Business Management HL: Unit 4 - Marketing
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Covers sections 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.5 & 4.6,
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Marketing
links the business to the customer by identifying/meeting the needs of customer’s profitability. It does this by promoting the right product at the right time to the right customers.
Market Orientation
Outward looking approach; establishing consumer demand through market research before producing and selling a product. This ensures that the product will sell well because the business know it is what their customers want.
Product Orientation
Inward looking approach; focusing on making the product first before attempting to sell it. Businesses usually do this when they believe that people need their product.
Market share
the percentage of sales in the total market sold by one business
Firms sales in a given time period x100
Total market sales in time period
Market growth
percentage change in the total size of a market (volume or value) over a period of time
market size(2nd year)-market size(1st year)
market size 1st year
Market leadership
a firm with the largest market share in a given market
Importance of market share
provides useful insights into the firm’s revenues, growth and profit margins
Role of market planning
document outlining the firm’s marketing strategies to be used in order to achieve these objectives. usually developed after the conduct of a marketing audit
Segmentation
a distinct group of customers with similar characteristics such as age, gender and similar wants or needs
targeting
means that each distinctive market segment can have its own marketing mix
positioning
analysing consumer perceptions of current brands
niche market
a narrow, smaller or more specific market segment
mass market
a large or broad market that ignores specific market segments
Importance of having a USP
Helps establish a firm’s competitive advantage, builds customer loyalty, improves revenue and makes the product/service easy to sell
How can organisations differentiate themselves and their products from competitors
Product differentiation
Service differentiation
Price differentiation
Distribution differentiation
Relationship differentiation
Image/reputation differentiation
sales forecasting
uses quantitative methods to try predict a firms future sales
advantages of sales forecasting
accurately predicting sales reduces uncertainty
helps manage stock and cash flow
aids in the decision making process
disadvantages of sales forecasting
time consuming
ignores qualitative external factors (political, social, economic)
the entry of competitors into a market may be unforeseen
may be based on present technology which can be rendered obsolete due to technological processes
why organisations carry out market research
To identify consumer’s needs and wants
To assist a business in predicting what is likely to happen in the future
To reduce risk of product failure
To measure effectiveness of a marketing strategy
To provide latest information on activities happening in the market
how organisations carry out market research
Primary and secondary market research
surveys
questionnaires sent to specific target audiences to gather first-hand information
interviews
bringing in a selection of people to interview in order to gain information. They can be conducted one-on-one, telephone or online
focus groups
small groups brought together to discuss a product or idea
observations
getting information by carefully watching a trying to understand certain things or people’s behaviour
market analyses
commercial publications or market intelligence reports that gather data about particular markets. highly detailed reports usually conducted by specialist market research agents
academic journals
publications of scholarly articles written by experts. Experts usually include professors, graduate students or others with first-hand experience
government publications
documents produced by the government that provide an official record of government activities and cover a wide variety of topics. issued locally, regionally or nationally.
media articles
texts written and submitted for publication. e.g. newspapers & magazines
online content
gathering information from the internet or websites
qualitative research
information that relies on non-numerical data such as quality, opinion and characteristics
quantitative research
information that relies on numerical and/or measurable data
quota sampling
segmenting a given population into a number of groups that share certain characteristics
random sampling
every member in the population has an equal chance of being selected, since the sample in chosen randomly
convenience sampling
research groups are selected based on their easy access and proximity to the researcher.
7 Ps of marketing
Product
Price
People
Place
Physical Evidence
Promotion
Processes
Product (7 Ps)
a good or service that is offered in a market. Can be tangible or intangible and aims to satisfy the needs and wants of consumers
Product life cycle
Different stages that a product is likely to go through from its initial design and launch to its decline
product portfolio
includes all the products or services provided by an organisation
marketing mix
set of controllable variables that a company uses to influence and meet the needs of its target customers in the most effective and efficient way possible.
Extension strategies
attempt by firms to stop sales from falling by lengthening or extending the product’s life cycle
Extension strategies include…
selling existing products into new markets
finding new uses for the product
changing the product’s packaging
targeting different market segments
developing new promotional strategies
investment
the act of buying an asset to make a profit from its use
profit
the money you have left after paying for business expenses
cash flow
a measurement of the amount of cash that comes into and out of your business in a particular period of time
branding awareness
the ability of customers to recognise the existence and availability of a firm’s good or service
branding development
any plan to improve or strengthen the image of a product in the market.
brand loyalty
when customers become committed to a firm’s brand and are willing to make repeat purchases over time.
brand value
how much a brand is worth based on its reputation, potential income and market value. it is the extra money a business can make from its products because of its brand name
the importance of branding
gives customers a clear image with which they can associate the business
Price (7 Ps)
the only P concerned with profit. the money customers pay for having or using a good or service.
Cost-plus (mark-up) pricing
adding a mark-up to the average cost of producing a product
Penetration pricing
setting a low initial pricing and increasing over time. aim is to get a large number of customers quickly
Loss leader
company sells at below their average costs with the aim to attract customers so they will buy something else
premium pricing
sustained substantially higher prices than competitors to give the impression of superiority
predatory pricing
eliminates any opposition by putting your prices lower than your competitors average costs to drive them out of business (illegal)
Dynamic pricing
firms change pricing on an on-going basis in response to an on-going supply and demand
Competitive pricing
taking into account what your competitors are doing
Contribution pricing
calculating the variable cost per unit and setting the price above that
Price elasticity of demand
measures how much demand for a product changes when there is a change in price.
Change in quantity = new q - original q
original q
Change in price = new p - original p
original p
PED >±1 = price elastic
PED <±1 = price inelastic
PED =±1 = unit elasticity
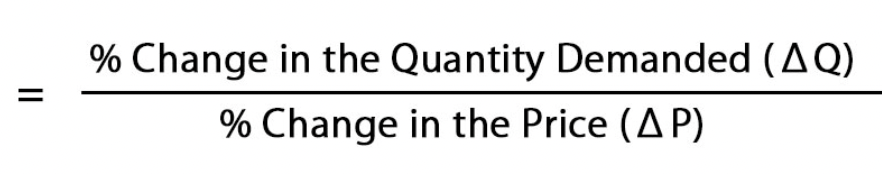
Promotion (7 Ps)
Doing what competitors do but bigger, better, faster, cheaper, etc.
Above the line promotion
paid for communication that uses mass media. the control or responsibility is passed onto another organisation.
e.g. TV, radio, internet
Below the line promotion
direct control over the promotional activities. focuses on promotional activities to a specific group of customers.
e.g. personal selling, public relations, sales promotion
Through the line promotion
mixture of above and below the line. aim is to gain greater brand awareness & visibility.
e.g. TV advert released followed by magazine adverts
social media marketing as a promotional strategy
uses social networking websites to market a firm’s product. incorporates the use of technological concepts and techniques with the aim of growing a business through different media.
Place (7 Ps)
how the product reaches the intended user. it is concerned with how the product is distributed to make it available to consumers
Channel of distribution
the path taken by a product from the producer or manufacturer to the final consumer
Zero intermediary channel
when a product is sold directly from the producer to the consumer.
e.g. airline ticket booking
One intermediary channel
involves the use of one intermediary (such as a retailer or agent) to sell the products from the producer to the consumer. usually working on a large scale or with expensive products.
e.g. selling jewellery through retailers
Two intermediaries channel
when two intermediaries (usually wholesaler and retailers) are used by producers to sell the product to the consumer. particularly useful when selling goods over large geographical distances.
One intermediary channel advantages & disadvantages
Advantages:
- Promotion and customer service are done by the retailer
- The cost of holding stock is incurred by the retailer
- Retailer assists in selling the product at convenient places to consumers
Disadvantages:
- Retailers profit mark-up is included in selling price, so product may be expensive for consumers
- The producer may not be aware of the promotional strategy used by the retailer
Zero intermediary channel advantages & disadvantages
Advantages:
- Cheap
- Fast
- Ideal for perishable products
- Producer is key decision-maker
Disadvantages:
- Promotion is done by producer, which can be time-consuming and expensive
- Producer incurs all storage and delivery costs
Two intermediary channel advantages & disadvantages
Advantages:
- Wholesaler incurs storage costs which reduces costs for producer
- Wholesaler breaks the bulk for retailer by providing large quantities in smaller batches
- Appropriate when selling over long distances
Disadvantages:
- Two profit mark-ups could lead to a more expensive product offered to consumers
- This channel further reduces the producer’s responsibility for promoting products
People (7 Ps)
selecting, recruiting, hiring and retaining the correct staff with the right skills and abilities for the production and sale of a good/service
importance of employee-customer relationships in marketing a service
they are the face of the company which makes their relationship vital for maintaining a good image. often purchasing experiences can be effected often by the people we purchase from
Processes
procedures & policies dealing with how an organisations product is provided and delivered.
Direct processes
add value at the customer interface as the customer experiences the service
Indirect processes
support the service before, during and after it has been consumed
Physical evidence
the tangible or visible touch points that are observable to customers.
importance of tangible physical evidence in marketing a service
many customers like to touch, smell, see, etc products before they purchase since it can act as a point of differentiation.
Benefits of a 7 Ps marketing mix model
brings together marketing ideas and concepts in a simple manner, making it easier to market a good/service
assists businesses in strategy formulation all the way to strategy implementation
allows business to vary its marketing activities based on customer needs, resource availability and market conditions
Drawbacks of a 7 Ps marketing mix model
misses out on addressing issues related to business productivity
can become complicated when adding the extra 3 Ps (people, processes, physical evidence)
Opportunities of entering and operating internationally
larger market (greater reach & expands customer base)
diversification (spreads risks by investing in other countries)
enhanced brand image (makes business seem more “successful”)
gaining economies of scale (reduces average cost of production and makes business more competitive)
forms business relationships (may offer better prices for inputs)
Threats of entering and operating internationally
economic challenges (fluctuating exchange & interest rates)
political challenges (governments easily change regulations)
legal challenges (consumer protection laws and intellectual property rights)
social challenges (disparities in countries)
technological challenges (LEDCs lack infrastructure, internet and communication systems)