Arterial Blood Gas
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
radial, femoral, PaO2, point, carboxyhemoglobin
Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Introduction
-Arterial blood specimen is gathered often from the ______, brachial, or ______ artery via an arterial stick or an indwelling arterial line. The specimen is then taken on ice for immediate analysis.
-Information included on a typical ABG report are: pH, PaCO2, ____, base excess, HCO3-, and SaO2 (both are calculated)
-____ of care lab values are available upon request, as are abnormal hemoglobin values like ______________ (CO poisoning) and methemoglobin
oxygen, acid-base, compensate, clinical
Indications of ABG
-Assess issues with ________ exchange (oxygenation), carbon dioxide exchange (ventilation), ____-____ disturbances ± determine etiology, and abnormal hemoglobins
-Ongoing monitoring of above problems
-Assess patient’s ability to ___________ for above problems
-Assess effectiveness of _________ interventions
collateral, infection, Raynaud’s
Contraindications of ABG
-Inadequate _________ circulation of hand (Allen’s Test)
-Local _________, thrombus, or distorted anatomy at the puncture site
-Severe peripheral vascular disease of the artery selected for sampling
-Active ________’_ Syndrome
-Relative: coagulopathy
pain, bleeding, hematoma, infection, nerve
Complications of ABGs
-Common: local _____ and paresthesia, bruising, and local minor __________
-Less common: vasovagal response, local __________ from moderate or major bleeding, and artery vasospasm
-Rare: ________ at the puncture site, arterial occlusion from local hematoma, air or thrombus embolism, local anesthetic anaphylactic reaction, local ______ injury, pseudoaneurysm formation, and vessel laceration
regulated, 7.35
pH must be precisely __________ to maintain optimal cellular function (_.__-7.45)
<, acidosis
pH _ 7.35 = acidemia or ___________
>, alkalemia
pH _ 7.35 = ___________ or alkalosis
bicarbonate, carbon dioxide
The body’s pH is directly proportionate to its level of ____________ and indirectly to _______ _______ (CO2)
Kidneys, metabolic, lungs, respiratory
Acid-base balance is achieved mainly by the ___________, which regulate HCO3- (bicarbonate) and make up the __________ component. This process also relies on the _______, which regulate CO2 and make up the __________ component.
slower
The kidneys respond to an acid-base disturbance much ________ than the lungs can
increase, CO2
Respiratory Acidosis
-___________ in ___ (can be acute or chronic)
-Common causes: CNS depression (drugs, intoxication, CNS event), neuromuscular disorder, pulmonary disease, and OSA
decrease, CO2
Respiratory Alkalosis
-__________ in ___ (can be acute or chronic)
-Common causes: CNS process, drugs (particularly salicylates), progesterone, sepsis, pulmonary processes, and anxiety
decrease, GI, renal, endocrine, carbonic, renal
Metabolic Acidosis: Non-Anion Gap Acidosis
-___________ in bicarb (typically __ losses, _____ losses, or NaCl overload)
-Common Causes: USEDCAR
Ureteroenterostomy
Saline infusion (NaCl)
_________ causes
Diarrhea
________ anhydrase inhibitors (acetazolamide)
Ammonium chloride
_______ tubular acidosis
bicarb, methanol, isoniazid, lactic
Metabolic Acidosis: Elevated Anion Gap
-Decrease in _______
-Common Causes: MUDPILES
___________
Uremia
DKA
Propylene glycol
___________ (hint: one of the TB meds)
______ acidosis
Ethylene glycol
Salicylates
increase, Cl, low, high, diuretic
Metabolic Alkalosis
-_________ in bicarb, typically driven by loss of __ (either renal or non-renal loss). If non-renal loss, urine Cl is ___. If renal loss, urine Cl is _____.
-Common causes: nausea/vomiting, ________ therapy (“contracture alkalosis”), posthypercapia, mineralocorticoid use, and hyperaldosteronism
immediately, CO2, days, bicarbonate, hydrogen
Compensatory Mechanisms
-Pulmonary system: occurs nearly _________. “Blows off” ___ by increasing respiratory rate and tidal volume.
-Renal system: takes hours to _____. During acidosis, the kidneys generate __________ and add it to the blood. During alkalosis, Type B intercalated cells in the collecting duct will reclaim _________ ions
7.35-7.45, 24, 40, 90, 95
Important ABG Values: Standards
-pH: _.__-_.__
-HCO3-: __ mEq/L
-PaCO2: __ mmHg
-PaO2: __
-O2 saturation: > __%
pH, primary, compensation, maximal, mixed, etiology
8 Step Systematic Approach to ABG Interpretation
Identify __
Determine ________ process
Determine if ___________ occurred
Determine ________ compensation
Identify ______ disorders
Calculate serum anion gap
Assess pulmonary status
Determine underlying __________/most likely diagnosis
decrease, increase, increase, decrease
Primary Process: Metabolic vs Respiratory
-Acidemia: low pH < 7.35
Metabolic acidosis = _________ in HCO3-
Respiratory acidosis = ___________ in CO2
-Alkalemia: high pH > 7.45
Metabolic alkalosis = _________ in HCO3-
Respiratory alkalosis = _________ in PaCO2
Mixed Disorder
issue in both metabolic and respiratory components, intervene immediately
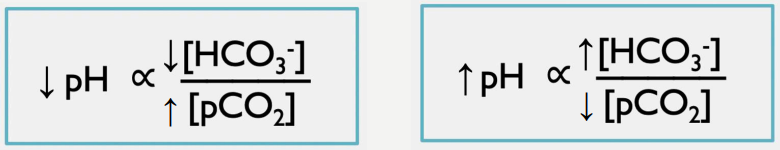
Metabolic and respiratory acidosis
What mixed disorder are these findings indicative of?
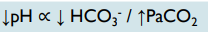
Metabolic and respiratory alkalosis
What mixed disorder are these findings indicative of?
respiratory, decrease, increase, metabolic, increase, decrease
Determine if Compensation Has Occurred
-Primary metabolic disturbance → ___________ compensation
Metabolic acidosis = compensatory _________ in PaCO2
Metabolic alkalosis = compensatory _________ in PaCO2
-Primary respiratory disturbance → __________ compensation
Respiratory acidosis = compensatory _________ in HCO3-
Respiratory alkalosis = compensatory _________ in HCO3-
drop, 1.5, 8
Compensatory Equations: Metabolic Acidosis
-With a compensatory _____ in PaCO2
-Expected PaCO2 = (_._ x actual HCO3-) + _ (±2)
-AKA Winter’s Formula
rise, 0.7
Compensatory Equations: Metabolic Alkalosis
-With a compensatory _______ in PaCO2
-Expected PaCO2 = (_._ x actual HCO3-) + 20
rise, 1, 10, 4, 10
Compensatory Equations: Respiratory Acidosis
-With a compensatory _______ in HCO3-
-Acute: Expected HCO3- = 25 + _ [(actual PaCO2-40) / __]
-Chronic (> 3 days): Expected HCO3- = 25 + _ [(actual PaCO2 - 40) / __] ± 2
drop, 2, 5
Compensatory Equations: Respiratory Alkalosis
-With compensatory _______ in HCO3-
-Acute ( < 3 days): Expected HCO3- = 25 - _ [(40-actual PaCO2) / 10]
-Chronic ( > 3 days): Expected HCO3- = 25 - _ [(40-actual PaCO2) / 10] ± 2
less, same, more, both
Identifying Mixed Disorders
-If the compensatory change is ____ than expected → mixed acid-base disorder of the ____ type
-If the compensatory change is ______ than expected → mixed disorder with ____ acidosis and alkalosis present
Na, etiology, plasma, 8-15
Anion Gap
-Anion Gap = __ - (Cl + HCO3)
-Helps identify _______, only in the setting of metabolic acidosis
-Often means that there are too many unmeasured anions in _______. Normal gap is = _-__ mEq/L
Osmolal Gap
-Used in patients with AGMA and concern for toxic alcohols or unexplained AGMA
-Formula: Measured Osm - Calculated Osm (2 x Na + Glucose/18 + BUN/2.8)
-Normal gap = < 10 mOsm/kg
-Anything higher than 10 indicates the possible presence of osmotically active substances like methanol, ethylene glycol, isopropanol, and mannitol
Delta Gap
-Purpose: used when an anion gap metabolic acidosis (AGMA) is identified to check for additional processes
-Formula: (Measured AG - Normal AG)
-If the value is greater than the change in HCO3-, consider concurrent metabolic alkalosis
lactic, diarrhea, vomiting, obesity, CNS
Identify Likely Etiology
-Metabolic acidosis
AGMA: ____ acidosis, ketoacidosis, uremia
NAGMA: _______, normal saline
-Metabolic alkalosis
GI tract losses of acid: _______, NG suction
Diuretics
-Respiratory acidosis: hypoventilation from any cause
COPD, ________ hypoventilation syndrome, narcotic use, mechanical under-ventilation
-Respiratory alkalosis: hyperventilation from any cause
Anxiety, pregnancy, mechanical over-ventilation, ___ disorder
VBG
venous blood gas
-cannot evaluate PaO2 or SaO2
-pH and CO2 are correlated but not identical