Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Images
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
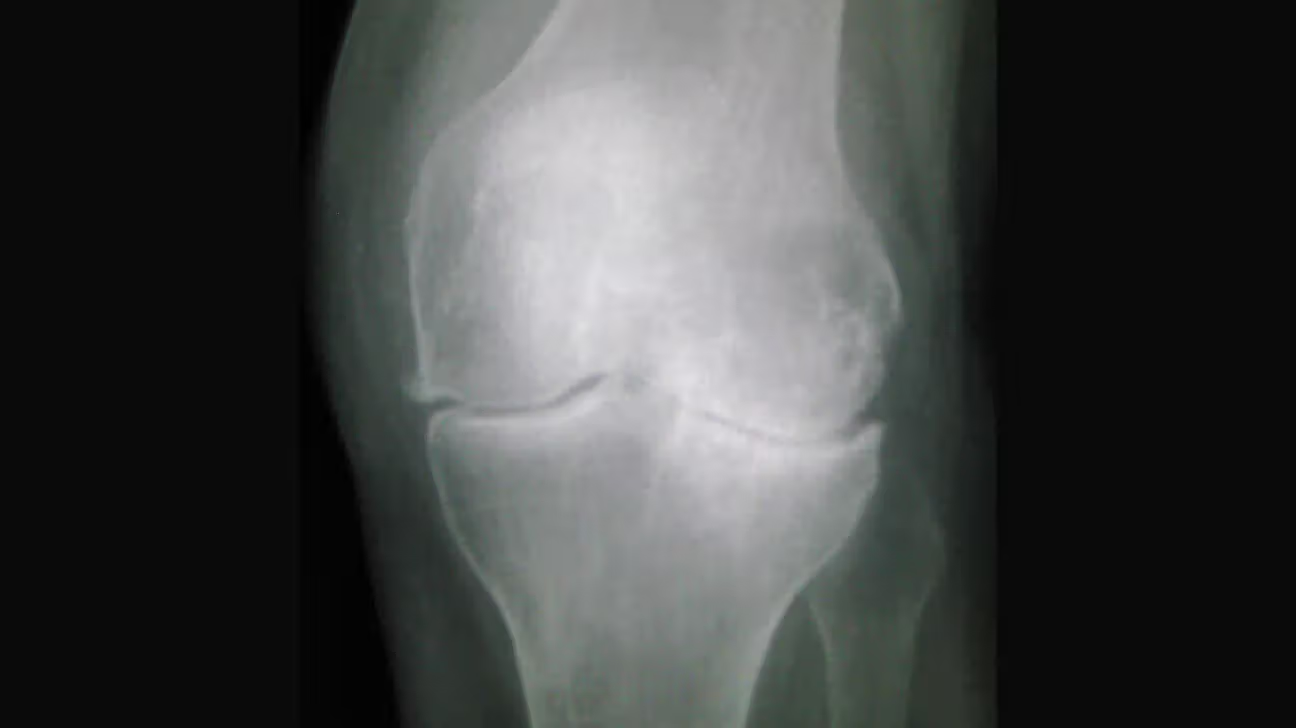
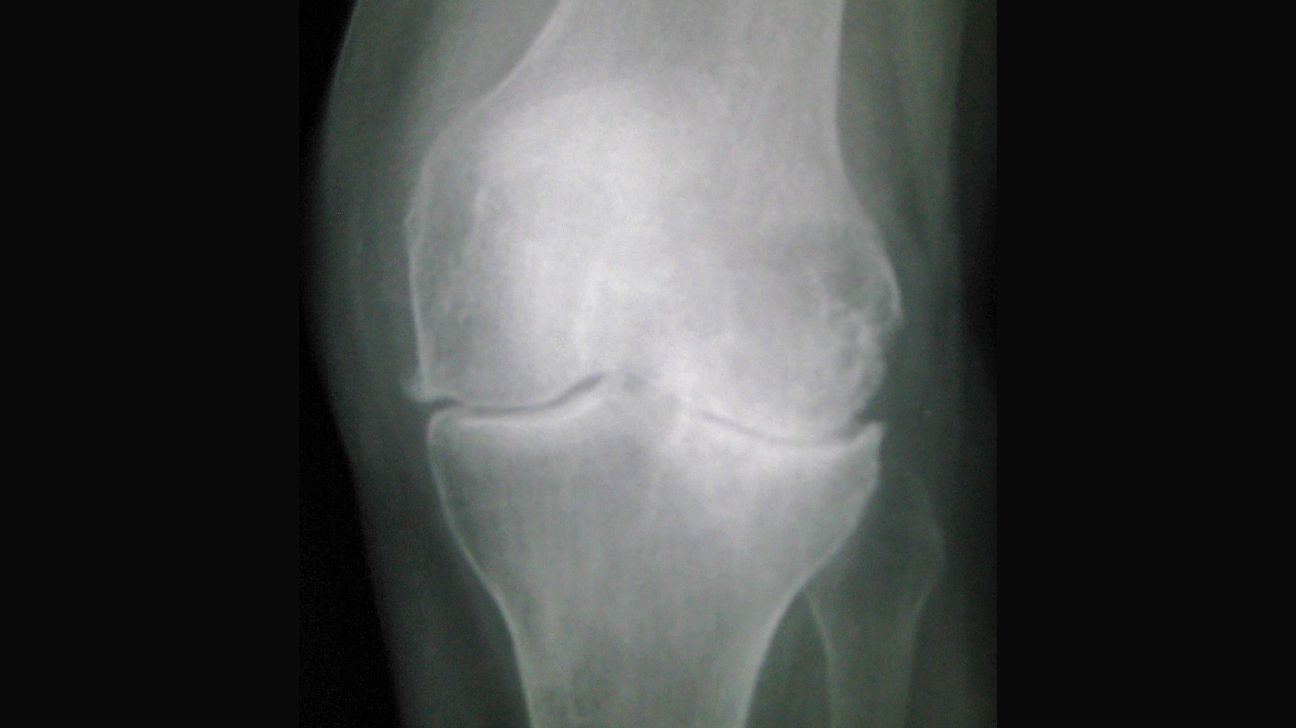
-
Osteoarthritis.
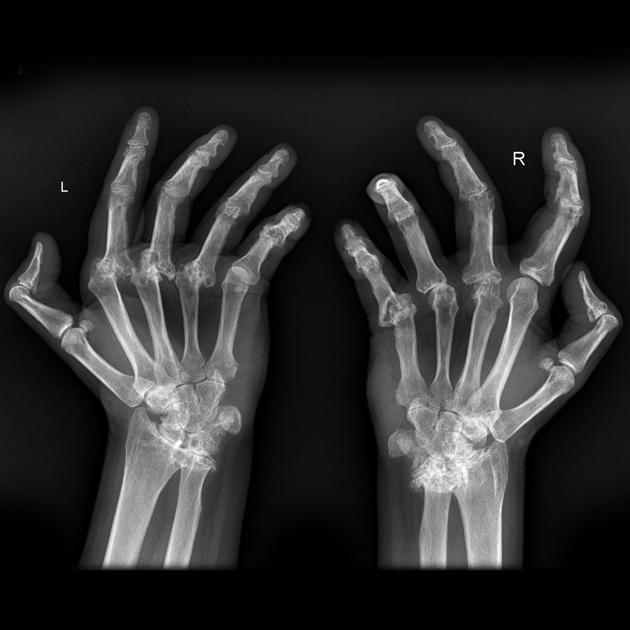
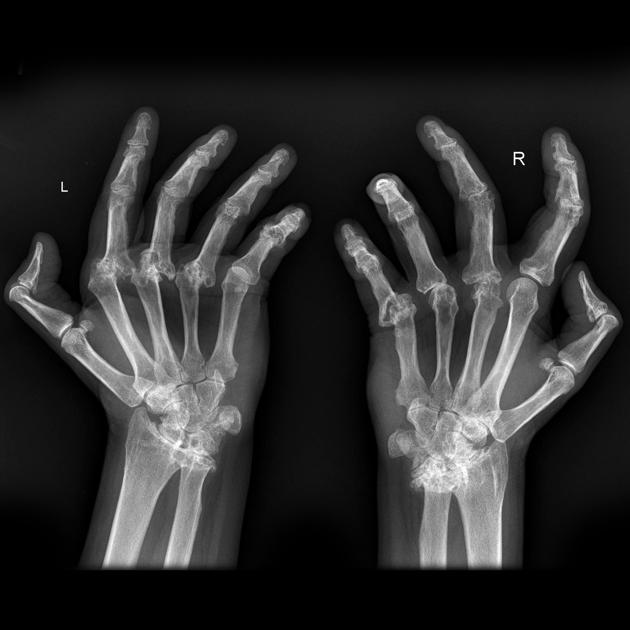
-
Rheumatoid arthritis.

-
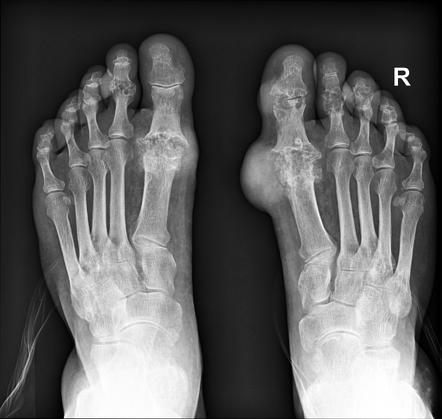
Gout
-
Osteoporosis (note Fractures in spine)
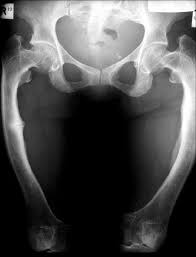
-
Rickets/osteomalacia.

-
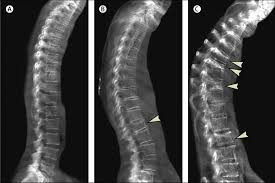
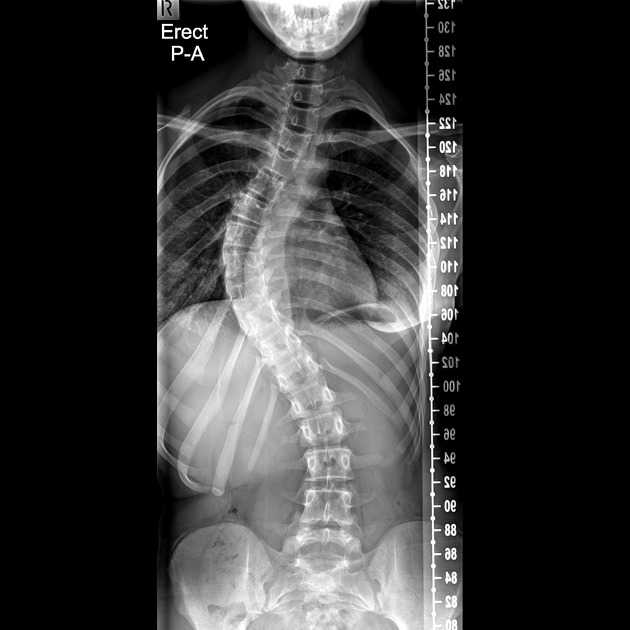
Scoliosis.
-
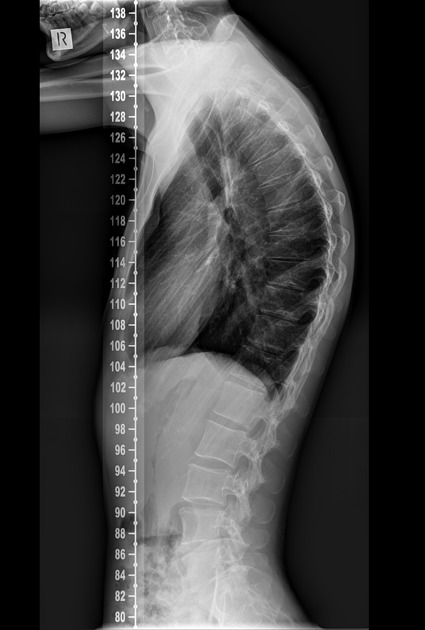
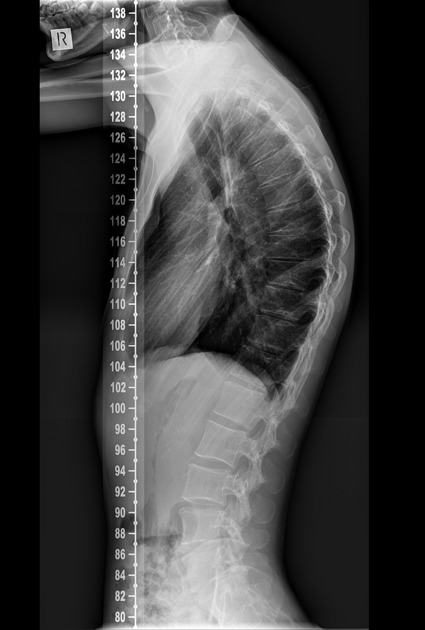
Kyphosis
-
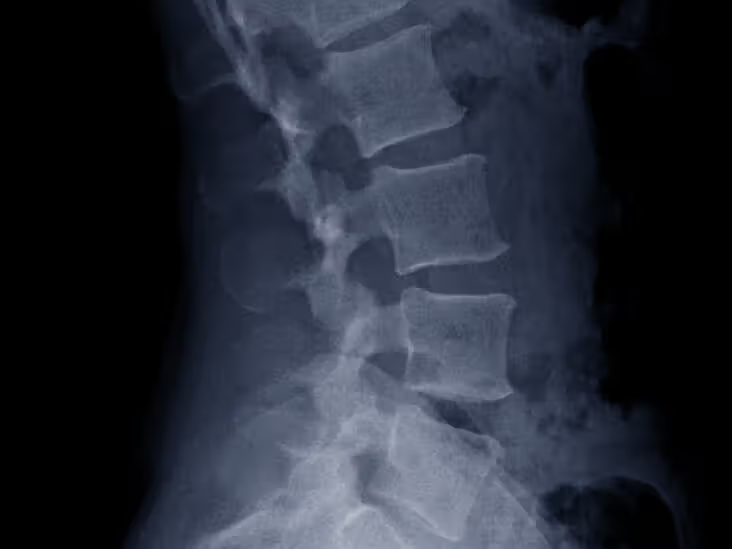
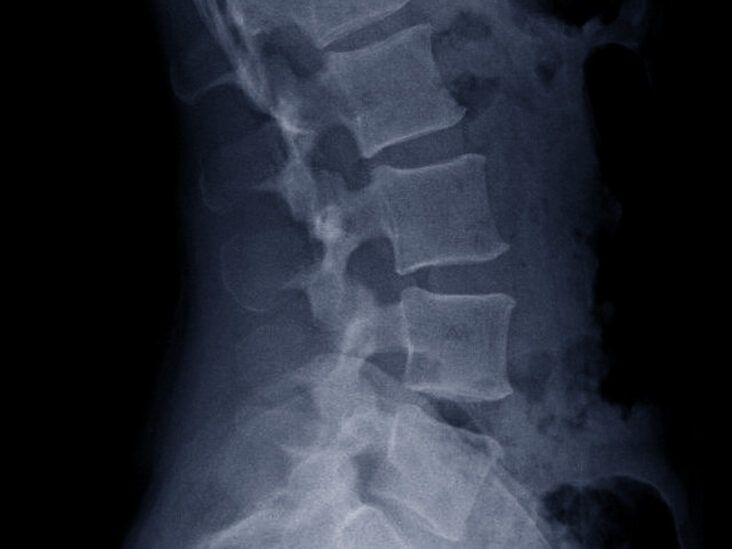
Lordosis.
-
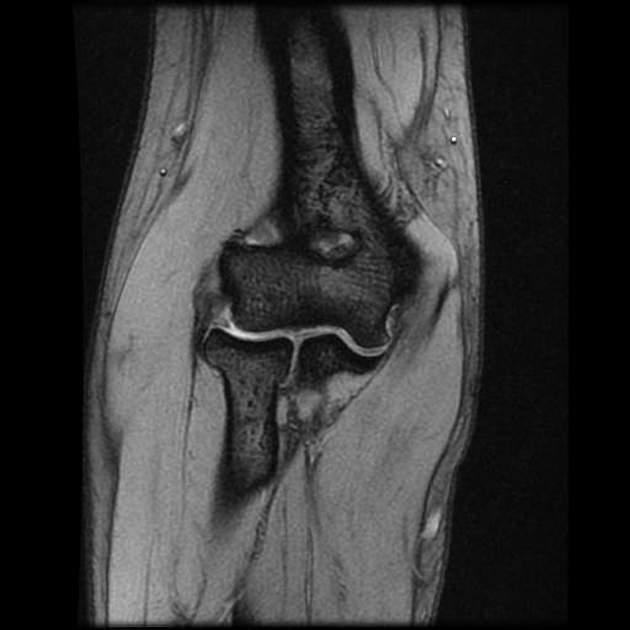
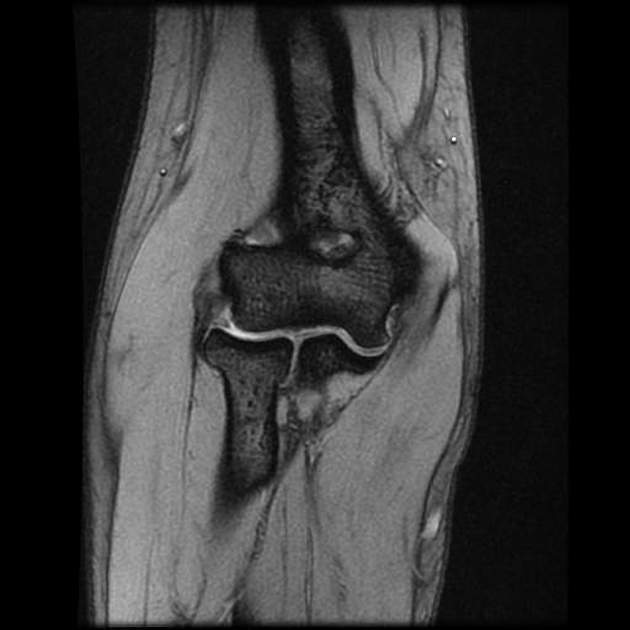
Lateral epicondylitis/tennis elbow (look for thickening of the common extensor’s origin which is a tendon).
-
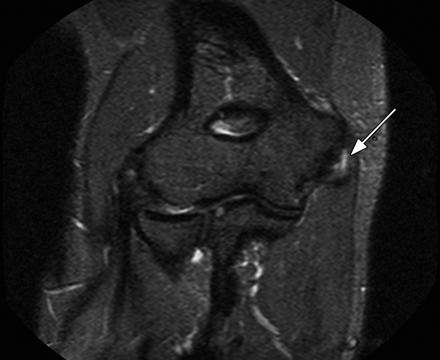
golfer’s elbow/medial epicondylitis.
-
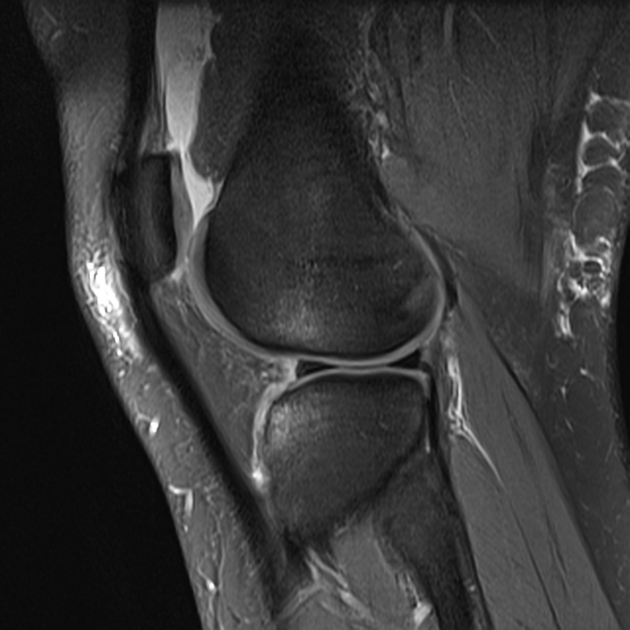
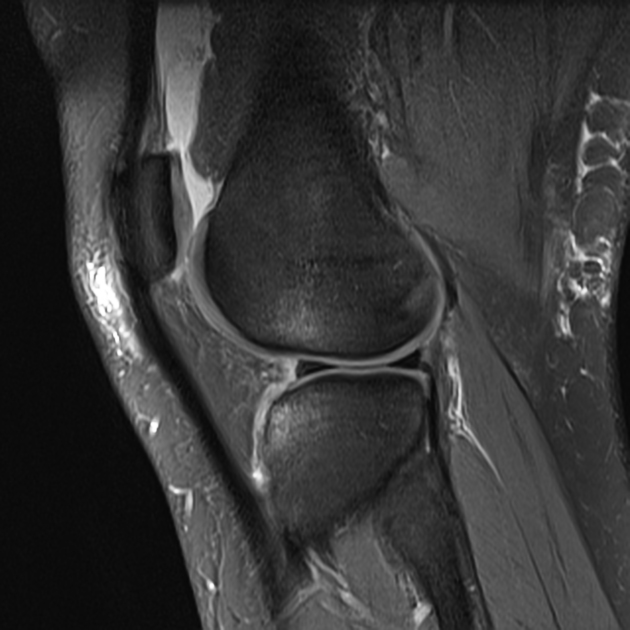
Cruciate ligament tears of the knee.
-
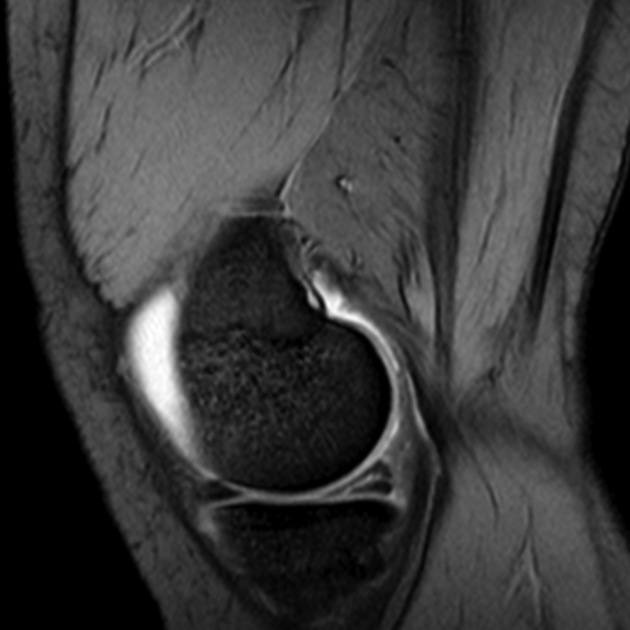
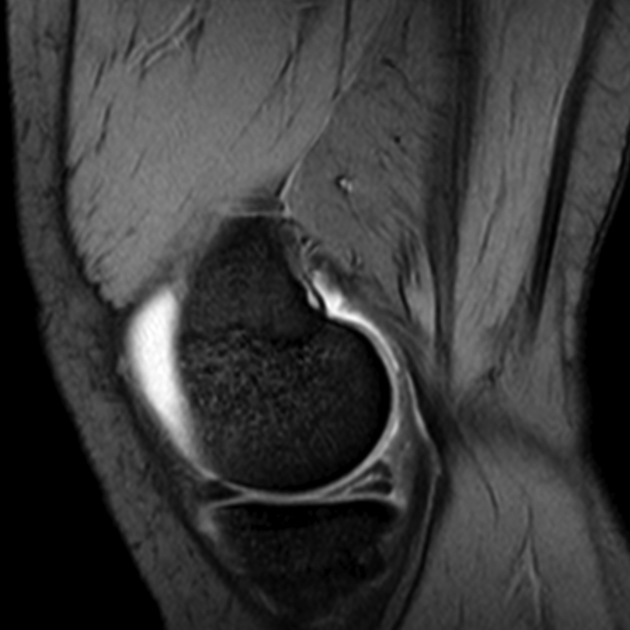
Meniscus tears of the knee.

-
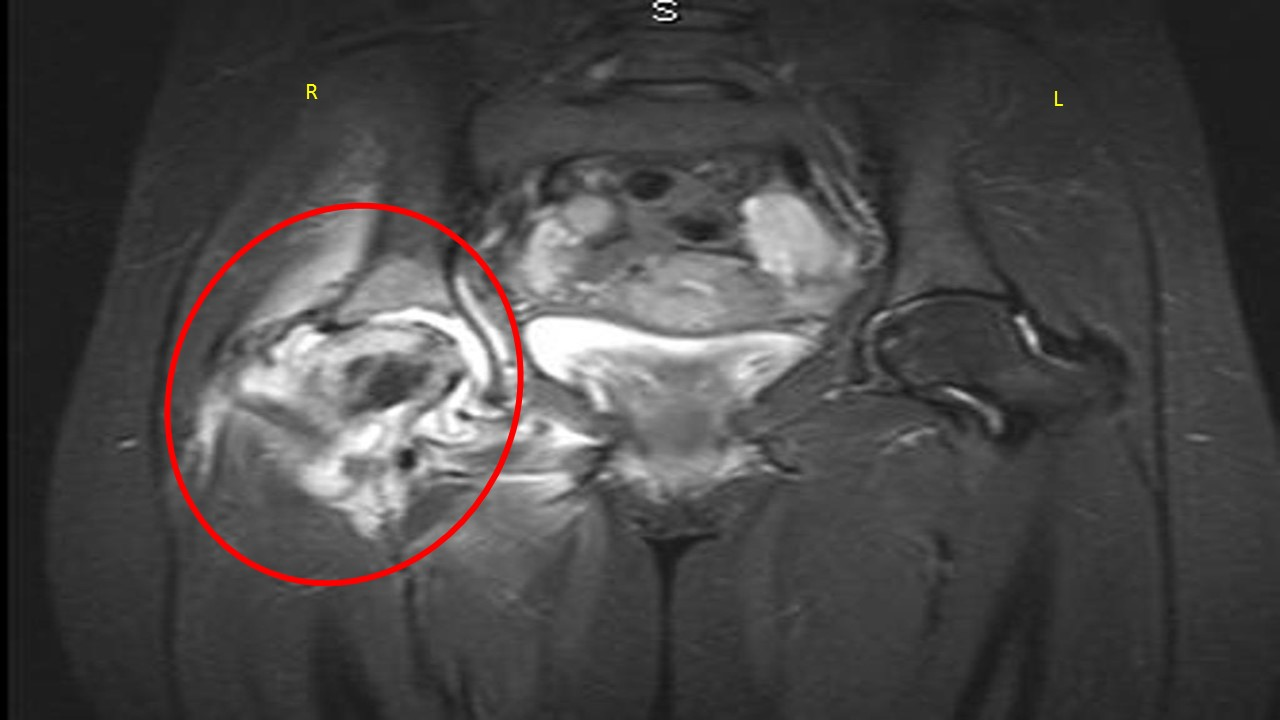
septic arthritis.
What is HPV? What are its symptoms? Risk factors? How is it treated?
1) Viral infection with over 100 strains; some cause warts, others linked to cancers.
2) Warts on skin/genitals, and in high-risk strains, asymptomatic until cancers develop (e.g., cervical cancer).
3) Unprotected sex, multiple partners, weakened immunity, and lack of vaccination.
4) Vaccination, wart removal (cryotherapy, topical agents), and monitoring for cancerous changes
What are boils? What are their symptoms? Risk factors? How is treated?
1) Painful skin abscess caused by infected hair follicles or sweat glands.
2) Red, swollen bump, often with pus; may rupture and drain.
3) Poor hygiene, weakened immunity, and close contact with infected individuals.
4) Warm compresses, drainage, antibiotics (if severe), and hygiene improvements.
What are carbuncles? What are their symptoms? Risk factors? How are they treated?
1) Clusters of boils forming a larger infected area.
2) Multiple red, swollen, pus-filled lumps; fever and fatigue in severe cases.
3) Same as boils, plus diabetes or other chronic conditions.
4) Warm compresses, drainage, antibiotics, and addressing underlying health conditions.
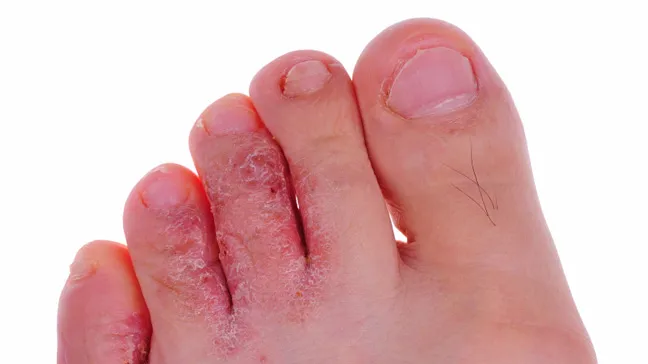
What is Athlete’s foot? What are its symptoms? Risk factors? How is it treated?
1) Fungal infection of the feet (tinea pedis).
2) Itchy, scaly skin between toes, redness, and cracking.
3) Sweaty feet, damp footwear, shared surfaces (e.g., showers, locker rooms).
4) Antifungal creams, powders, and keeping feet dry; oral antifungals for severe cases.
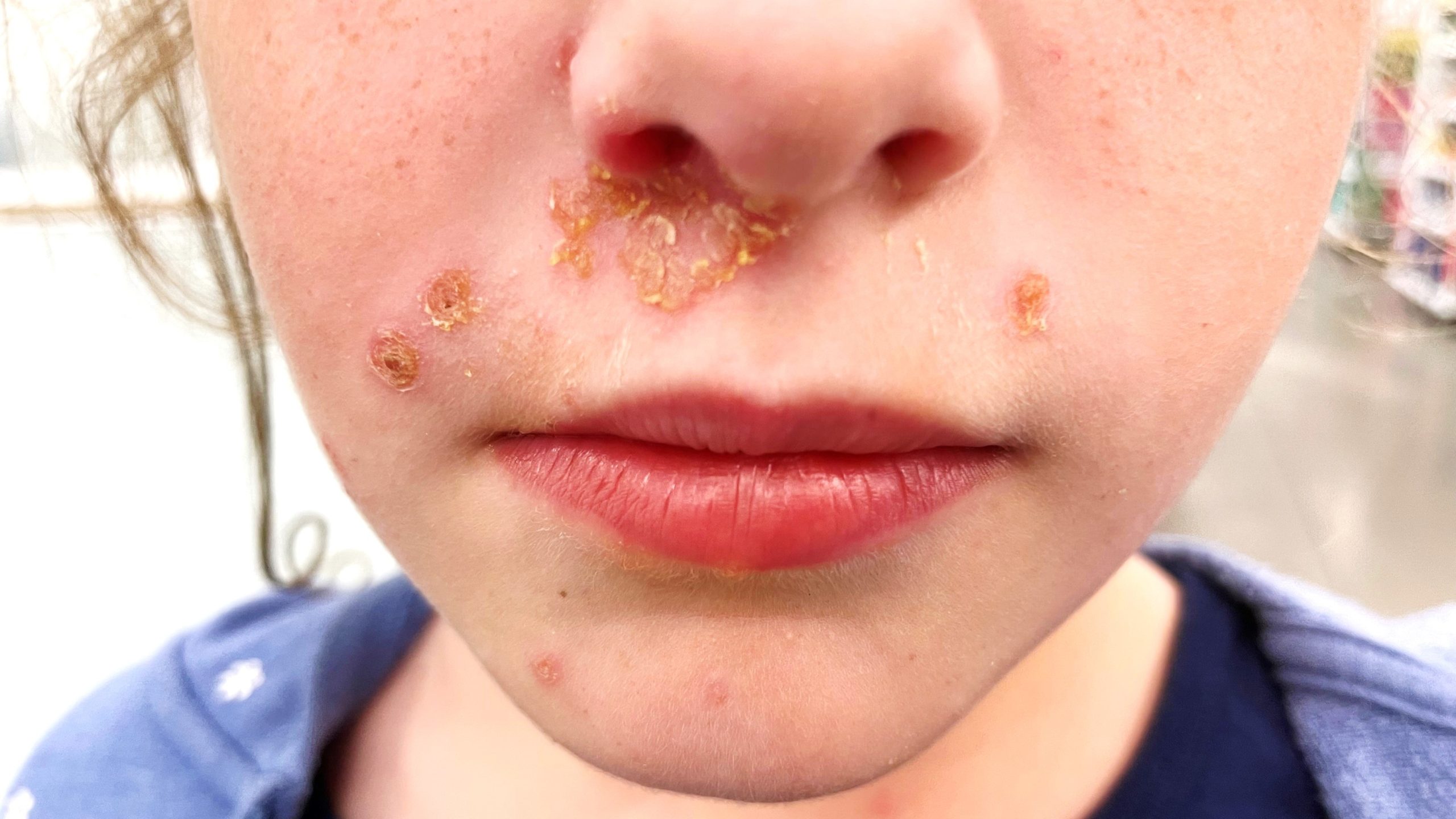
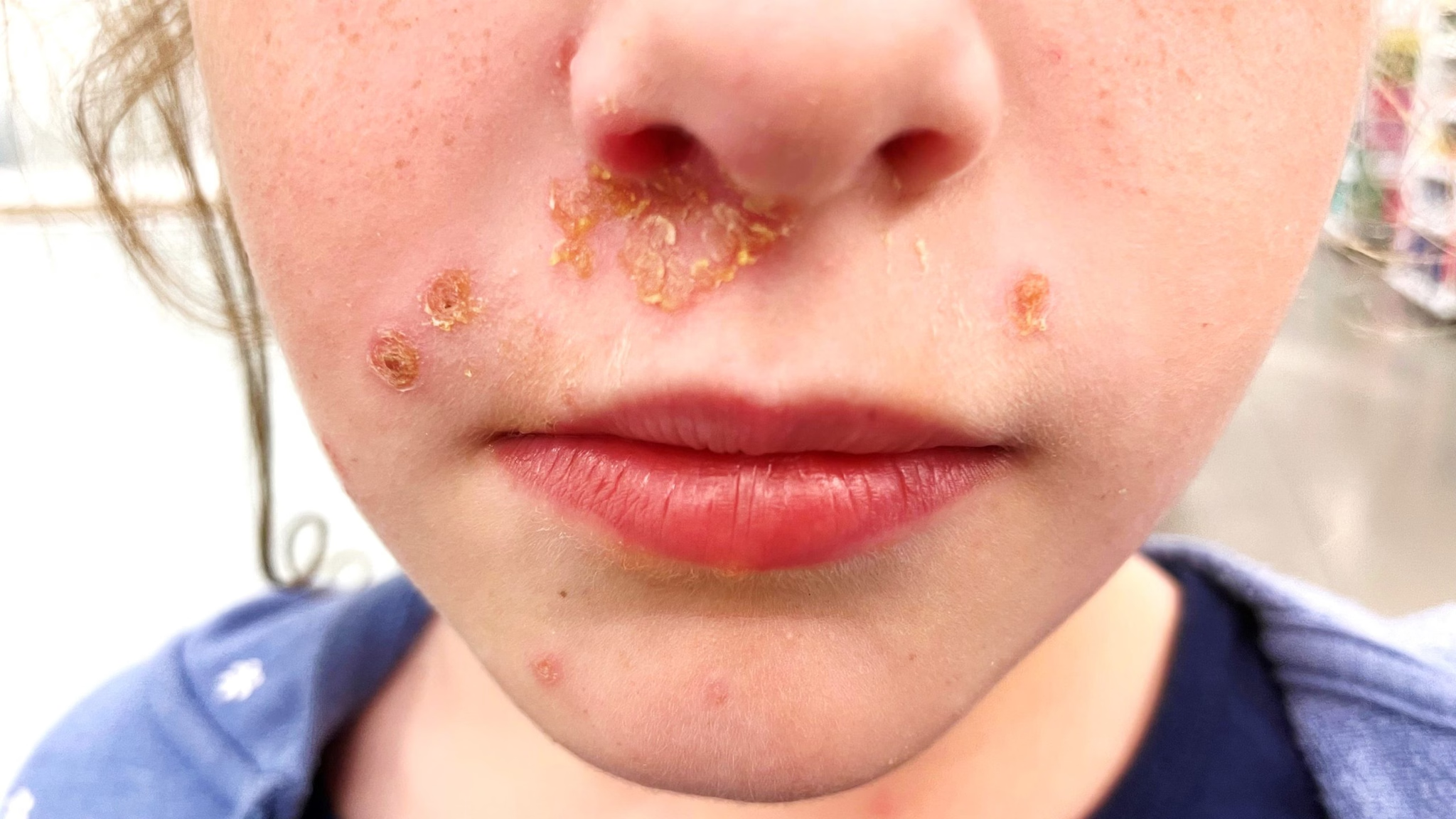
What is impetigo? What are its symptoms? Risk factors? How is it treated?
1) Highly contagious bacterial skin infection (often caused by Staphylococcus or Streptococcus).
2) Red sores that rupture, ooze, and form a yellow crust, often around the mouth or nose.
3) Young age, close contact, warm climates, and skin injuries.
4) Topical or oral antibiotics and hygiene improvements to prevent spread.
What is erysipelas? What are its symptoms? Risk factors? How is it treated?
1) Superficial bacterial skin infection caused by Streptococcus.
2) Red, raised rash with sharp borders, fever, chills, and swollen lymph nodes.
3) Skin breaks, diabetes, lymphedema, and weakened immunity.
4) Antibiotics (penicillin or related drugs) and managing underlying conditions.
What is cellulitis? What are its symptoms? Risk factors? How is it treated?
1) Bacterial infection of deeper skin layers and underlying tissue.
2) Redness, swelling, warmth, tenderness, and fever; can spread rapidly.
3) Skin wounds, obesity, diabetes, and immune suppression.
4) Oral or IV antibiotics, wound care, and addressing entry points of infection.
What is Hansen’s disease? What are its symptoms? Risk factors? How is it treated?
1) Chronic bacterial infection (Mycobacterium leprae), also known as leprosy.
2) Skin lesions, numbness, muscle weakness, and disfigurement in advanced cases.
3) Close contact with untreated individuals, genetic susceptibility, and poor living conditions.
4) Antibiotics (multidrug therapy) and supportive care.
What is chickenpox? What are its symptoms? Risk factors? How is it treated?
1) Viral infection caused by Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV).
2) Itchy, blister-like rash, fever, fatigue, and headache.
3) Lack of vaccination and exposure to infected individuals.
4) Symptomatic care (antihistamines, fever reducers); antivirals in severe cases.
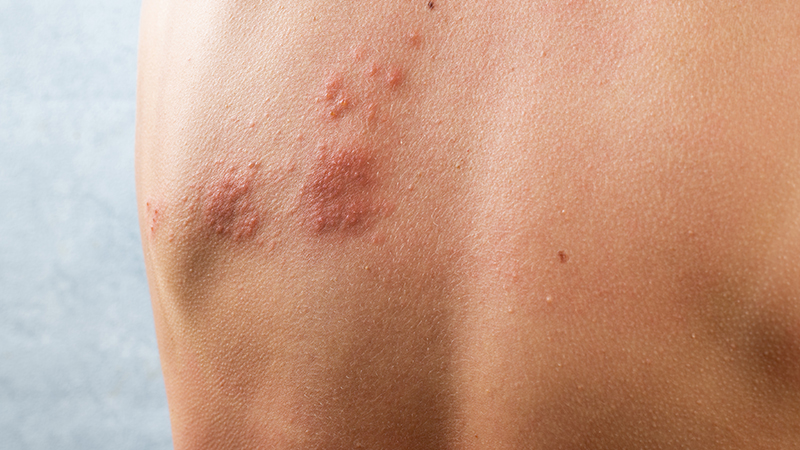
What is shingles? What are its symptoms? Risk factors? How is it treated?
1) Reactivation of latent Varicella-Zoster Virus.
2) Painful rash, often in a band-like pattern; may cause nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia).
3) Prior chickenpox infection, aging, stress, and immune suppression.
4) Antivirals (e.g., acyclovir), pain management, and shingles vaccination for prevention.
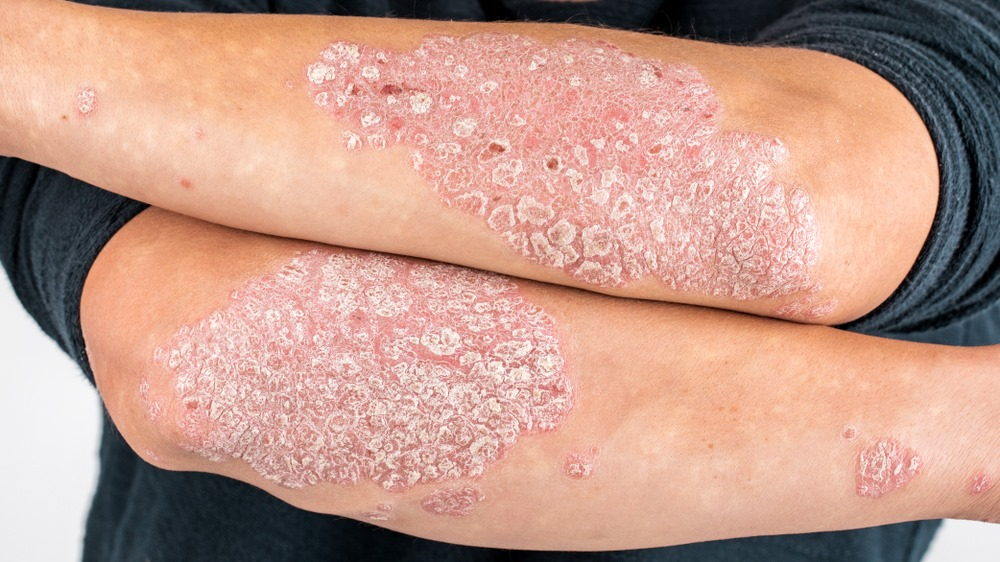
What is psoriasis? What are its symptoms? Risk factors? How is it treated?
1) Chronic autoimmune skin disorder causing rapid skin cell buildup.
2) Thick, scaly plaques, itching, redness, and cracking skin.
3) Family history, stress, smoking, infections, and certain medications.
4) Topical treatments (steroids, vitamin D analogs), phototherapy, and systemic medications (biologics).
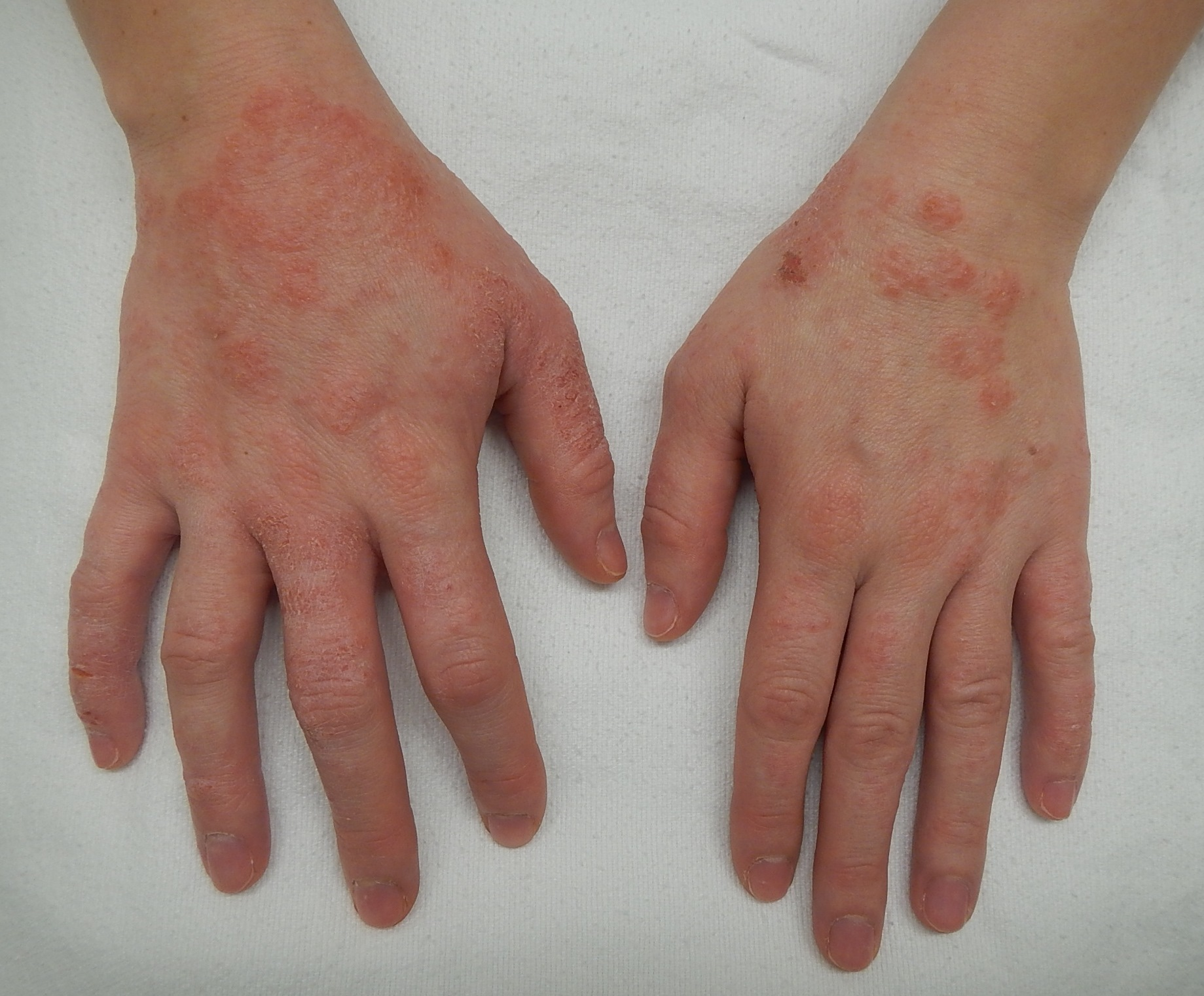
What is dermatitis? What are its symptoms? Risk factors? How is it treated?
1) Inflammation of the skin; includes atopic dermatitis (eczema) and contact dermatitis.
2) Redness, itching, swelling, and sometimes blistering or scaling.
3) Allergens, irritants, stress, and genetic predisposition.
4) Avoiding triggers, moisturizers, corticosteroids, and antihistamines.
What is Kaposi’s sarcoma? What are its symptoms? Risk factors? How is it treated?
1) Cancer of blood vessels, associated with Human Herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8).
2) Purple or brown skin lesions, often on extremities; may involve organs.
3) HIV/AIDS, immune suppression, and HHV-8 infection.
4) Antiretroviral therapy (if HIV-related), chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
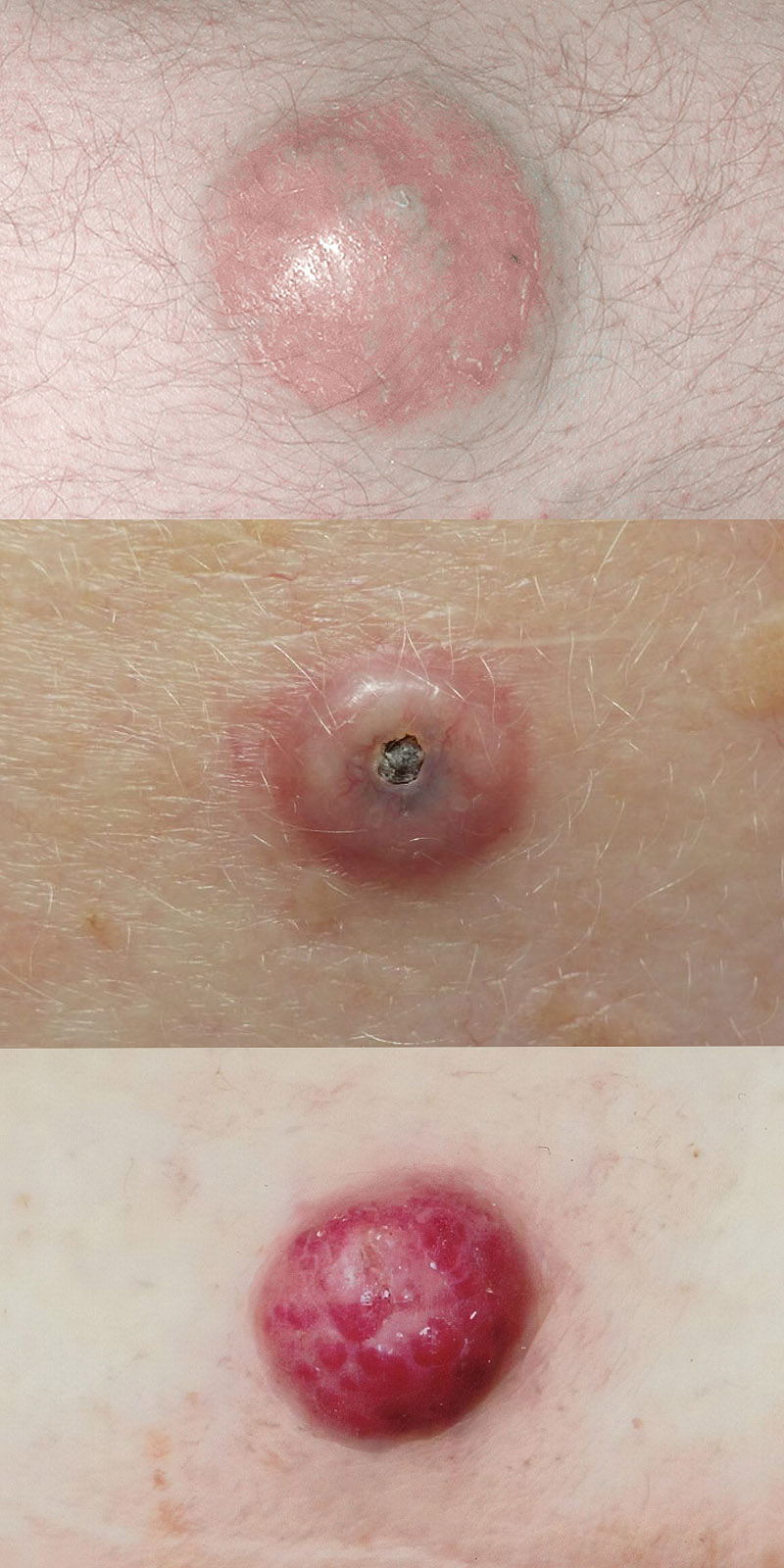
What is Merkel cell carcinoma? What are its symptoms? Risk factors? How is it treated?
1) Rare, aggressive skin cancer originating in Merkel cells.
2) Firm, painless nodules on sun-exposed areas, often red or purple.
3) UV exposure, older age, immune suppression, and Merkel cell polyomavirus.
4) Surgical removal, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy (e.g., checkpoint inhibitors).
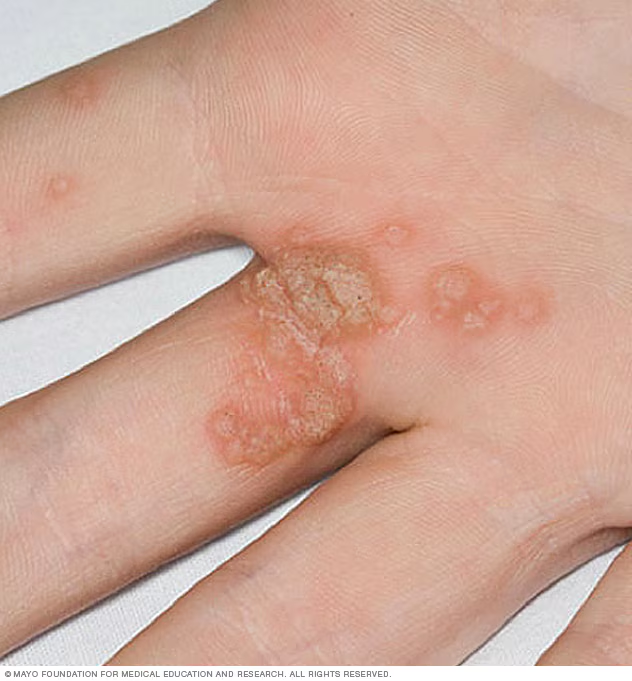

-
HPV
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-GettyImages-1449527392-530881506fc444b4a0821e4c84186b1f.jpg)
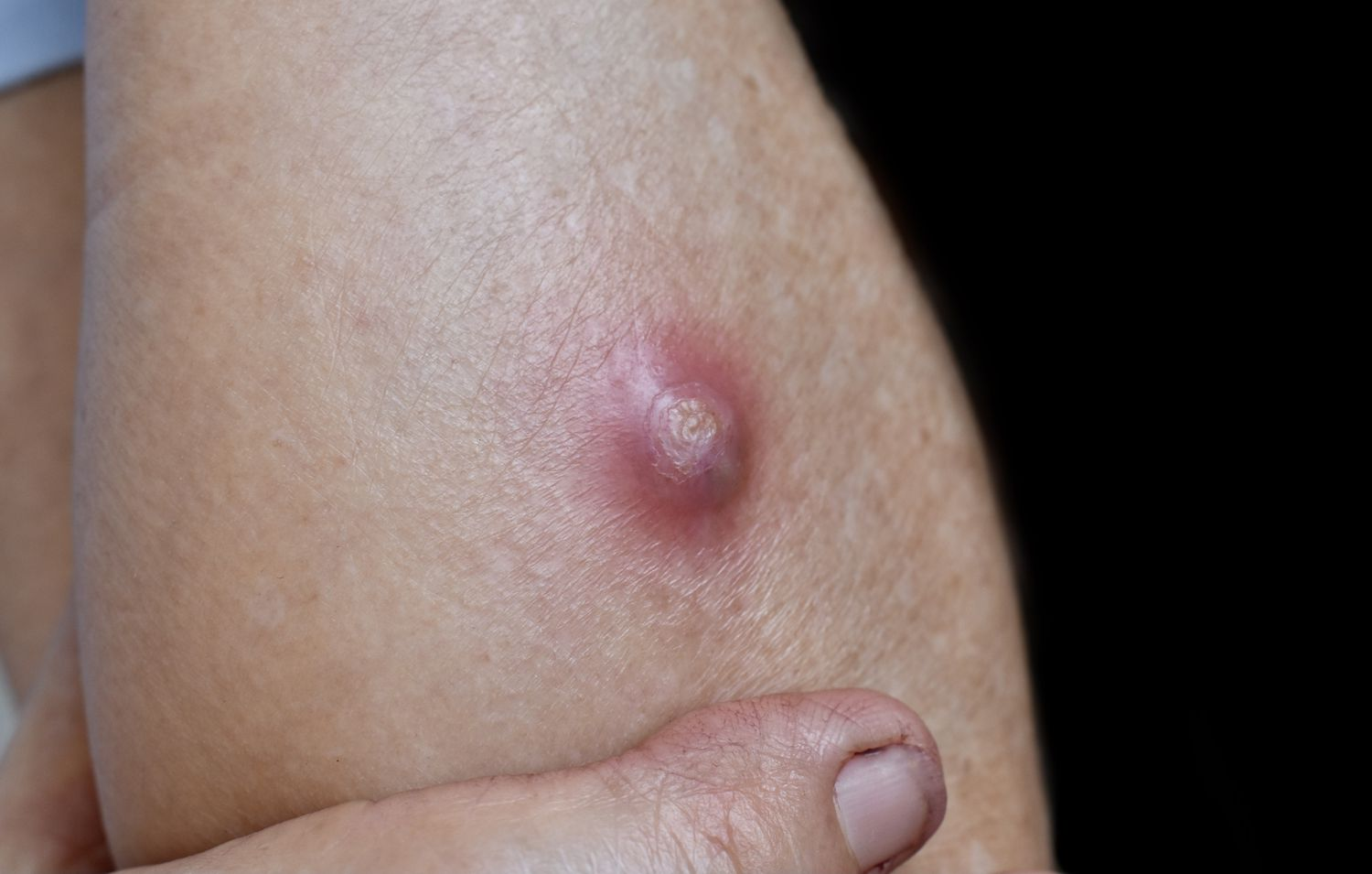
-
boil
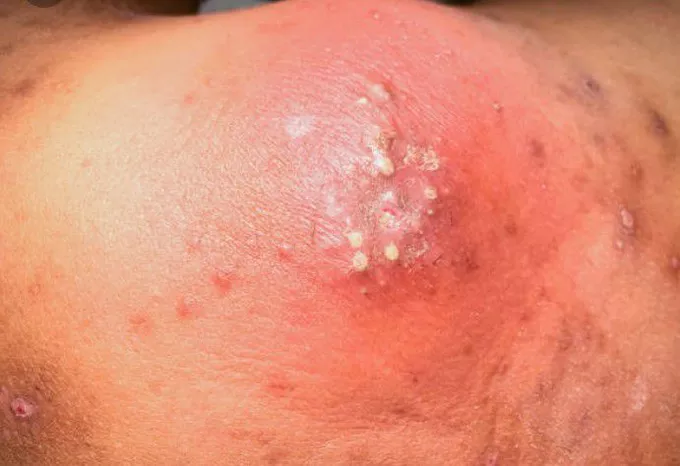
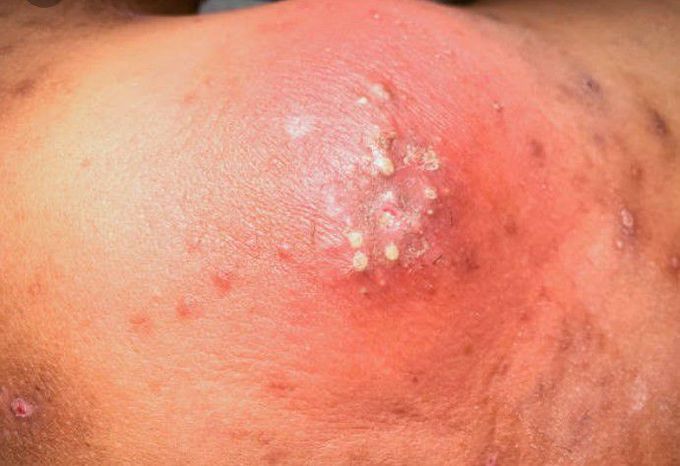
-
carbuncles.

-
Athlete’s foot.
-
-
impetigo
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/erysipelas4-099ddec307c74900993c0bd5e954043e.jpg)
-
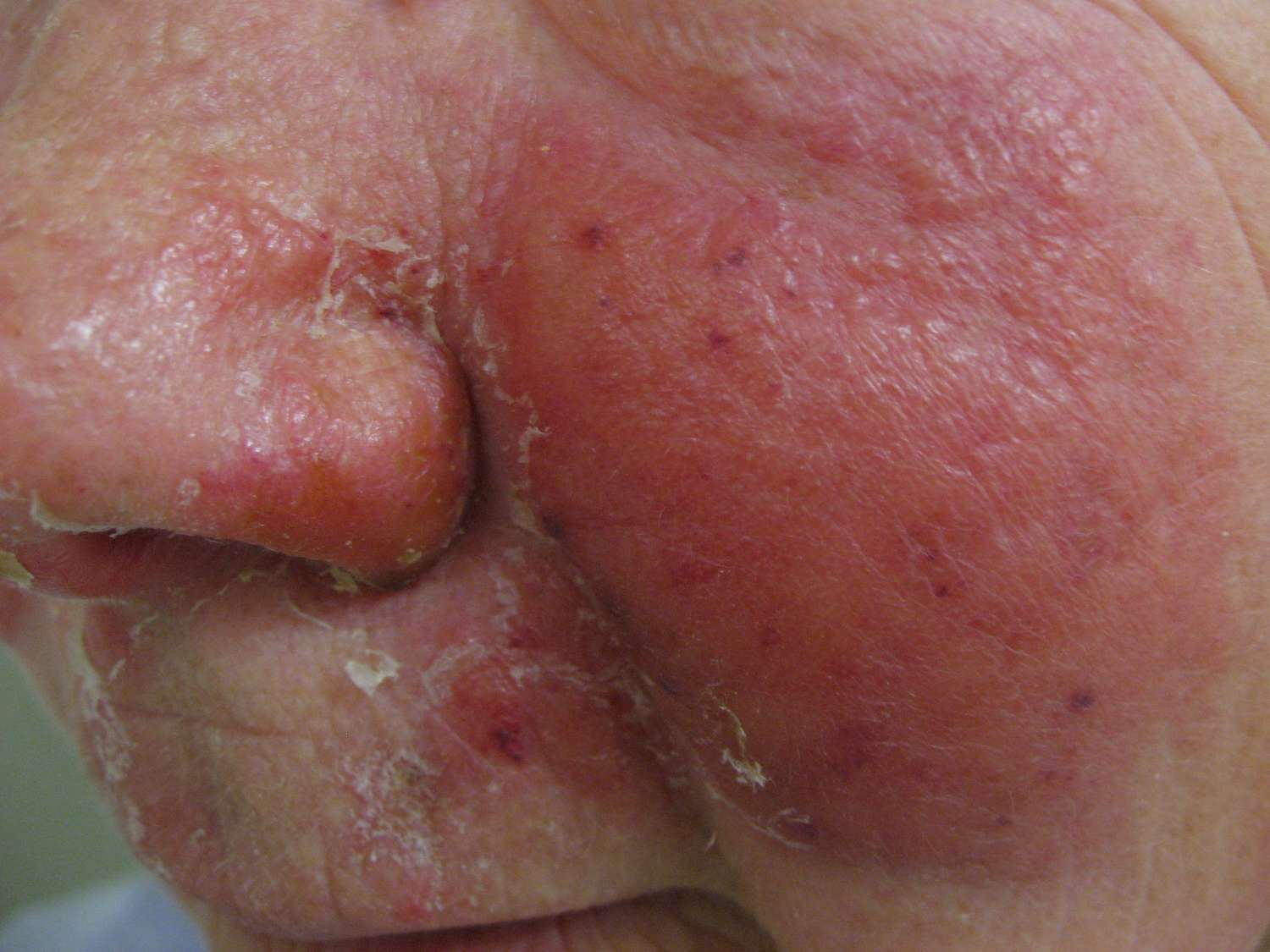
erysipelas/St. Anthony’s Fire.

-
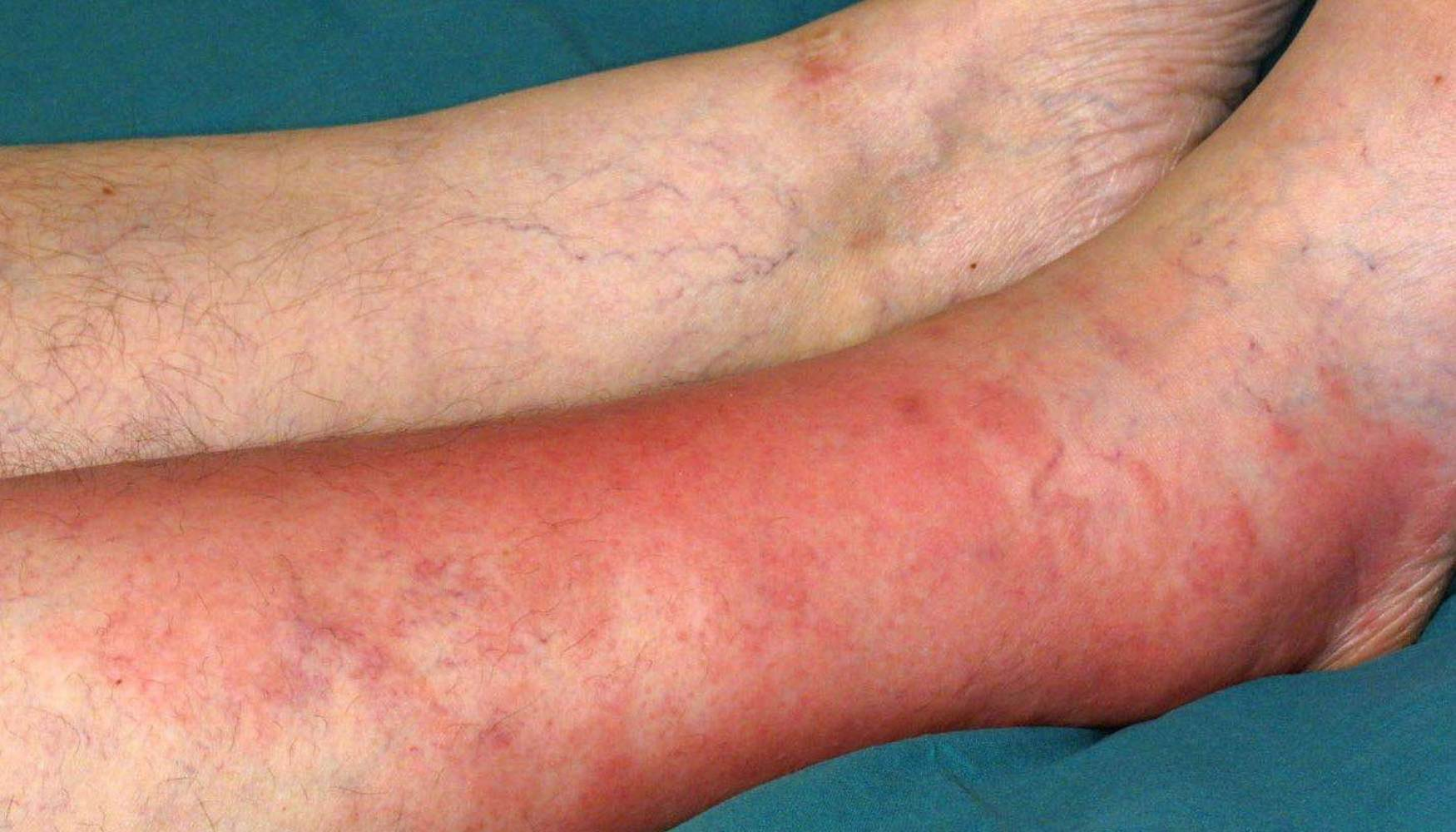
-
Cellulitis.
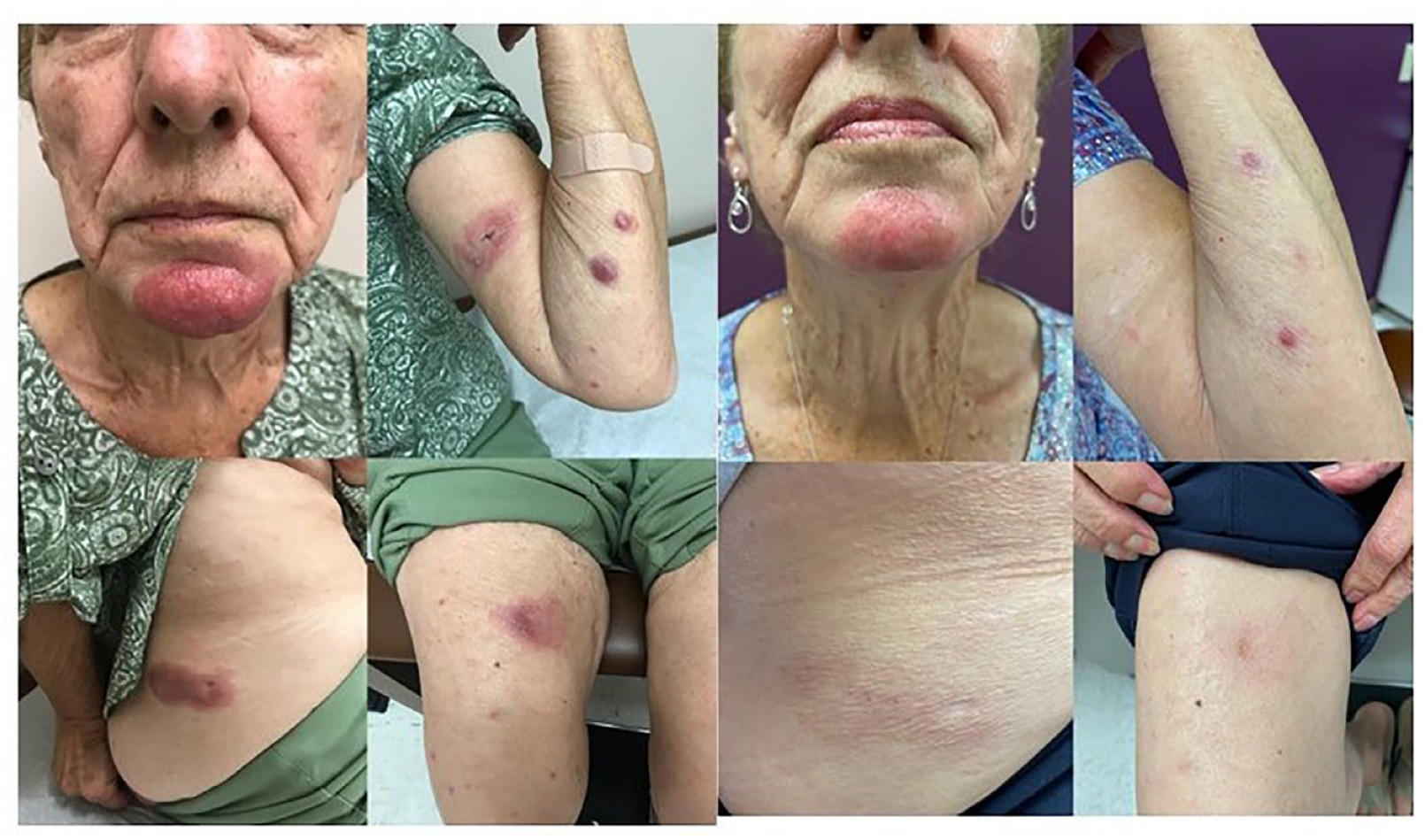

-
Hansen’s disease/Leprosy.
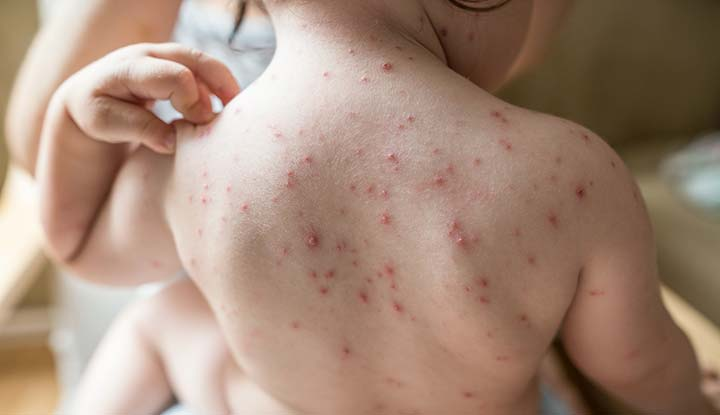
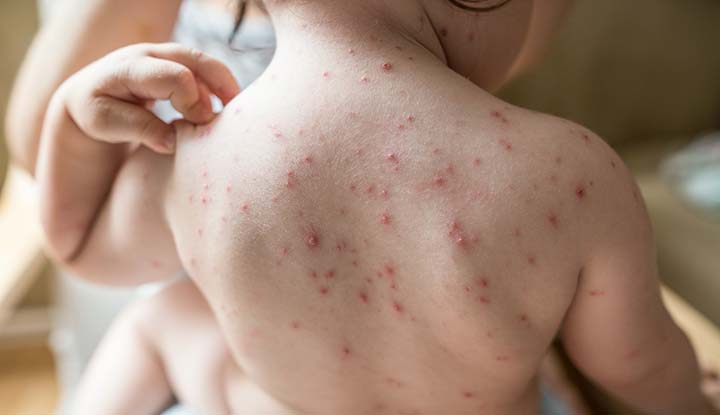
-
Chickenpox.

-
Shingles

-
Psoriasis

-
dermatitis

-
Kaposi’s sarcoma.
-
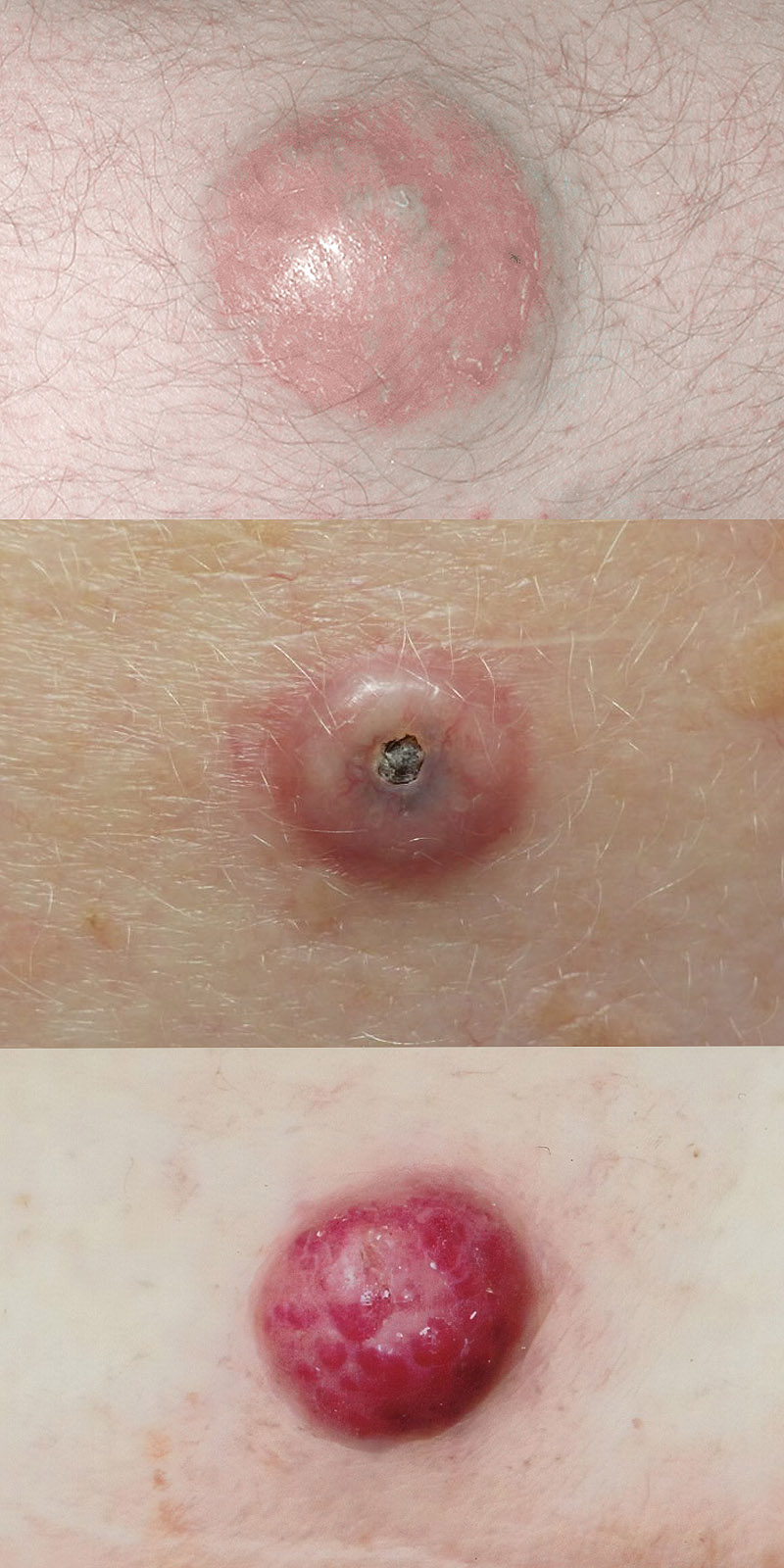
Merkel cell carcinoma
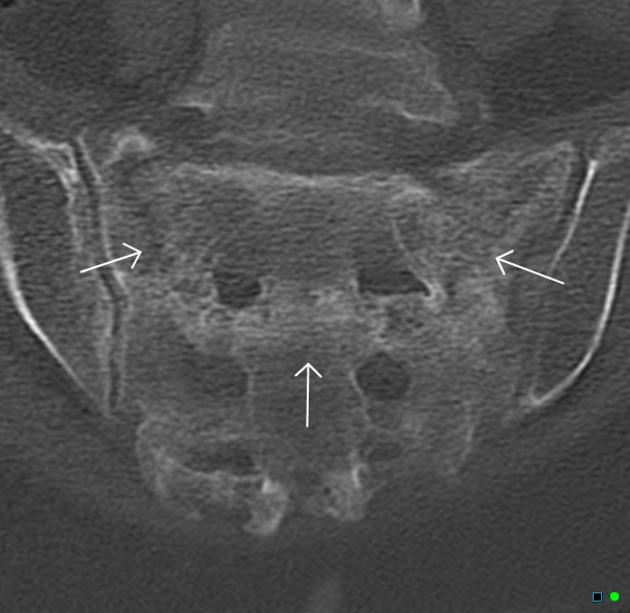
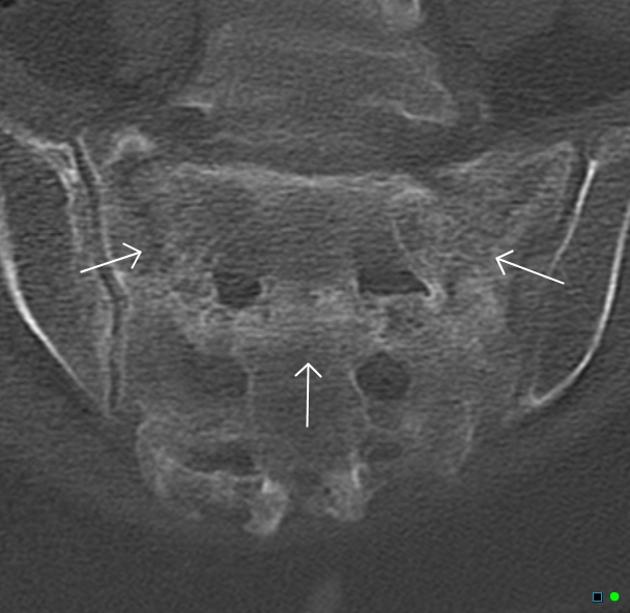
Sacral insufficiency fracture
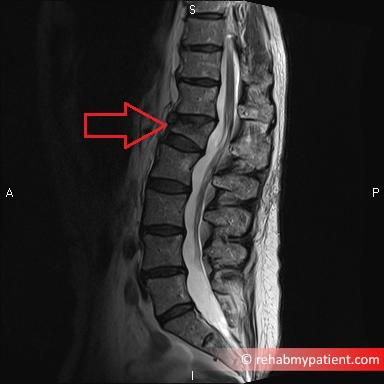
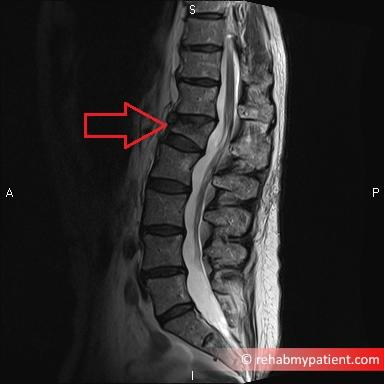
Wedge fracture
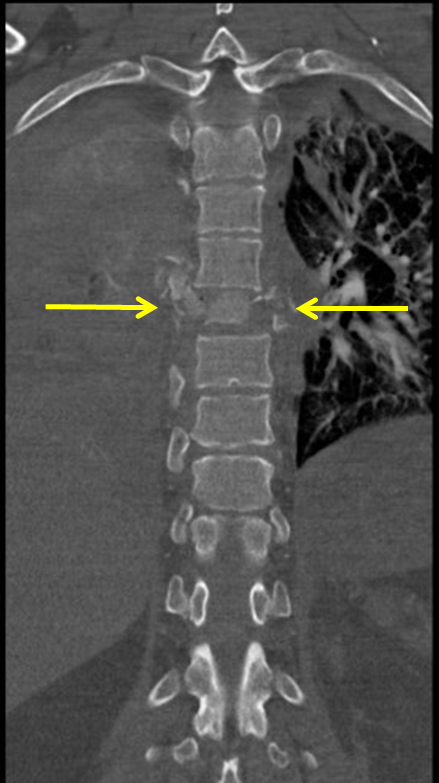

Burst fracture of spine
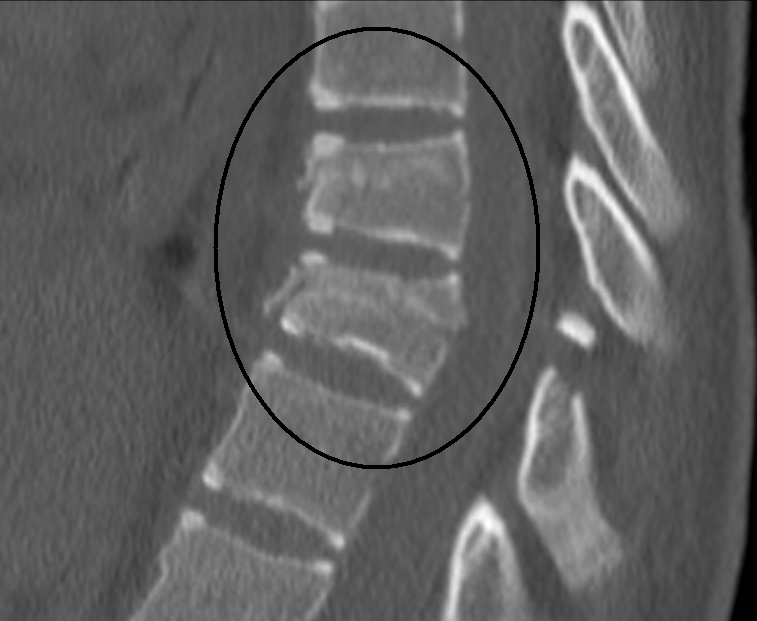
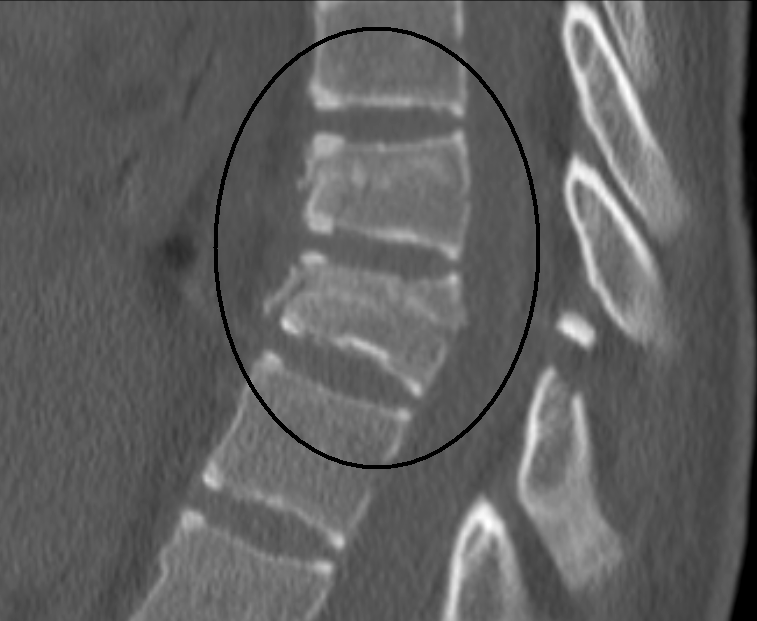
Seatbelt fracture AKA chance fracture
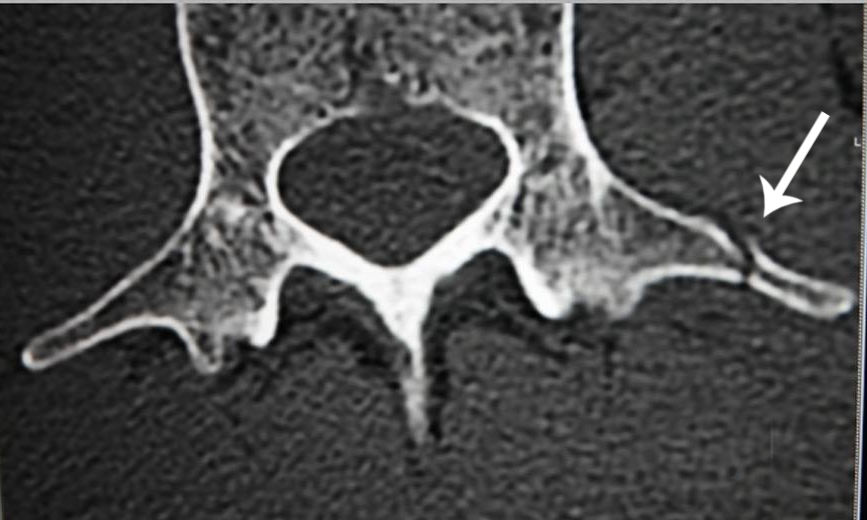
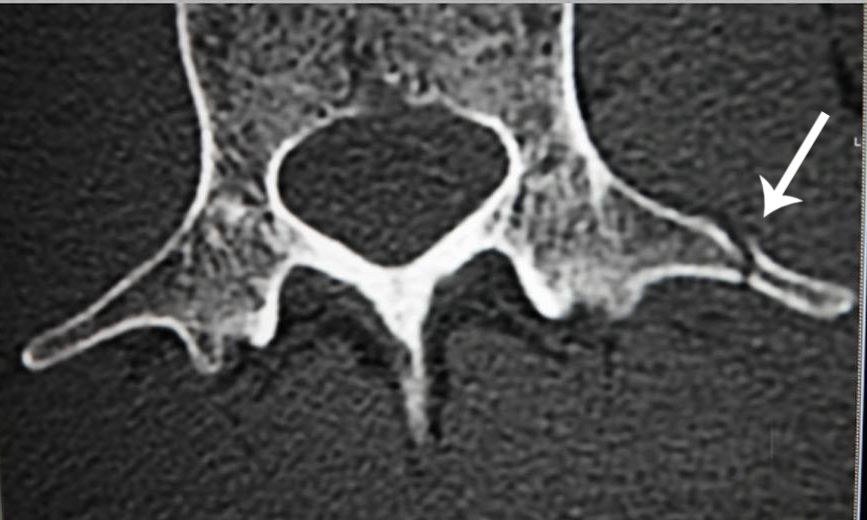
Transverse process fracture
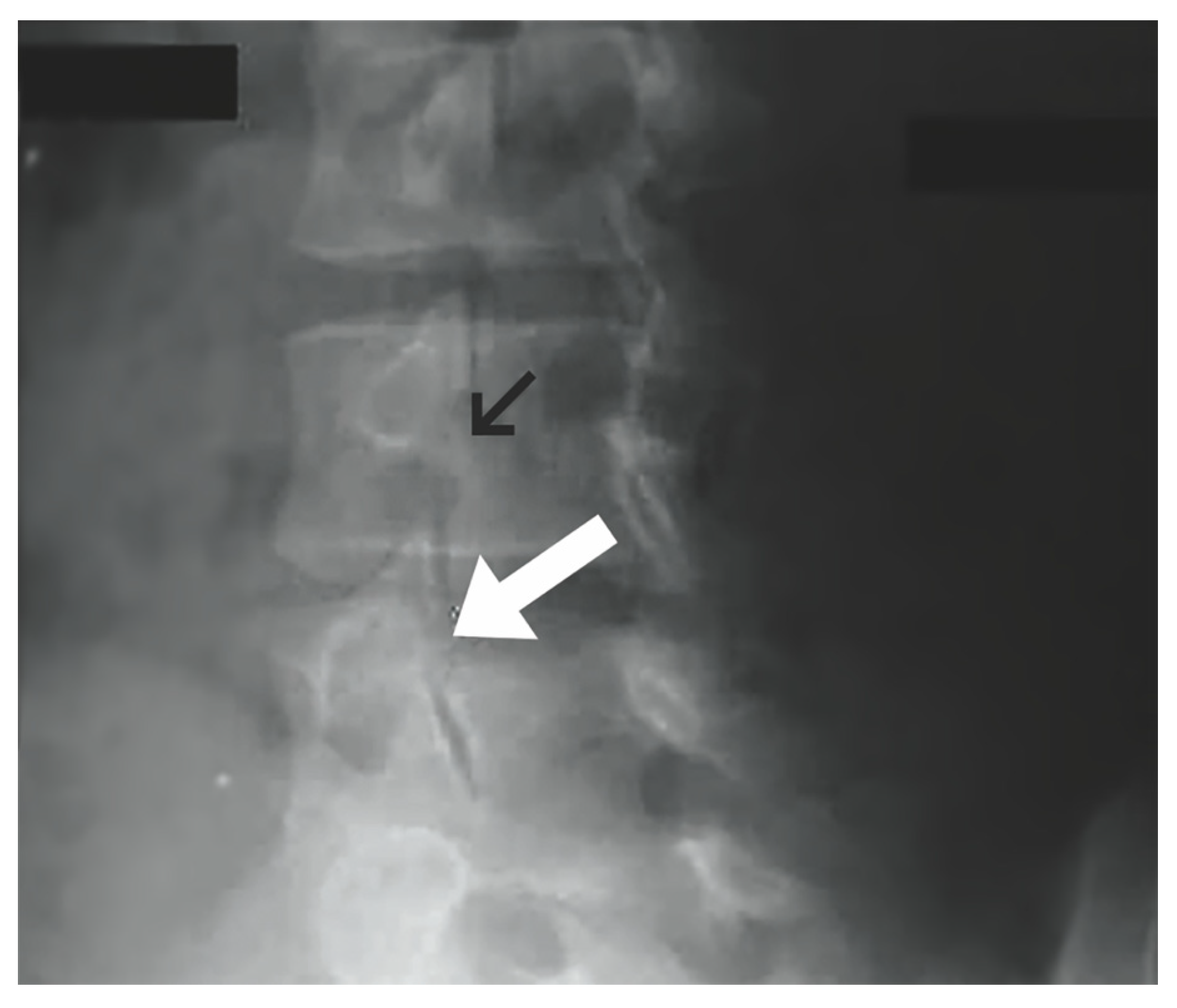

Spondylosis
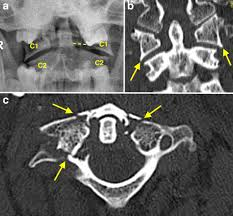
Jefferson fracture
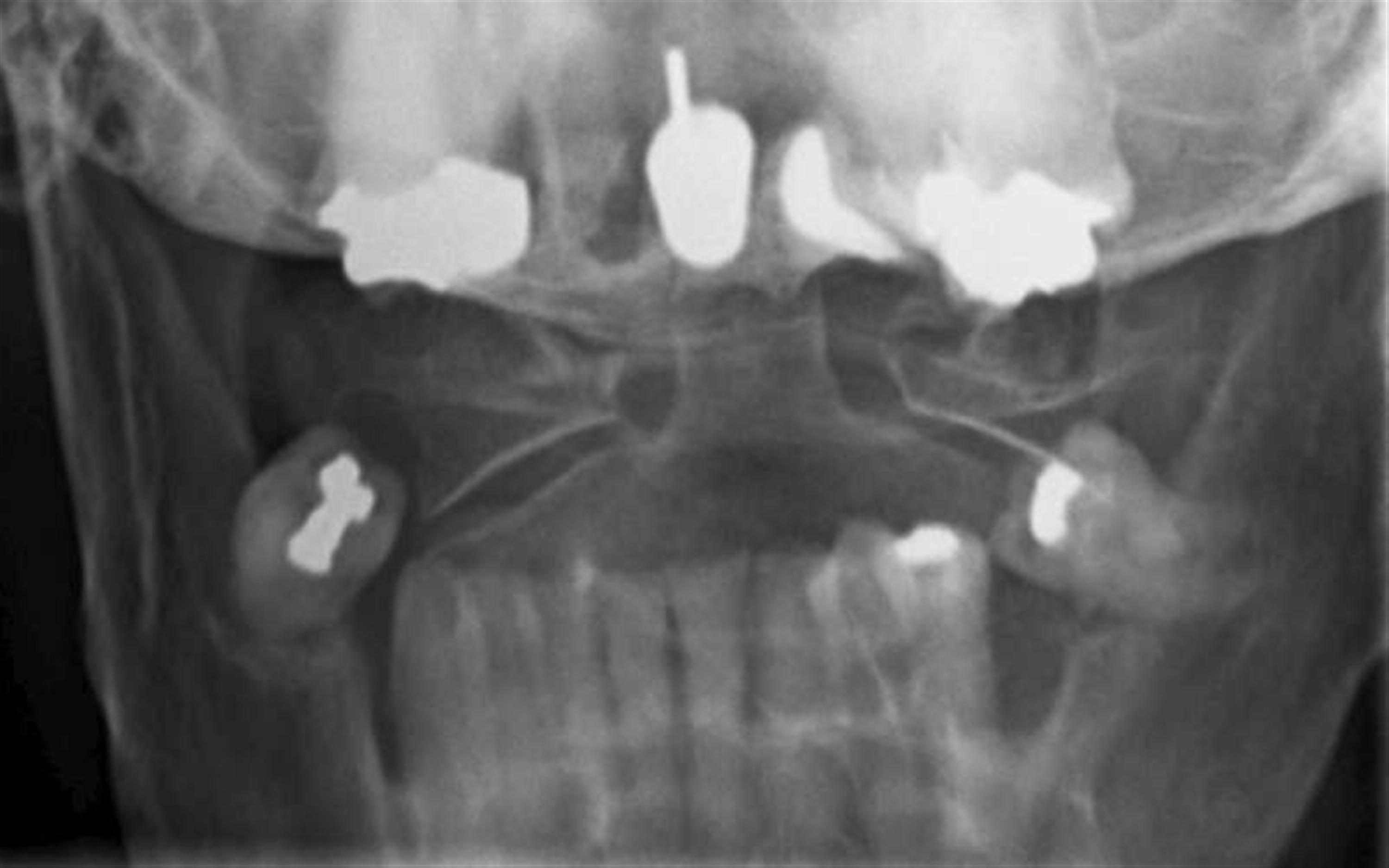

Odontoid fracture.
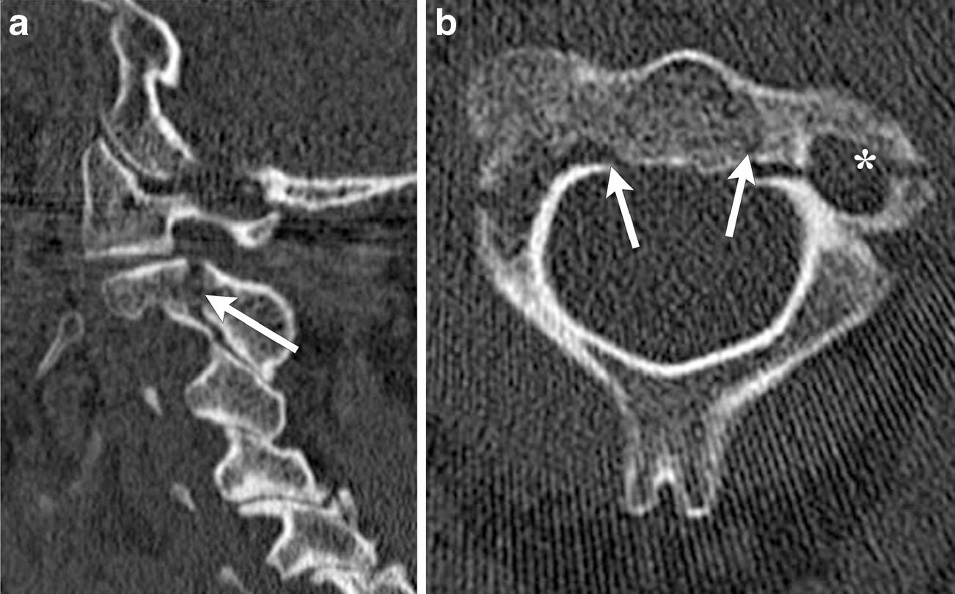

Hangman’s fracture.
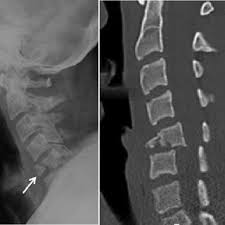
Flexion teardrop.
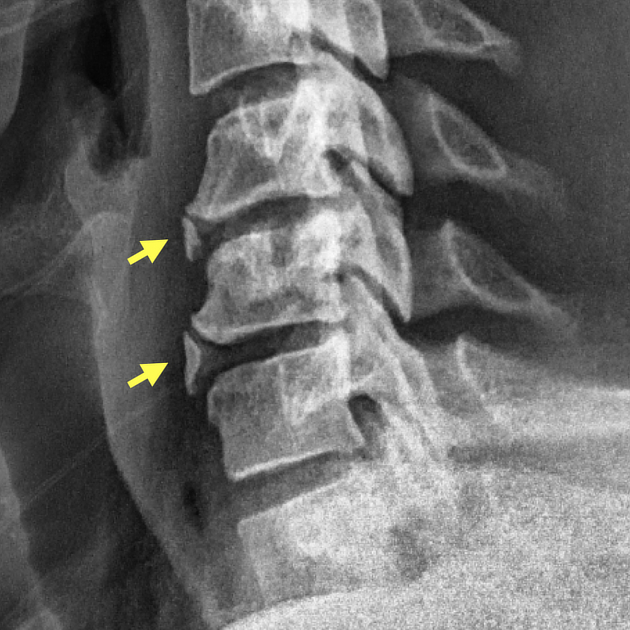

Extension teardrop.
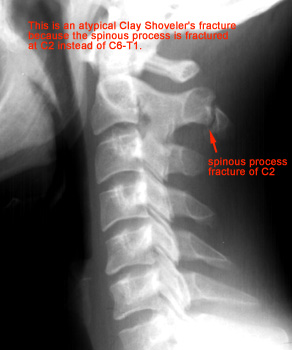

Clay shoveler’s fracture.
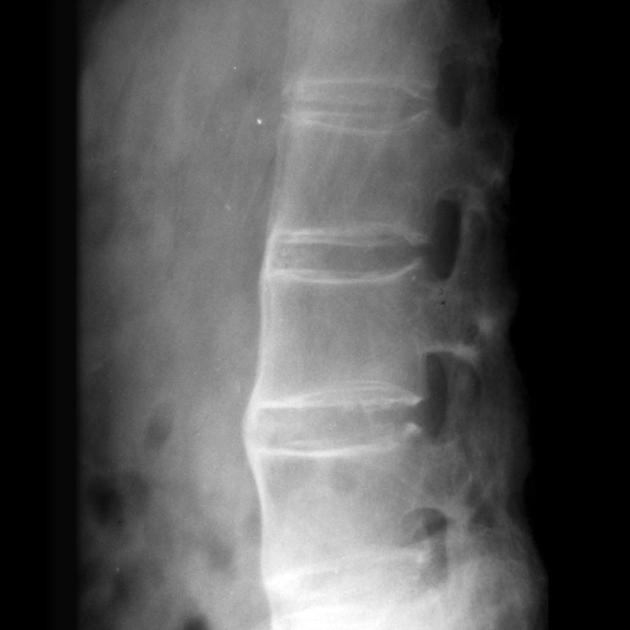
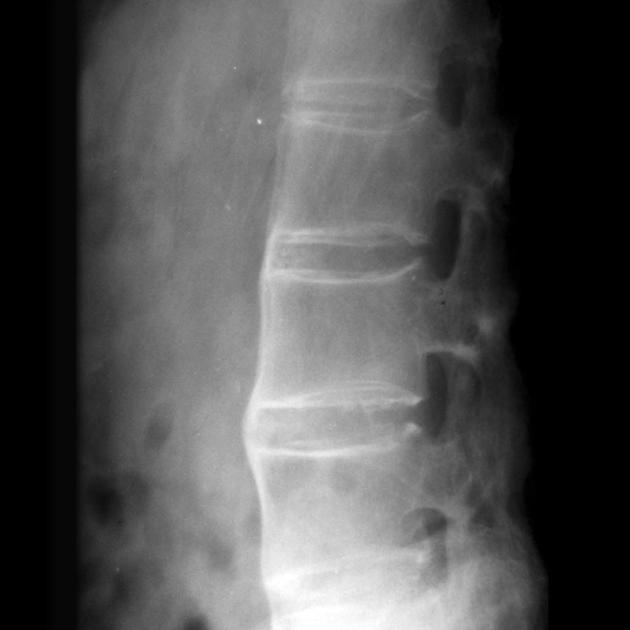
Ankylosing spondylitis
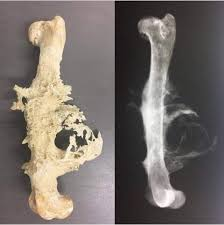
Osteosarcoma
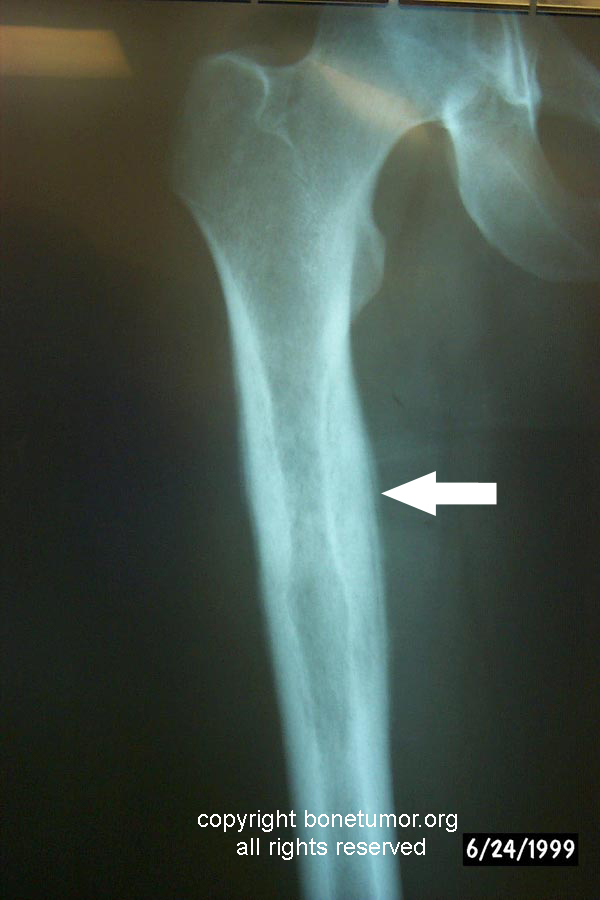
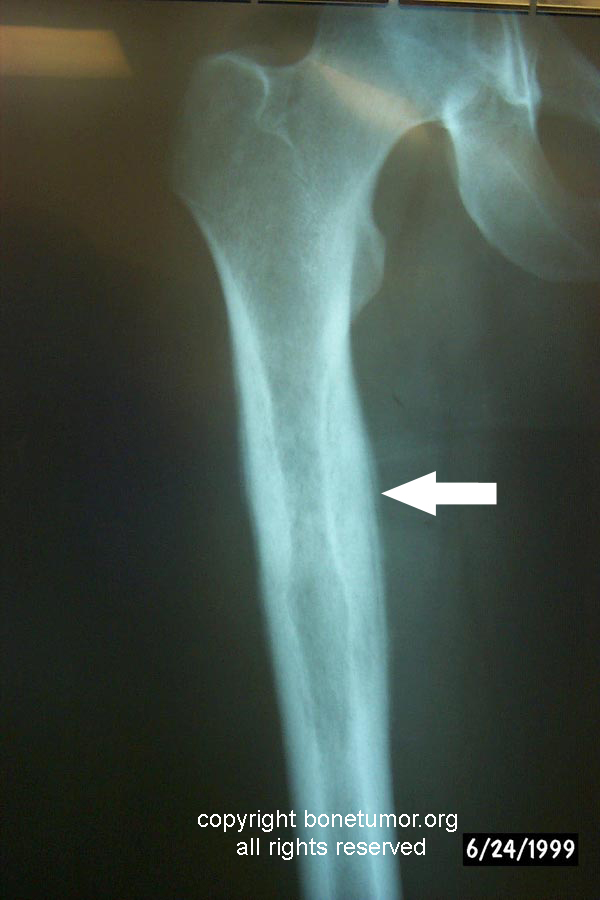
Ewing sarcoma
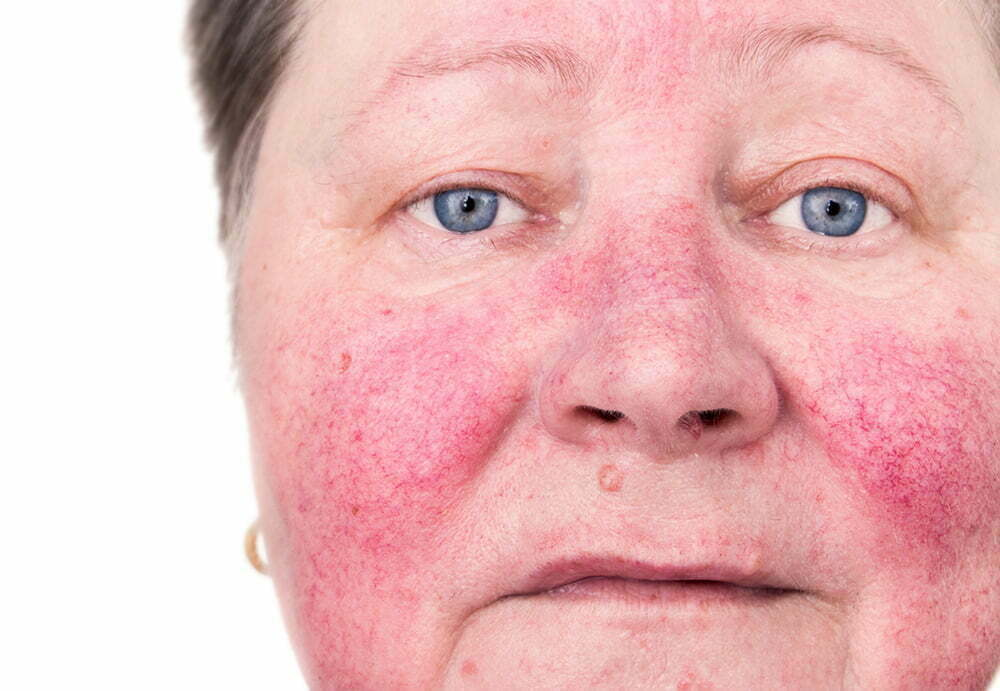

Rosacea
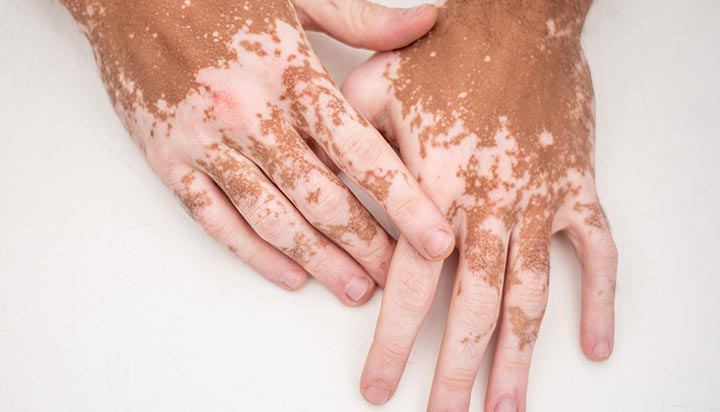
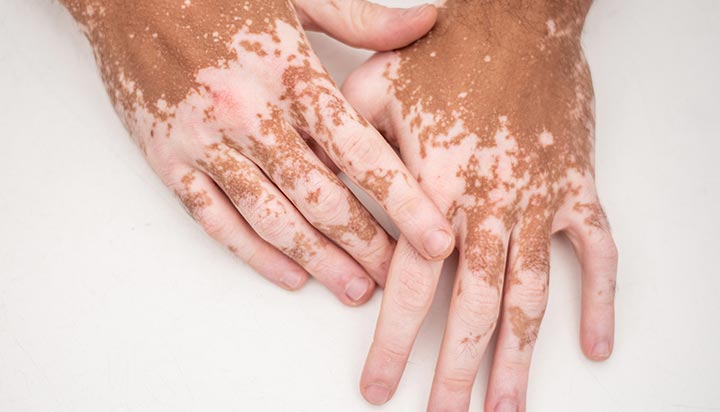


vitiligo
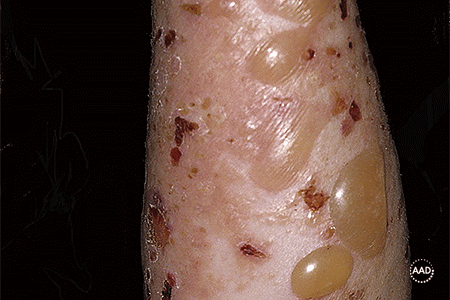
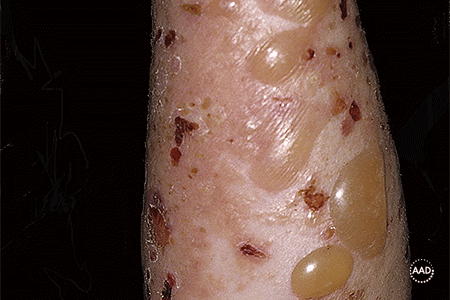
bullous pemphigoid

stevens Johnson syndrome
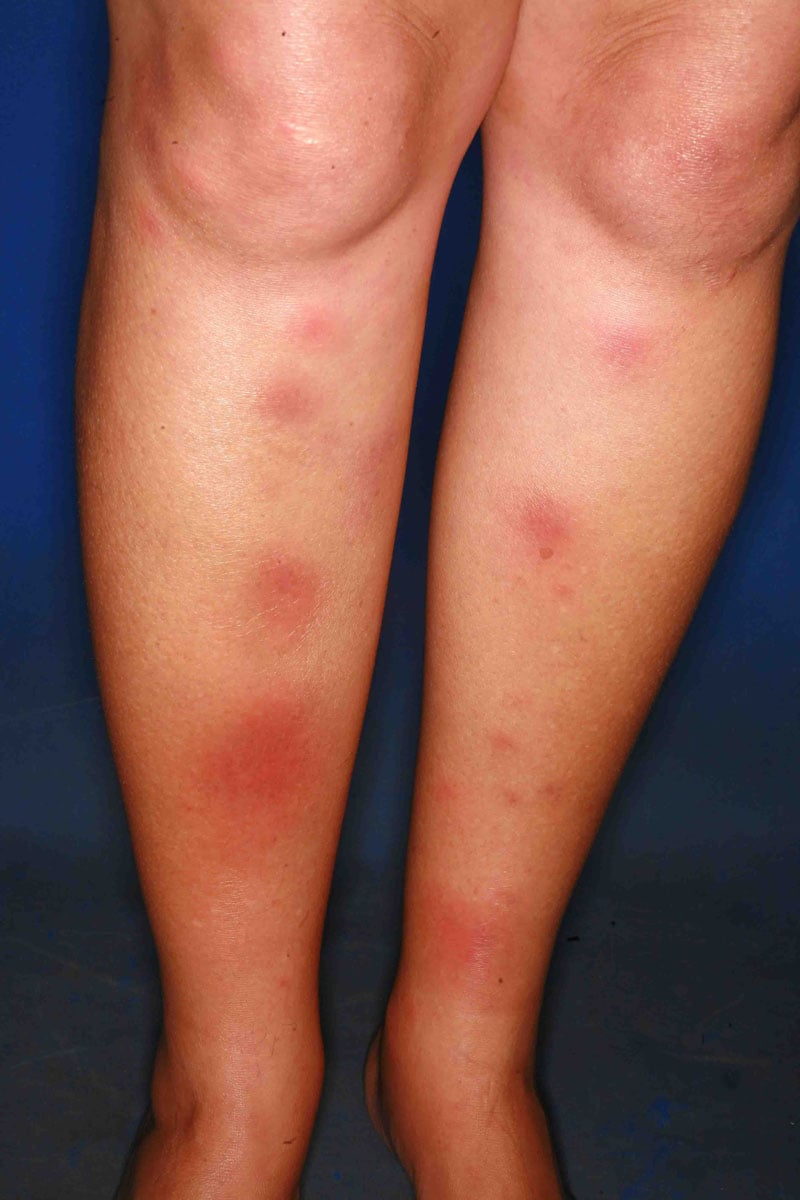

erythema nodosum
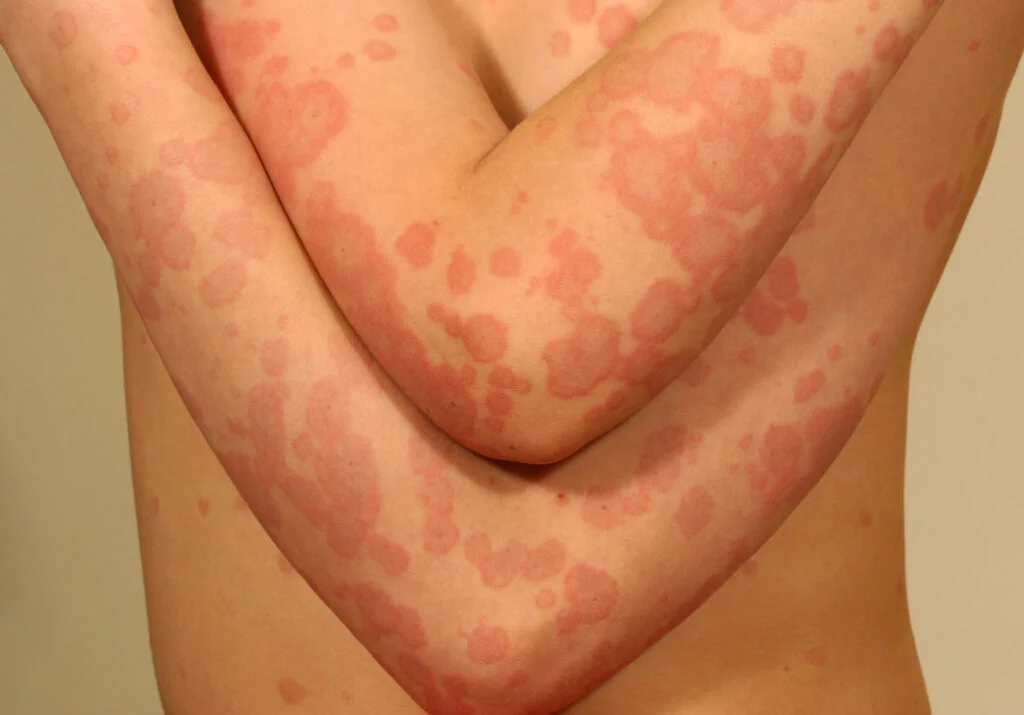

erythema multiforme
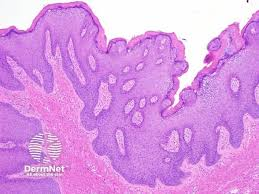
HPV wart/verruca.
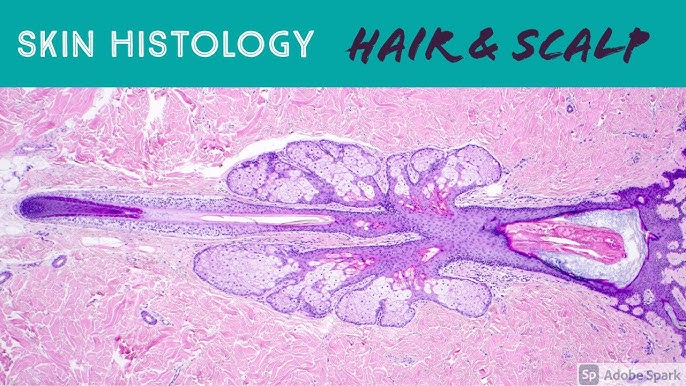

boil/carbuncle.