15 - The Kidneys
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Main Functions of the Kidneys
Regulation of ECF volume and blood pressure
Regulation of osmolarity
Maintenance of ion balance
Homeostatic regulations of pH
Excretion of wastes
Production of hormones
1) Regulation of ECF volume and blood pressure
If ECF volume decreases, blood pressure decreases, and blood flow to brain and organs decreases
Kidneys work with cardiovascular system to maintain BP and tissue perfusion
2) Regulation of Osmolarity
Through thirst and drinking
Reabsorption of water (i.e. producing more concentrated urine)
Sensors for osmolarity found in hypothalamus and the kidney (macula densa)
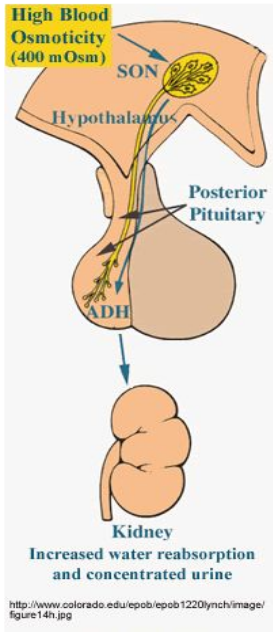
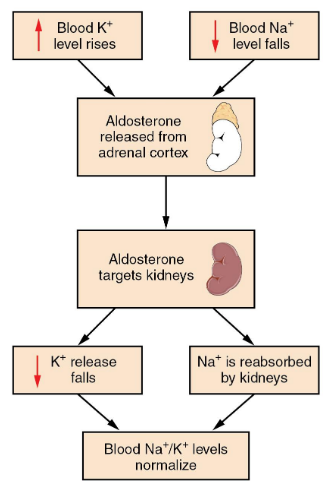
3) Maintenance of Ion Balance
Balance dietary intake with urinary loss (Na+, Ca2+, K+, etc.)
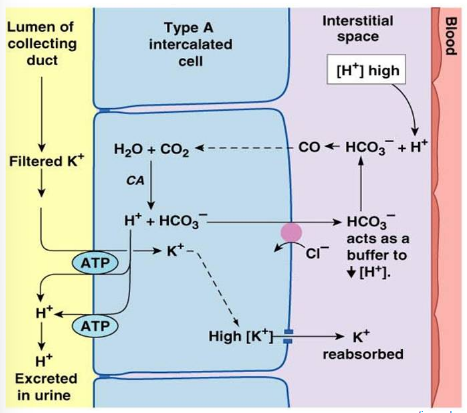
4) Homeostatic Regulation
Kidneys remove H+ and conserve HCO3- when pH decreases (perform the opposite when pH increases)
Not as big of a role as the lungs in pH balance
5) Excretion of wastes
Removal of metabolic waste products and foreign substances
6) Production of Hormones
Erythropoietin for RBC synthesis
Renin for Na+ balance
Vitamin D for Ca2+ balance
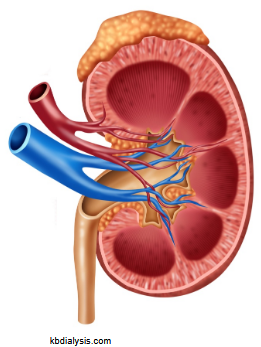
Characteristics of the Kidneys
Have a renal artery and vein
Receives 20-25% of cardiac output (but only represents 0.4% of body weight)
Acts on plasma flowing through it to produce urine
Outer surface - the renal cortex
Inner surface - the renal medulla
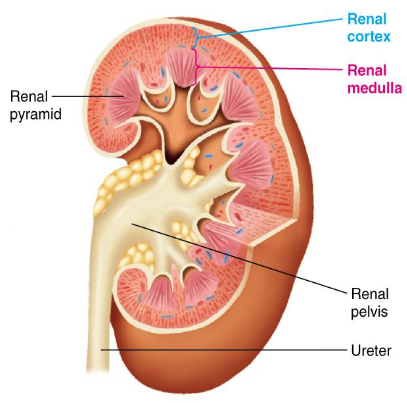
Characteristics of the Ureters
Hollow tube leading from kidney to bladder
One for each kidney
Characteristics of the Bladder
Temporarily stores urine
Hollow, distensible, smooth muscle-walled sac
Periodically empties to the outside of the body through the urethra
Characteristics of the Urethra
Conveys urine to the outside of the body
Females = straight and short
Males = longer and curved
Dual functions:
Route for eliminating urine from the bladder
Passageway for semen from reproductive organs
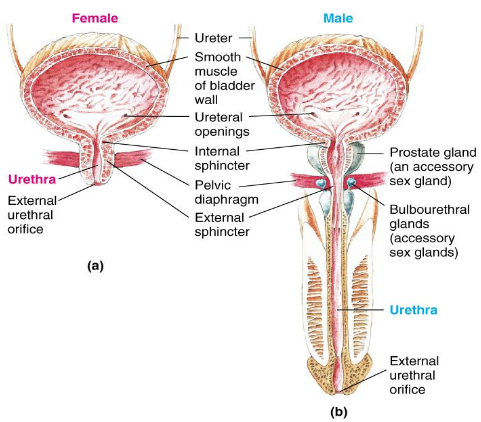
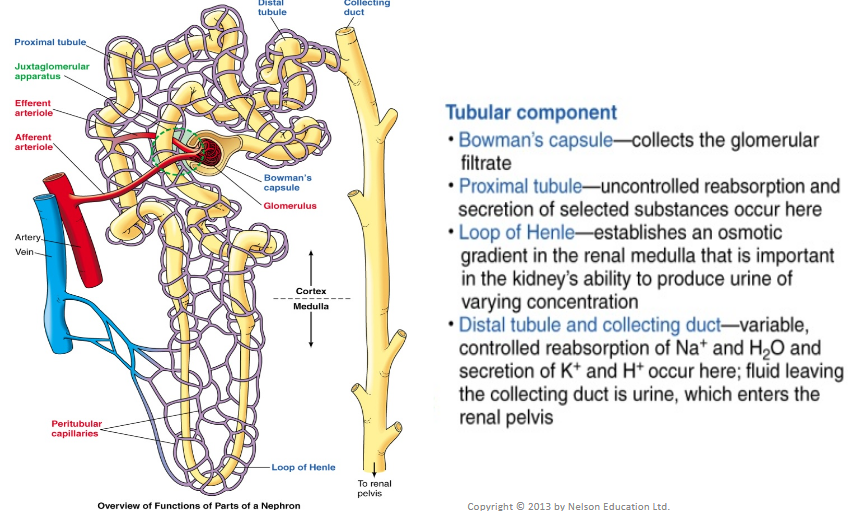
Characteristics of the Nephron
Functional unit of the kidney
Smallest unit that can perform all the functions of the kidney
The arrangement of the nephrons produces two distinct regions:
Renal cortex (granular in appearance)
Renal medulla (made up of striated triangles called renal pyramids)
Two types of nephrons are distinguished by location and length of their structures
Juxtamedullary nephrons
Cortical nephrons (80% of all nephrons)
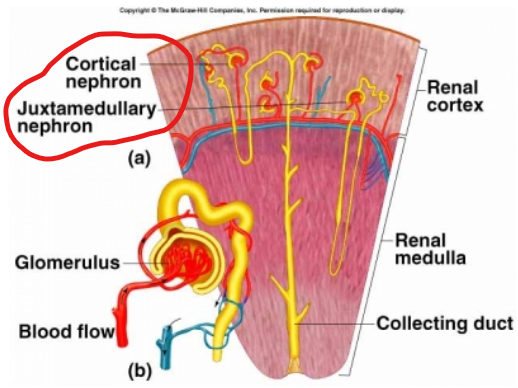
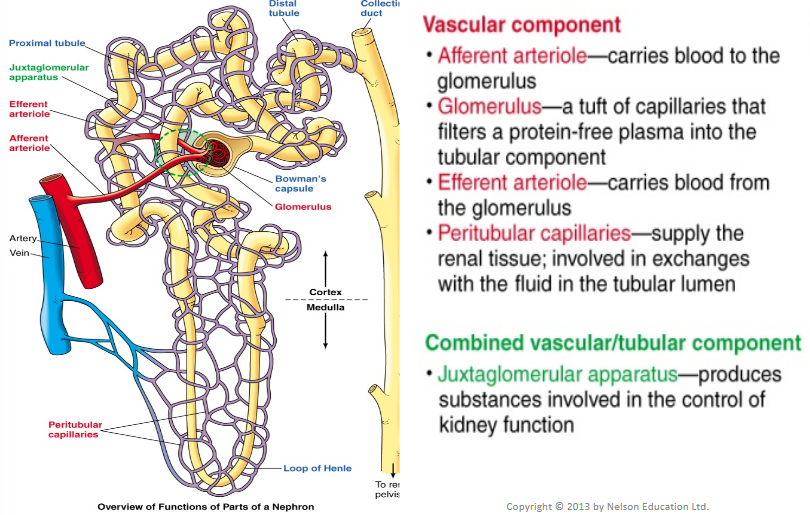
Components of the Nephron (2)
Vascular component
Tubular component
Both components have countercurrent flow - essential to function
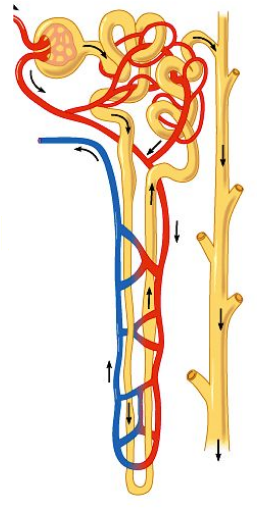
The Glomerulus - Vascular Component
Dominant part of the vascular component
Water and solutes are filtered as blood passes through the glomerulus
From the renal artery, in-flowing blood passes through afferent arterioles which deliver blood to glomerulus
Filtered fluid then passes through nephron’s tubular component
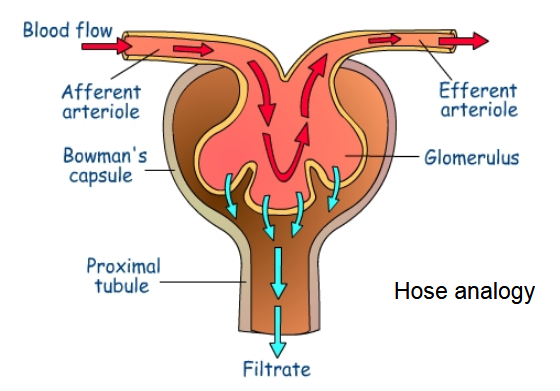
Vascular Component of the Nephron
Efferent arteriole transports blood from glomerulus
Efferent arteriole breaks down into peritubular capillaries which surround tubular part of nephron
Peritubular capillaries join into venules which transport blood into the renal vein
Tubular Component of the Nephron
Hollow, fluid-filled tube formed by a single layer of epithelial cells
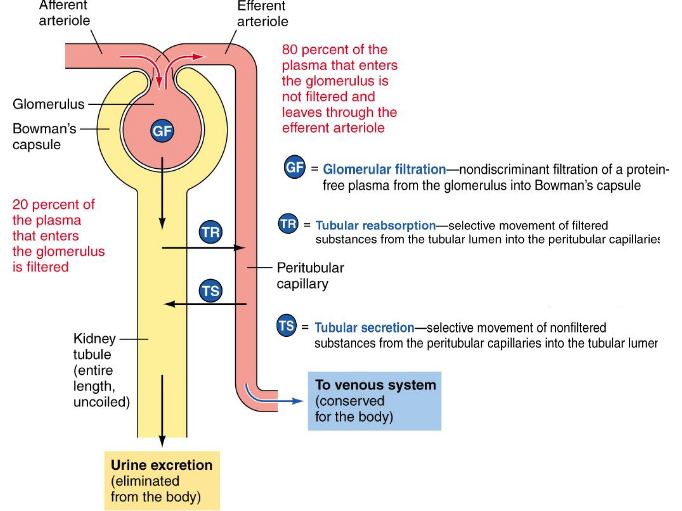
The 3 Basic Renal Processes
Glomerular filtriation - movement of fluid from the blood into the lumen of the nephron
Tubular reabsorption - substances from filtrate moved back into the blood (peritubular capillaries)
Tubular secretion - removes molecules from blood and adds them to filtrate in the lumen
Items in the lumen are destined to be removed, if the body wants to keep it must be removed/reabsorbed
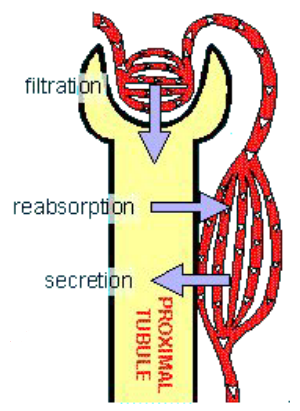
1) Glomerular Filtration
First step in urine formation
Filtrate similar to plasma in composition (but has no plasma proteins)
20% of plasma that enters glomerulus is filtered (180L/day of filtered fluid formed)
Transfer between kidney tubules and pertubular capillaries ensures that enough fluid is kept in the system
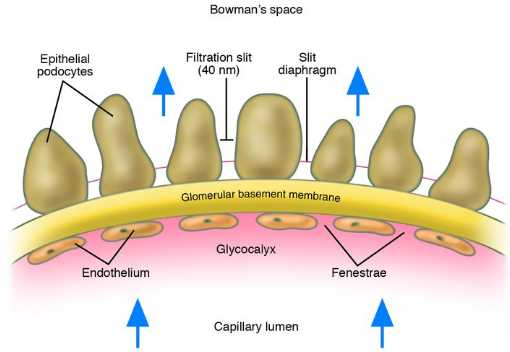
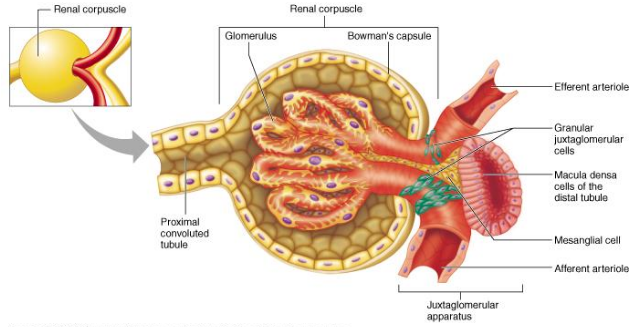
Renal Corpuscle
Glomerular capillaries surrounded by Bowman’s capsule

3 Filtration barriers components had to pass through - Glomerular Filtration
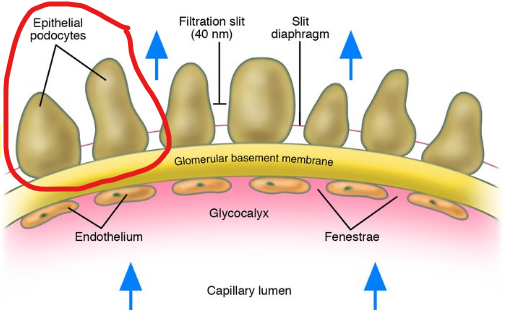
Glomerular capillary epithelium (fenestrated)
The pores in the glomerular capillaries are fairly large (to allow for bulk fluid to move out of the vessel)
Basal lamina (aka. basement membrane)
Epithelium of Bowman’s capsule
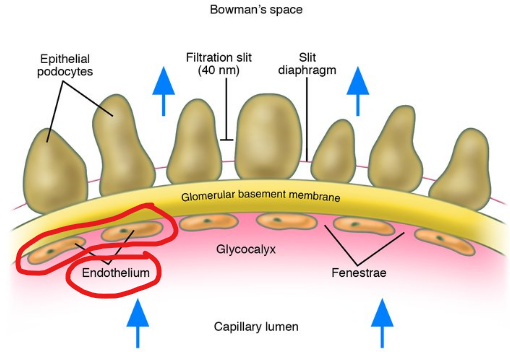
1) Glomerular Capillary Wall
Single layer of flattened endothelial cells
Large pores
100x more permeable to water and solute than other capillaries
HIGHLY permeable
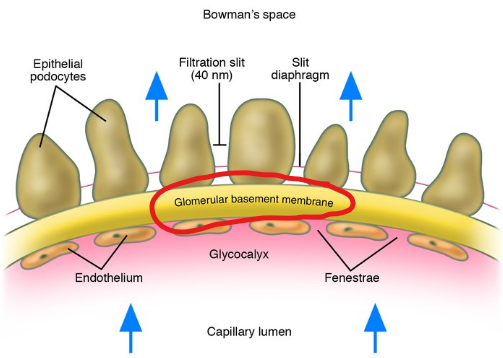
2) Basal Lamina
Basement membrane
Acellular gelatinous layer
Composed of collagen & glycoproteins
Negatively charged glycoproteins repel negatively charged plasma proteins
3) Epithelium of Bowman’s Capsule
Consists of podocytes (special endothelial cells)
Podocyte “feet” mingle with neightbouring podocyte “feet”
Sits between the feet used for filtration
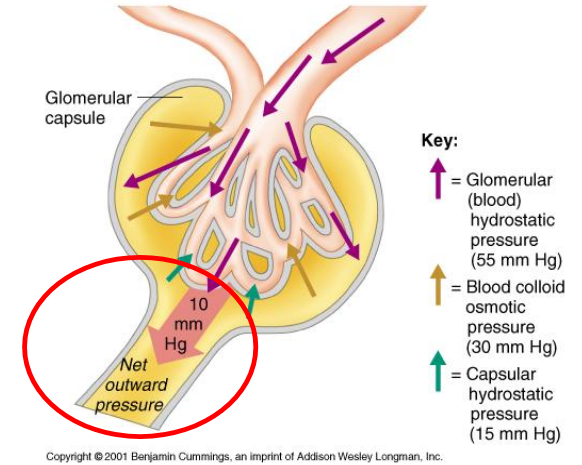
Physical Forces Involved in Glomerular Filtration (3)
Glomerular capillary blood (hydrostatic) pressure
Plasma-colloid osmotic pressure
Bowman’s capsule hydrostatic pressure
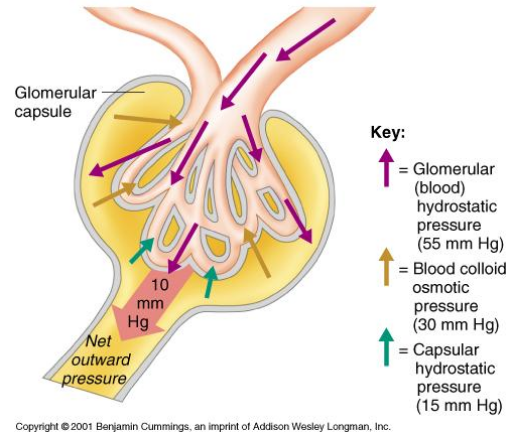
1) Hydrostatic pressure of blood
Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries
Depends on:
Contraction of the heart
Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Major force producing glomerular filtration
~55 mmHg
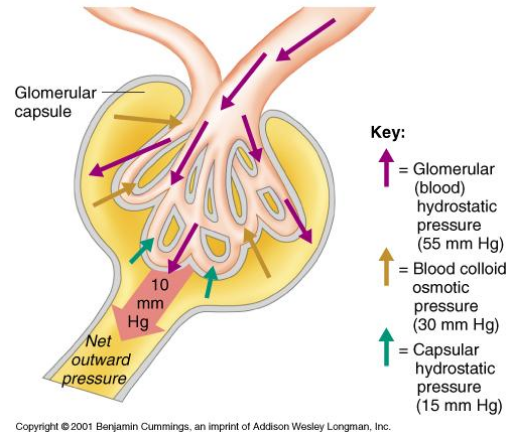
2) Plasma-Colloid Osmotic Pressure
Causes by unequal distribution of plasma proteins across glomerular membrane
Opposes filtration (favours movement back into the capillaries)
~30 mmHg
3) Bowman’s Capsule Hydrostatic Pressure
Pressure exerted by fluid in initial part of tubule
Tends to push fluid out of Bowman’s capsule
Opposes filtration
~15 mmHg
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Volume of fluid that filters into Bowman’s capsule per unit time
Influenced by net filtration pressure and filtration coefficient
Filtration coefficient has two components:
Surface area of glomerular capillaries available for filtration (mesangial cells & constriction)
Permeability of interface between the capillary and Bowman’s capsule (podocytes)
Controlled Adjustments in GFR
GFR too high = an excess of water and solutes is lost due to high urine output
GFR too low = waste builds up
Glomerular capillary BP can be controlled to adjust GFR to suite the body’s need
Two major control mechanisms:
Autoregulation
Extrinsic sympathetic control
Autoregulation
Prevents spontaneous changes in GRF
Myogenic mechanism (contraction in response to stretch — muscle)
Tubuloglomerular feedback (TGF)
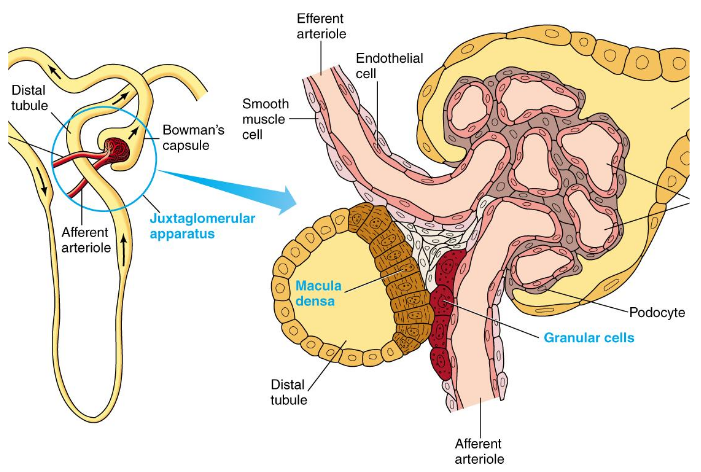
Tubuloglomerular Feedback
Involves juxtaglomerular apparatus (where tubule passes through angle formed by afferent and efferent arterioles)
Specialized tubular cells (macula densa) detected changes in salt level of fluid flowing by
Increased GFR = increased salt delivery
Release of ATP from macula densa cells results in increased adenosine levels
Adenosine causes vasoconstriction in adjacent afferent arteriole and decreased GFR
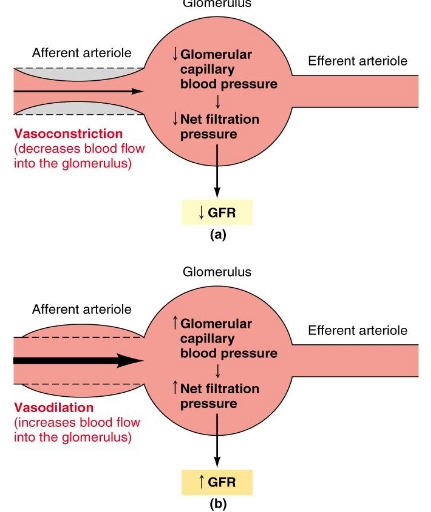
Extrinsic Sympathetic Control
Overrides autoregulatory responses
Aimed at long-term regulation of arterial blood pressure
Mediated by smpathetic nervous system input to afferent arterioles (increase peripheral resistance)
Baroreceptor reflex causes vasoconstriction of afferent arteriole when BP is low
Decreased GFR = decreased urine output; conservation of plasma volume
Tubular Reabsorption