Genetics Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/200
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:35 PM on 2/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
201 Terms
1
New cards
What is a genotype?
the sum of genes
2
New cards
What is the most common chromosome?
X chromosome
3
New cards
What was the first cloned gene sequence?
beta-globin
4
New cards
What is a karyotype?
the number and visual appearance of the __chromosomes__ in the cell __nuclei__ of an __organism__ or species.
5
New cards
What is a phenotype?
everything that is not the DNA or genotype
6
New cards
What does it mean to be macroscopic?
you do not need anything to view it
7
New cards
What does it mean to be microscopic?
you need a microscope to view it
8
New cards
What decides how you look?
protein
9
New cards
What makes up genetic material?
proteins
10
New cards
What makes up proteins?
amino acids
11
New cards
What is a nuclear location?
part of the chromosome is in the nucleus
12
New cards
What type of strands do viruses have?
double and single stranded DNA and RNA
13
New cards
How did the mouse die from the S cells when there was only dead S cells being put in the body?
the S cells told the R cells to become S cells and ended up killing the mouse
14
New cards
What does DNA stand for?
dexyribo-nucleic-acid
15
New cards
What does RNA stand for?
ribo-nucleic-acid
16
New cards
What base pairs are in DNA?
adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine
17
New cards
What base pairs are in RNA?
adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil
18
New cards
What are polymers of nucleotides?
polynucleotides
19
New cards
What makes up a nucleotide?
sugar, phosphate, nitrogenous base
20
New cards
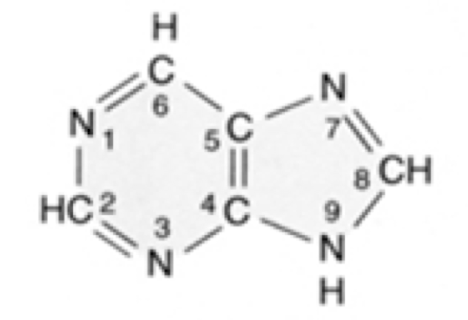
What nucleic acid is this?
purine
21
New cards
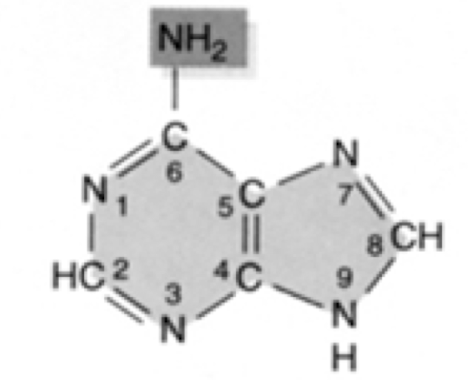
What nucleic acid is this?
adenine
22
New cards
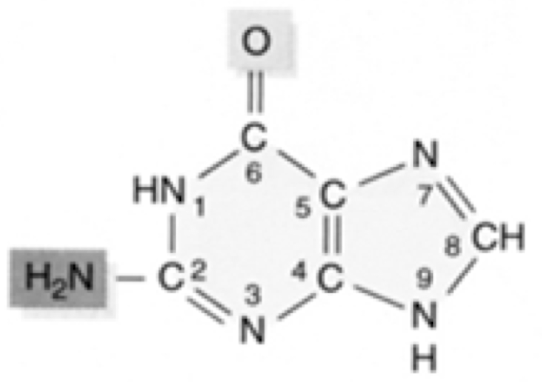
What nucleic acid is this?
guanine
23
New cards
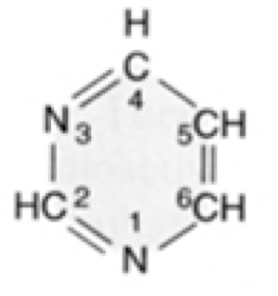
What nucleic acid is this?
pyrimidine
24
New cards
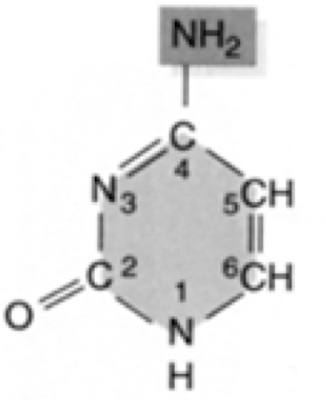
What nucleic acid is this?
cytosine
25
New cards
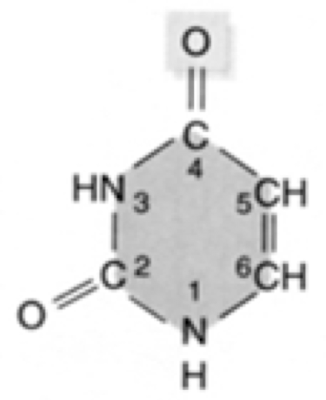
What nucleic acid is this?
Uracil
26
New cards
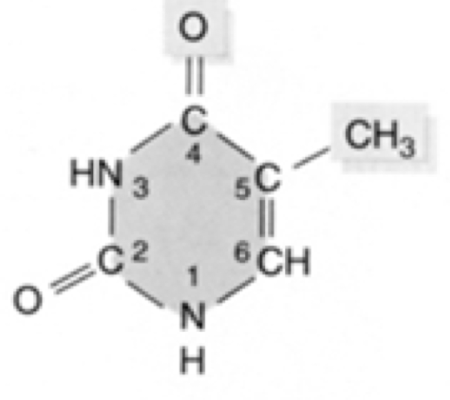
What nucleic acid is this?
thymine
27
New cards
What are the building blocks of DNA?
nucleotides
28
New cards
Is DNA or RNA more stable?
DNA
29
New cards
What does a nucleoside contain?
a sugar and base
30
New cards
What does a nucleotide contain?
sugar, base and a phosphate group
31
New cards
What end is the 5’ end?
phosphate
32
New cards
What end is the 3’ end?
hydroxyl group
33
New cards
How many nucleotides are in a polynucleotide?
30+
34
New cards
What is Chargaff’s rule?
A=T and G=C
35
New cards
Who found that DNA is a double helix and when?
Watson and Crick
36
New cards
Why can hydrogen bonds form?
because of the polarity they attract
37
New cards
How many hydrogen bonds do A=T and G=C make?
A=T - 2
G=C -3
G=C -3
38
New cards
What is the diameter of a double helix?
2 nm
39
New cards
What is the distance of 1 turn of the helix and how many base pairs are there?
3\.4 nm with 10 base pairs per turn
40
New cards
What much DNA is in one cell?
2 m
41
New cards
What percentage of a cell does DNA take up?
50%
42
New cards
What are the characteristics of the double helix?
antiparallel strands
complementary bases inside forming H-bonds
sugar-phosphate backbone to the outside
complementary bases inside forming H-bonds
sugar-phosphate backbone to the outside
43
New cards
What makes up the energy of the double helix?
1/3 bonding energy- base pairing (hydrogen bonds)
2/3 bonding energy- base stacking (interaction of aromatic ring system)
2/3 bonding energy- base stacking (interaction of aromatic ring system)
44
New cards
How many chromosomes are in the human genome? How many nucleotide pairs are there?
46 chromosomes and 6.6 x 10^9 nucleotide pairs
45
New cards
How long are DNA loops?
40,000 base pairs long
46
New cards
What is a primer?
short RNA molecule
47
New cards
What type of model is DNA replication?
semiconservative model
48
New cards
What is the semiconservative model?
one strand becomes the template for the replication
49
New cards
What is the conservative model?
The entire molecule is replicated and not split
50
New cards
What is the dispersive model?
bits and pieces of the molecule are broken up and replicated
51
New cards
What is DNA polymerase?
the product is DNA and the reaction is a polymerase
52
New cards
What does it mean to be primer dependent?
needs a short nucleic acid to start, roughly 10 nucleotides long. The enzyme is primase that makes small RNA molecules
53
New cards
What is helicase?
unwinds DNA
54
New cards
What is primase?
makes RNA primer
55
New cards
What is DNA ligase?
puts DNA fragments together
56
New cards
What is gyrase?
winds the DNA together
57
New cards
What does helicase use to separate the DNA strands?
ATP
58
New cards
What is the replication fork?
where helicase opens up the DNA
59
New cards
What are the 2 DNA strands called?
leading strand and lagging strand
60
New cards
What is another name for the lagging strand?
okazaki fragments
61
New cards
What are the 4 steps of discontinuous replication of the lagging strand?
\-primer synthesis by primase
\-elongation by DNA polymerase III
\-primer removal and gap filling by DNA polymerase I
\-ligation of nicks by DNA ligase
\-elongation by DNA polymerase III
\-primer removal and gap filling by DNA polymerase I
\-ligation of nicks by DNA ligase
62
New cards
What does exonuclease do?
removes the primer and proof reads the DNA and puts the correct nucleotide in
63
New cards
How long does it take to replicate an E. Coli genome?
84 minutes
64
New cards
What is the advantage of using an RNA primer?
removal of error containing fragments which arise at the beginning of the polymerization
65
New cards
What is the advantage of using an RNA primer? Why 5’ to 3’ synthesis?
after nucleotide removal during proofreading the energy for the next synthesis step comes from the incoming dNTP
66
New cards
What is positive supercoiling?
unwinding of the DNA at the replication form leading to over twisting of the double helix
67
New cards
What is the role of the topoisomerases?
gives the DNA the opportunity to rotate back from its supercoil to relieve stress
68
New cards
How much does the DNA molecule rotate per minute?
2400
69
New cards
What is the central dogma?
DNA→ RNA → protein
70
New cards
What is it called when RNA→DNA?
reverse transcriptase
71
New cards
What does a telomere do?
repeats 5-8 nucleotide pattern to stop the strand from decreasing
72
New cards
What is half a chromosome called?
chromatid
73
New cards
What is an exon?
it codes for a protein
74
New cards
\`How much of a human gene is introns?
95%
75
New cards
What is the longest exon and what is it on?
17106 bp on TTN
76
New cards
How many chromosomes are in a human?
46
77
New cards
What is the composition of chromosomes by mass?
1/3 DNA
1/3 histones
1/3 non-histone proteins
1/3 histones
1/3 non-histone proteins
78
New cards
What type of charge does DNA have?
negatively charged
79
New cards
What type of charge does Lysine and arginine have?
positively charged
80
New cards
What does a motor protein do and where is it?
its in the middle of non-histone proteins because of the microtubules from the spindle fibers
81
New cards
What is the order of chromatin compaction and by how much?
nucleosomes (7 fold)
superhelix (40-50 fold)
radial loop-scaffold (10,000 fold)
superhelix (40-50 fold)
radial loop-scaffold (10,000 fold)
82
New cards
What are the features of yeast cells?
they do not have histones, they are not that compact
83
New cards
What pattern is the superhelix in?
solenoid and zigzag
84
New cards
How are the chromatin arranged?
in radial loops
85
New cards
What blocks transcription?
histones
86
New cards
What is chromatin remodeling?
they move the nucleosomes
87
New cards
What does acetlyation/lysine do?
it makes the nucleosomes/chromatid structure more loose
88
New cards
What happens when you take away the acetylation?
the nucleosomes become tighter and you may not be able to do transcription
89
New cards
What is a lysine?
a positively charged amino acid
90
New cards
What is a characteristic of an acid?
donates hydrogen
91
New cards
What is a characteristic of actyline?
negatively charged
92
New cards
What does lysine + acetyline =
neutral + DNA = loosens the DNA structure
93
New cards
What things help with the “opening” of chromatin?
\-DNA binding proteins
\-histone modifying enzymes
\-nucleosome remodeling complexes
\-histone modifying enzymes
\-nucleosome remodeling complexes
94
New cards
What happens during the maintenance of histone modification?
the old histones act like a template while putting the new histones in
95
New cards
What is a chromosome in regards to chromatin?
a highly condensed chromatin
96
New cards
What is constitutive?
typically a highly repetitive sequence that is always condensed/compact
97
New cards
What is facultative?
condensation varies with cell type, developmental stage, chromosome
98
New cards
What is heterochromatin?
chromatin that is never released
99
New cards
What is an example of facultative heterochromatin?
inactived x-chromosome in females
100
New cards
What is a mutation?
a heritable change of the DNA sequence of an organism