1.0 protein binding lipoproteins
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Lipoproteins
are biochemical assemblies that transport hydrophobic molecules (e.g. lipids) in water dominant compartments such as blood plasma + extracellular fluids.
Lipoproteins are complex particles that have a central hydrophobic core of non-polar lipids,
primarily cholesteryl esters and triglycerides.
This hydrophobic core is surrounded by a hydrophilic membrane consisting of
phospholipids
free cholesterol,
apolipoproteins
Plasma lipoproteins, found in blood plasma, are typically divided into five main classes based on
size,
lipid composition,
apolipoprotein content
apolipoprotein
serum proteins that mediate carriage of cholesterol and other lipids in the serum
these 5 main classes are
High Density Lipoproteins (HDL),
Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL),
Intermediate Density Lipoproteins (IDL),
Very Low Density Lipoproteins (VLDL) and
Ultra Low Density Lipoproteins (ULDL).
Because lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, are insoluble in water these
lipids must be transported in association with proteins (lipoproteins) in the circulation.
Large quantities of fatty acids from meals must be transported as triglycerides
to avoid toxicity.
These lipoproteins play a key role in
the absorption and transport of dietary lipids by the small intestine,
in the transport of lipids from the liver to peripheral tissues,
and the transport of lipids from peripheral tissues to the liver and intestine (reverse cholesterol transport).
A secondary function is to transport toxic foreign hydrophobic and amphipathic compounds, such as
bacterial toxins,
from areas of invasion
and infection.
amphipathic
a molecule especially protein having both hydrophobic and hydrophobic parts
Within the peripheral vascular system, Chylomicron remnants, VLDL, IDL, and LDL are all pro-atherogenic
while HDL is anti-atherogenic.
pro-atherogenic
structures that cause cellular dysfunction in the vessel wall
these dysfunctions can include
chromic inflammation/abnormal cell growth
and procoagulant surface
cellular dysfunction ultimately lead to
stiffening or occlusion of the peripheral vascular system
Similarly to dietary lipids and toxic compounds,
drugs may rely on lipoproteins to transport through blood plasma,
these drugs will exist in bound (pharmacologically inactive) or unbound (pharmacologically active) forms in the peripheral vascular system
depending on their affinity to these plasma lipoproteins.
In cases where this interaction is reversible, a chemical equilibrium will exist between the bound and unbound states, with shifts in this equilibrium directly affecting therapeutic effects:
Lipoprotein + drug ⇌ Lipoprotein-drug complex
A drug's half-life is directly affected by the drugs affinity to lipoprotein binding and the shift in its equilibrium.
Bound drugs may act as a reservoir or depot, which from which the drug is slowly released as the unbound form
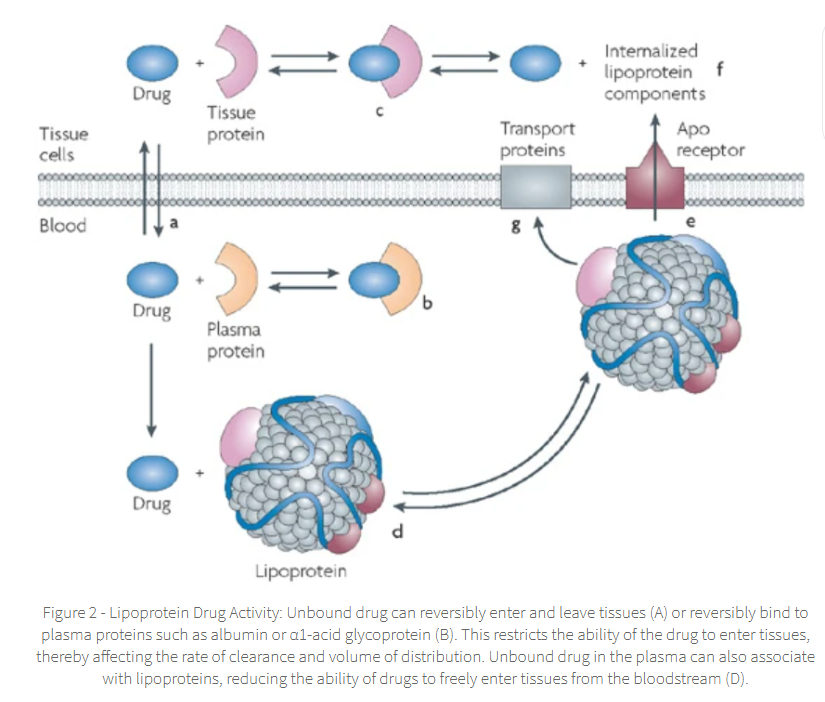
As the unbound form is metabolized and/or excreted from the body,
the bound fraction is released in order to maintain equilibrium, maintaining a constant therapeutic dose for longer periods of time.
Concomitant drug administration may influence the lipoprotein-drug equilibrium,
with one drug displacing another from their lipoprotein carriers.
Increased unbound fractions of a drug may result in increased observed therapeutic and side-effects
with a direct effect on patient outcome.
Also consider -
Drugs that can affect lipoprotein levels such as Fibrates (e.g. Fenofibrate and Bezafibrate) and Isotretinoin.