Longitudinal and Transverse waves
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Define a transverse wave
A wave in which the oscillation of particles (or fields), moves at right angles to the direction of energy transfer
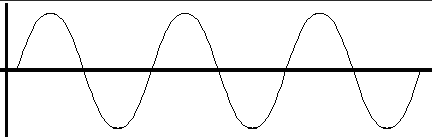
Define a longitudinal wave
A wave where the oscillations move parallel to the energy transfer


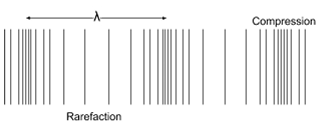
in this diagram of a longitudinal wave, what is the name for the more and less dense parts of the wave?
The denser parts are Compressions
The less dense parts are rarefactions
What is a ‘polarised’ wave?
A wave that only moves in one plane (e.g up and down), only transverse waves can be polarised.
What are some applications for polarisation?
Polarized sunglasses reduce glare
LCD screens use polarization to control light
Polarizing filters in photography enhance colors
Polarization is used in 3D glasses for different images to each eye
Polarization is used in scientific research to analyze materials
What is superposition?
Superposition is where the displacements of two waves are combined as they pass each other, the resultant displacement is the vector sum of each wave’s displacement.
What are the 2 types of interference that can occur during superposition, and when do they occur?
Constructive interference - occurs when 2 waves have displacement in the same direction.
Destructive interference - occurs when one wave has positive displacement and the other has negative displacement, if the waves have equal but opposite, then total destructive interference occurs.
When is a stationary wave formed, and how much energy does it transfer?
when the superposition of 2 progressive waves, travelling in opposite directions in the same plane, with the same frequency, wavelength and amplitude.
No energy is transferred by a stationary wave.
Define an ‘antinode’ and describe how they are formed.
Regions of maximum amplitude, which are formed when waves meet in phase and constructive interference occurs.
Define an ‘node’ and describe how they are formed.
They’re regions of no displacement, which are formed when waves that are completely out of phase have destructive interference.
What are the harmonics of a stationary wave?
A wave corresponding to the amount of antinodes the wave has, 1 antinode=The first harmonic ect.
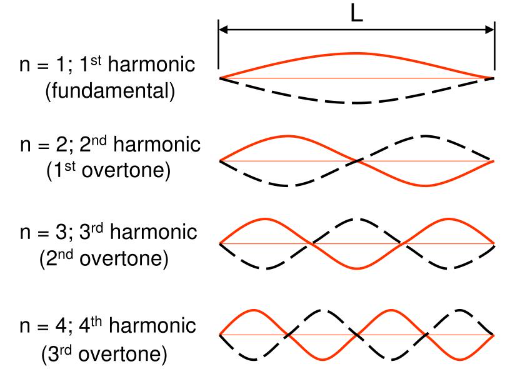
What is the equation for which you can find the frequency in a vibrating string?

How could you relate the frequency of the first harmonic (f) to the nth harmonic
frequency of the nth harmonic = nf