Psych of Aging Chapters 5, Psych of Aging Ch 6, Psych of Aging Ch. 7, Psych of Aging Chapter 9
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/122
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:38 AM on 11/9/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
1
New cards
activities of daily living (ADLs)
basic self-care tasks such as eating, bathing, toileting, walking, and dressing
2
New cards
instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs)
actions that require some intellectual competence and planning such as using the phone, shopping, making meals, household tasks, taking meds, and doing laundry
3
New cards
Risk factors such as smoking, drinking, unhealthy eating, sedentary lifestyle, and obesity are related to what
chronic diseases (cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, etc.)
4
New cards
noncommunicable disease
diseases caused by environmental and behavioral factors (cancer, cardiovascular disease) 41 million people worldwide (85% occur in lower-income countries)
5
New cards
cardiovascular disease
number one cause of death worldwide, a set of abnormal conditions that develop in the heart and arteries
6
New cards
Atherosclerosis
the process of fatty deposits collecting at an abnormally high rate, substantially reducing the width of the arteries and limiting the circulation of the blood; accelerated due to diet and lack of exercise
7
New cards
Arteiosclerosis
thickening and hardening of the arteries; everyone experiences some degree of this
8
New cards
myocardial infarction
acute condition in which the blood supply to part of the heart muscle is severely reduced or blocked
9
New cards
Hyperextension
chronic abnormally elevated blood pressure; a sign that the heart and blood vessels are being overworked
10
New cards
what age group has the highest rates of physical inactivity?
older adults age 75+
11
New cards
one person dies every 35 seconds in the U.S. from which disease
cardiovascular disease
12
New cards
congestive heart failure
heart is unable to pump its required amount of blood
13
New cards
cerebrovascular accident
another name for stroke
14
New cards
stroke
an artery leading to the brain bursts or is clogged by a blood clot or another particle
15
New cards
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
a "mini-stroke" caused by the blockage of a blood vessel, which resolves (goes away) within 24 hours
16
New cards
stroke belt
8 states with increased stroke mortality in southeast US
17
New cards
metabolic syndrome
A cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
18
New cards
mederteranian diet
diet used to reduce the risk of developing metabolic syndrome
19
New cards
low income countries
where are cancer deaths most common?
20
New cards
cancer
develops when random mutations occur that cause the body's cells to malfunction due to a mistake in cell division or in response to injuries from environmental factors such as radiation or chemicals
21
New cards
being overweight and obesity
What are some risk factors for cancer among women
22
New cards
Cancer alley
areas where people are breathing in toxins
23
New cards
70%
What percent of cancer deaths are from low income areas
24
New cards
radiation, surgery, chemo, targeted drug therapies
cancer treatments
25
New cards
arthritis
inflammation of a joint
26
New cards
Osteoarthritis
bone spurs, loss of fluid in the joints
27
New cards
Osteoporosis
loss of bone density
28
New cards
type 1 diabetes
genetic disorder in which the body cannot produce enough insulin
29
New cards
type 2 diabetes
lifestyle progressive disorder in which body cells become less responsive to insulin
30
New cards
chronic bronchitis
inflammation and excess mucus
31
New cards
Emphysema
damaged air sacs
32
New cards
Alzheimer's disease
a progressive and irreversible brain disorder characterized by gradual deterioration of memory, reasoning, language, and, finally, physical functioning
33
New cards
normal aging
processes of aging that represent a gradual decline of systems and body functions at a normal rate
34
New cards
APOE gene
- Indicates risk but not everyone with the gene develops Alzheimer's disease
35
New cards
mental activity, social support, physical activity, Mediterranean diet, limited alcohol
these may reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease
36
New cards
Anticholinesterase, glutamate, anti-beta amyloia digomers
Medical treatment for Alzheimer's disease
37
New cards
reaction time
processing speed and attention
38
New cards
Brinley Plot
a graph where the average response time of older adults is graphed as a function of the average response time of younger adults
39
New cards
General Slowing
loss of attentional resources leads to longer times to respond
40
New cards
inhibitory deficit
inability to tune out irrelevant information
41
New cards
Stroop Task
older adults are capable of showing inhibition levels comparable to those of young adults when stimuli is presented in two modalities
42
New cards
UFOV (useful field of view)
area from which one can extract visual information in a single glance without turning one's head or moving one's eyes
43
New cards
they have low travel speeds
why do rotaries and roundabouts reduce collisions
44
New cards
working memory
what you're actively thinking about right now
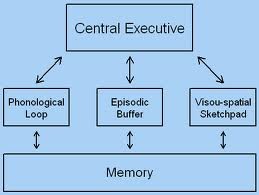
45
New cards
Default Network
When our brain is at rest, deactivates when our working memory engages
46
New cards
eposodic memory
long term memory for events (declines)
47
New cards
source memory
recall of when, where, and how information was acquired (declines)
48
New cards
false memory
an inaccurate memory that feels as real as an accurate memory (declines)
49
New cards
retrieval memory
the process of getting information out of memory storage (decline)
50
New cards
prospective memory
wanting to do something and forgetting (declines)
51
New cards
semantic memory
memory for knowledge about the world (remains stable)
52
New cards
flashbulb memory
a clear memory of an emotionally significant moment or event (911) (remains stable)
53
New cards
implicit memory
skills we learn through repetition (driving) (remains stable)
54
New cards
procedural memory
doing procedures (walk, brush teeth) (remains stable)
55
New cards
scaffolding theory of memory
•According to the scaffolding theory, older adults can recruit alternate neural circuits as needed by task demands as shown by these potential routes.
56
New cards
reminiscence bump
older adults tend to think about the "good ol days"
57
New cards
Accumulation of information theory
accumulation of info takes longer to process (takes older adults longer to sift through all the knowledge they have)
58
New cards
psychosocial influence on memory
stress and depression, memory, stereotype threat
59
New cards
smoking, diet, aerobic exercise, strength training
factors that influence memory
60
New cards
method of loci
way to improve long term memory by using a mental map-ex: mentally imagining a place you know well and mentally walking through each room
61
New cards
executive functioning
the cognitive abilities and processes that allow humans to plan, allocate mental resources. Declines over time
62
New cards
WCST
sort cards depicting various pictures & symbols
-assesses a person's ability to switch sets, reason abstractly, and solve problems
(ie, executive fxns) > localized in the frontal lobes
-poor performance in schizophrenics
-assesses a person's ability to switch sets, reason abstractly, and solve problems
(ie, executive fxns) > localized in the frontal lobes
-poor performance in schizophrenics
63
New cards
semantic memory, gist of story, gestures, experiences, etc
What are some abilities that contribute to stability
64
New cards
Verbal Comprehension Index
tests on the WISC-IV that tap verbal skills such as knowledge of vocabulary and general information
65
New cards
Perceptual Reasoning Index
tests on the WISC-IV, such as block design and picture completion, that tap nonverbal visual-processing abilities.
66
New cards
Processing Speed Index
Timed tests on the WISC-IV, such as symbol search, that measure how rapidly an examinee processes information
67
New cards
working memory index
tests on the WISC-IV, such as digit span, that measure working memory efficiency
68
New cards
elderspeak
A condescending way of speaking to older adults that resembles baby talk, with simple and short sentences, exaggerated emphasis, repetition, and a slower rate and a higher pitch than used in normal speech.
69
New cards
everyday problem solving
1.) assess situation
2.) decide on desired end state
3.) transform current state into desired state
2.) decide on desired end state
3.) transform current state into desired state
70
New cards
Top-down problem solving
Solving begins at the highest-level, also known as the strategic thought. From there, the problem is broken down, identifying and developing the elements at the next level down. (typically used to solve a small problem)
71
New cards
Bottom-up problem solving
Begins with the tactical, granular, specific details. Starts with a list of issues, then organizing them into like groups. Those groups can often be grouped further, building levels up, until, finally, the key drivers and governing thought are reached. (typically used to solve a larger problem)
72
New cards
Everyday problems test (EPT)
a test that measures reaction time, knowledge, experience, and education
73
New cards
The trolly problem
test of post formal logic because there is no "right" answer to the question
74
New cards
stereotype threat
a self-confirming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype
75
New cards
Cattell-Horn-Carroll model of intelligence
motor, perception, controlled attention, knowledge
76
New cards
g factor
the ability to reason and solve problems, or general intelligence; general intelligence/knowledge
77
New cards
number
According to the Seattle Longitudinal Study, tests of __________ showed the greatest decline related to aging
78
New cards
fluid intelligence
our ability to reason speedily and abstractly; tends to decrease during late adulthood ex: problem solving
79
New cards
crystallized intelligence
our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; tends to increase with age ex: knowledge you gain from your career
80
New cards
openness fluid crystallized intelligence (OFCI)
model regarding personality openness as a protective factor against cognitive decline in later adulthood
81
New cards
lifespan conceptualism
understand cultural impact
82
New cards
Value Relativism
Life goals/values/beliefs differ depending on individual and culture (differences are respected)
83
New cards
factual/procedural knowledge
know how things work, understand other perspectives
84
New cards
management of uncertainty
understand that life is uncertain and flexible
85
New cards
marriage
the legal binding between two people, defined as a union between partners
86
New cards
2013
year that same sex marriage became legal
87
New cards
Massachusetts
same sex marriage was first legalized in which state?
88
New cards
widowed
By the age of 85, 33% of men and 70% of women are ___________
89
New cards
women
more likely to initiate divorce
90
New cards
Cohabitation
Living together without being married; more people are doing this than in the 70's
91
New cards
cohabitation effect
couples who cohabit before marriage are more likely to divorce
92
New cards
10%
______% of adults 18 and older are divorced
93
New cards
save face
divorce is not totally one person's fault, may help the divorce partners to feel less negative about the experience
94
New cards
resilience after loss
most common; pre-loss acceptance, new normal
95
New cards
chronic grief
least frequent; pre-loss dependency
96
New cards
widowhood effect/broken heart syndrome
the impact of the death is so strong that surviving spouses tend to die earlier than expected
97
New cards
socioemotional selectivity theory
looking at the bright side of relationships, rather than the negative
98
New cards
social exchange theory
benefits outweigh the costs of relationship
99
New cards
equity theory
how much effort each person contributes to a relationship is based on
100
New cards
similarity theory
based on the concept that we fall in love with people who are similar to us in important ways