Anatomy Practical 2 (Bones)
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
171 Terms
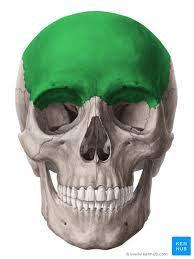
Frontal bone
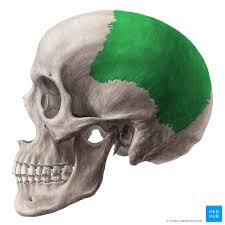
Parietal bone
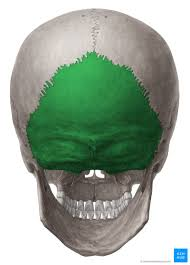
Occipital bone
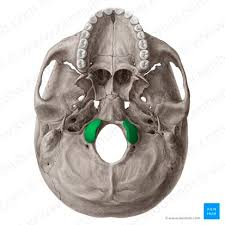
Occipital condyles
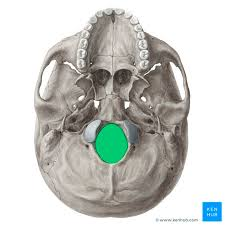
Foramen magnum
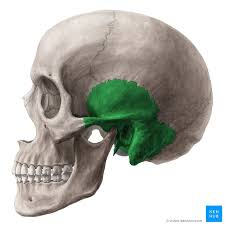
Temporal bone
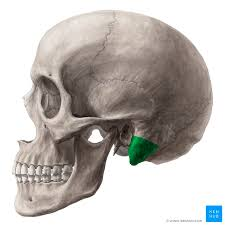
Mastoid process
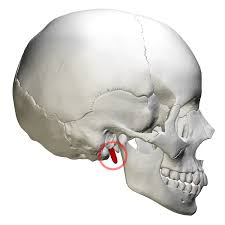
Styloid process
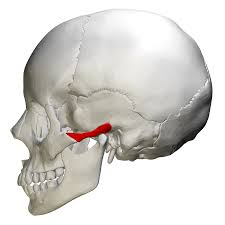
Zygomatic process
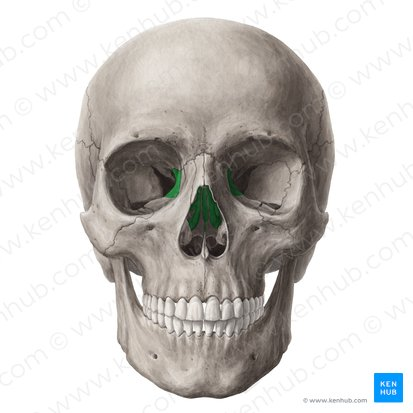
Ethmoid bone
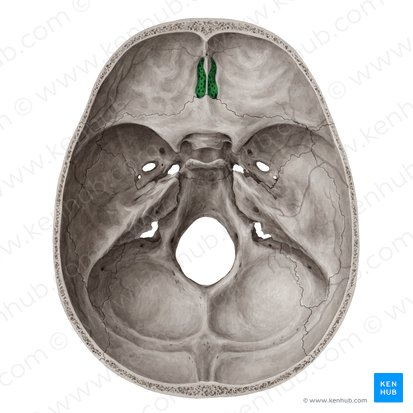
Cribriform plate
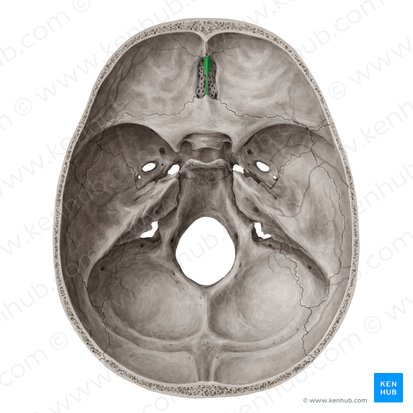
Crista galli
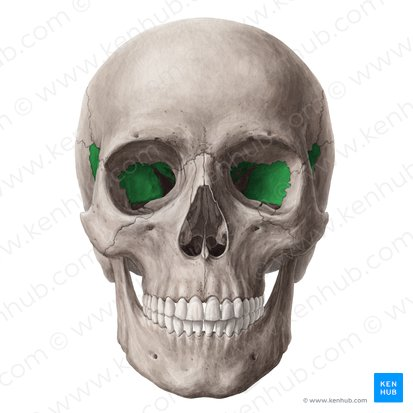
Sphenoid bone
Optic canal
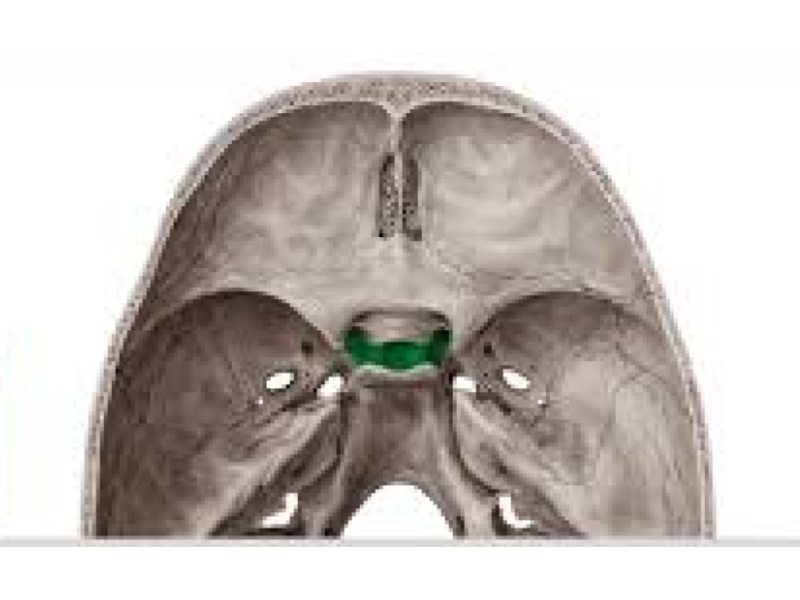
Sella turcica
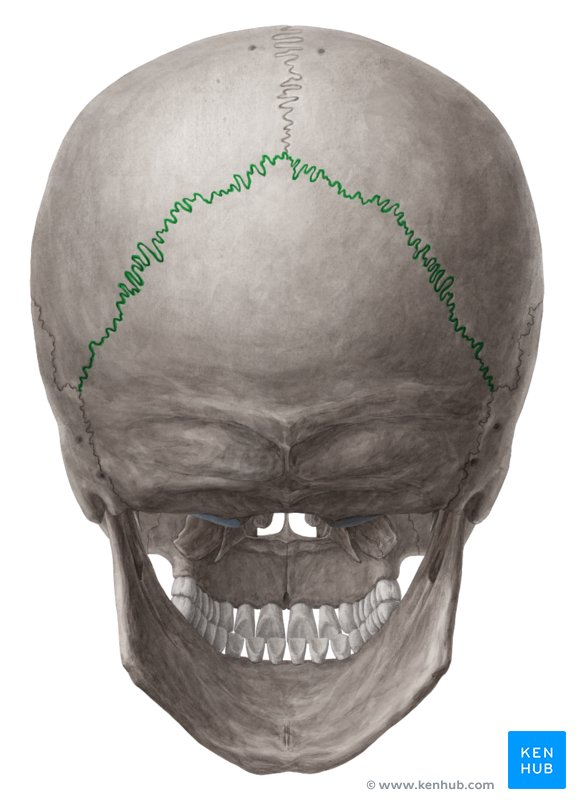
Lambdoid suture
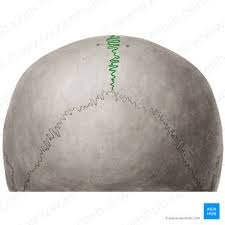
Sagittal suture
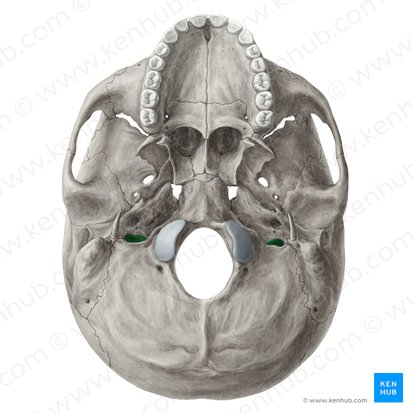
Jugular foramina
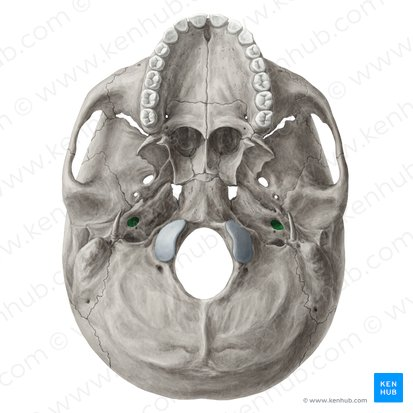
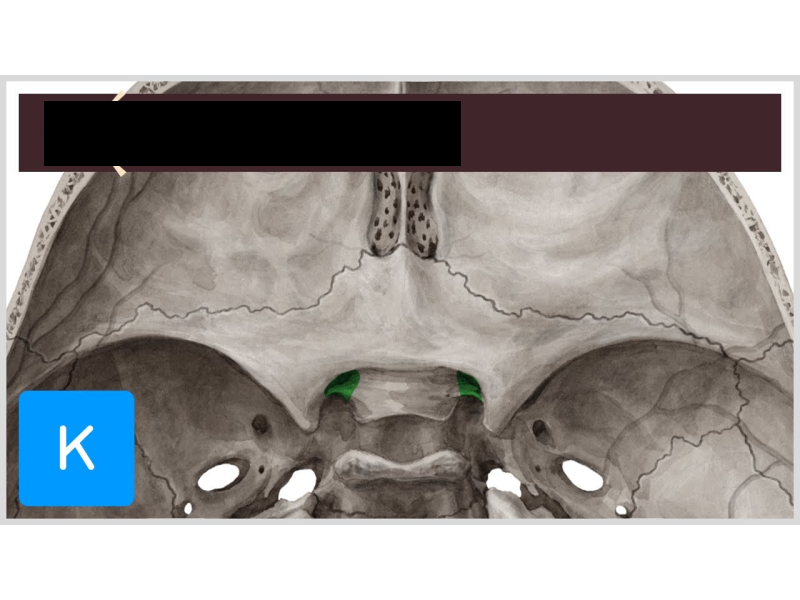
Carotid canals
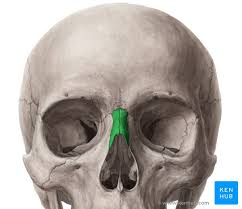
Nasal bones
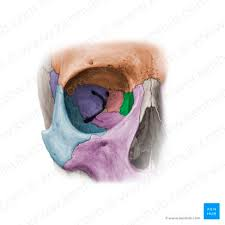
Lacrimal bones
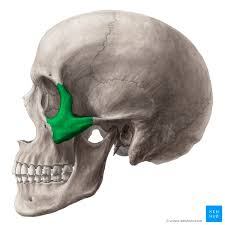
Zygomatic bone
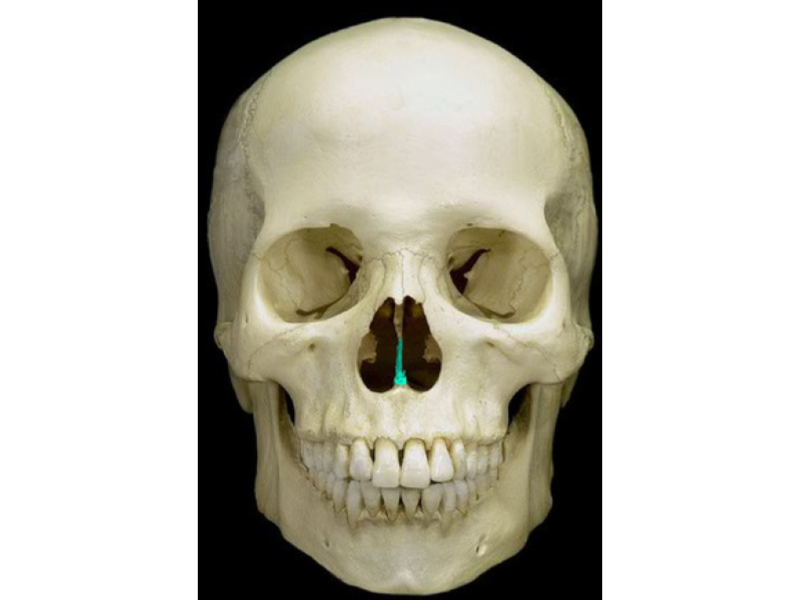
Vomer
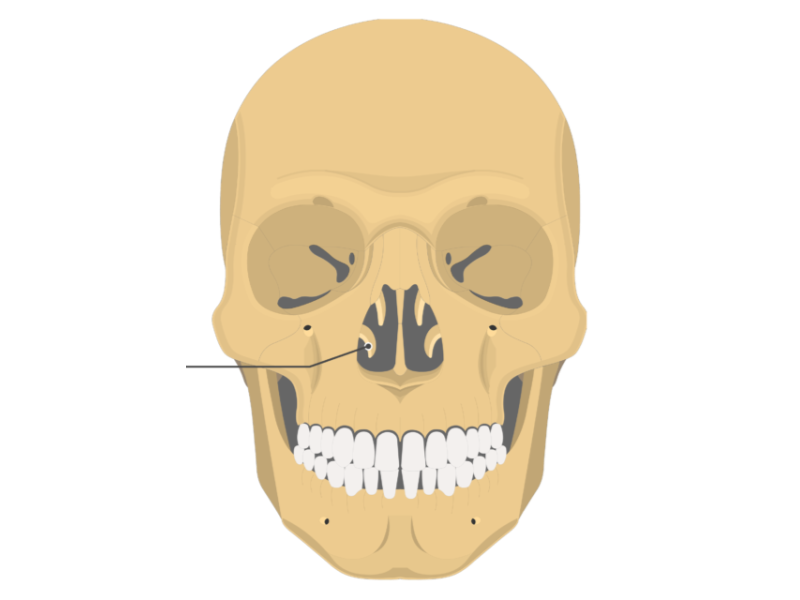
Inferior nasal concha
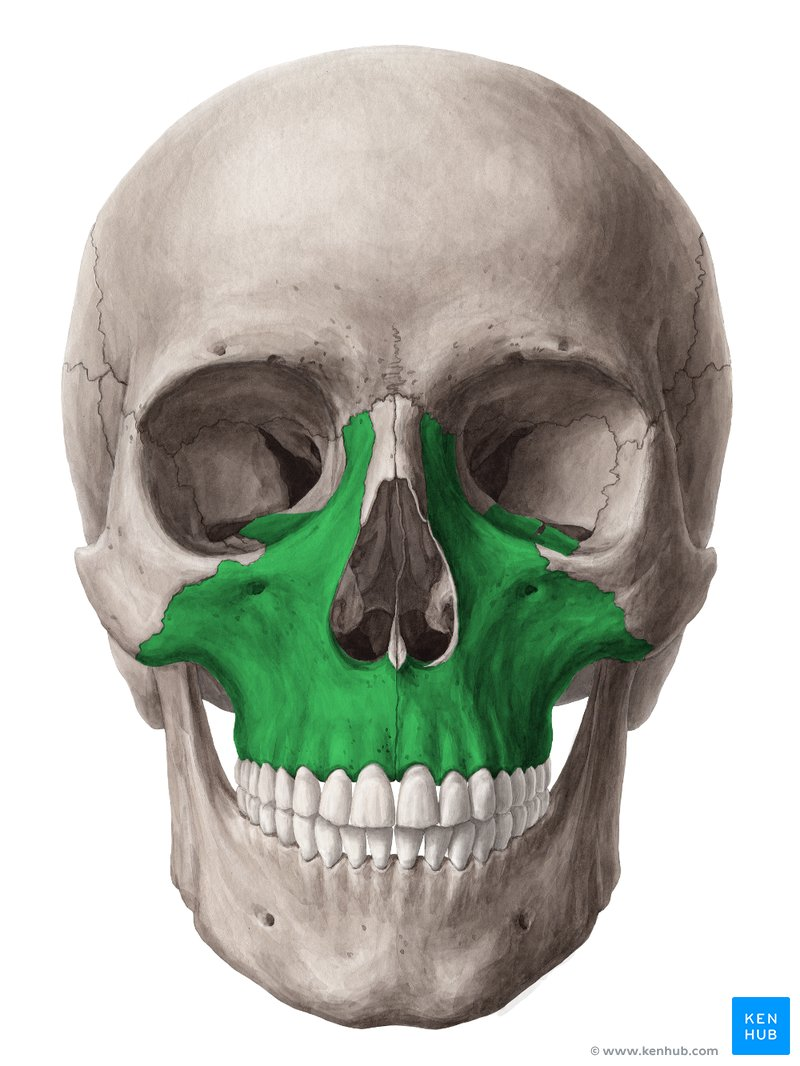
Maxilla
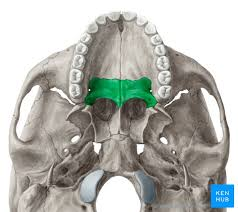
Palatine bone
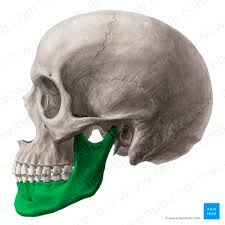
Mandible
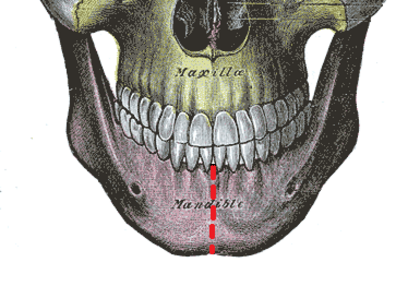
Mandibular symphysis
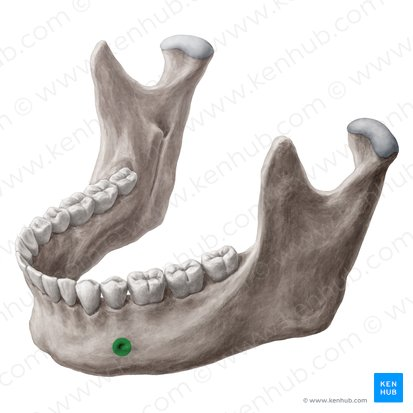
Mental foramina
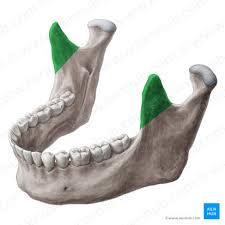
Coronoid process
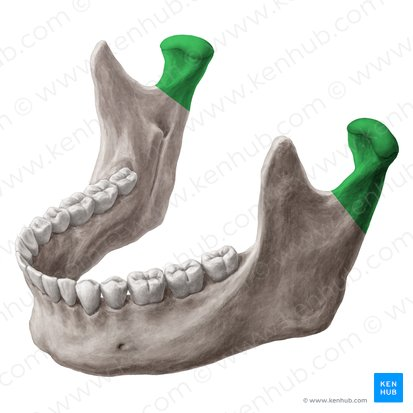
Condylar process
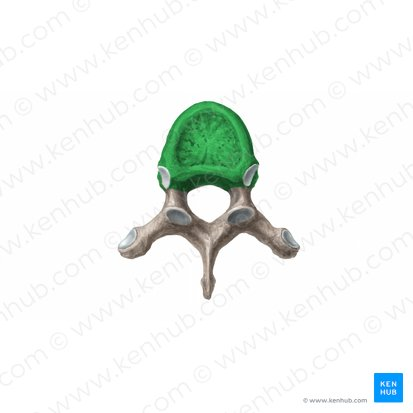

Centrum (body)
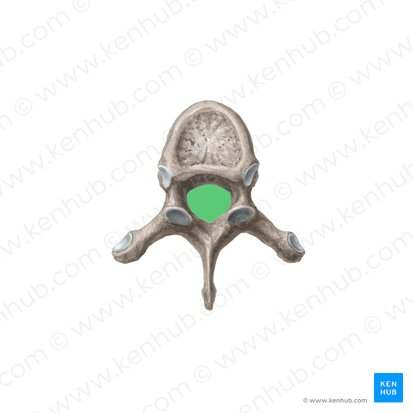
Vertebral canal
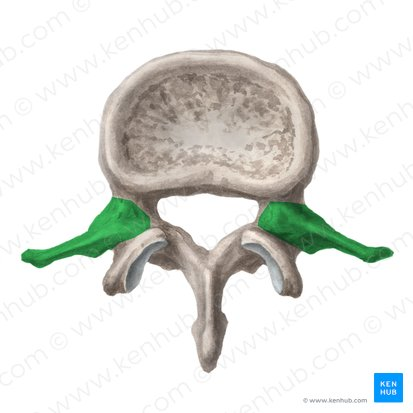
Transverse process
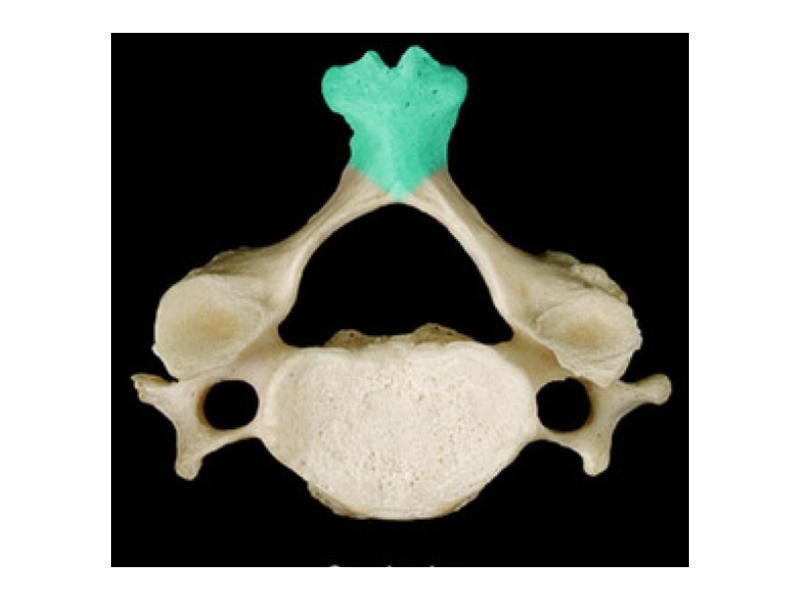
Spinous process

Atlas
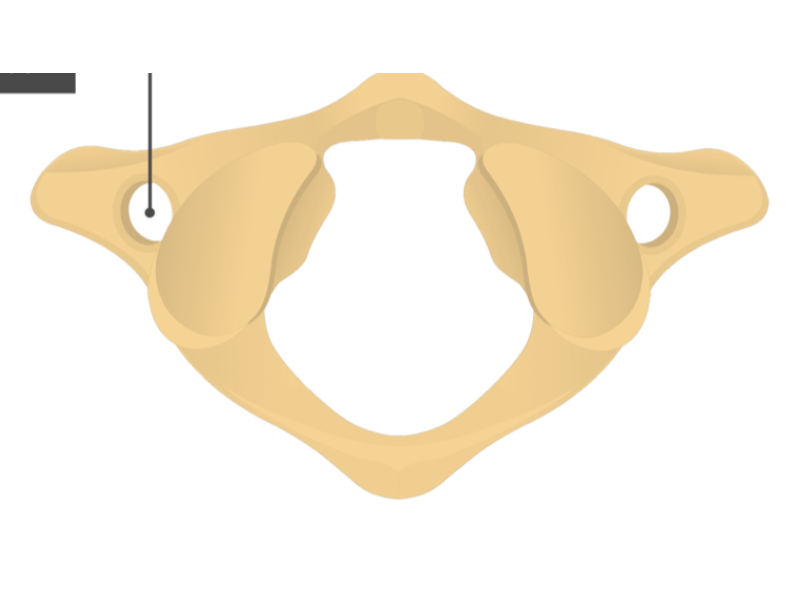
Transverse foramen
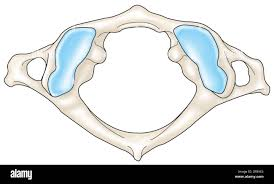
Superior articular facet
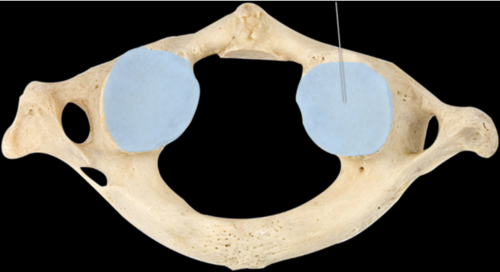
Inferior articular facet
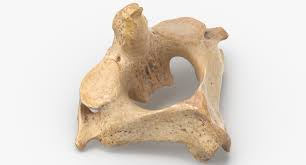
Axis
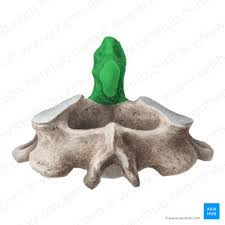
Dens
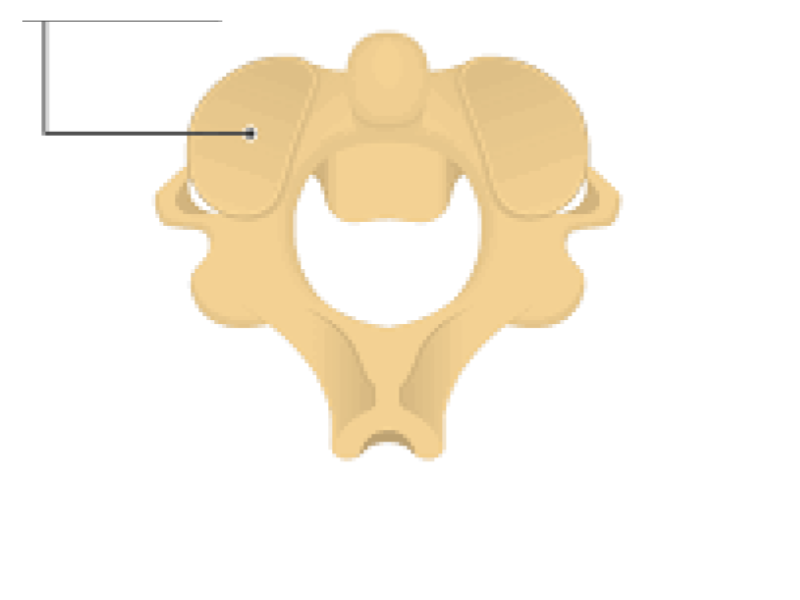
Superior articular facet
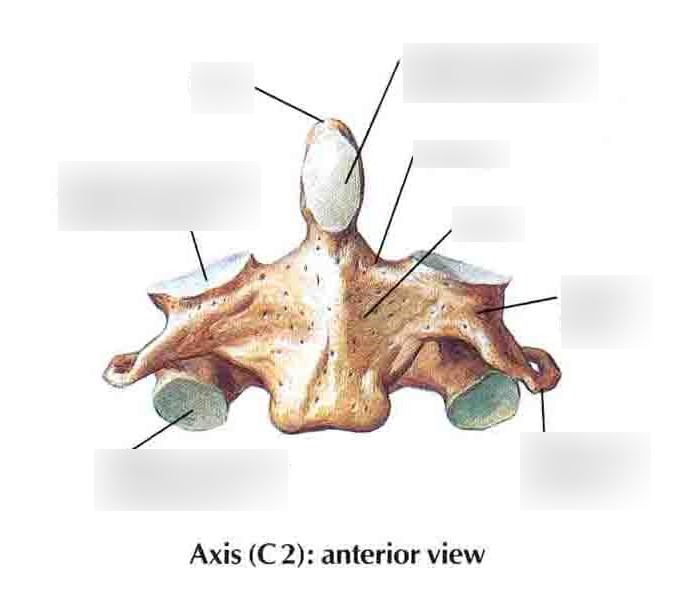
Inferior articular facet
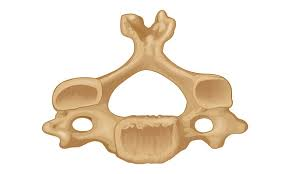
Cervical vertebrae
How does the transverse process for cervical vertebrae look different from that for other vertebrae? Why is this?
They have a transverse foramen, a hole through which the vertebral arteries and veins pass to supply the brain
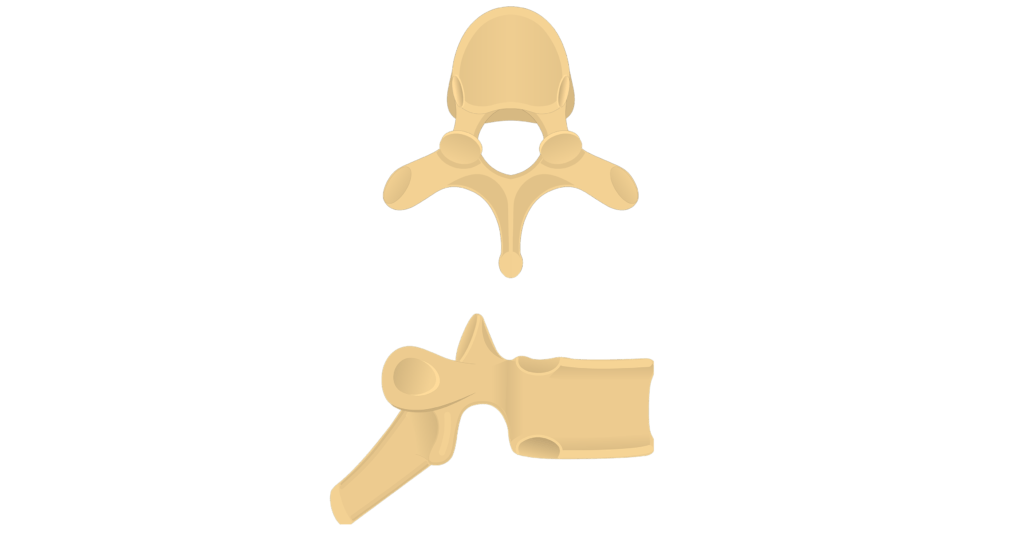
Thoracic vertebrae
Articular processes for ribs
Inferior notch
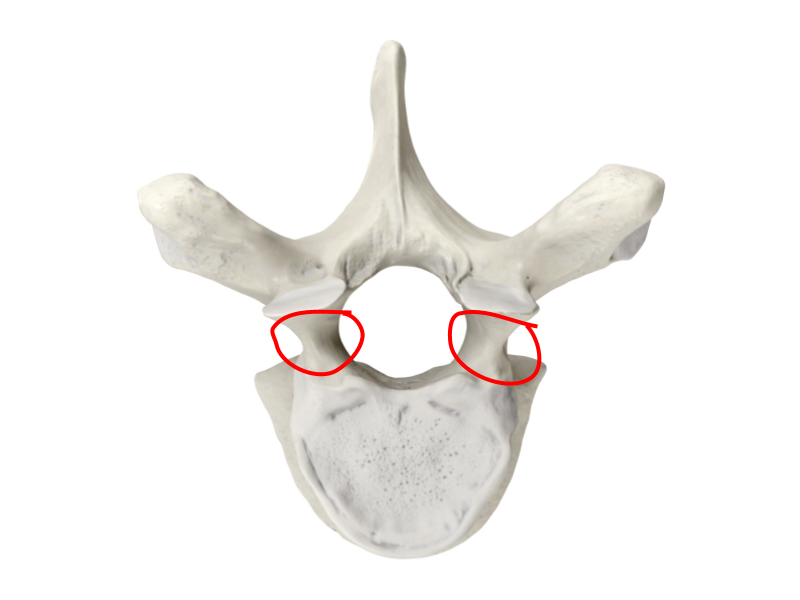
Superior articular process
Superior articular facet
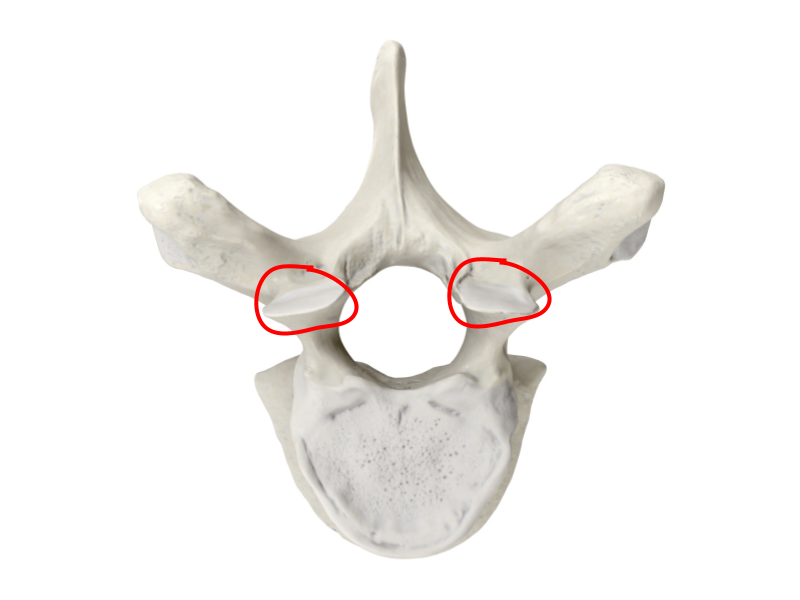
Lumbar vertebrae
Inferior articular process
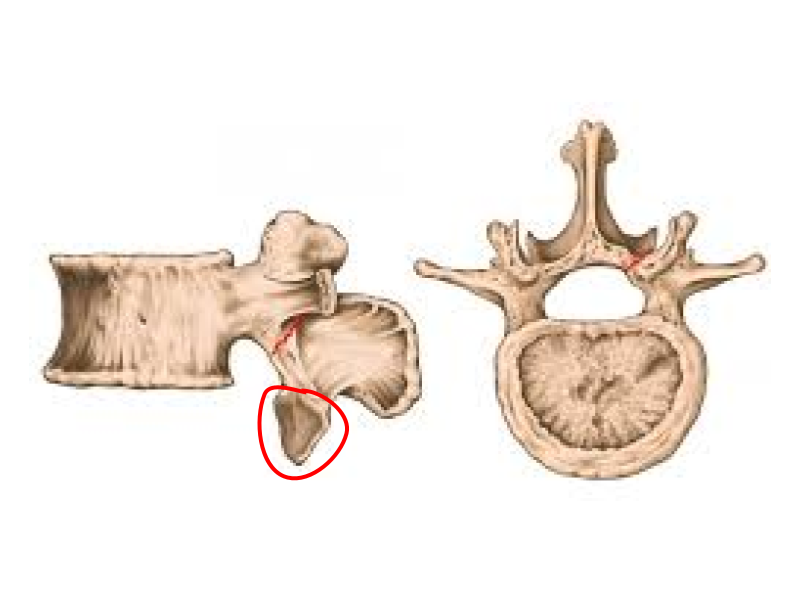
Inferior articular facet
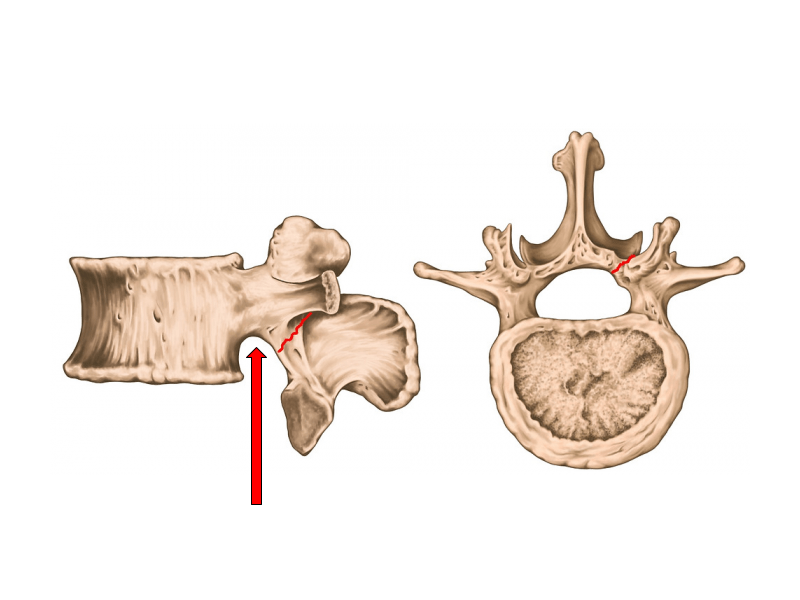
Inferior notch
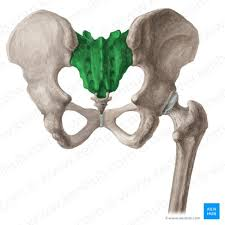
Sacrum
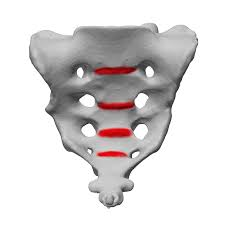
Transverse ridges
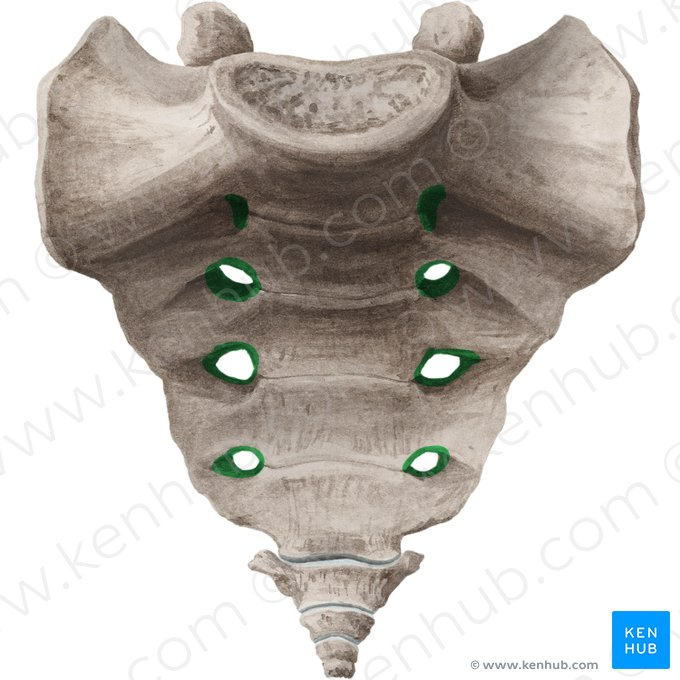
Sacral foramina
Coccyx
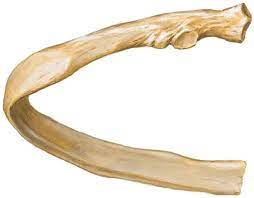
Rib
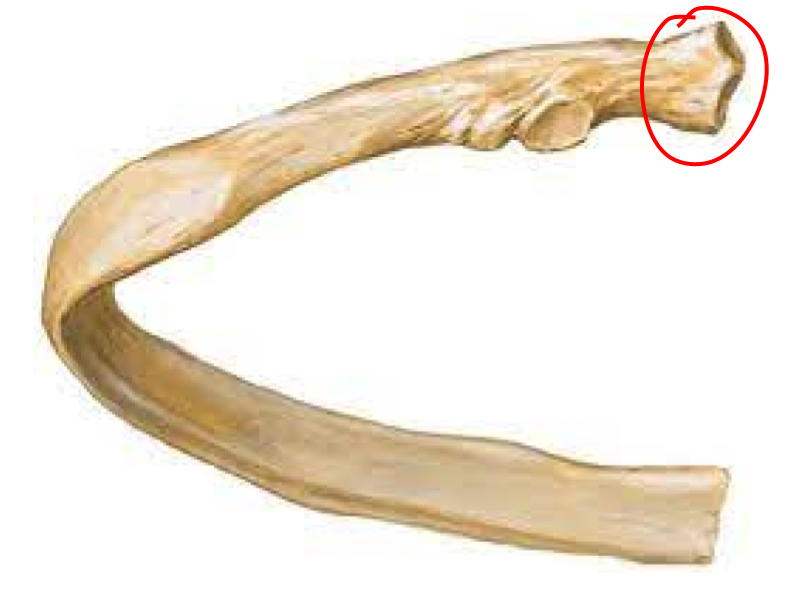
Head
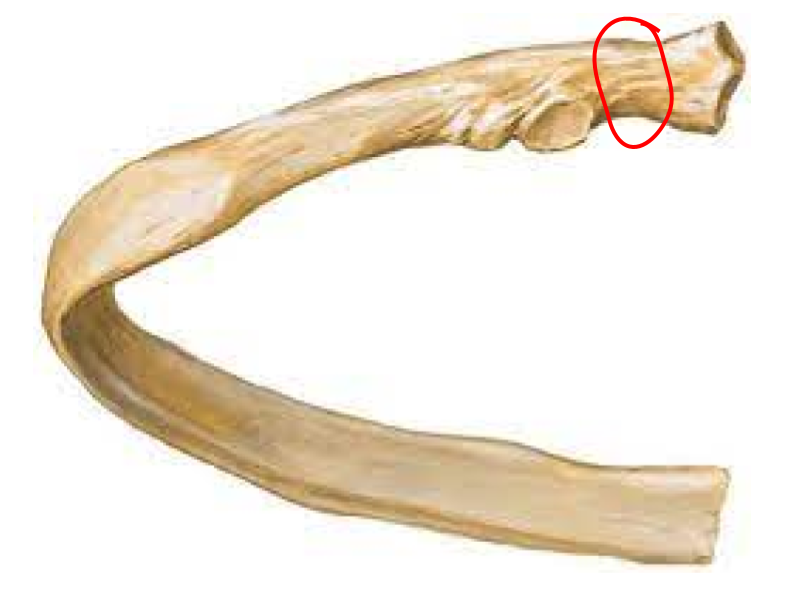
Neck
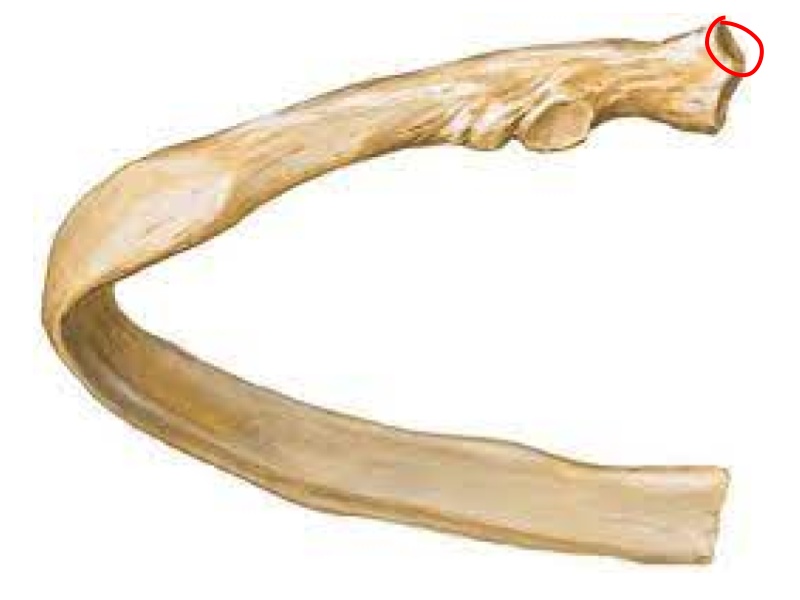
Superior articular facet
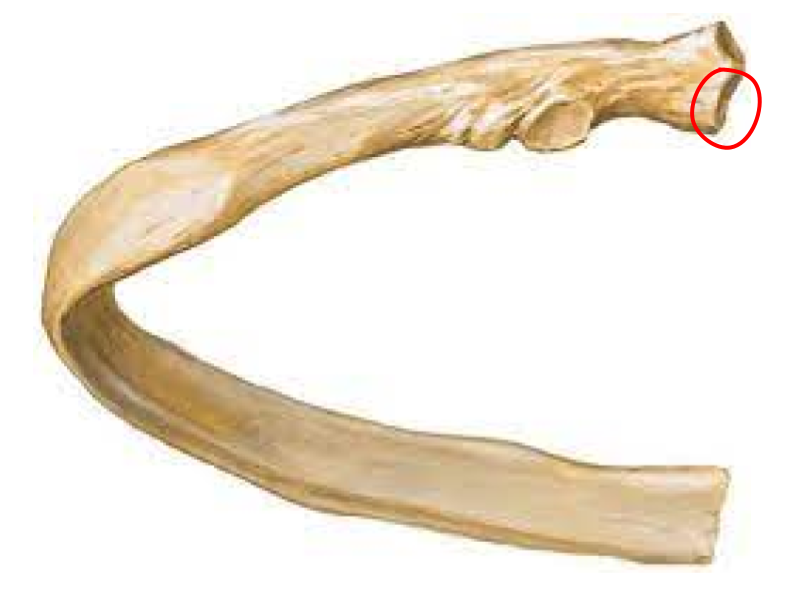
Inferior articular facet
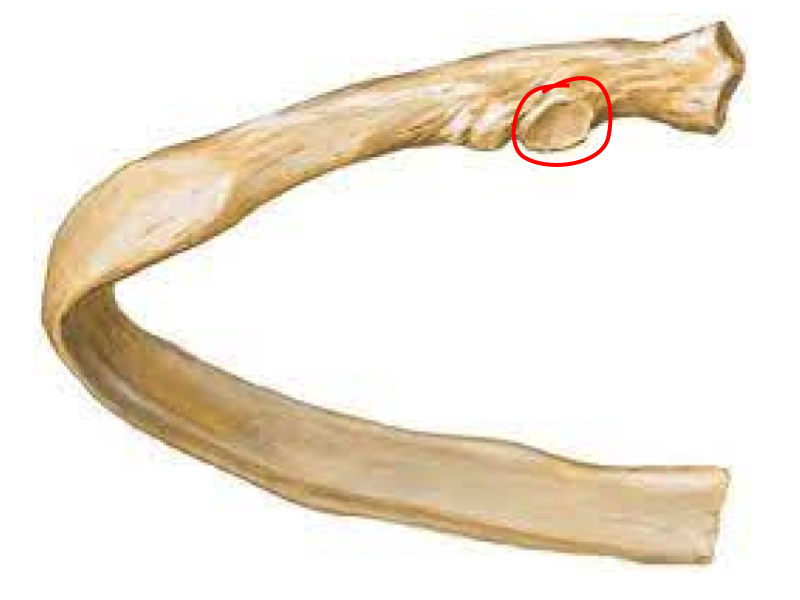
Articular facet of tubercle/transverse process of vertebrae
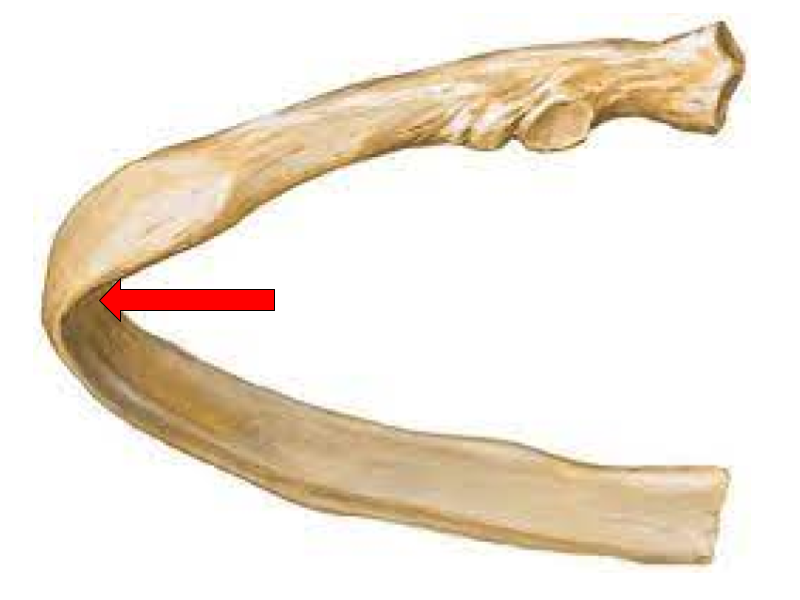
Angle
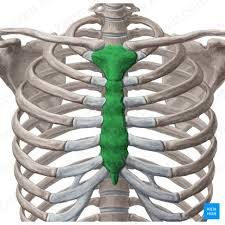
Sternum

Manubrium
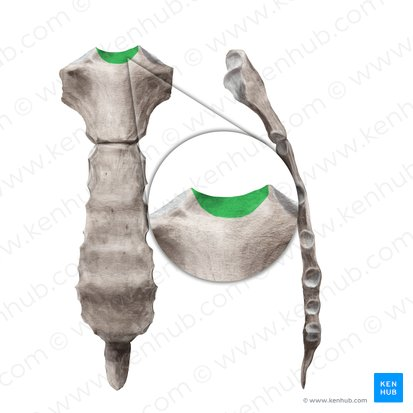
Jugular notch
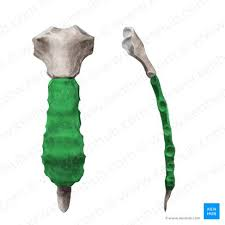
Body
Xiphoid process
Hyoid bone
Clavicle
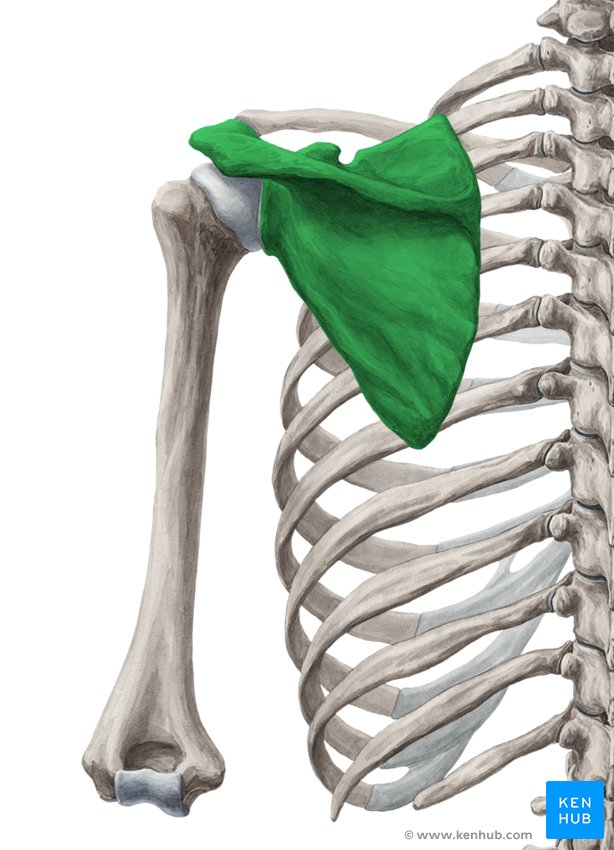
Scapula
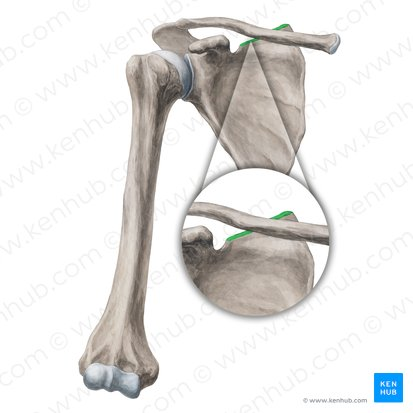
Superior border
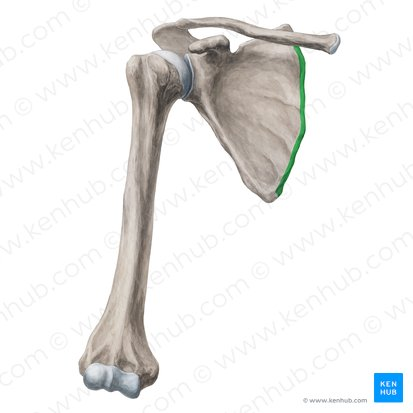
Medial border
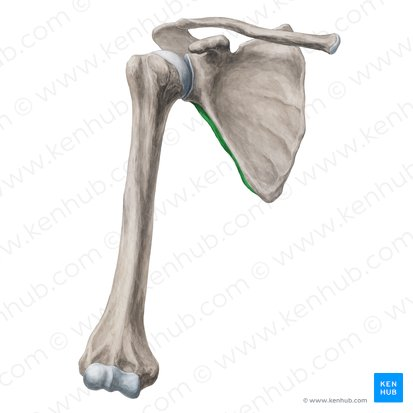
Lateral border
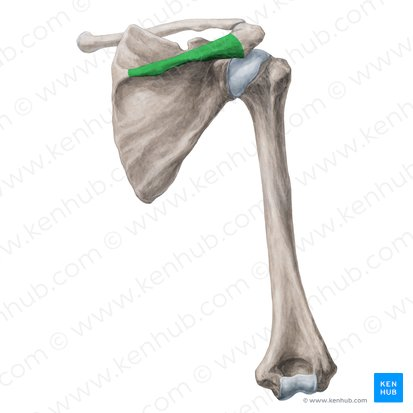
Scapular spine
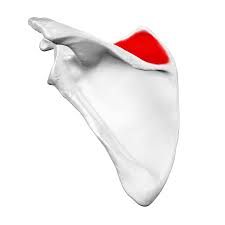
Supraspinous fossa
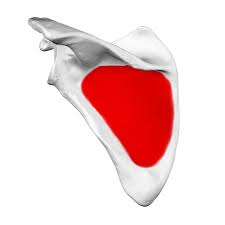
Infraspinous fossa
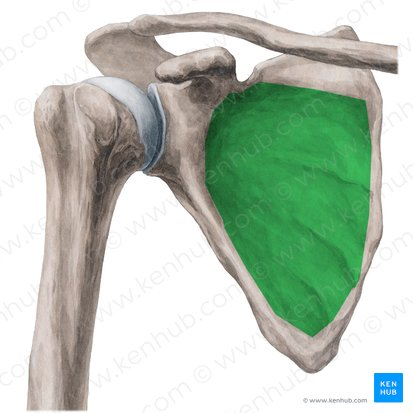
Subscapular fossa
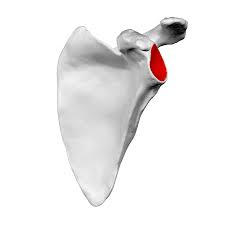
Glenoid cavity
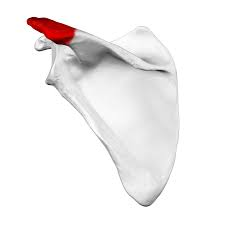
Acromion
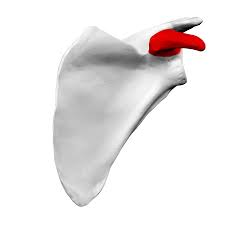
Coracoid process
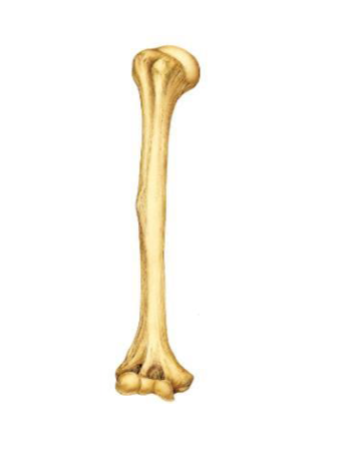
Humerus
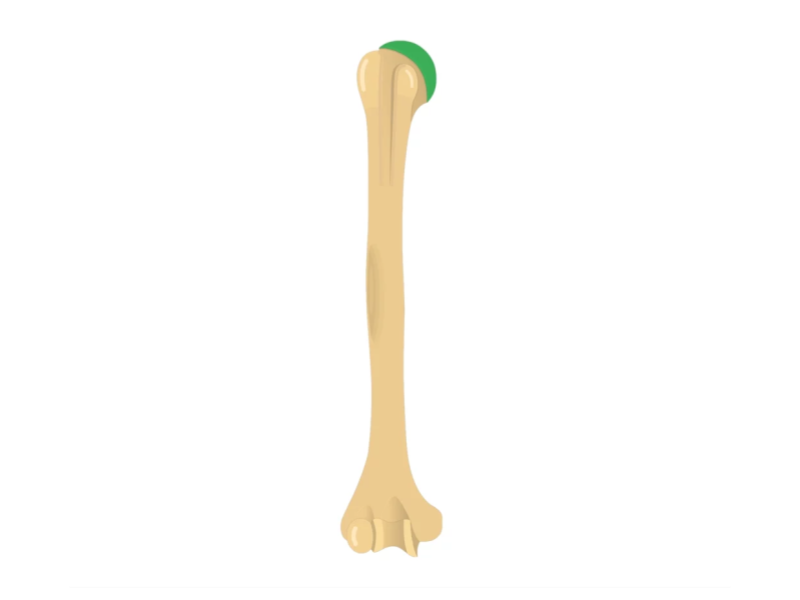
Head
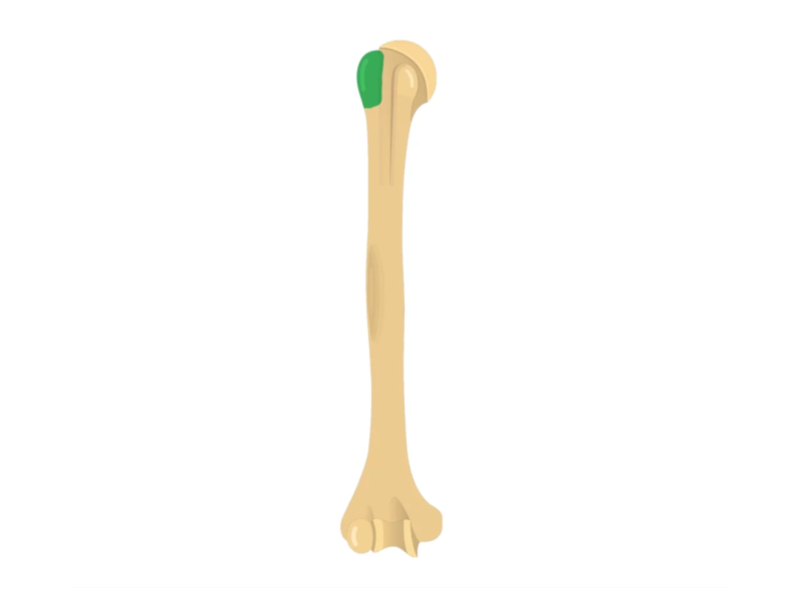
Greater tubercle
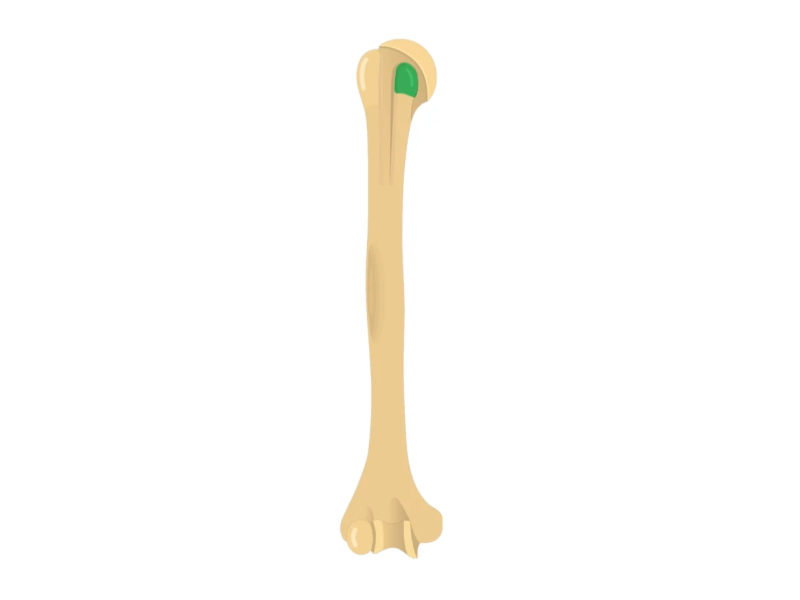
Lesser tubercle
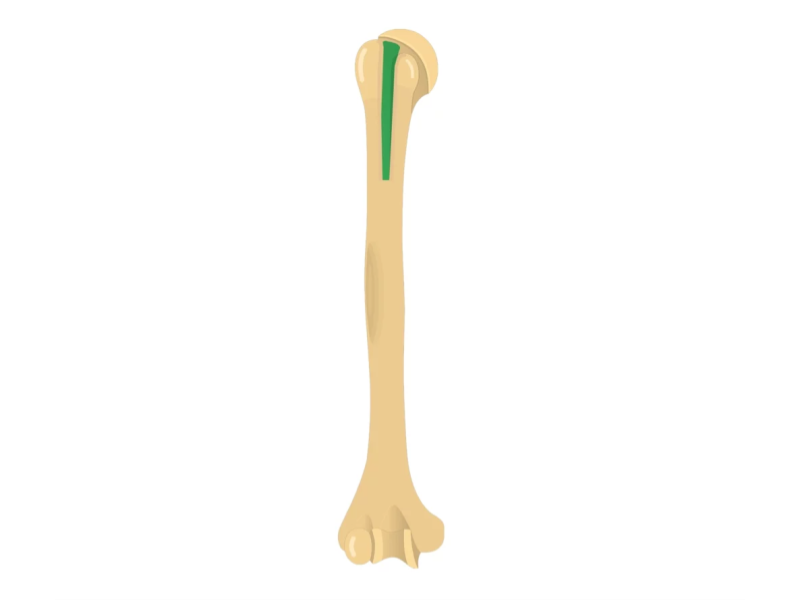
Intertubercular sulcus
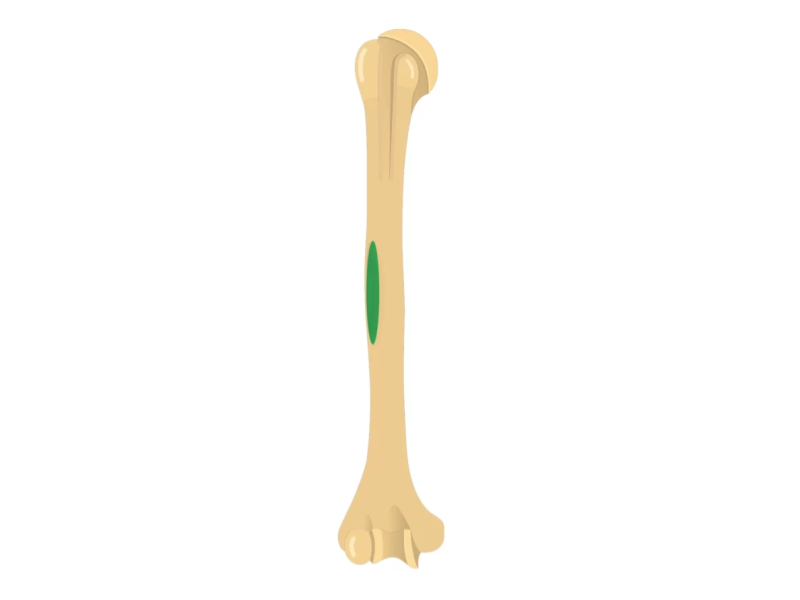
Deltoid tuberosity
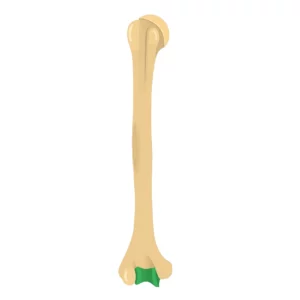
Trochlea
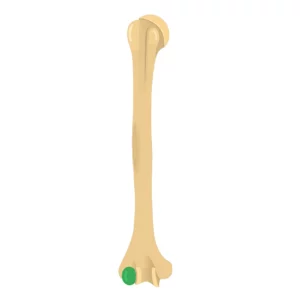
Capitulum
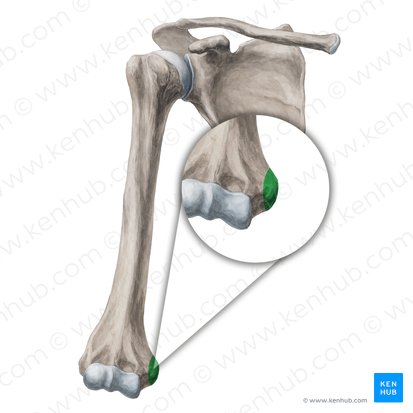
Medial epicondyle
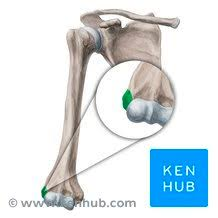
Lateral epicondyle
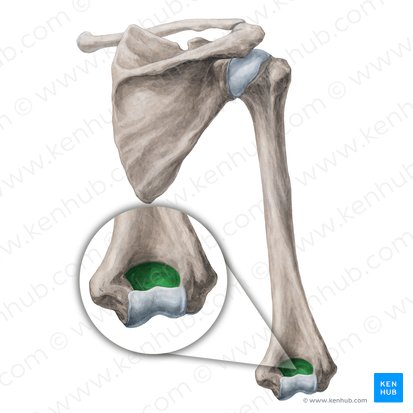
Olecranon fossa
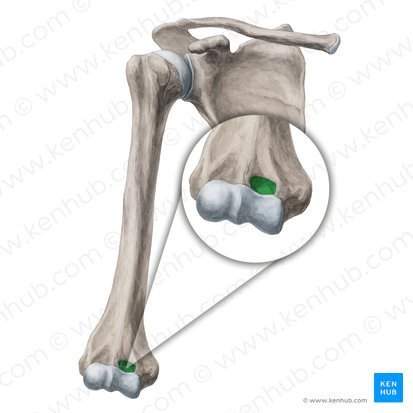
Coronoid fossa
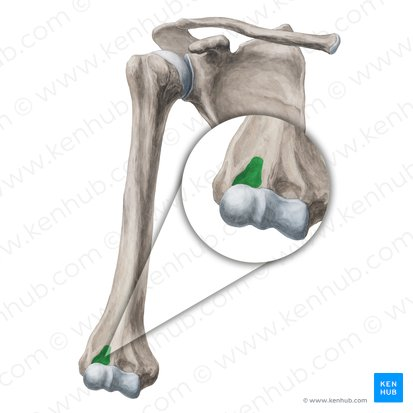
Radial fossa
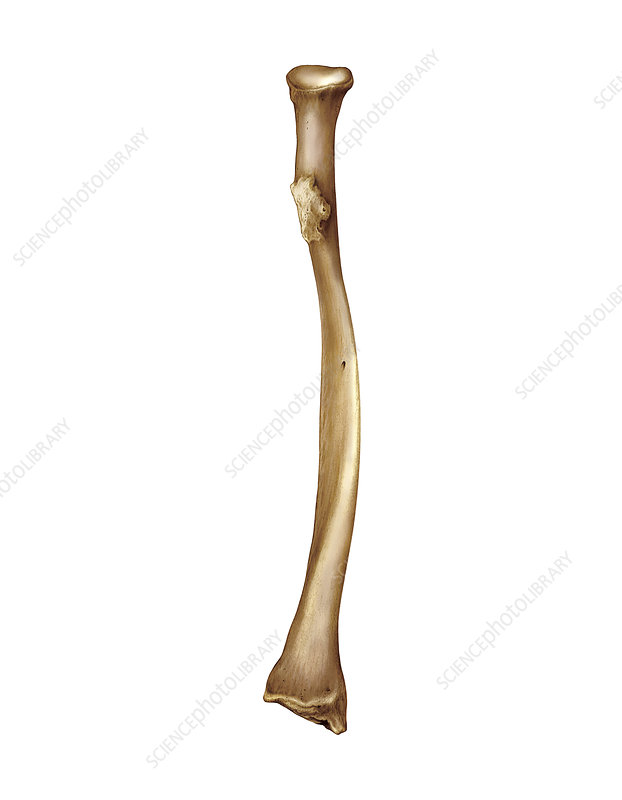
Radius
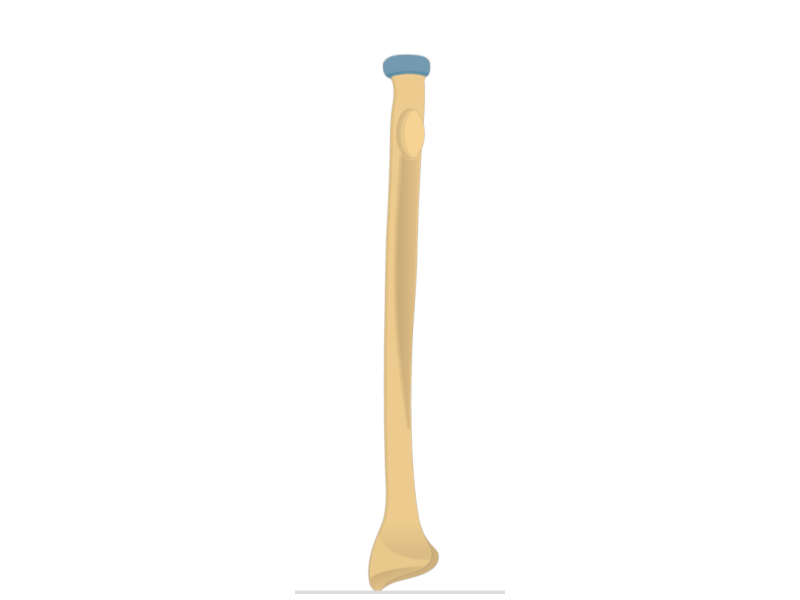
Head
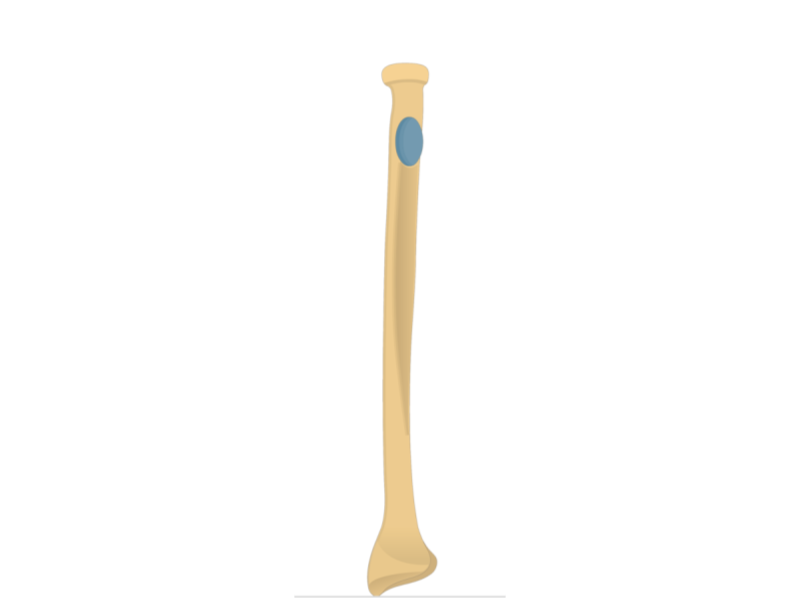
Radial tuberosity
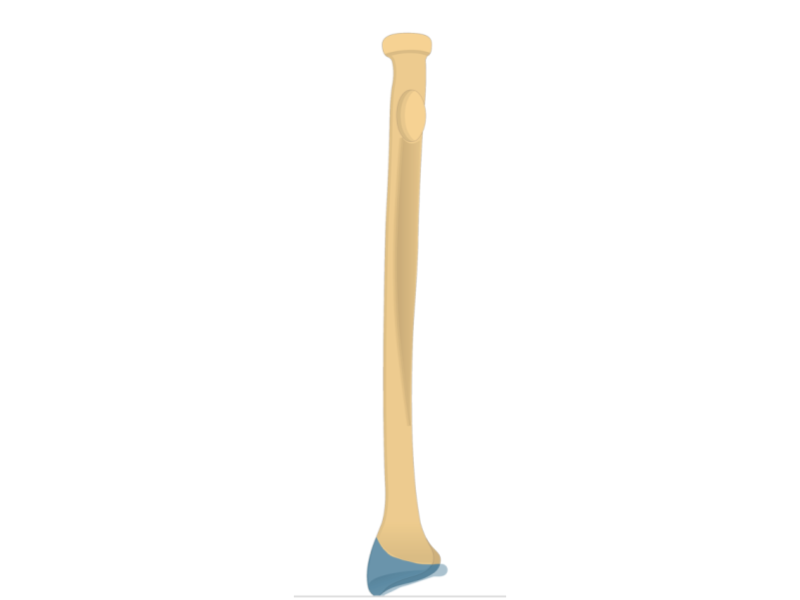
Styloid process