Cognition: Thinking/problem solving and intelligence/testing
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mid unit ngl but it was sorta easy at least
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Cognition
All mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
Metacognition
Cognition about our cognition; keeping track of and evaluating our mental processes
Analysis and reflection is useful to lead to improved academic performance
Concept
A mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, or people
Prototype
A mental image or best example of a category
Matching new items to a prototype is a quick and easy method for sorting items into categories (feathered creatures compared to crows)
Schema
A concept or framework that organises and interprets information (categorise what type of question each question is on a test)
Have to be added to or adjusted when we learn new information
Assimilation
Adapting our current schemas (understandings) to incorporate new information (using knowledge you have learnt on a test)
Accomodation
Adapting current schemas/understandings to incorporate new information (knowing what you got wrong on a test and adapting your knowledge to what is the right answer)
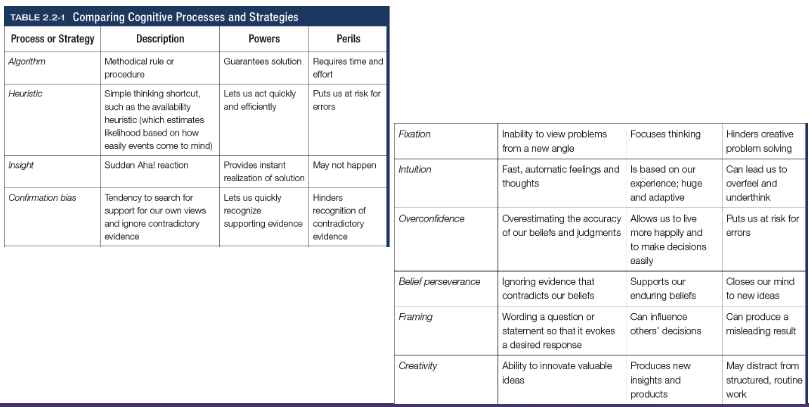
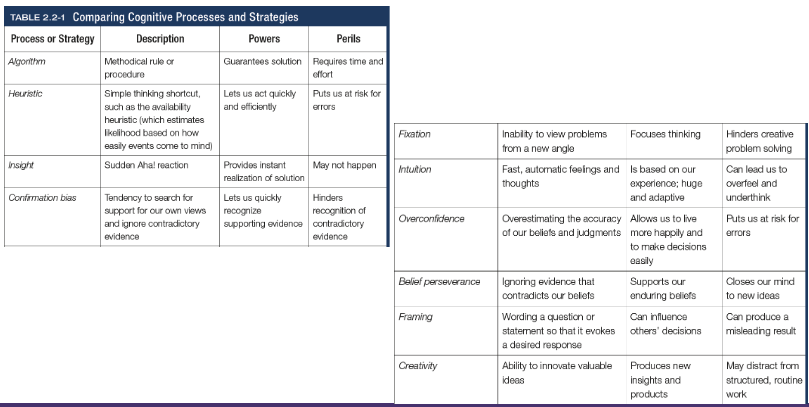
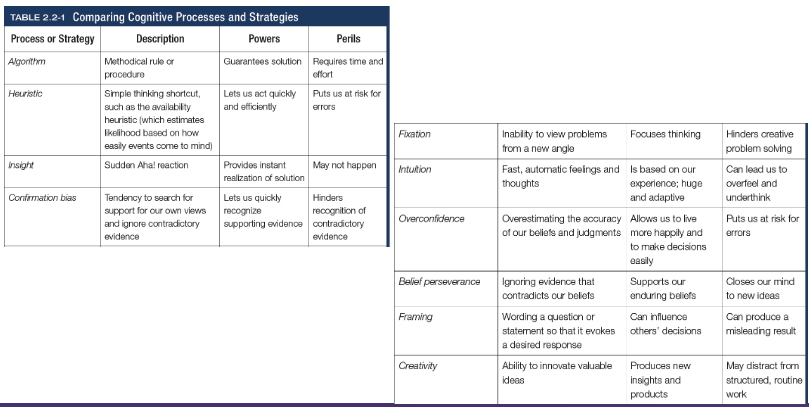
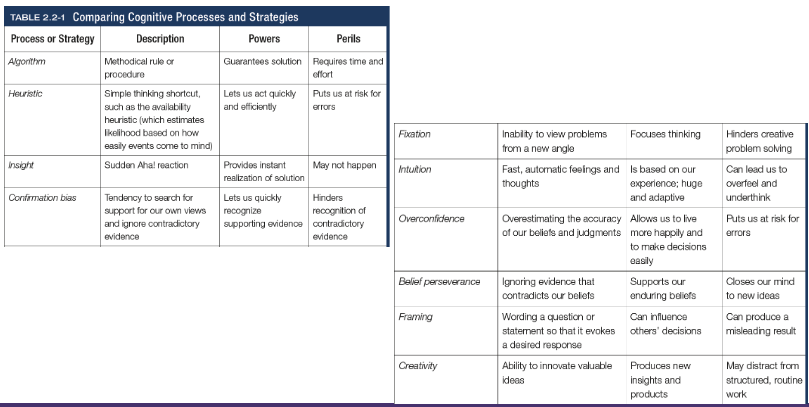
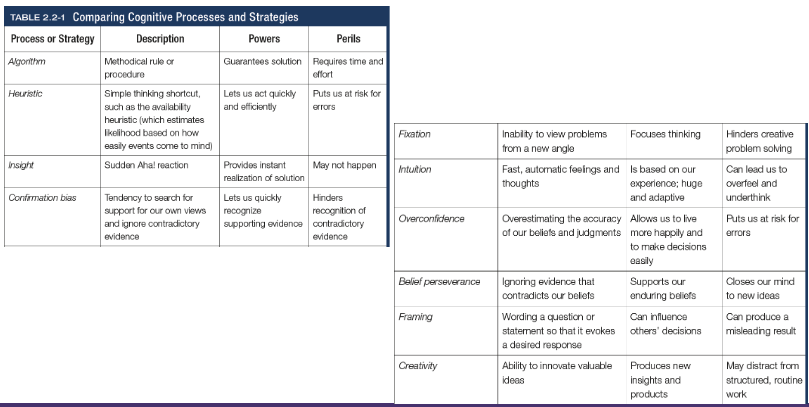
Creativity
The ability to produce new and novel ideas
Aptitude plays a role but is not the only factor in fostering it
Convergent thinking
Narrowing the available problem solutions to determine the single best solutions (cross out wrong answers on a test)
Divergent thinking
Expanding the number of possible problem solutions; creative thinking that diverges in different directions
Leads to more novel solutions
Robert Sternberg’s 5 components of creativity (EImVInC)
Expertise (expert skill and knowledge)
Imaginative thinking skills (using your imagination to generate new thinking skills)
Venturesome personality (adventurous, risk-taking, open to new information and insights)
Intrinsic motivation (drive to engage in activities because they are enjoyable)
Creative environment (encouragement of creative thinking)
Executive functioning
Cognitive skills that work together, enabling us to generate, organise, plan, and implement goal-directed behaviour
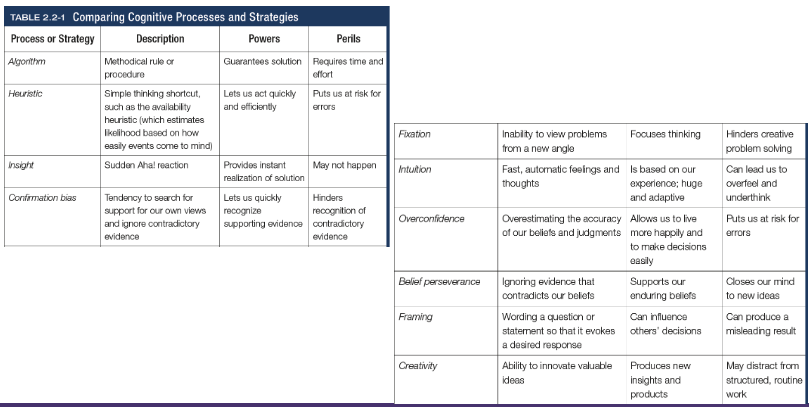
Algorithm
A methodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem, which contrasts with the usually speedier and more error prone heuristics
Heuristics
A simple thinking strategy - a mental shortcut - that often allows us to make judgements and solve problems efficiently (categorisation)
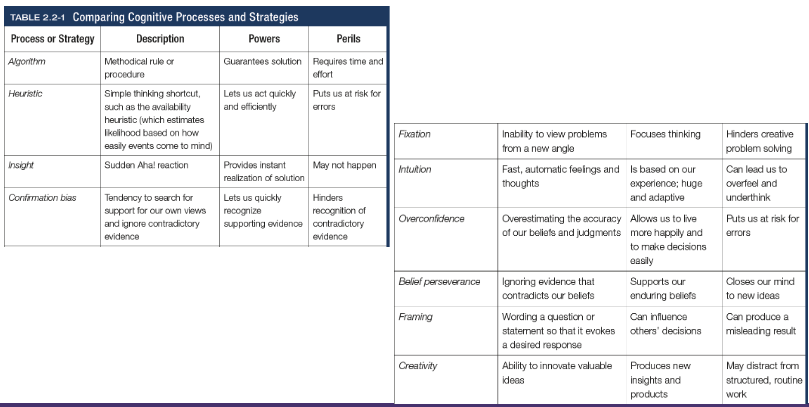
Insight
A sudden realisation of a problem’s solution; contrasts with strategy-based solutions
Confirmation bias
Tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence
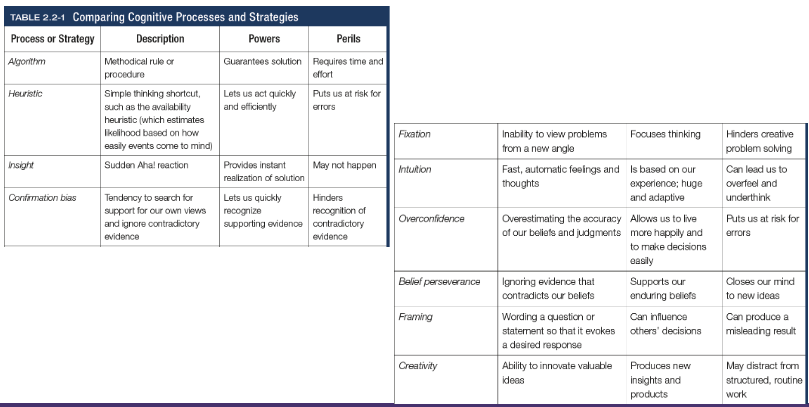
Fixation
In cognition, an inability to see the problem from a new perspective; an obstacle in problem solving
Mental set
Tendency to approach a problem in one particular way, often a way that has been successful in the past
Intuition
An effortless, immediate, automatic feeling or thought, as contrasted to explicit conscious reasoning
Representativeness heuristic
Judging the likelihood of events in terms of how well they seem to represent or match particular prototypes; may lead us to ignore other relevant information
Availability heuristic
Judging the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory; if instances come readily to mind, we assume such events are common
Overconfidence
The tendency to more confident than correct - to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgements
Lead to underplanning or planning fallacy, falling short on time or costs
Procrastination is an example
May have extreme effects in the real world
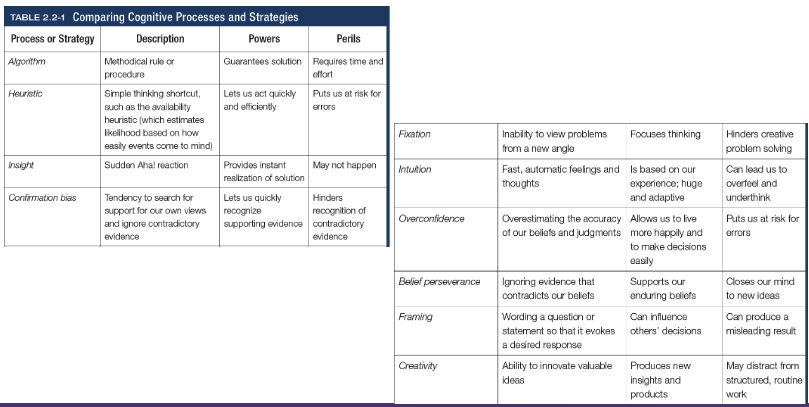
Belief preserverance
The persistence of one’s initial conceptions even after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited
Work together with confirmation bias; can be decreased if we open our minds and think critically
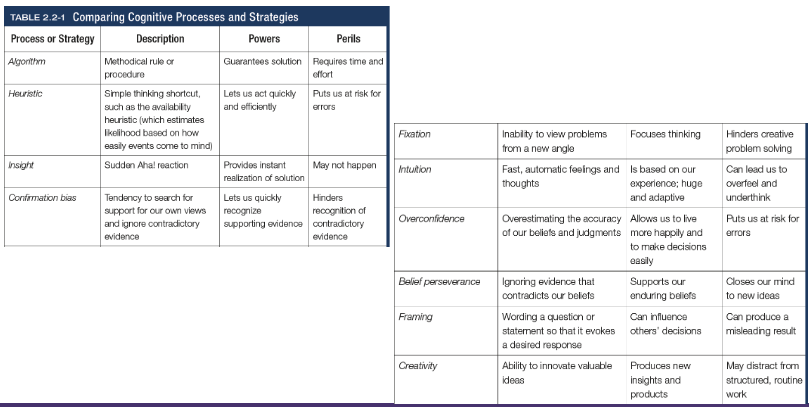
Framing
The way an issues is posed; how an issue is framed can significantly affect decisions and judgement
Nudge
Framing choices in a way that encourages people to make beneficial decisions
Intelligence
The ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations
Influences of nature and nurture debated
If intelligence is stable or if it can grow through experience
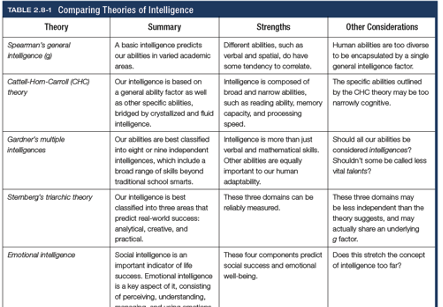
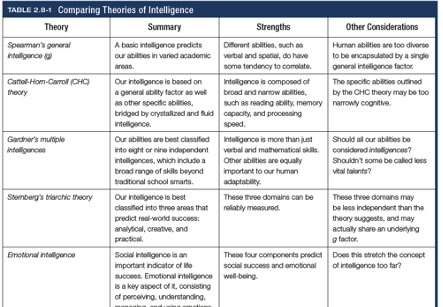
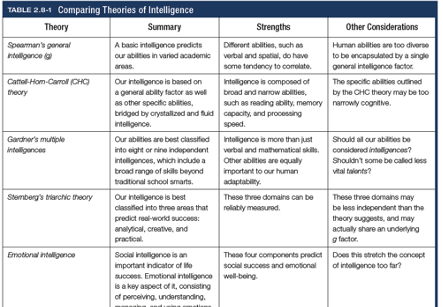
Charles Spearman’s general intelligence(g)
According to Charles Spearman and others, underlies all mental abilities and is therefore measured by every task on an intelligence test
Factor analysis
A statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items (called factors) on a test; used to identify different dimensions of performance that underlie a person’s total score
L. L. Thurstone’s clusters of primary mental abilities
Word fluency
Verbal comprehension
Spatial ability
Perceptual speed
Numerical ability
Inductive reasoning
Memory
Fluid intelligence (Gf)
Our ability to reason speedily and abstractly; tends to decrease with age
Crystallised intelligence (Gc)
Our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; tends to increase with age
Cattell-Horn-Carroll (CHC) theory
Theory that intelligence is based on g as well as specific abilities bridged by Gf and Gc
Savant syndrome
A condition in which a person otherwise limited in men tal ability has an exceptional skill
Grit
In psychology, passion and perseverance in the pursuit of long-term goals
Howard Gardner
Argues that intelligence should be measured in plurality rather than singularity (8 relatively independent intelligences)
Different parts of the brain have different roles in intelligence
Savant syndrome is a clear example
Gardner’s 8 intelligences
Linguistic
Logical-mathematical
Musical
Spatial
Bodily
Kinesthetic
Interpersonal
Intrapersonal
Naturalistic
Effects of general intelligence on the real world
Predict performance on complex tasks in various jobs
Correlated with exceptional achievements and increased education
It alone cannot predict overall success
Success is a combination of talent and grit
Intelligence and environment both play a role
Emotional intelligence
The ability to perceive, understand, manage, and use emotions
Has been overlooked
The higher it is the happier the person is
4 abilities of emotional intelligence (PUMU)
Perceiving
Understanding
Managing
UsingS
Sternberg’s triarchic theory
Intelligence is best classified into 3 areas that predict real-world success
Creative
Analytical
Practical
(CAP)
Intelligence test
Method for assessing an individual’s mental aptitudes and comparing them with those of others, using numerical scores
Achievement test
Test designed to assess what a person has learnt
Aptitude test
A test designed to predict a person’s future performance - capability to learn
Correlates with general intelligence
Simon Benet’s Mental age
A measure of intelligence test performance devised by Simon Benet; the level of performance typically associated with children of a certain chronological age
Lewis Terman’s Stanford-Binet
Widely used American revision (Terman at Stanford University) of Binet’s original intelligence test
Intelligence Quotient (IQ) by William Stern
Defined originally as the ratio of mental age to chronical age multiplied by 100, and the average performance is assigned a score of 100
(mental/chronological) * 100
Francis Galton’s eugenics
Measure abilities to limit people’s reproductive rights, but his theories were discarded; however his contributions on genetic influence on intelligence and the terms nature and nurture remain
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
The WAIS and it companion versions for children are the most widely used intelligence test that contain both verbal and performance subtests
Psychometrics
The scientific study of the measurement of human abilities, attitudes, and traits
Standardisation
Defining uniform testing procedures and meaningful scores by comparison with the performance of a pretested group
Tests must be periodically restandardised to adapt to changes in the population
Normal curve
The bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many physical and psychological attributes
Most scores fall near the average and fewer and fewer scores lie near the extremes
Flynn effect
The rise in an intelligent test performance over time and across cultures
Caused by better education, nutrition, and better standards
Acts as a counterargument to eugenics
Reliability
The extent to which a test yields consistent results, as assessed by the consistency of scores on 2 halves of the test, on alternate forms of the test, or on retesting.
Validity
The extent to which a test measures or predicts what it’s supposed to
Content validity
The extent to which a test samples the behaviour that is of interest
Predictive validity
Success with which a test predicts the behaviour it is designed to predict; correlation between test scores and criterion behaviour