Physics : P2
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
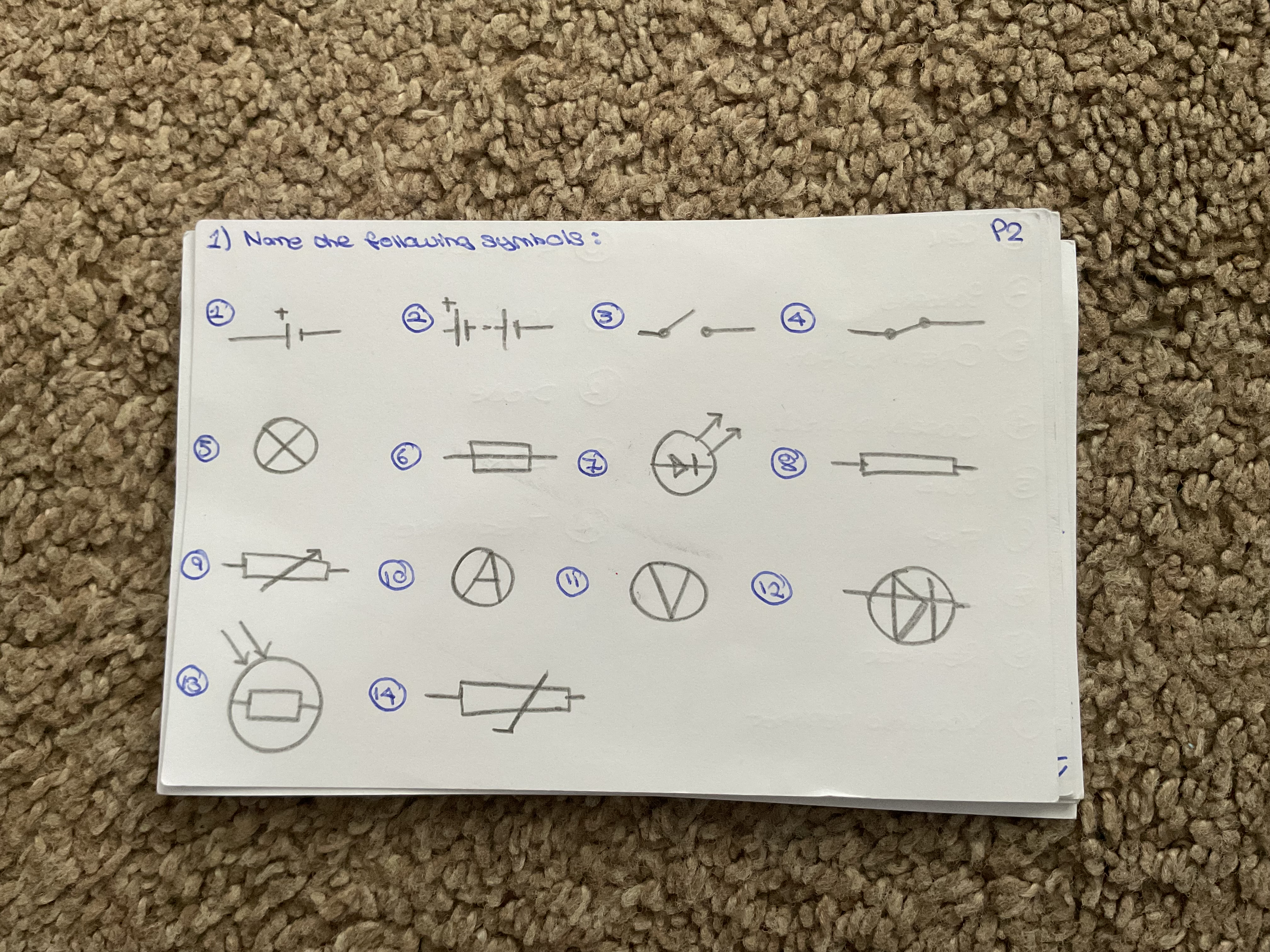
Name each symbol
Cell
Battery
Open switch
Closed switch
Bulb
Fuse
LED
Resistor
Variable resistor
Ammeter
Voltmeter
Diode
LDR
Thermistor
What is charge?
The amount of electricity travelling in a circuit.
What is the symbol for charge?
Coulombs
What is the formula for charge?
Charge = current x time
Q = I x T
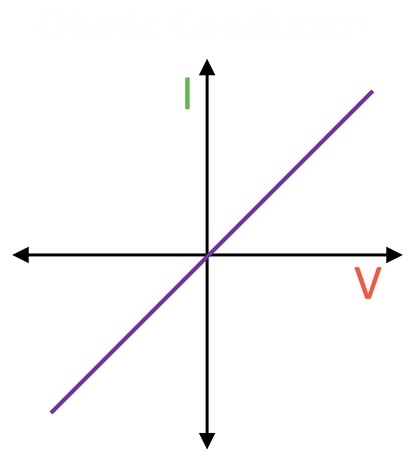
What does the graph show?
Ohmic conductor
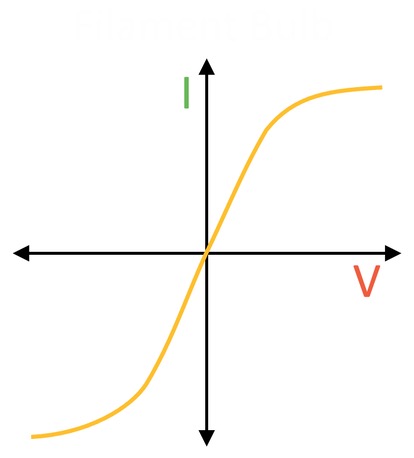
What does the graph show?
Filament bulb
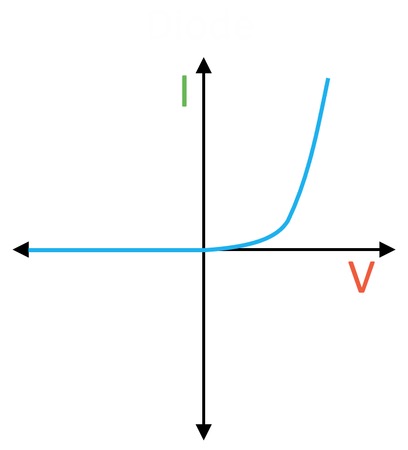
What does the graph show?
Diode
What is a diode used for and why?
To prevent the current from flowing backwards, as resistance is higher backwards.
How can a circuit be used to determine resistance? (PRACTICAL)
Set up a circuit with a bulb component
Set the variable resistor to low and close the switch to allow current to flow
Use an ammeter and voltmeter and note the readings
Increase the variable resistor to medium and retake readings
Do the same at the highest resistance
Plot the results on a graph and work out using Ohm’s law.
Find the negative reports by reversing the wires and performing the experiment again
What is a parallel circuit?
A circuit where each component is separately connected to the power supply.
Where is an ammeter placed in a parallel circuit?
In the main loop.
What are the benefits of a parallel circuit?
If one loop is taken out (e.g. a bulb is blown) the others aren’t affected
Components can be switched on or off without interference.
What is a series circuit?
A circuit where the different components are connected in a line, end to end.
Where would a voltmeter/ammeter be placed?
In parallel to the circuit.
What happens in one e.g. bulb blows in a series circuit?
The whole circuit will not work.
How is potential difference shared in a parallel circuit?
All components receive the full source of potential difference; the voltage is the same throughout
How is current calculated in a parallel circuit?
The total current is equal to the total current of each individual component.
How is potential difference and current shared in a series circuit?
PD = shared between all components
Current = the same at all points/components
Define current and its units.
The flow of charge.
Amps (A)
What is the rule for current in a series circuit?
The same at all points.
What is the equation for current?
I = V/R
Current = voltage/resistance
Define potential difference and its units.
The electrical work done by a cell.
Volts (V)
What is the rule for PD in a series circuit?
Shared across all components.
What is the equation for PD?
V = I x R
Voltage = current x resistance
Define resistance and its units.
A measure of how much a current is reduced. Ohms (Ω).
What is the rule for resistance in a series circuit?
Total resistance = each individual components resistance added together.
What is the equation for resistance?
R = V/I
Resistance = volts/charge
Define power and its units.
Power is the energy transferred by an appliance per second and is measured in watts (W).
What is the equation for energy transferred?
Energy transferred = power x time
E =P x T
Energy transferred = voltage x charge
E =Q x V
What is the equation for power?
Power = potential difference x current
P = V x I
What is the equation for the relationship between power, current and resistance?
Power = current(squared) x resistance
P = I(squared) x R
What is the equation for the relationship between the primary and secondary coil?
Power in primary coil = power in secondary coil
PD in primary x Current in primary = PD in secondary x Current in secondary
Vp x Ip = Vs x Is
How do transformers work?
A primary coil with an alternating potential difference causes a current to flow.
A magnetic field around the coil induces an alternating magnetic field around the iron core.
This includes a PD in the secondary coil causing a second current to flow.
The number of coils determines the current transferred which causes either a step up (increasing power) or step down (decreasing power) transformer.
What is the national grid?
A giant network of cables and transformers (pylons) which transfer electrical power from the power station to the consumer.
How does the national grid work?
Coal power station burns fuel or water which turns to steam to spin turbines.
Step up transformers will make PD high (400,000V)
As it passes through the pylons the PD is kept high but a lower current is given to reduce energy waste
The step down transformer brings down the PD back to a safe level (230V)
Define a transformer.
An electrical device that changes the voltage of an alternating current.
How do step-up transformers work and why?
A increases PD, decreases current to reduce heat loss.
How do step-down transformers work and why?
Decrease PD, increase current to make safer to consumer.
What is an alternating current?
A current that alternates PD direction constantly to produce an alternating current.
What is a direct current?
The PD and therefore current go in one direction and flows that way.
What are the 3 wires of a plug? What is their function and PD?
Brown wire (live wire) = carries PD from main to appliance = 230V
Blue wire (neutral wire) = completes the circuit = 0V
Green and yellow wire (Earth wire) = carries current if a fault occurs = 0V
How does light intensity impact an LDR?
As light intensity increases, the resistance of the LDR increases e.g. in darkness the resistance is highest and visa versa.
How does temperature impact a thermistor?
A thermistor’s resistance decreases as the temperature increases. In hot conditions the resistance drops. In cold conditions, the resistance increases.
What is the relationship between current and PD?
Current is directly proportional to PD.
What happens to resistance and temperature as current increases?
As current increases, resistance increases.
As temperature increases current must also be increasing (thermal energy loss).
How does resistance affect current?
Current decreases as resistance increases.
How does PD affect current?
PD increases as current increases.
How do we calculate resistance? (PRACTICAL)
Attach the crocodile clip top the wire level at 0cm on the ruler.
Attach the second crocodile clip at a short distance from the first clip.
Write down the length of wire between the two clips.
Close the switch and then record the current through the wire and PD across it.
Use a voltmeter and ammeter.
Use R = I/V to calculate the resistance of the wire.
Open the switch and move the second clip along the wire.
Repeat steps for a range of lengths.