2 +I2–>2HI the rate of appearance of HI is twice the rate of disappearance of H2 or I2-proportional to moles(coefficients). To make the rates for all species equal:
1H2+1I2+1/2HI(1 is half of 2 so the rate for HI has to be 1/2)(make it half of a rate to get it to one(which is the rate of the reactants).
Graphs of concentration vs.time
Calculates instantaneous rates(rates at a particular instant)
-slope of the tangent for the products and the negative slope of the tangent for the reactants. Use rise/run formula.
rate=slope=change in concentration/change in time
Rate laws
Used to study the rate at which the overall reaction proceeds

Reaction orders
Indicate how the rate is affected by reactant concentration. Only found by analysis.
Zero Reaction Order
The rate of the reaction is not affected by the concentration of a species. (Anything raised to 0 is 1)(ex:2 times A^0 is always 1)
Rates stay the same.

First reaction order
Changes in the reaction rate are proportional to the changes in the concentration of a species. Anything to the first power is itself.

Second reaction order
Changes in the reaction rate are proportional to the square of the changes in the concentration of a species. Doubling A=reaction rate quadruples.

Overall order of reaction
The sum of the individual reaction orders(exponents) in the rate law
Units for the rate constant k depending on the overall reaction order
What must happen for a reaction to occur?
Particles must collide with each other with sufficient energy and at proper angles/orientation
When do reaction rates increase?
In the presence of a catalyst and when the rate of collisions increase
What are collision rates dependent on?
Upon the concentration and surface area of reactants(for processes higher than zero order) as well as temperature collision will result in a chemical reaction. Greater concentration=greater collisions but for systems in the same volume and temperature. Greater surface rea=smaller pieces of a material=more collisions bc the molecules have access to multiple pieces instead of one large one.
You can increase the concentration of gases by
Increasing the pressure which decreases the volume and increases the concentration of gases only. For solids and liquids you need to add more to have a greater concentration but for gases you can increase the pressure and have a higher concentration.
Collision rates and temperature
CR’s increase as the temp increases(increases average KE and average velocity of particles). Increased temp also means the value of the rate constant k will increase the rate for any rate law. B