DNA and protein synthesis terms
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
DNA replication
Each strand acts as a template for a new strand
Helicase
The enzyme that untwists and unzips the double helix. (Breaks hydrogen bonds)
Topiosomerase
A protein that reduces the super-coiling that occurs as the helices unwinds the double helix.
Primase
Joins the RNA nucleotides together to make the primer.
DNA polymerase
The enzyme that catalyzes elongation of DNA. ( bonds the free nucleotide to the backbone)
DNA ligase
An enzyme that joins fragments of DNA during lagging strand replication
Protein Synthesis
Contains transcription then translation
Transcription
DNA → mRNA
RNA Polymerase separates DNA and the free RNA nucleotides match up to the DNA by base pairing
Translation
mRNA → polypeptide
The tRNA matches with an mRNA codon to attach the amino acid to the polypeptide chain.
DNA
Made of phosphate, deoxyrobse sugar and nitrogenous bases( adenine thymine cytosine guanine)
mRNA
Messenger RNA is single stranded and carries information from DNA to the ribosome. mRNA contains codons which are complementary to the DNA base pair sequence.
tRNA
Transfer RNA - the interpreter… the tRNA finds its specific amino acid, the tRNA anticodon matches with mRNA codon. Amino acid attaches to polypeptide chain.
Ribosome
Made of protein and ribosomal DNA. Contains 2 subunits - large +small
Also has 3 binding sites for tRNA ( p (polypetide) A (amino acid ) E (exit))
Exon
Coding sections in eukaryotic mRNA transcripts that will be translated ( exons are expressed)
Intron
Noncoding RNA sections (cut out before translation)
Promoter
Often has a tata box, this tells RNA polymerase where to begin.
RNA polymerase
An enzyme that transcribes a DNA sequence into RNA molecules
Codon
Made of 3 nucleotides that code for an amino acid.
Point Mutation
A change in just one nucleotide pair of a gene (two strands of DNA)
Substitution
Changes one nucleotide pair
Deletion
Removes a nucleotide pair
Insertion
Adds a nucleotide pair
Silent Mutation
Doesn't affect amino acid sequence (substitution)
Missense mutation
Codes for one wrong amino acid ( substitution)
Frameshift mutation
Shifts the reading frame (groups of three) (insertion or deletion)
Nonsense mutation
Codon changes to a stop codon (substitution, insertion, or deletion)
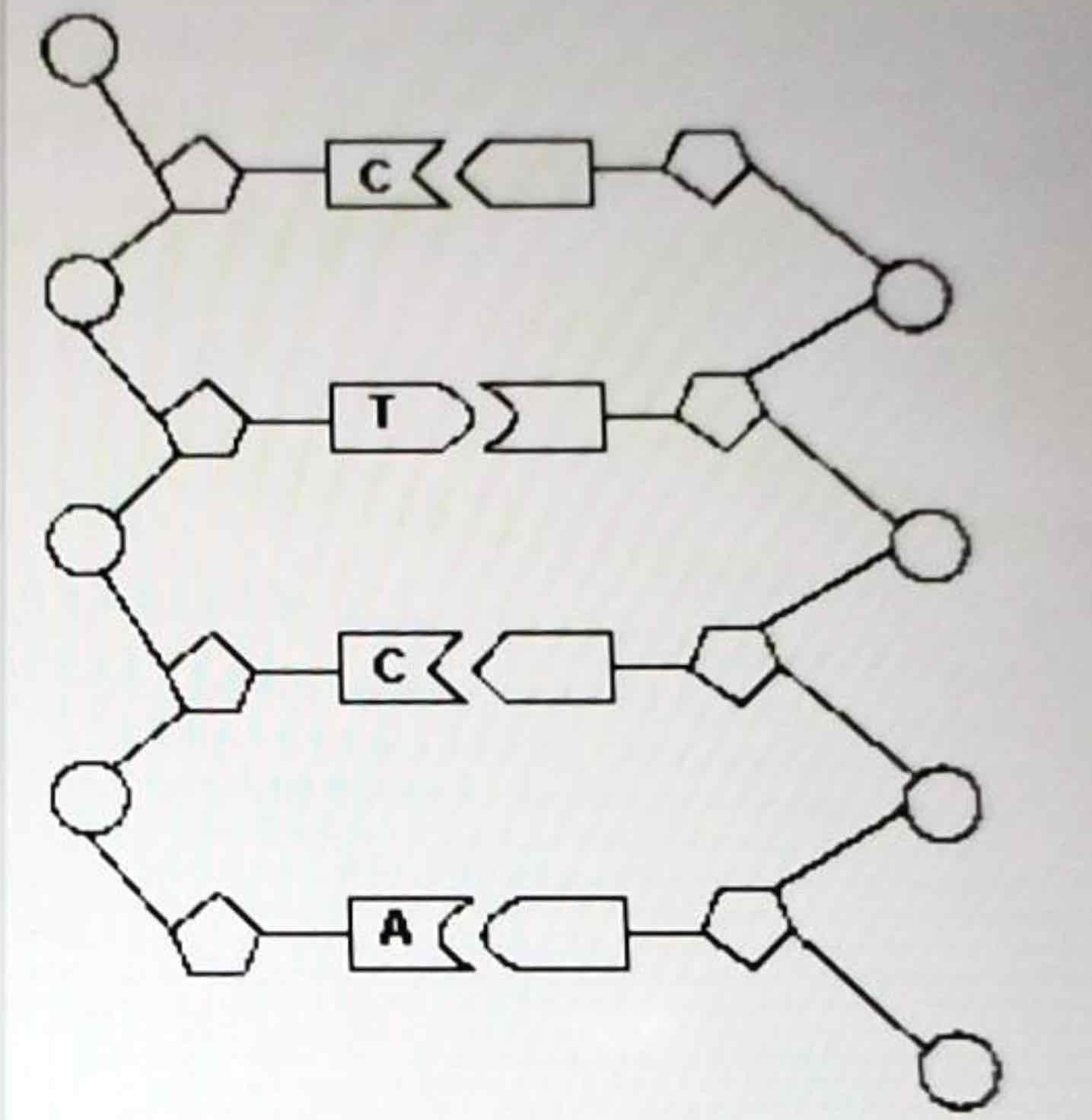
Label the following: nucleotide, deoxyribose sugars, phosphate, and nitrogenous base
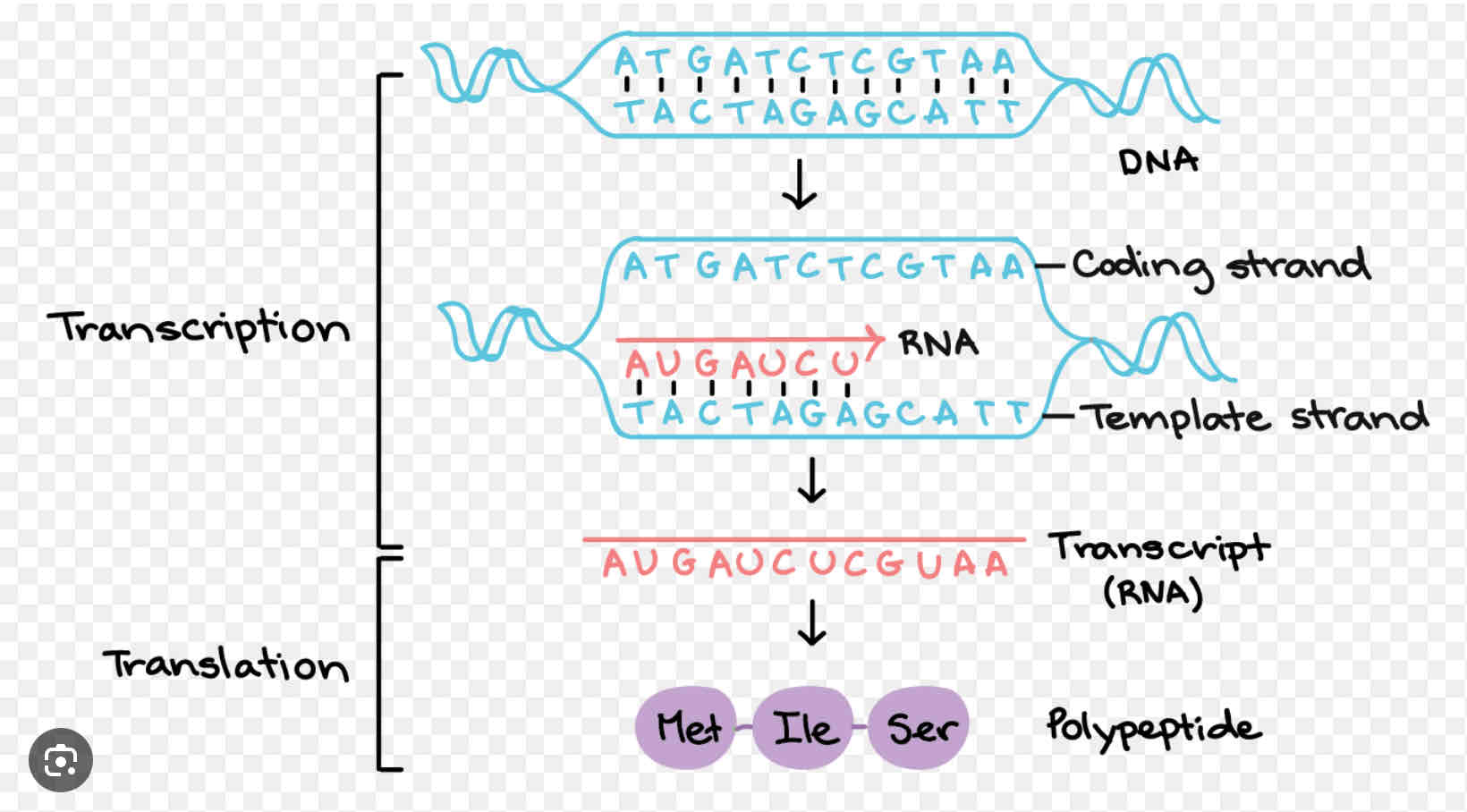
Be able to determine which DNA strand is the template strand and which is the coding strand
What type of bond is along the backbone of DNA between the nucleotides?
covalent bonds
What type of bond is between the complementary base pairs?
Hydrogen bond
What type of bond is between amino acids and a polypeptide chain?
Peptide bonds