Kin 312-Scientific Measurement and Motor Control
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
2 general categories of measuring motor performance
1) performance outcome measures
2) performance production measures
2) performance production measures
2
New cards
performance outcome measures
measures the result/outcome of a skill
ex: distance thrown, speed, reaction time
ex: distance thrown, speed, reaction time
3
New cards
performance production measures
inform us about how the nervous system, muscular system, and limbs are acting to produce the performance outcome
ex: EEG, EMG, force, limb kinematics
ex: EEG, EMG, force, limb kinematics
4
New cards
types of performance outcome measures
-reaction time (RT)
-movement time (MT)
-response time
-movement time (MT)
-response time
5
New cards
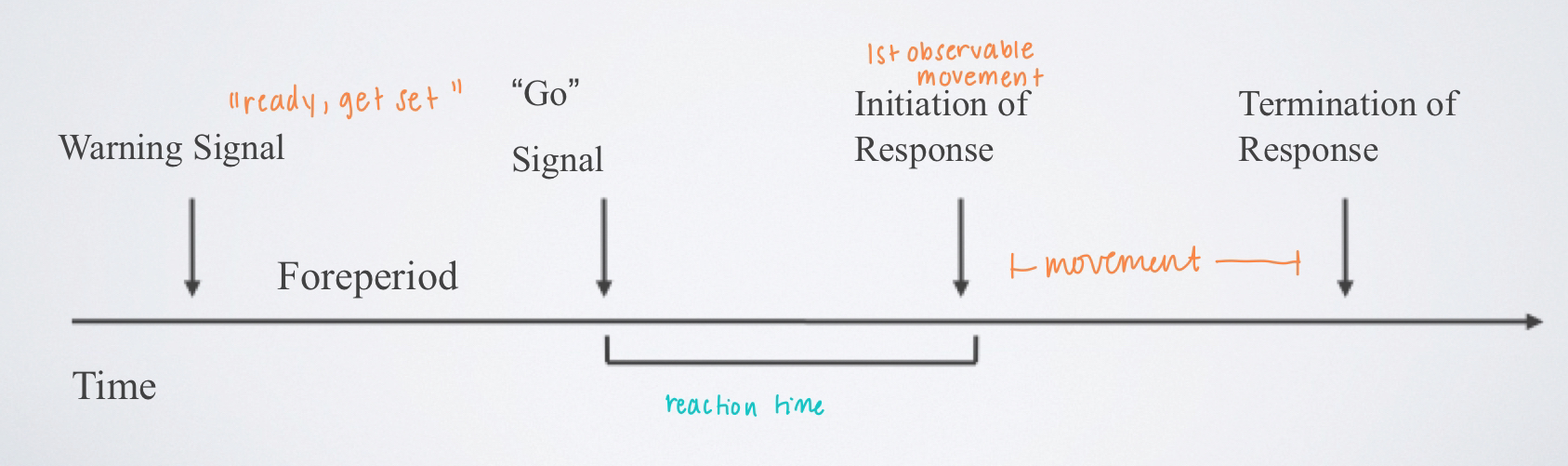
reaction time (RT)
indicates how long it takes to prepare and initiate movement
6
New cards
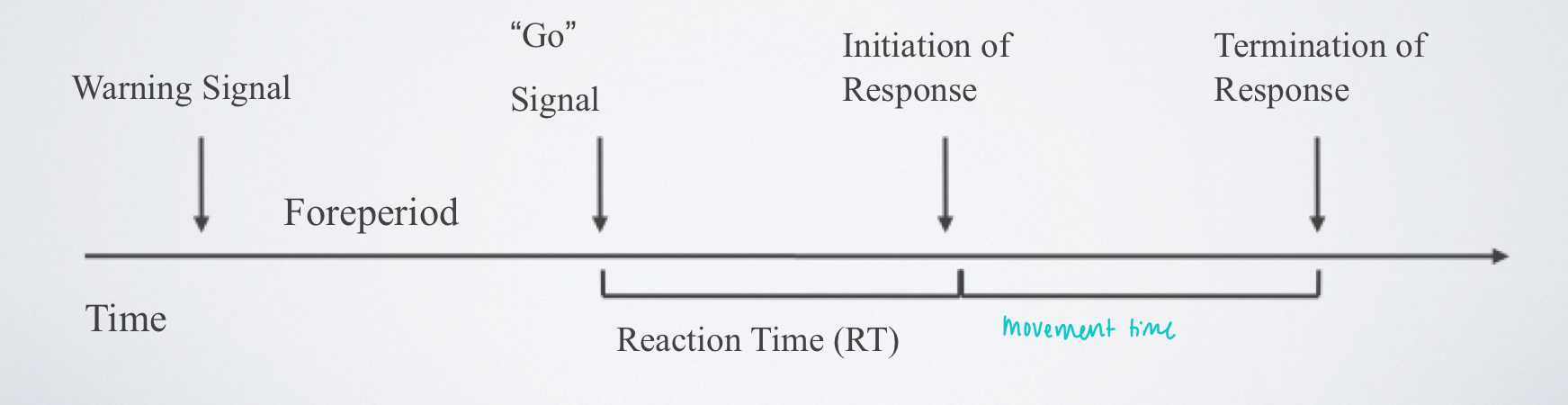
movement time (MT)
the interval of time between the initiation of a movement and the completion of the movement
7
New cards
response time
the time interval involving both reaction time and movement time; the time from the onset of a signal to the completion of a response
-aka: RT + MT
-aka: RT + MT
8
New cards
types of reaction time
-simple reaction time
-choice reaction time
-discrimination reaction time
-fractionated reaction time
-choice reaction time
-discrimination reaction time
-fractionated reaction time
9
New cards
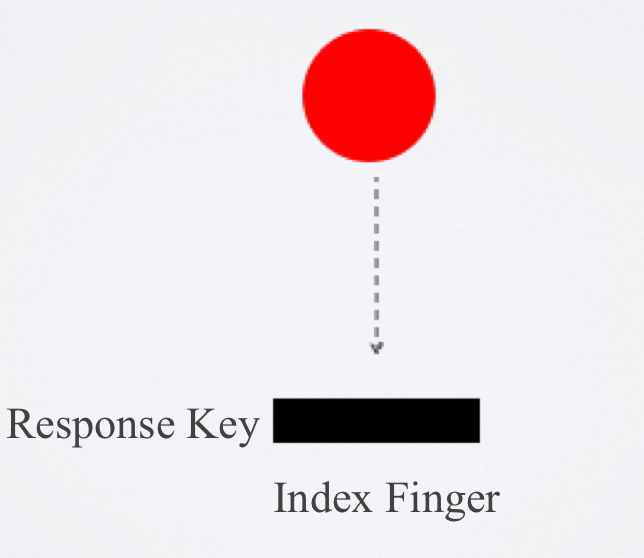
simple reaction time
the reaction time that involves 1 signal/stimulus and 1 response
10
New cards
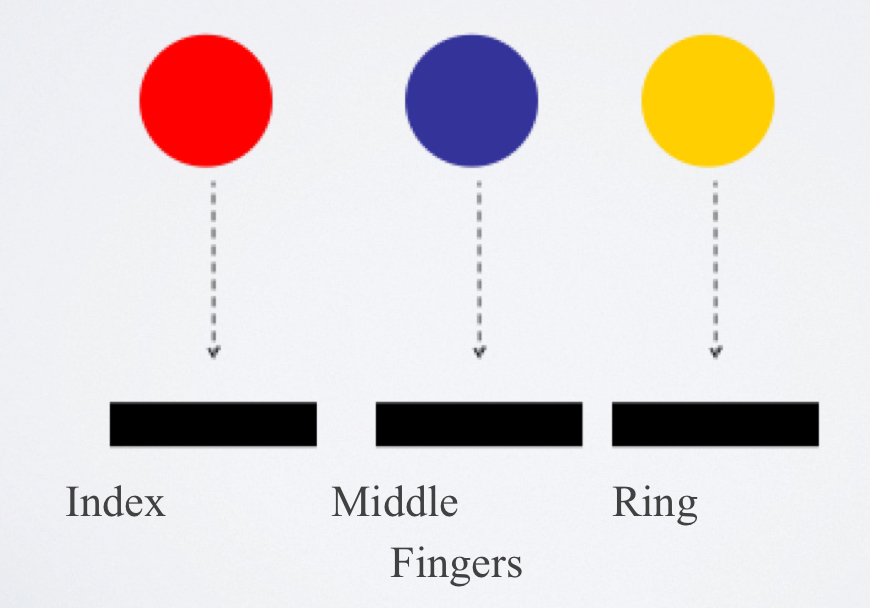
choice reaction time
the reaction time that involves more than one signal & each signal requires its own specified response
11
New cards
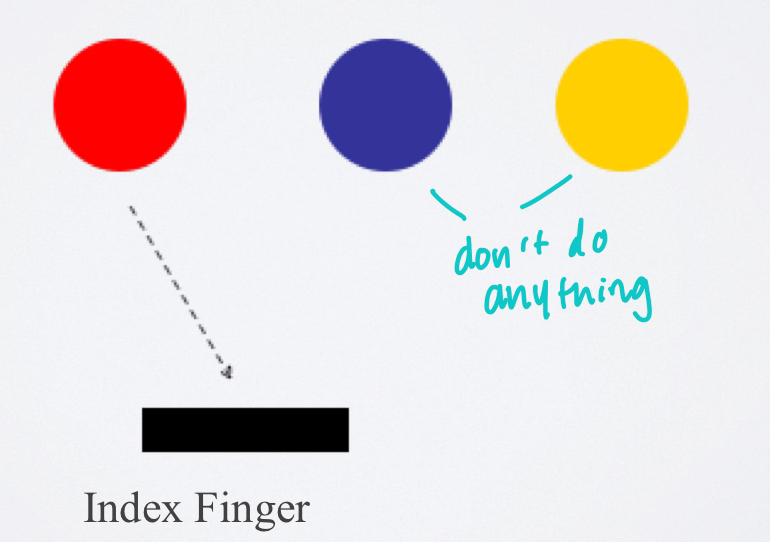
discrimination reaction time
the reaction time that involves more than one signal but only one response--which is to only one of the signals--the other signals require no response
12
New cards
reaction time related to movement and response time
-reaction time does NOT predict movement
-movement time does NOT predict reaction time
-RT and MT are SEPARATE motor abilities
-when comparing individuals, they may have differing rates of both RT and MT
-movement time does NOT predict reaction time
-RT and MT are SEPARATE motor abilities
-when comparing individuals, they may have differing rates of both RT and MT
13
New cards
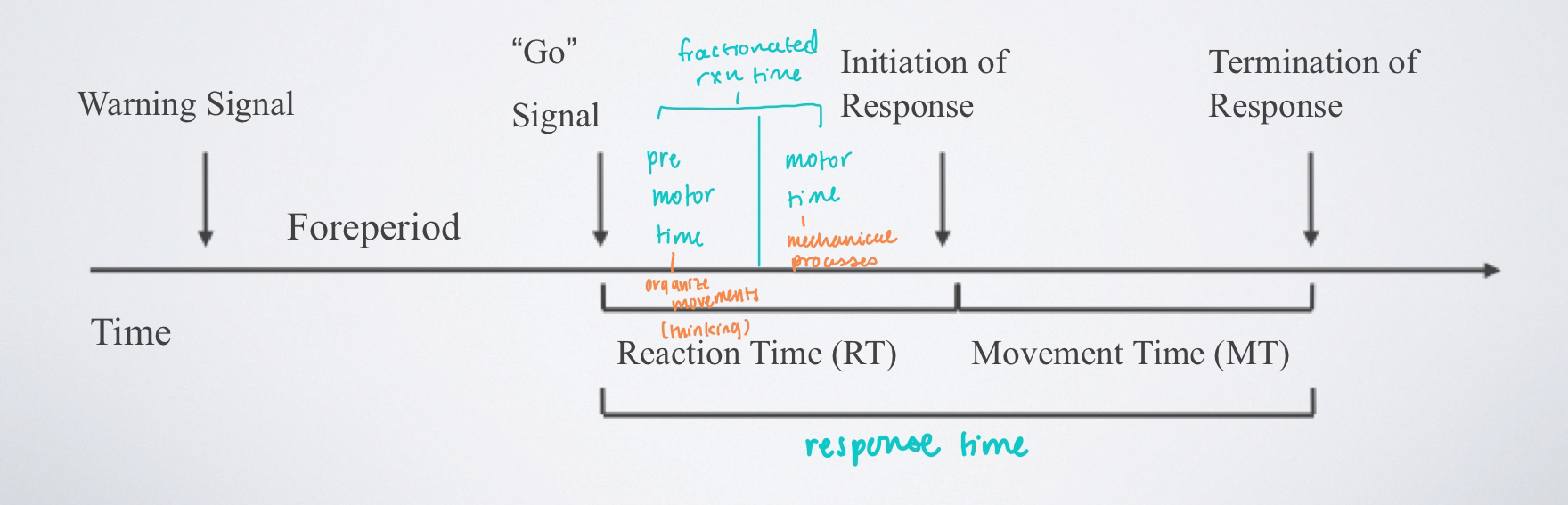
fractionated reaction time (FRT)
-requires the use of EMG to partition into 2 parts:
1) premotor time (PRMOT)
2) motor time (MOT)
-allow researchers to identify if changes in movement RT are due to cognitive processes or mechanical features of the limb(s)
1) premotor time (PRMOT)
2) motor time (MOT)
-allow researchers to identify if changes in movement RT are due to cognitive processes or mechanical features of the limb(s)
14
New cards
premotor time (PRMOT)
time that elapses between the presentation of a stimulus and the first change in EMG(muscle) activity
15
New cards
motor time (MOT)
begins with 1st change in EMG activity and ends when movement begins
16
New cards
error measures for 1 dimensional actions
absolute error
constant error
variable error
constant error
variable error
17
New cards
absolute error
a measure of error without regard to direction
ex: distance from target
ex: distance from target

18
New cards
constant error
signed deviation from the target (biases)
ex: directional biases (given + or - )
ex: directional biases (given + or - )
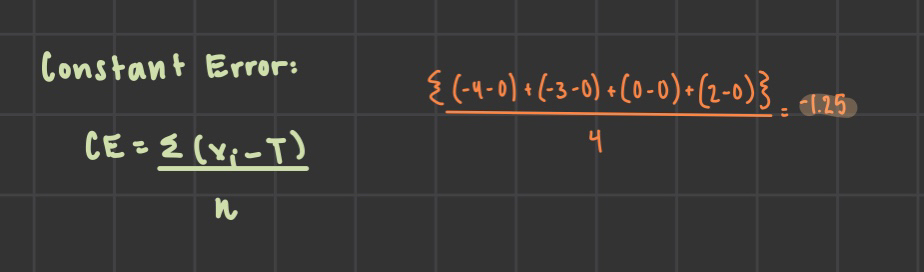
19
New cards
variable error
an error score that represents the variability of performance consistency
-standard deviation of a series of constant error scores
-standard deviation of a series of constant error scores

20
New cards
error measures for 2 dimensional actions
radial error
root-mean-squared error (RMSE)
root-mean-squared error (RMSE)
21
New cards
radial error
use the pythagorean theory to solve
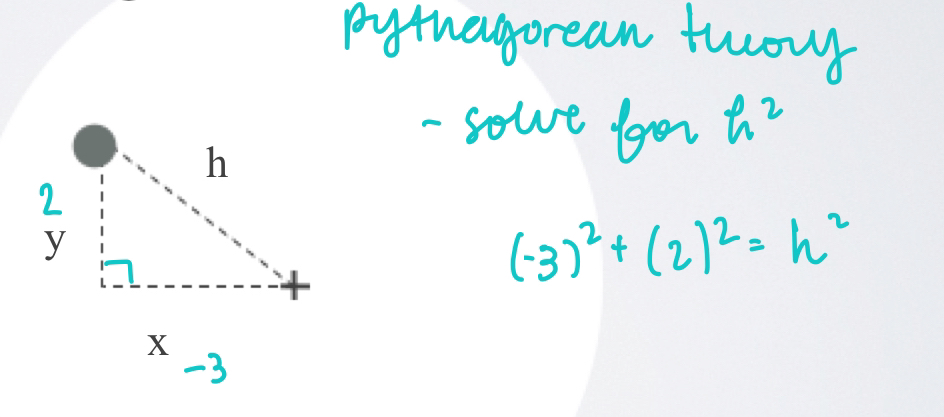
22
New cards
root-mean-squared error (RMSE)
-error measure for continuous skills
-indicates the amount of error between the performance curve produced and the criterion performance curve for a specific amount of time
-ex: tracking
-indicates the amount of error between the performance curve produced and the criterion performance curve for a specific amount of time
-ex: tracking
23
New cards
kinematic measures
-kinematics: the description of motion without regard to force or mass; displacement
-displacement: describes changes in spatial location as a person carries out a movement
-velocity: rate of change in an object position with respect to time
-acceleration: change in velocity during movement
-displacement: describes changes in spatial location as a person carries out a movement
-velocity: rate of change in an object position with respect to time
-acceleration: change in velocity during movement
24
New cards
kinetic measures
-kinetics: force as the cause of motion
-measuring tools: force plate, strain gauge
-measuring tools: force plate, strain gauge
25
New cards
EMG
(electromyography)
-measures electrical activity in muscles
-measures electrical activity in muscles
26
New cards
EEG
(electroencephalography)
-measures brain activity
-measures brain activity
27
New cards
PET
(position emission tomography)
-used for measuring the concentration of positron-emitting radioisotopes within different body tissues
-used for measuring the concentration of positron-emitting radioisotopes within different body tissues
28
New cards
fMRI
(functional magnetic resonance imaging)
-visualizes brain function through change in fluid flow (cerebrospinal fluid, blood)
-visualizes brain function through change in fluid flow (cerebrospinal fluid, blood)
29
New cards
lesions
remove portion of brain matter to see its effect on function (performed on lab animals or people with lesions already such as stroke victims)