Topic 2- Motion and Forces
1/47
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Scalar Quantities
Distance
Speed
Mass
Energy
Vector Quantities
Displacement
Velocity
Acceleration
Force
Weight
Momentum
acceleration formula
acceleration = change in velocity over time (m/s2)
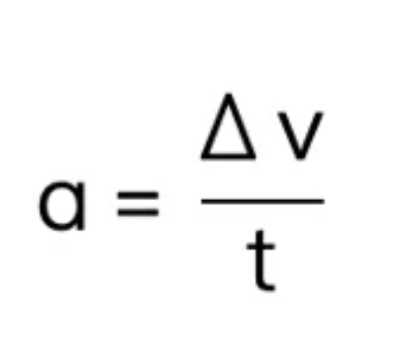
free fall (acceleration towards the earth in the absence of air resistance)
10 m/s2
typical acceleration of:
family car
falling object
rocket
formula 1 car
fighter jet
in m/s2
2-3
10
30
50
90-120
formula to use with constant accelerations (time taken not known)
v2 - u2 = 2ax
(x = distance travelled) (a = acceleration)
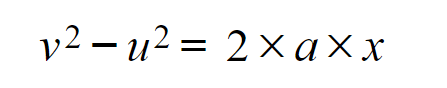
gradient of a velocity-time graph =
acceleration
area under a velocity-time graph
distance travelled
typical speeds of:
walking
running
cycling
car
passenger aeroplane
sound
in m/s:
1.5
3
6
10 to 30
200-250
330-340
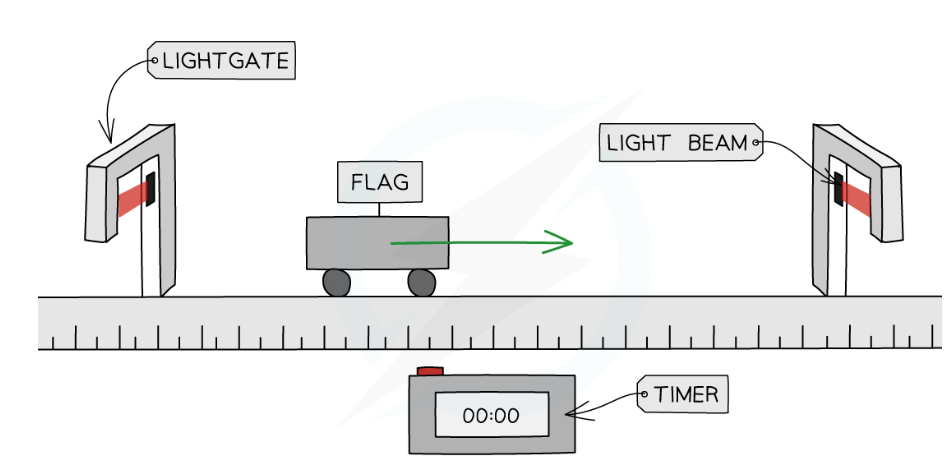
using 2 light gates to measure speed
gates are a set distance apart
timer starts when object passes through 1st light gate
timer stops when object passes through 2nd light gate
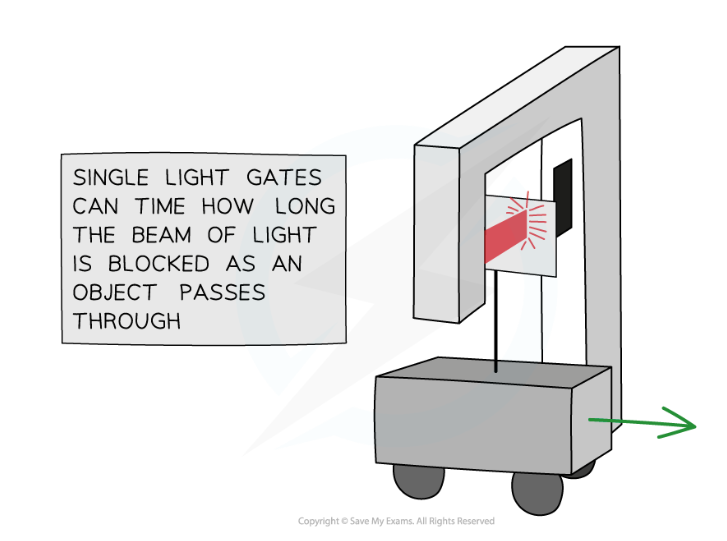
single light gates to measure speed
timer measures how long the light beam is blocked for
use the length of the marker as the distance
Newton’s First Law
Objects that are at rest will remain at rest, and objects that are moving will continue moving at a constant velocity, unless acted on by a resultant force

when the resultant force on a body is not zero
the speed and direction of the object can change
Newton’s Second Law
the acceleration of an object is proportional to the resultant force acting on it and inversely proportional to the object’s mass
the bigger the resultant force…
the larger the acceleration
the greater the object’s mass…
the smaller the acceleration
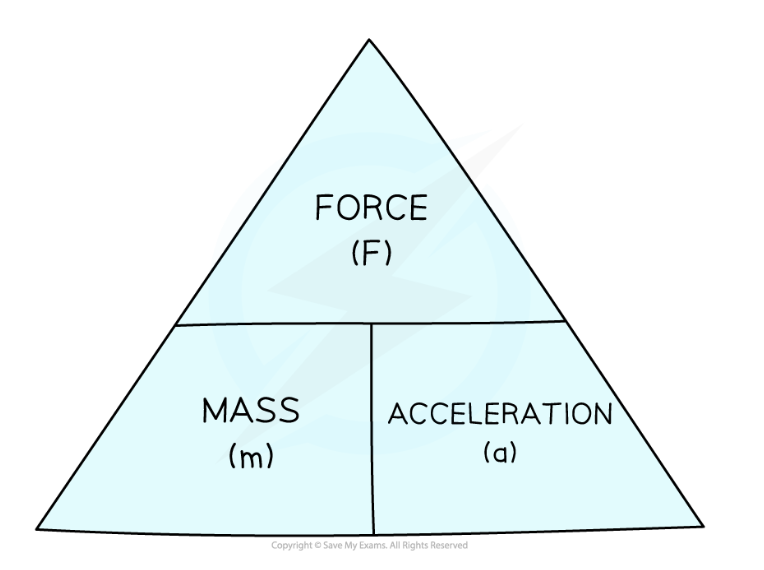
Newton’s Second Law FORMULA
f = ma
Newton’s Third Law
whenever 2 objects interact, the forces they exert on each other are equal and opposite
Difference between Newton’s first and third laws
Newtons 1st law: forces act on one object
Newton’s 3rd law: forces act on two objects
weight (not formula)
the force acting on an object due to gravitational attraction
how to measure weight directly
newtonmeter
how to measure weight indirectly
find mass, then multiply by g (~10)
circular motion:
constant speed?
constant velocity?
is there acceleration?
constant speed
changing direction, therefore changing velocity
acceleration is a vector therefore yes
when an object is moving in a circle, there must be acceleration. if there is acceleration, there must be a resultant force. What is this called?
centripetal force
centripetal force
the resultant perpendicular force towards the centre of the circle required to keep a body in uniform circular motion (can be any force keeping an object moving in a circle)
examples of centripetal force
tension
friction
gravitational
momentum formula
p = mv
p = momentum (kgm/s)
m = mass
v = velocity
what is momentum?
what keeps and object moving in the same direction
momentum changes if:
the object accelerates or decelerates
changes direction
changes mass
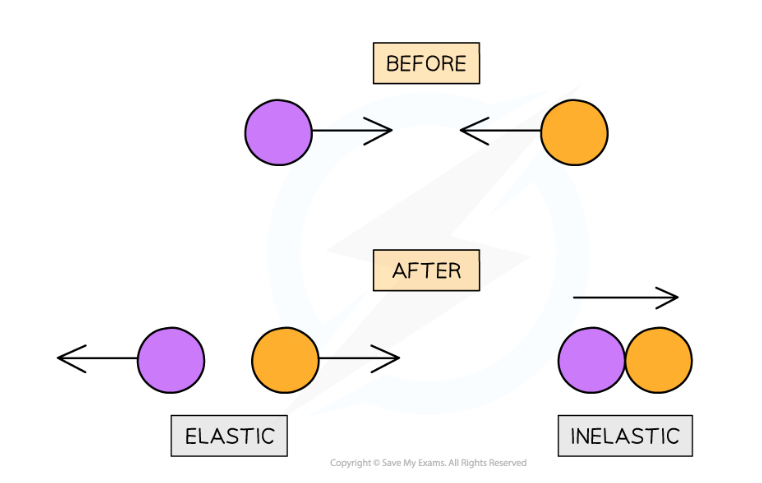
elastic collision (what happens to mass and velocity)
after a collision objects move in opposite directions
they have different velocities
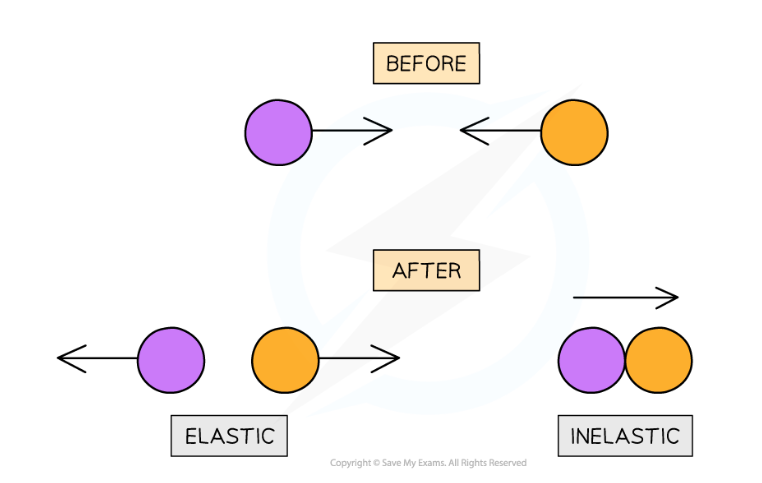
inelastic collision (what happens to mass and velocity)
after a collision objects move in the same direction
they have a combined mass and velocity
momentum is always ___ in a collision
conserved
to analyse a collision in an exam:
state velocity and direction of each object before and after
state inelastic/elastic
describe energy transfers
conservation of momentum
in a closed system, The total momentum before a collision = The total momentum after a collision
Newton’s 3rd law in collisions
when two objects collide, they exert force of each other (that is equal and opposite)
this means that one object will speed up and one object will slow down
therefore acceleration will be different
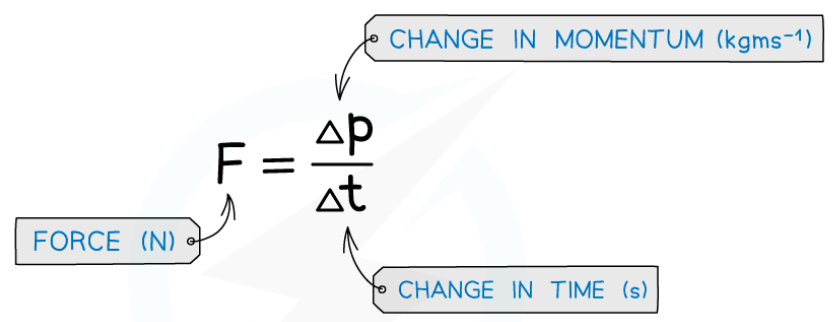
what is the formula relating force and change in momentum? (explain!)
Force = change in momentum / time
A force acting on an object makes it accelerate, so its momentum changes. The force is the rate of change in momentum.
what is inertia?
an object’s resistance to a change in motion (the tendency of an object to continue in its state of rest, or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force)
what is inertial mass?
how difficult it is to change the velocity of an object (the ratio between the force applied to it and the acceleration it experiences)
inertial mass formula
inertial mass = f/a
the inertial mass applied to an object is ____ to its acceleration as a result of a force
inversely proportional
dangers of large decelerations
overheating of brakes (due to friction)
loss of control causing collision and/or injury
how to measure reaction times
dropping ruler
typical reaction time for someone who is alert
0.2-0.9 seconds
factors affecting braking distance
speed
vehicle condition
road condition
vehicle mass
factors affecting thinking distance
tiredness
distractions
intoxication
reaction distance =
speed of car x drivers reaction time
for a given braking force, the stopping distance of a car depends on the…
speed of the vehicle
braking distance formula
breaking distance = (½ x mass x velocity2) / breaking force