1. General Physics
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:57 AM on 9/18/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
1
New cards
Define a ruler.
A ruler is used to measure length for distances from 1 millimeter to 1 metre.
2
New cards
State the formula to find the volume for a regular object.
width x height x length
3
New cards
Describe how to find the volume for an irregular object.
Measure by displacement :
Put the object into a measuring cylinder with water. When the object added, it displaces water, making water level rise. Measure this rise. This is the volume.
Put the object into a measuring cylinder with water. When the object added, it displaces water, making water level rise. Measure this rise. This is the volume.
4
New cards
What tools can be used to find large distances?
A trundle wheel
Tape measure
Tape measure

5
New cards
What tools can be used to find mass?
A balance
A scale
A scale
6
New cards
What tools can be used to find length?
A metre rule
Tape measure
Vernier calipers
Tape measure
Vernier calipers
7
New cards
What tools can be used to find volume?
A measuring cylinder
Micrometer screw gauge
Micrometer screw gauge
8
New cards
What tools can be used to find time?
A stop clock
An electronic timer
An electronic timer
9
New cards
Describe a micrometer screw gauge, and how to use it.
A micrometer screw gauge is used to find very small distances(less than a centimetre).
It has two scales; the main scale and the rotating scale/ fractional scale.
The units of the main scale is in millimetres (mm) and the fractional scale is 1/100th of the main scale, therefore it is 0.01mm
To measure:
Thickness of object = main scale reading + fractional scale reading
It has two scales; the main scale and the rotating scale/ fractional scale.
The units of the main scale is in millimetres (mm) and the fractional scale is 1/100th of the main scale, therefore it is 0.01mm
To measure:
Thickness of object = main scale reading + fractional scale reading
10
New cards
What can be used to measure time intervals?
Stopclocks and stopwatches.
11
New cards
What is a significant factor to consider when measuring time?
Human reaction time.
12
New cards
What is the difference between an analogue clock and a digital clock?
In analogue clocks:
Time is found by clock's hands
A small wheel (the balance wheel) oscillates to and fro
In digital clocks:
Gives direct reading of time in numerals
The oscillations are produced by a tiny quartz crystal.
Time is found by clock's hands
A small wheel (the balance wheel) oscillates to and fro
In digital clocks:
Gives direct reading of time in numerals
The oscillations are produced by a tiny quartz crystal.
13
New cards
How would an accurate measure of the width of a single piece of paper be measured?
By taking multiple readings.
Instead of trying to measure a single piece of paper, measure 100 and from that divide the measurement by the total number of pieces of paper. This is finding the average.
Instead of trying to measure a single piece of paper, measure 100 and from that divide the measurement by the total number of pieces of paper. This is finding the average.
14
New cards
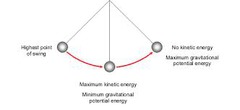
What tool would require multiple readings to be taken for an accurate measurement?
A pendulum
15
New cards
Define speed.
Speed is the distance moved by an object each
second. It's units are metres per second (m/s)
second. It's units are metres per second (m/s)
16
New cards
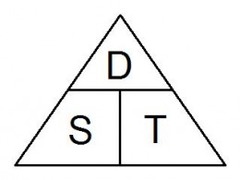
State the formula of speed.
speed= distance/time
s=d/t
s=d/t
17
New cards
Define velocity.
Velocity is a similar quantity to speed, but includes a direction. It is a vector quantity while speed is a scalar quanity.
It is speed in a given direction.
It is speed in a given direction.
18
New cards
Distance moved in a stated direction is called....?
Displacement
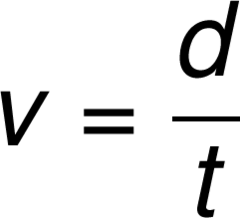
19
New cards
Define acceleration.
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity: In other words, how much the velocity of an object changes by every second. It is a vector quantity. It's units are m/s^2
20
New cards
State the formula of acceleration.
acceleration = change in velocity/time taken
a=(v-e)/t
a=(v-e)/t
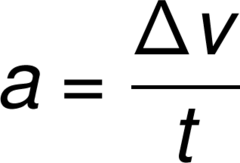
21
New cards
An acceleration is ______________ if the velocity increases and
negative if it ___________________. A negative acceleration is also
called a _________________ or ____________________.
negative if it ___________________. A negative acceleration is also
called a _________________ or ____________________.
Positive
Decreases
Deceleration
Retardation
Decreases
Deceleration
Retardation
22
New cards
In distance-time graphs:
A horizontal line means __________________
A straight line means ___________ ___________
If the gradient _____________ the object is speeding up (accelerating)
If the gradient ________________ the object is slowing down (decelerating)
If the line is going down, the object is moving ______________
A horizontal line means __________________
A straight line means ___________ ___________
If the gradient _____________ the object is speeding up (accelerating)
If the gradient ________________ the object is slowing down (decelerating)
If the line is going down, the object is moving ______________
Stationary
Constant speed
Increases
Decreases
Backwards
Constant speed
Increases
Decreases
Backwards
23
New cards
State how to calculate speed in a distance-time graph.
The speed of an object is given by the gradient of the line.
speed = gradient = rise/run
speed = gradient = rise/run
24
New cards
What are distance-time graphs also called?
Position-time graphs
Displacement-time graphs
Displacement-time graphs
25
New cards
Define velocity-time graph.
A Velocity-time graph shows how the velocity (or speed) of an object changes over
time.
time.
26
New cards
If the line is _____________, the velocity is constant (no acceleration)
If the line slopes upwards, then the object is ___________
If the line goes down then the object is ____________
If the line slopes upwards, then the object is ___________
If the line goes down then the object is ____________
Horizontal
Accelerating
Decelerating
Accelerating
Decelerating
27
New cards
State how to find distance moved in a velocity-time graph.
distance = area beneath the graph
(do NOT use the distance-speed-time equation)
(do NOT use the distance-speed-time equation)
28
New cards
What does the gradient of a velocity-time graph represent? How is it found?
Acceleration
acceleration = gradient = rise/run
(m/s^2)
acceleration = gradient = rise/run
(m/s^2)
29
New cards
Define the oscillation of a pendulum.
The number of swings/ period time
30
New cards
In the absence of _______________, all objects fall with the same ___________________, regardless of their mass
Air resistance
Acceleration
Acceleration
31
New cards
State the gravitational field strength near the Earth's surface.
9.8 m/s^2 or 10 m/s^2
Units are also N/kg
Units are also N/kg
32
New cards
The acceleration caused by the pull of the Earth's gravity is called the ____________________. This quantity is given the symbol __ and its value is 10m/s2 close to the surface of the _________.
Acceleration of freefall
g
Earth
g
Earth
33
New cards
Will the speed of a falling object change the longer it falls for?
Yes, it will increase.
34
New cards
Define terminal velocity.
The constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of gravity
35
New cards
The force of gravity is called....?
Weight
Gravitational attraction
Gravitational Force
(do NOT refer to it as gravity/ gravitational field strength/ gravitational potential)
Gravitational attraction
Gravitational Force
(do NOT refer to it as gravity/ gravitational field strength/ gravitational potential)
36
New cards
Define mass.
A measure of the amount of matter in an object. It is measured in kilograms, kg.
37
New cards
Define weight.
A measure of the force of gravity on an object. It is measured in Newtons, N.
The size of this force depends on the gravitational field strength (often called gravity, g, for short)
The size of this force depends on the gravitational field strength (often called gravity, g, for short)
38
New cards
State the formula for weight.
weight = mass * gravitational field strength
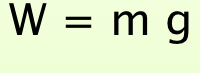
39
New cards
What factors is weight affected by?
Mass and acceleration.
Therefore if there is motion, acceleration changes and so does weight but since mass is only affected by the amount of matter in an object, no matter what forces are acting on it, it will not change.
Therefore if there is motion, acceleration changes and so does weight but since mass is only affected by the amount of matter in an object, no matter what forces are acting on it, it will not change.
40
New cards
Define inertia.
Inertia:
the resistance in change of velocity.
the resistance in change of velocity.
41
New cards
Describe the mass and weight for the same object on two different planets.
The mass is the same
The gravitational field strength, g, on the two planets will be different, so the weight will be different.
The gravitational field strength, g, on the two planets will be different, so the weight will be different.
42
New cards
The weight and mass of an object can be compared using a...?
Balance
43
New cards
State the two significant effects of mass in physics.
The mass of an object's opposed any attempt to change that object's motion The greater the mass of an object, the more difficult it is to speed it up, slow it down or change its direction. This property of mass is sometimes referred to as inertia
Mass is also the source of an object's weight - the force of gravity on a mass. The greater the mass, the greater the weight.
Mass is also the source of an object's weight - the force of gravity on a mass. The greater the mass, the greater the weight.
44
New cards
Define density and state its formula.
Density is the mass per unit volume of a material
Its units are g/cm^3 or kg/m^3
density = mass/volume
Its units are g/cm^3 or kg/m^3
density = mass/volume
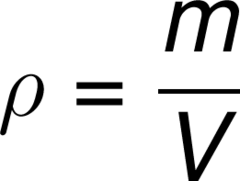
45
New cards
An object will float in a liquid if the average density of that object is ______ than the density of the liquid it is placed in.
Less
46
New cards
Density of water?
1g/cm^3
47
New cards
State how to find the volume:
Sphere
Cylinder
Cube
Sphere
Cylinder
Cube
Sphere
v=4/3 πr^3
Cylinder
v=πr^2 * L
Cube
d^3
v=4/3 πr^3
Cylinder
v=πr^2 * L
Cube
d^3
48
New cards
To find the volume of an irregular object, use a?
Eureka can or measuring cylinders and measure by displacement
49
New cards
Describe how forces may change the size, shape and motion of a body.
o Bending
o Twisting
o Compression
o Extension
o Twisting
o Compression
o Extension
50
New cards
Define Hooke's Law.
The extension of a spring is proportional to the applied force(load), provided the limit of proportionality is not exceeded
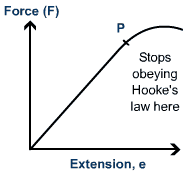
51
New cards
State Hooke's Law Formula.
force = springs constant * extension
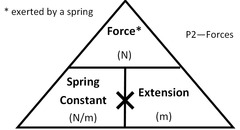
52
New cards
State Newton's first law of motion.
If no external force is acting on it, an object will, if stationary, remain stationary, and if moving, keep moving at a steady speed in the same straight line.
53
New cards
State Newton's second law of motion.
The change of motion of the body is proportional
to the net force imposed on the body and is in the
direction of the net force.
F=ma
to the net force imposed on the body and is in the
direction of the net force.
F=ma
54
New cards
State Newton's third law of motion.
if object A exerts a force on object B, then object B
will exert an equal but opposite force on object A
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
will exert an equal but opposite force on object A
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
55
New cards
If there is no resultant force acting on an object(forces are balanced), an object will...?
Remain stationary/at rest
Continue at a constant speed
Continue at a constant speed
56
New cards
Define friction.
A force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching. It always acts in the opposite direction to the direction in which the object is moving
57
New cards
Friction (including air resistance) results in energy _______ due to the transfer of energy from _________ to internal (heat)
Loss
Kinetic
Kinetic
58
New cards
The resultant force is also known as...?
The net force or the unbalanced force.
59
New cards
When an unbalanced (resultant) force acts on an object, it can affect its motion by....?
The object could speed up
The object could slow down
The object could change direction
The object could slow down
The object could change direction
60
New cards
State the formula for force.
force = mass * acceleration
f=ma
f=ma
61
New cards
State how force, mass and acceleration are related.
The greater the mass of the object, the smaller the
acceleration it is given by a particular force.
acceleration it is given by a particular force.
62
New cards
Describe qualitatively motion in a circular path due to a perpendicular force.
As the centripetal force acts upon an object moving in a circle at constant speed, the force always acts inward as the velocity of the object is directed tangent to the circle. This would mean that the force is always directed perpendicular to the direction that the object is being displaced.
63
New cards
The force needed to make something follow a circular path depends on a number of factors:
The mass of the object (a greater mass requires a greater force)
The speed of the object (a faster-moving object requires a greater force)
The radius of the circle (a smaller radius requires a greater force)
The speed of the object (a faster-moving object requires a greater force)
The radius of the circle (a smaller radius requires a greater force)
64
New cards
Define centripetal force and centrifugal force.
Centripetal force: the force that is acting towards the
centre of a circle. It is a force that is needed, not caused, by circular motion.
Centrifugal force: the force acting away from the centre of a circle. The centrifugal force is the reaction to the centripetal force. It has the same magnitude but opposite direction to centripetal force.
centre of a circle. It is a force that is needed, not caused, by circular motion.
Centrifugal force: the force acting away from the centre of a circle. The centrifugal force is the reaction to the centripetal force. It has the same magnitude but opposite direction to centripetal force.
65
New cards
Define moment and give an example involving it.
The turning effect of a force. Their units are N m, or
N cm.
e.g. opening/closing a door
turning a tap on or off
N cm.
e.g. opening/closing a door
turning a tap on or off
66
New cards
The size of the moment depends upon:
The size of the force
The distance between the force and the pivot
The moment of a force is greatest is if it acts 90° to the object it acts on
The distance between the force and the pivot
The moment of a force is greatest is if it acts 90° to the object it acts on
67
New cards
State the equation for moment of a force
moment of a force = force x distance to pivot
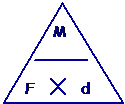
68
New cards
State the principle of moments.
For a system to be balanced, the sum of clockwise moments must be equal to the sum of anticlockwise moments
clockwise moments = anticlockwise moments
clockwise moments = anticlockwise moments
69
New cards
State the conditions for equilibrium.
The forces on the object must be balanced (there must be no resultant force)
The sum of clockwise moments on the object must equal the sum of anticlockwise moments (the principle of moments)
The sum of clockwise moments on the object must equal the sum of anticlockwise moments (the principle of moments)
70
New cards
Define the centre of mass/centre of gravity.
The point through which the weight of that object acts
71
New cards
Perform and describe an experiment to determine the position of the centre of mass of a plane lamina.
The irregular shape (a plane laminar) is suspended from a pivot and allowed to settle
A plumb line (lead weight) is then held next to the pivot and a pencil is used to draw a vertical line from the pivot (the centre of mass must be somewhere on this line)
The process is then repeated, suspending the shape from two different points
The centre of mass is located at the point where all three lines cross
A plumb line (lead weight) is then held next to the pivot and a pencil is used to draw a vertical line from the pivot (the centre of mass must be somewhere on this line)
The process is then repeated, suspending the shape from two different points
The centre of mass is located at the point where all three lines cross
72
New cards
Describe qualitatively the effect of the position of the centre of mass on the stability of simple objects
If the centre of mass is below the point of suspension of an object, it will be in stable equilibrium (e.g., a hanging pot). If the centre of mass is above the point of suspension of an object, it will be in unstable equilibrium (e.g., a pencil placed on the sharp end). If the line of action of the object's weight moves outside the base, there will be a resultant moment and it will topple.
73
New cards
Stable objects have...?
The most stable objects have a low centre of mass and a wide base
74
New cards
Define scalar and vector quanities.
Scalars are quantities that have only a magnitude
Vectors have both magnitude and direction
Vectors have both magnitude and direction
75
New cards
State common scalars and vectors
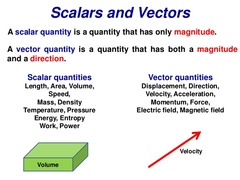
76
New cards
Describe how the resultant vector can be found graphically(vector addition).
o Draw arrows end-to-end, so that the end of one is
the start of the next.
o Choose a scale that gives a large triangle.
o Join the start of the first arrow to the end of the last arrow to find the resultant.
Tip to tip can also be used, that would form a parallelogram.
the start of the next.
o Choose a scale that gives a large triangle.
o Join the start of the first arrow to the end of the last arrow to find the resultant.
Tip to tip can also be used, that would form a parallelogram.
77
New cards
Define and state the formula of momentum.
momentum = mass × velocity
p = m × v
Momentum is defined as the product of mass and velocity. Its units are kg m/s. It is a vector quanity, meaning it can be negative as well as postive.
p = m × v
Momentum is defined as the product of mass and velocity. Its units are kg m/s. It is a vector quanity, meaning it can be negative as well as postive.
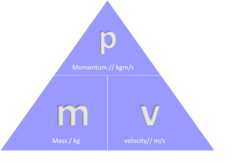
78
New cards
State principle of the conservation of momentum.
In the absence of external forces (such as friction), the total momentum of a system remains the same.
total momentum before = total momentum after
total momentum before = total momentum after
79
New cards
Define and state the formula for impulse.
impulse = change in momentum
F × t = mv - mu or ft = m(v-u)
impulse = force × time
impulse = F × t
F × t = mv - mu or ft = m(v-u)
impulse = force × time
impulse = F × t
80
New cards
Define energy.
Energy is the capacity of something to do work
81
New cards
State the law of conservation of energy.
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only transferred from one place to another.
82
New cards
List the types of energy.
Kinetic
Gravitational potential
Chemical
Elastic (strain)
Nuclear
Internal energy
Gravitational potential
Chemical
Elastic (strain)
Nuclear
Internal energy
83
New cards
State the four ways in which energy can be transferred from one form to another.
Forces (mechanical working)
Electrical currents (electrical working)
Heating - by conduction, convection and thermal radiation
Waves - light and sound carry energy
Electrical currents (electrical working)
Heating - by conduction, convection and thermal radiation
Waves - light and sound carry energy
84
New cards
When energy is transferred from one form to another, not all of the energy will end up in the desired form. This lost energy often ends up
being dissipated (spreading out into the environment). What is the form of this lost energy?
being dissipated (spreading out into the environment). What is the form of this lost energy?
Heat, sound and light.
85
New cards
Define gravitational potential energy. State the formula of g.p.e.
Energy an object possesses because of its height in a gravitational field.
gravitational potetntial energy = mass x gravitational field strength x height
GPE=mgh
gravitational potetntial energy = mass x gravitational field strength x height
GPE=mgh
86
New cards
Define kinetic energy. State its equation.
The kinetic energy (KE) of an object is the energy it has as a result of its speed.
Kinetic energy = 1/2 x mass x speed^2
Kinetic energy = 1/2 x mass x speed^2
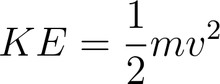
87
New cards
State the energy resources and their energy forms.
Fuels - chemical
Water - gpe
Waves - ke
Geothermal - internal
Nuclear fission - nuclear
Solar heating - light
Solar cells - light
Wing - ke
Water - gpe
Waves - ke
Geothermal - internal
Nuclear fission - nuclear
Solar heating - light
Solar cells - light
Wing - ke
88
New cards
What factors should be considered when giving the pros and cons of energy resources?
Reliability
Environmental impact
Cost
Scale
Renewability
Environmental impact
Cost
Scale
Renewability
89
New cards
Two advantages of all non-renewable fuels are...?
o their high energy density (i.e. they are concentrated sources) and the relatively small size of the energy transfer device (e.g. a furnace) which releases their energy
o their ready availability when energy demand increases suddenly or fluctuates seasonally.
o their ready availability when energy demand increases suddenly or fluctuates seasonally.
90
New cards
The Sun is the source of all energy except...?
Geothermal
Nuclear
Tidal
Nuclear
Tidal
91
New cards
The Sun's energy is produced through nuclear fusion. Define nuclear fusion.
Nuclear fusion involves the collision (and bonding) of hydrogen nuclei to form helium nuclei, releasing nuclear energy in the process
92
New cards
The efficiency of a system can be increased by:
o Reducing waste output (lubrication, thermal insulation etc)
o Recycling waste output (e.g., absorbing thermal waste and recycling it as input energy)
o Recycling waste output (e.g., absorbing thermal waste and recycling it as input energy)
93
New cards
Define efficiency.
Efficiency is a measure of how much useful work is done with the energy supplied.
94
New cards
State the equation for efficiency.
Efficiency = useful energy output ÷ total energy input
Efficiency = useful power output ÷ total power input
Efficiency = useful power output ÷ total power input
95
New cards
Define work done and state its formula.
Work is done whenever a force acts on an object that moves (or is moving) in the direction of the force
energy transferred (J) = work done (J)
work done = force × distance moved
W = F× d
Its units are joules(J) or Nm
energy transferred (J) = work done (J)
work done = force × distance moved
W = F× d
Its units are joules(J) or Nm
96
New cards
Define power and state its formula.
Because work done is equal to energy transferred, the power is also equal to the rate of doing work.
Power is the amount of energy transferred (rate of work done) every second.
power = energy transferred(work done)/ time
The unit of power is the Watt (W), or Joules per second (J/s)
Power is the amount of energy transferred (rate of work done) every second.
power = energy transferred(work done)/ time
The unit of power is the Watt (W), or Joules per second (J/s)
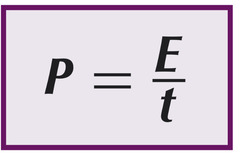
97
New cards
Define pressure and state its formula.
Pressure is the concentration of a force.
pressure = force/area
p = f/a
Its units are N/cm^2, N/m^2 or Pascals (Pa)
1 Pa is the same as 1 N/m^2
pressure = force/area
p = f/a
Its units are N/cm^2, N/m^2 or Pascals (Pa)
1 Pa is the same as 1 N/m^2
98
New cards
The pressure in a liquid when an object is immersed in it depends upon a couple of factors:
The depth of the liquid
The density of the liquid
The bigger either of these factors, the greater
the pressure
The density of the liquid
The bigger either of these factors, the greater
the pressure
99
New cards
Formula for pressure in liquids.
pressure = depth x density x gravitational field strength
P = hρg
P = hρg
100
New cards
Describe the simple mercury barometer and its use in measuring atmospheric pressure.
A barometer is a device that is used to measure air pressure. A simple barometer consists of a column of mercury in an inverted tube, sat in a tray of mercury exposed to the atmosphere. The weight of the mercury in the tube is balanced by atmospheric pressure pushing down on the mercury in the tray.
If atmospheric pressure increases, a greater length of mercury can be supported in the tube.
If atmospheric pressure decreases, then less mercury will be supported in the tube.
If atmospheric pressure increases, a greater length of mercury can be supported in the tube.
If atmospheric pressure decreases, then less mercury will be supported in the tube.