Class 14- Intro to h20, vitamins, water, soluble antioxidants
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
summary of importance of micronutrients
needed in small amount, non-caloric
Not endogenously synthesized at rates sufficient to meet requirements
Perform specific biological functions
If withdrawn from the diet, deficiency results
Consider: Absorption, Transport, Storage, Excretion, Toxicity Interactions and Requirements
what intermediary micronutrient roles
B complex
what are structural micronutrient roles
Ca and P in bones, minerals in metalloenzymes, hemoglobin
what hormonal micronutrient roles
Vit A as retenoic acid—> cel differentiation
Vit. D as calcitriol—> calcium availability
in order to be a vitamin..
NOT being able to be indigenously synthsised in body
-perform key functions
what are antioxidant micronutrient function
vit. A,C, E
mineral→ Se
what are electrolyte micronutrient function
Na, k, Cl
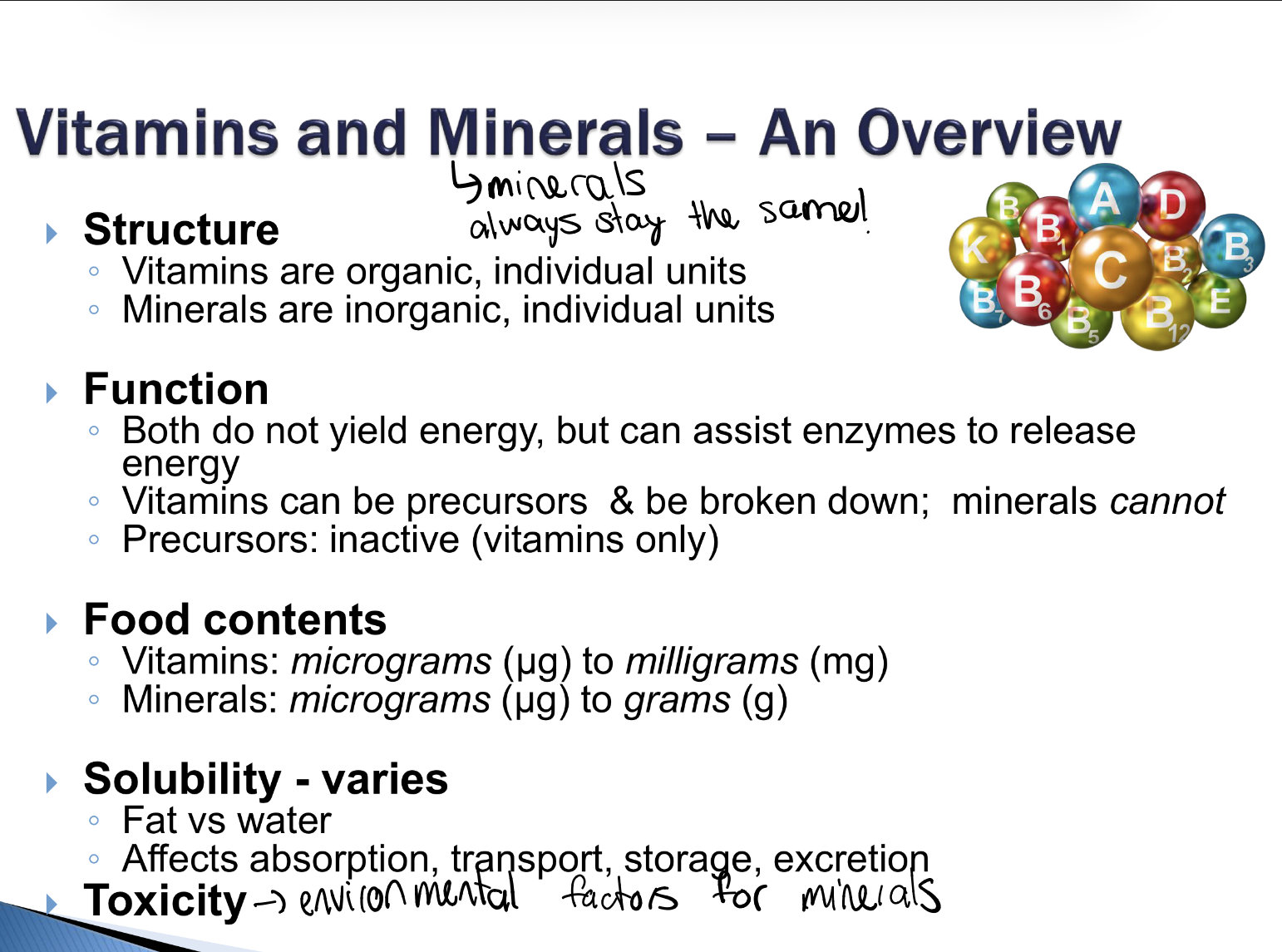
what are main differences in Vit an Minerals for structure, function, food content, solubility
what is bioavailability ? what is it influenced by?
Includes the rate and the extent to which a
nutrient is absorbed and then actually used
◦ Influenced by:
Efficiency of digestion
Transit time
Other foods present - e.g. binders, fibre
Food preparation/ cooking method
Source of the nutrient—> aka Synthetic and fortified foods influence bioavailability
overview of vitamins
Non-caloric nutrients
Body cannot synthesize or not enough made to meet needs
Organic: in fresh foods but they can be readily destroyed during processing/ heating
they are Individual units
Found in different forms: active form or precursors (vitamers or provitamins)
Can be broken down and reformed
Food: Needed in small amounts from the diet (mg or μg),
Bioavailability: varies
Required for metabolism, growth & maintenance of health
Deficiencies may lead to diseases
what are fat soluble vitamins
vit A, D, E,K
what are h20 soluble vitamins (9)
B VITAMINS:
thiamin, B1
riboflavin, B2
Niacin, B3
Folate
Vit. B12
Vit. B6
Biotin
Panthothenic acid
Vitamin C
how are h20 soluble absorbed, transported, stored, excreted, toxicity? requirements approx
how are fat soluble absorbed, transported, stored, excreted, toxicity? requirements approx
only need periodically because stored WITH fat

how are MAJOR minerals absorbed, transported, stored, excreted, toxicity? requirements approx
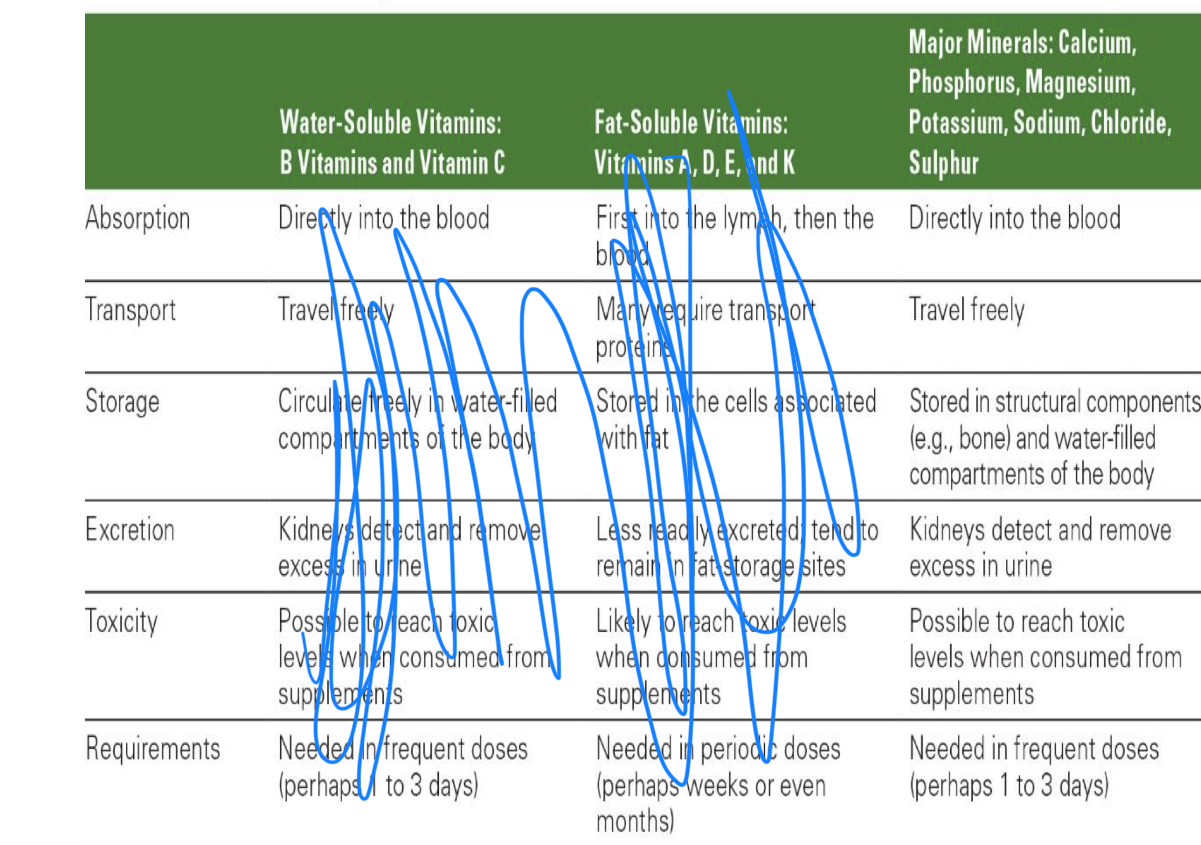
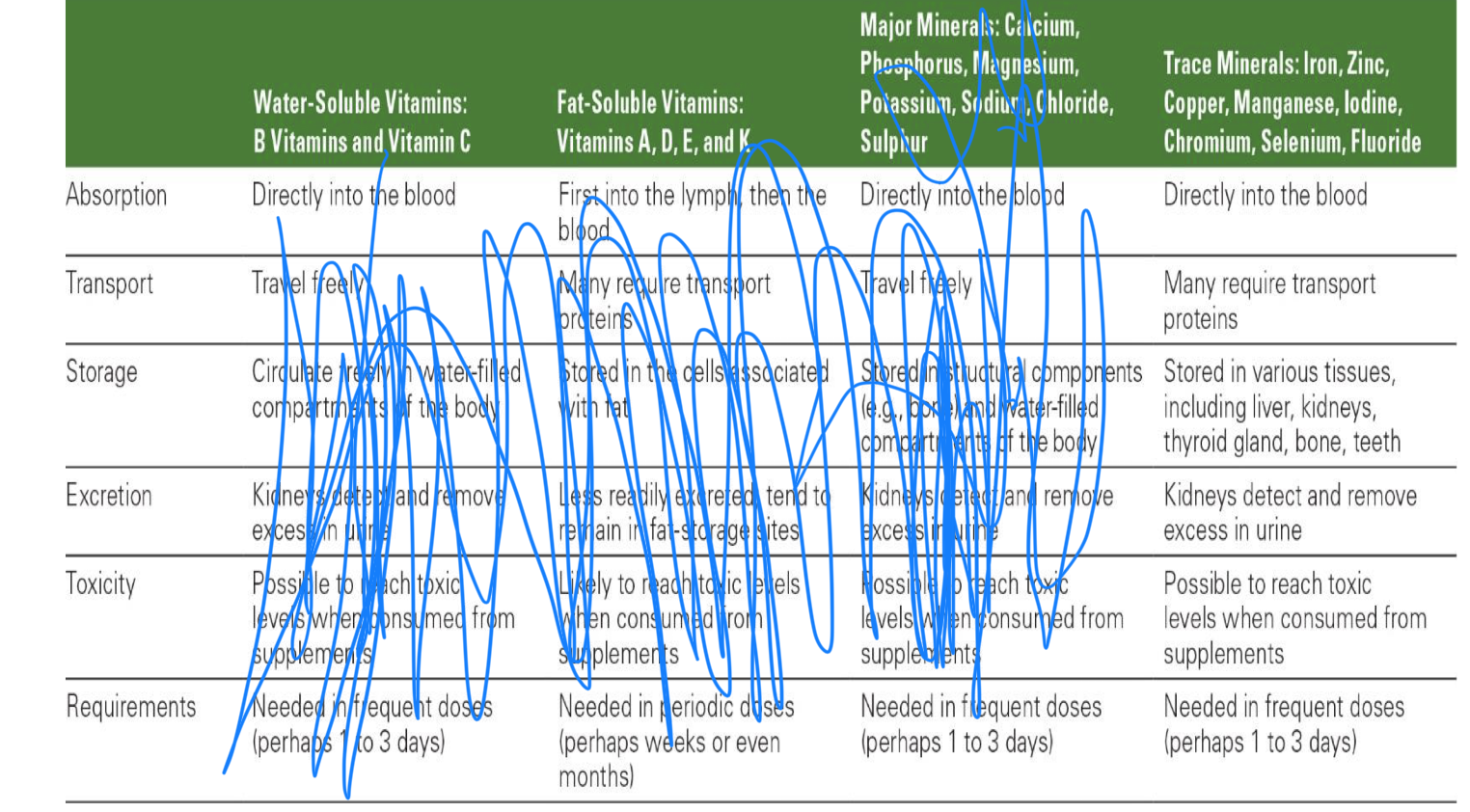
how are MINOR minerals absorbed, transported, stored, excreted, toxicity? requirements approx

what are 4 characteristics water-soluble vitamins share?
dissolve in h20
are easily absorbed and excreted
rarely meet toxic levels
NOT extensively stored in tissues
what happens with Vit. B deficiencies?

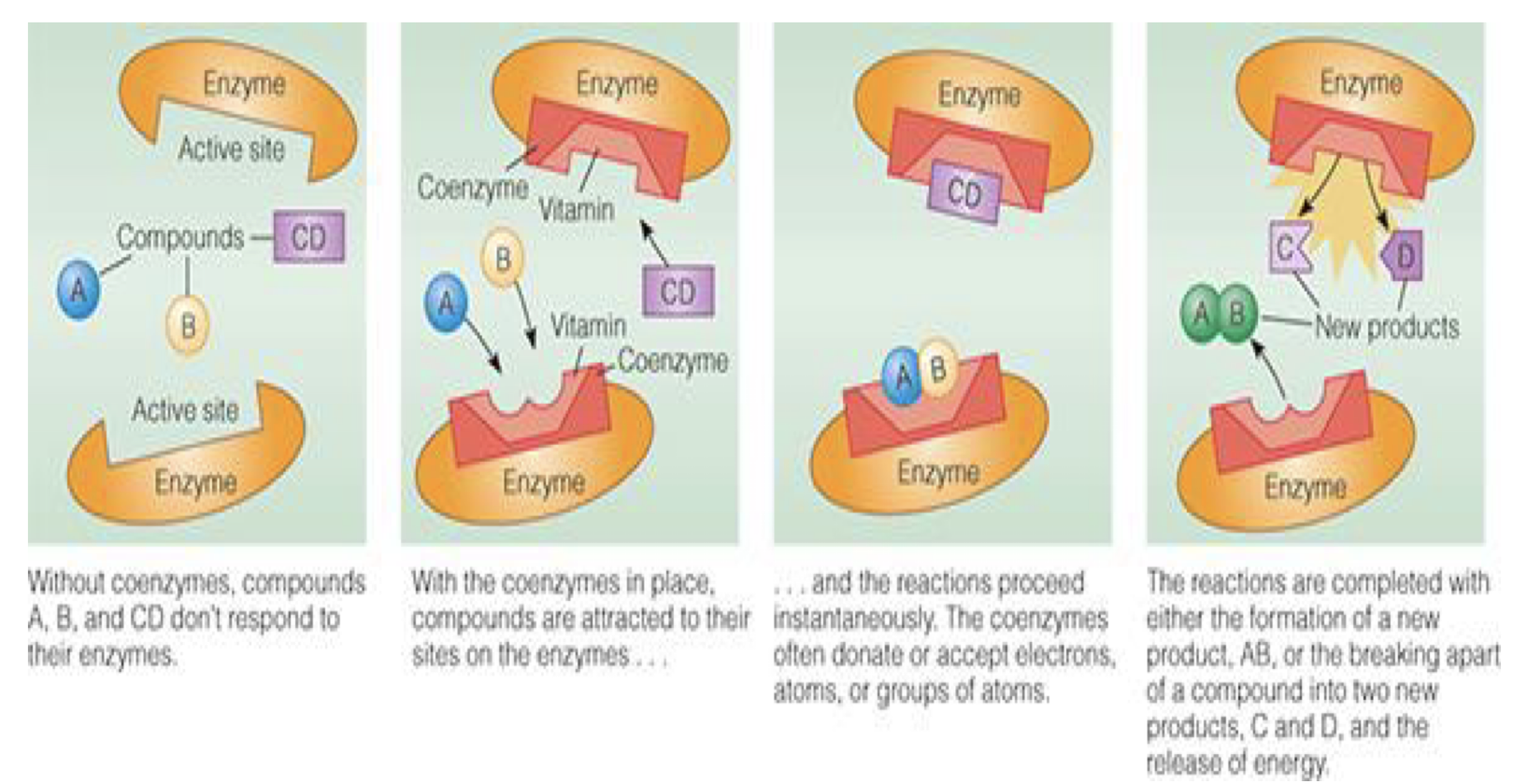
how do enzymes act as coenzymes
required for most enzymes to function!
what are common roles of B vitamins in brain, muscles, bone, liver, digestive tract
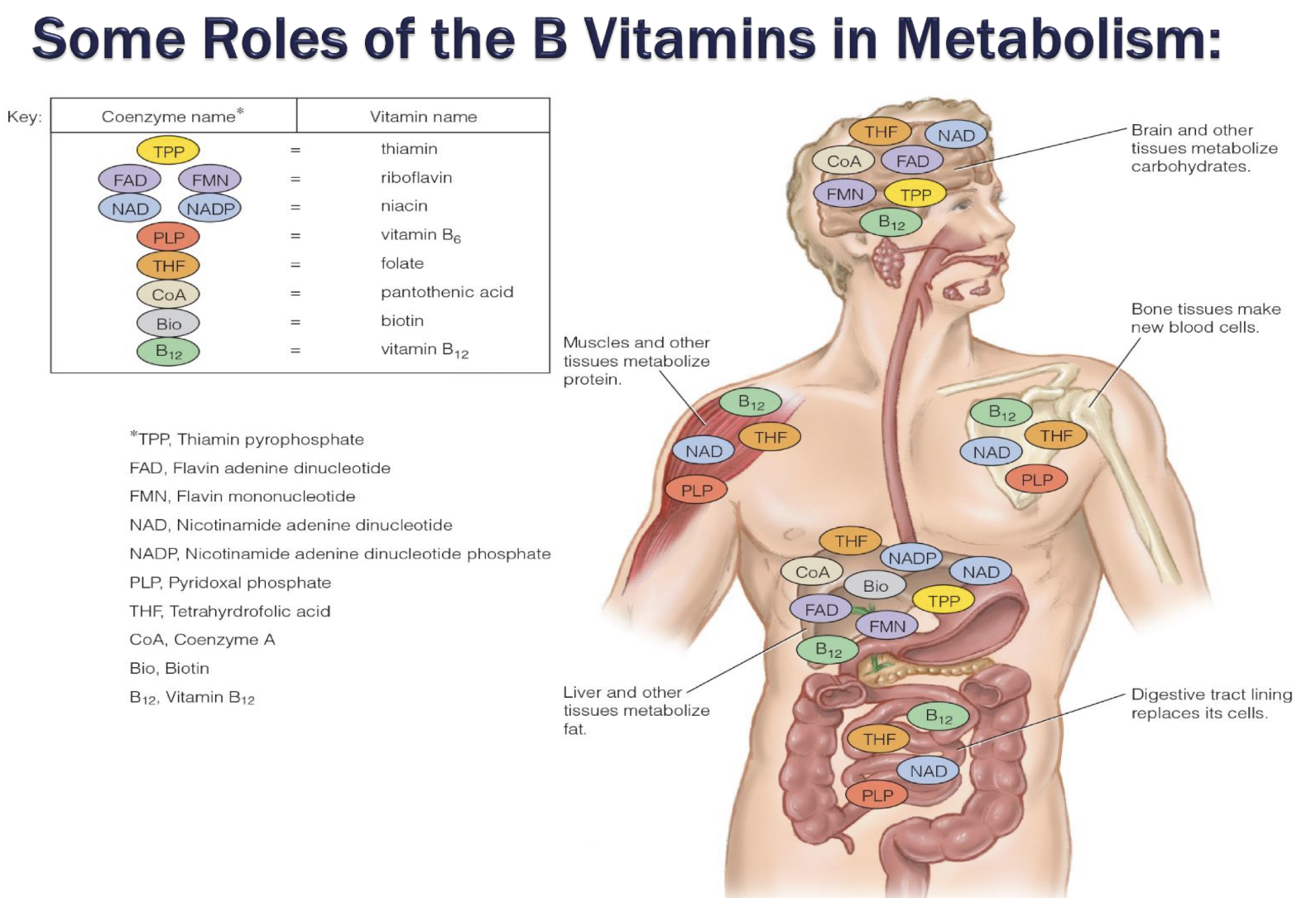
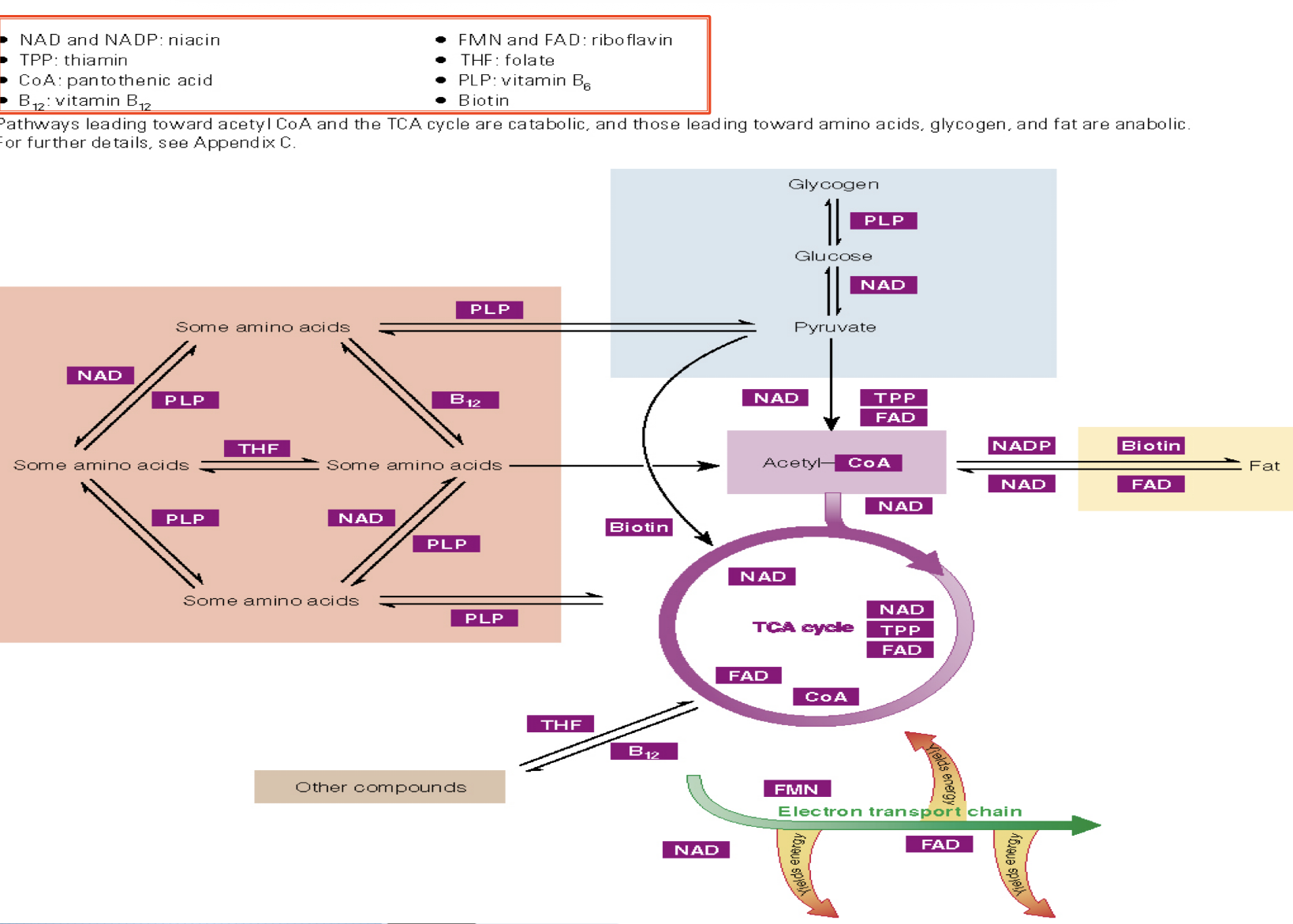
overview of vit. as coenzymes in pathways: leading to acetyl coA, TCA cycle, ETC —> catabolic, and amino acid, glycogen, fat —> anabolic
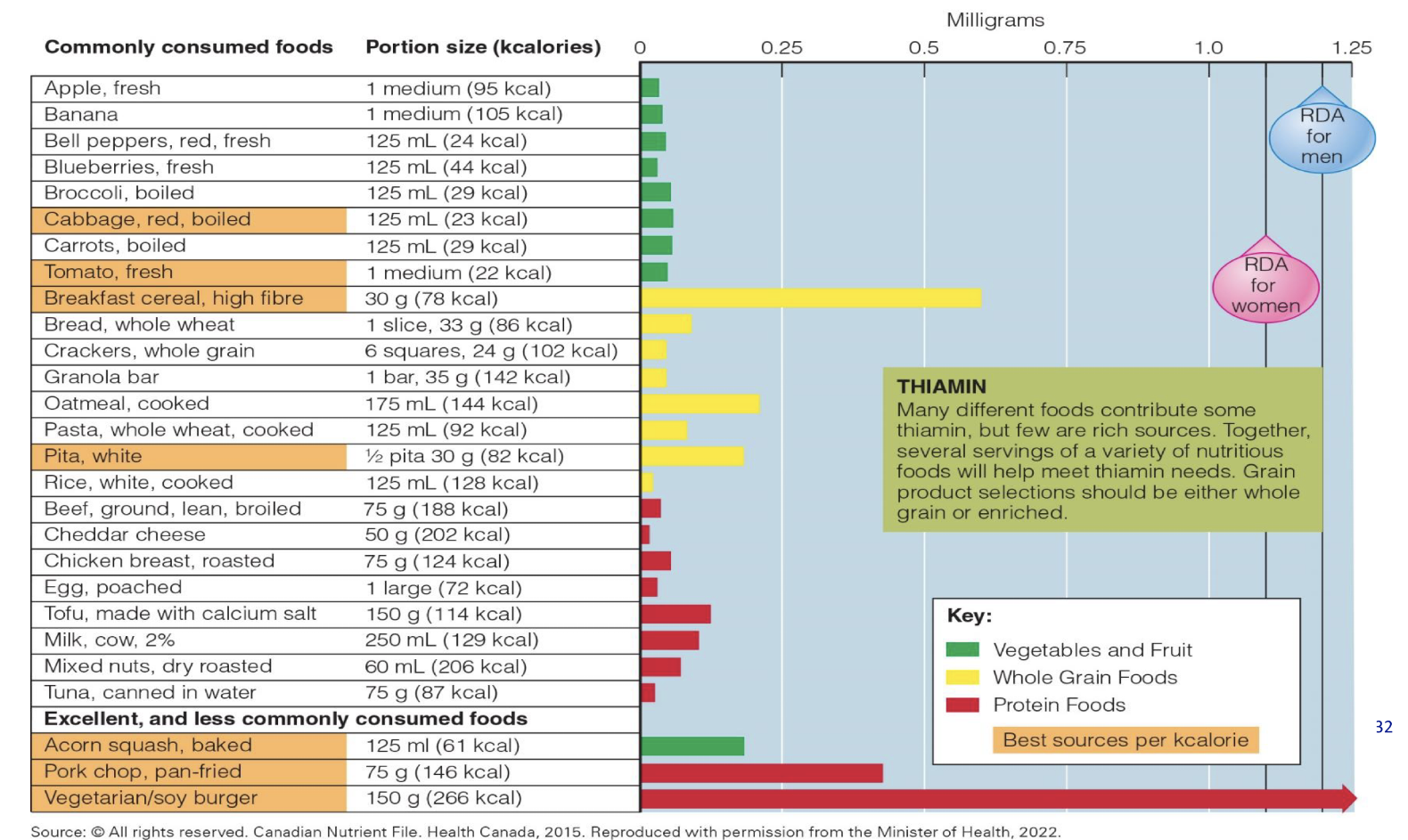
What are Thiamin roles, what are 2 forms of deficiencies
Part of coenzyme thiamin
pyrophosphate (TPP)
Assists in energy and EtOH
metabolism
Conversion of pyruvate to acetylCoA: TCA cycle, Nerve activity and muscle activity
its easy to get, Average intake meets or
exceeds rec’s with adequate kcal
Deficiency: Beriberi: wet(edema) vs dry(musculature)
-High risk with EtOH abuse, malnourished, food insecure
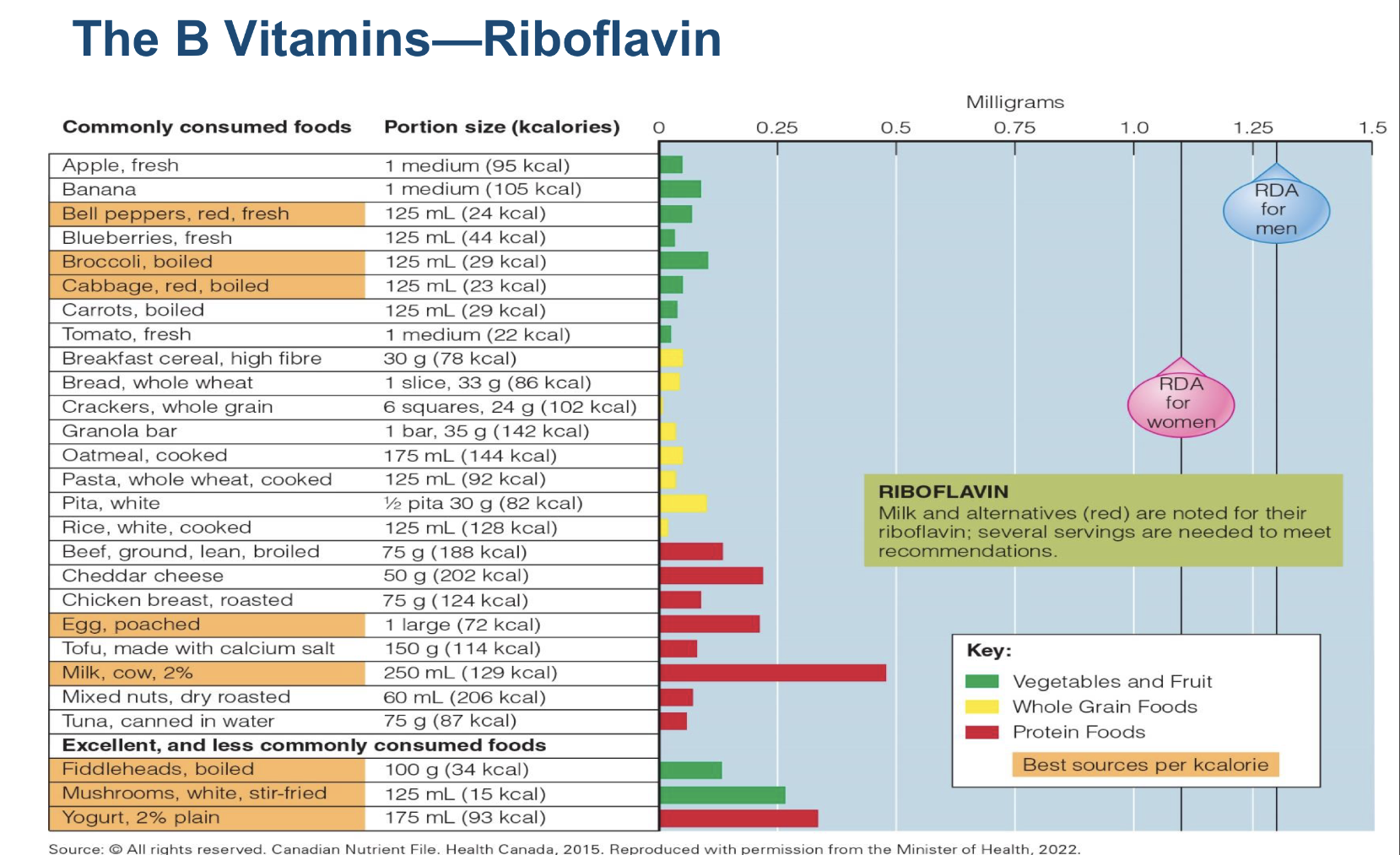
What are B6 roles, deficiency, toxicity? what can destroy it?
B6 aka riboflavin
a conenzymes in many energy rxns:
Flavin mononucleotide (FMN)
Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
it Accepts and donates 2 H (TCA cycle → Electron transport chain)
Deficiency:
◦ Inflammation of membranes- mouth, skin, eyes
Toxicity: No UL
UV light destroys Riboflavin!
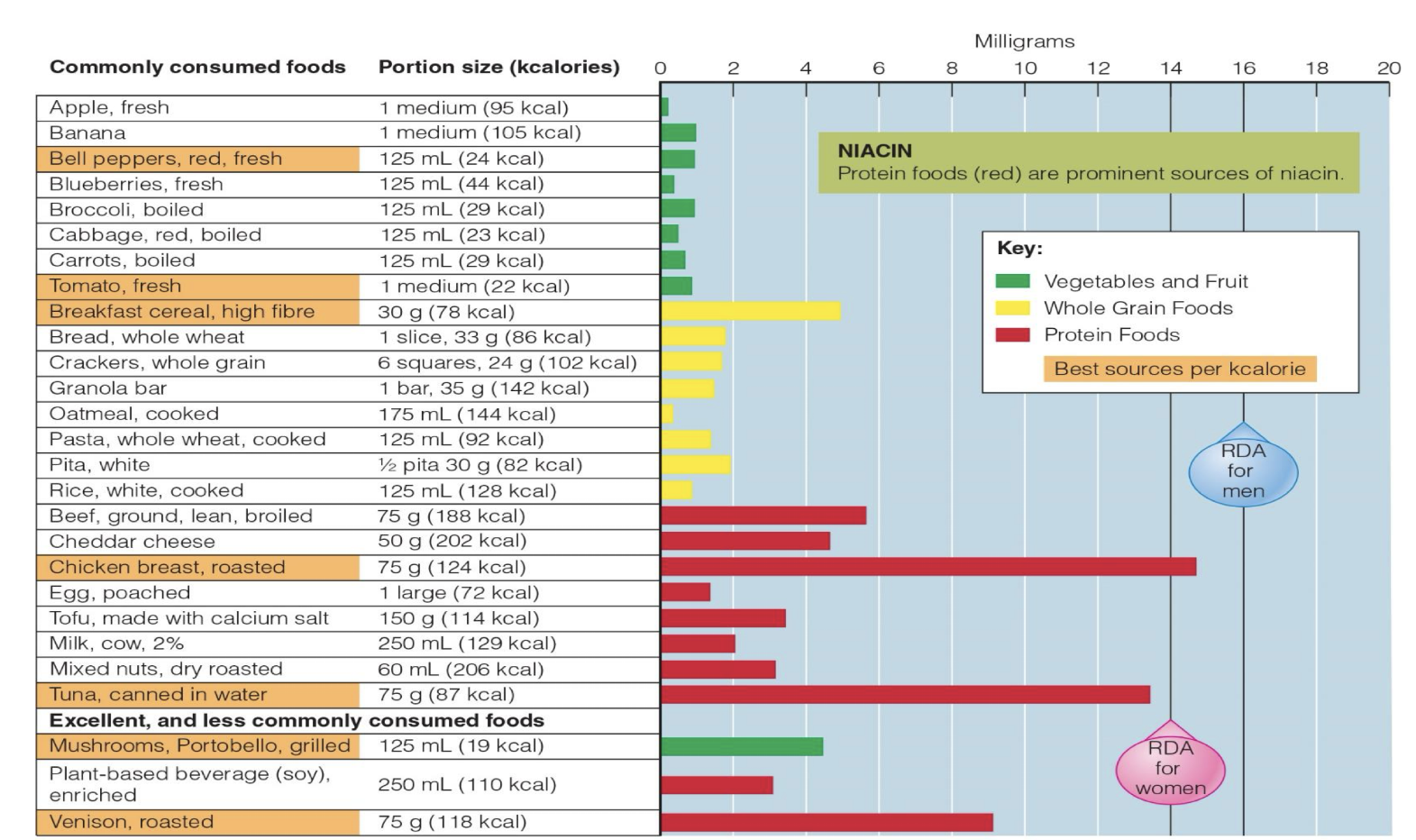
what are B3 , structures, what is is apart of? how can it be made in body and what it the equivalency?
B3 aka Niacin
Two chemical structures:
Nicotinic acid and nicotinamide
Part of two coenzymes:
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)
NADP (phosphate form)
can be Made from tryptophan (Trp): Occurs only AFTER protein synthesis needs have been met
Niacin equivalents (NE):
1 mg niacin + 60 mg of Trp = 2 NE
so 60mg=1mg niacin
what is B3 deficiency ? is toxicity a concern?
Niacin B3 deficiency:
PELLEGRA
4D symptoms: Dermatitis, diarrhea , dementia, death
Toxicity—> rare, must be consuming 3-4x RDA OR medications (niacin flushing)
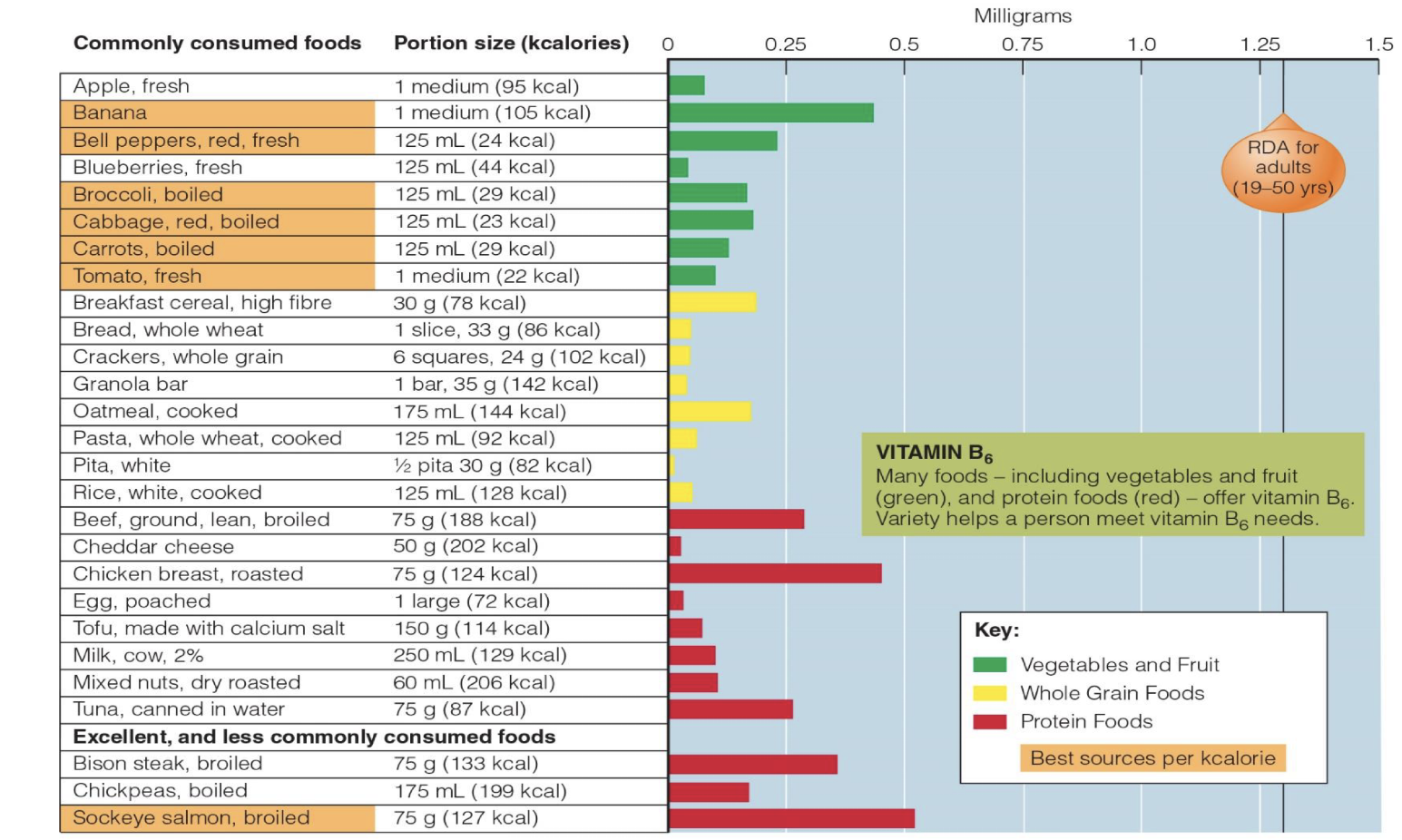
what are vit. B6 forms (what are they converted to?), what is it involved in?
three forms: pyridoxal, pyridoxine, pyridoxamine—> All converted to coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)
Functions:
• Stored in muscle
• Amino acid metabolism as coenzyme: Transfers amino group to keto acid, Tryptophan to niacin, serotonin
• Synthesis of heme, nucleic acids, lecithin
What are B12 key thing about structure, what is it CLOSELY related to? individual roles? why is it so important for digestion and absorption ? stored in?
large molecule, has centre Co (cobalt mineral)
WORKS WITH B12 for activation:
◦ Regeneration of methionine
◦ Synthesis of DNA and RNA
Roles of vitamin B12:
• Maintains sheath on nerve cells
• Bone cell activity and metabolism
VERY Impot. for Digestion and absorption
◦ Stomach → require hydrochloric acid(HCl) and intrinsicfactor (IF) : HCL and pepsin release B12 from proteins bound to it, then B12 binds to stomach IF then absorbed in terminal ileum
◦ Enteropathic circulation for both folate and B12 - Secreted in the bile and reabsorbed
stored in liver
what are common b12 foods, common deficiencies?
vit. b12= cobalamin
food: ONLY animal sources Food: only in animal sources (or fort. plant based)
Best bioavail: Fish, milk, eggs
Vegan: fortified plant beverages, B12 fortified nutritional yeast
Inactivated by microwave heating
deficiencies:
common in Vegan diet
Or Poor absorption if lack of IF and/or HCI, Rx interactions: antacids
Deficiency sex: fatigue, dementia, peripheral nerve degeneration - paralysis, anemia
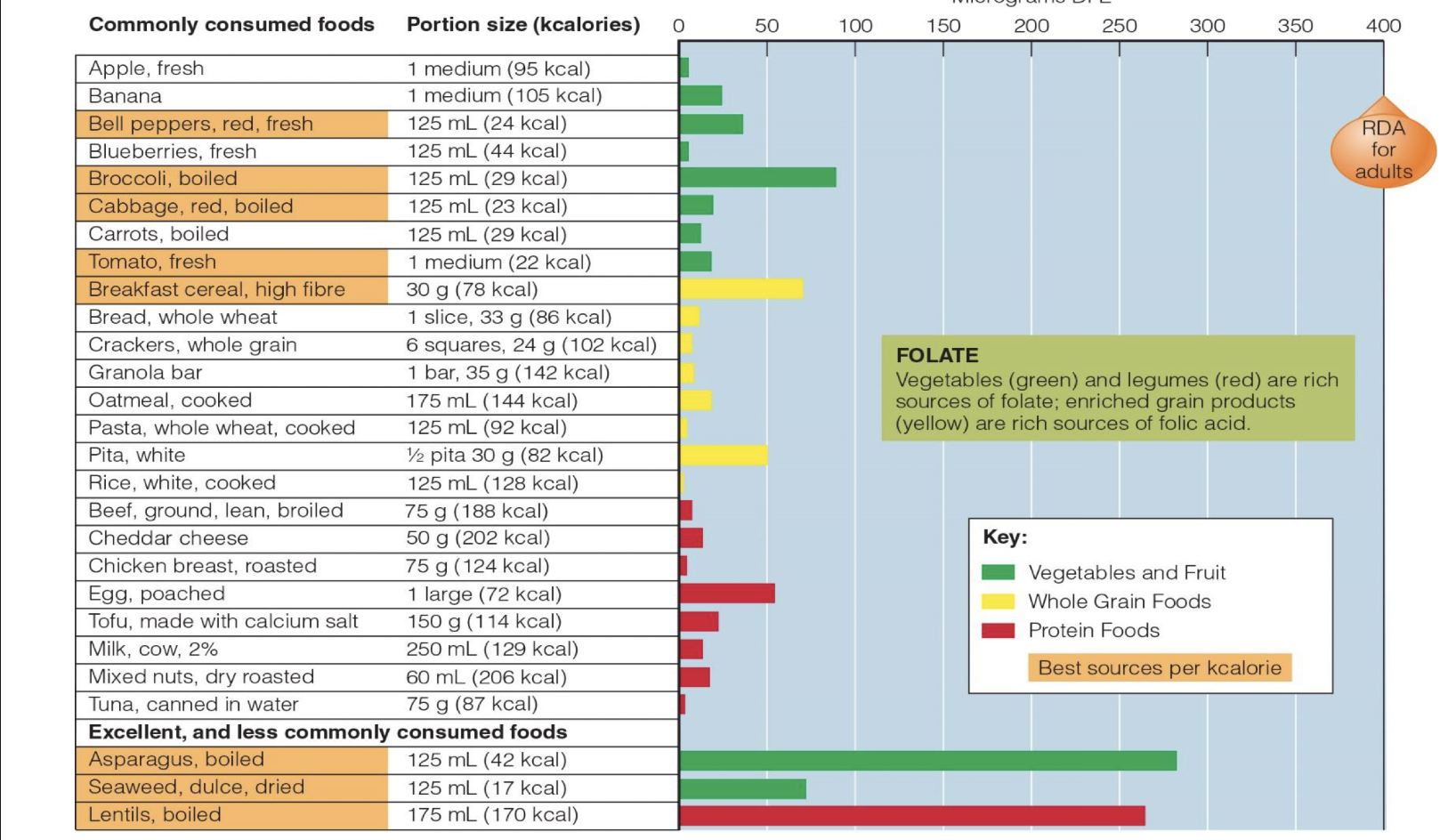
info on FOLATE, common names? what is primary coenzyme form?, what vitamin is it closely involved w? what does liver do with folate? is it in all flours in CAN
common name= folacin, folic acid
primary form = THF-tetrahydrofolate
roles:
◦ Transfers 1-carbon compounds during
metabolism
Synthesizes DNA
Regenerates methionine from homocysteine
works with vit. B12: Converts vitamin B12 to coenzyme form,
ALSO vit B12 is used to make folate
Liver converts excess folate to bile, it can be reabsorbed repeatedly (into bloodstream etc)
bioavailability differs based on source (supplement vs food)
WHITE flour must be fortified with synthetic folate mono glutamate (since 1998, has reduced neural tube deficiency)
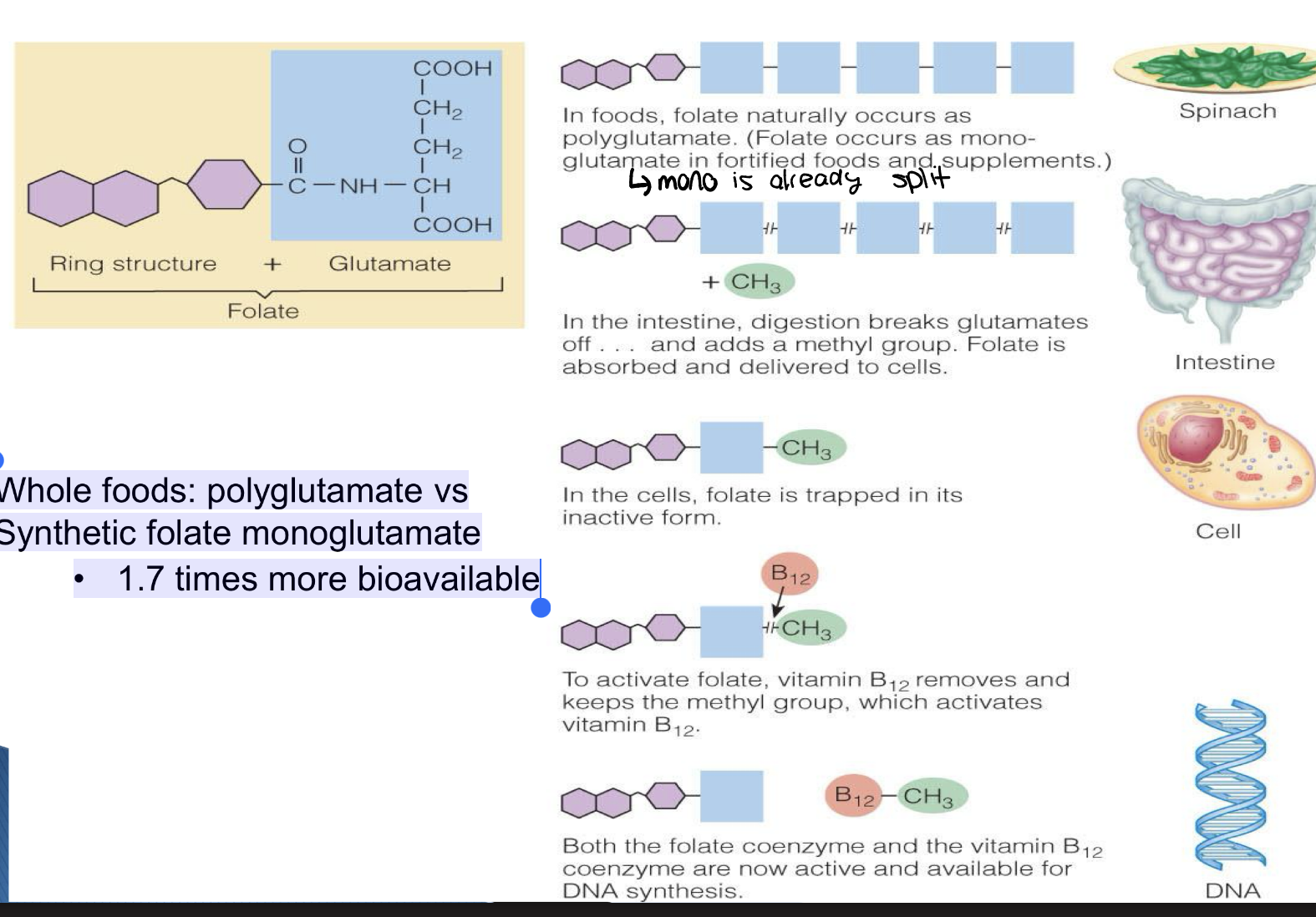
what are two forms of folate? how do they differ?
Monoglutamate -supplement, 1.7x more bioavailable bc already in MONO form
polyglutamate- Food, less bioavailables
Folate and B12 absorption metabolism, what happens in intestine, in cells, what is inactive from, how does it become inactivated, once activated what does it do?
what are folate recommendations? how is total folate calculated? what are RDA rec. for 14+ and during pregnancy?
RDA age 14+—> 400ug
Pregnancy —> 600ug

what are dangers of folate deficiency during pregnancy, what is affected? what are supplementation recommendations?
dangers= neural tube defects, can lead to death
Supplementation:
folic acid 400ug/day
start one month bf first conception through first trimester
what does folate deficiency look like? what are 2 types of causes? what is toxicity lvls?
deficiencies will impair cell division and protein synthesis:
◦ Megaloblastic anemia
◦ GI tract deterioration, smooth red tongue
◦ Mental confusion, irritability, fatigue
◦ Elevated Homocysteine/CVD Risk
◦ Drug interactions
◦ Neural tube defects – inadequacy pregnancy
2 cause types:
Primary cause: inadequate intake
Secondary cause: unusual metabolism or impaired absorption (eg GI tract injuries that hinder absorption and disrupt enterohepatic circulation)
Toxicity: UL=1000 ug; Set because of supplements, fortification can mask B12 deficiency symptoms
overall summary of B vitamins, deficiencies, toxicities food sources

overview of antioxidant nutrients, how do vit VS minerals act as antioxidants?
ANTIOXIDANTS WILL:
Protect cells from oxidative damage
Vitamins quench free radicals
VS
Minerals act as cofactors for enzymes
Phytochemicals
Oxidation is part of normal metabolism
Unpaired electron = free radical that Damages lipids, DNA, RNA, proteins
Antioxidants neutralize free radicals
overview of antioxidants in food,

what is oxidative stress effects, defence?
free radicals are the ‘bad guys’.
they damage lipids-Damage cell membranes, DNA, proteins
Free radicals target structures with double bonds or rich in electrons, which are easier to oxidize.
effects= cancer, CVD, cataracts, compromised immune function
antioxidants are defence
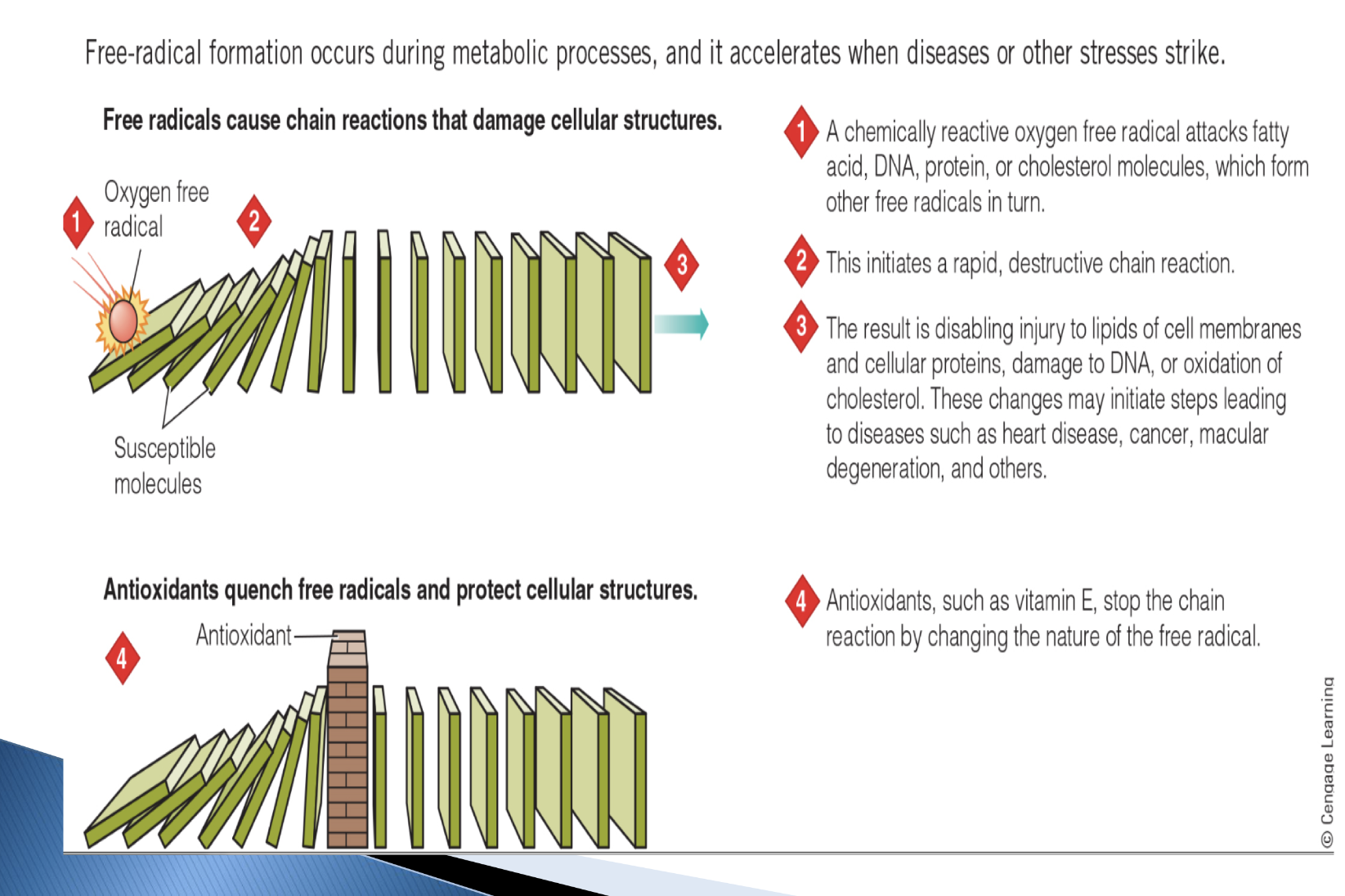
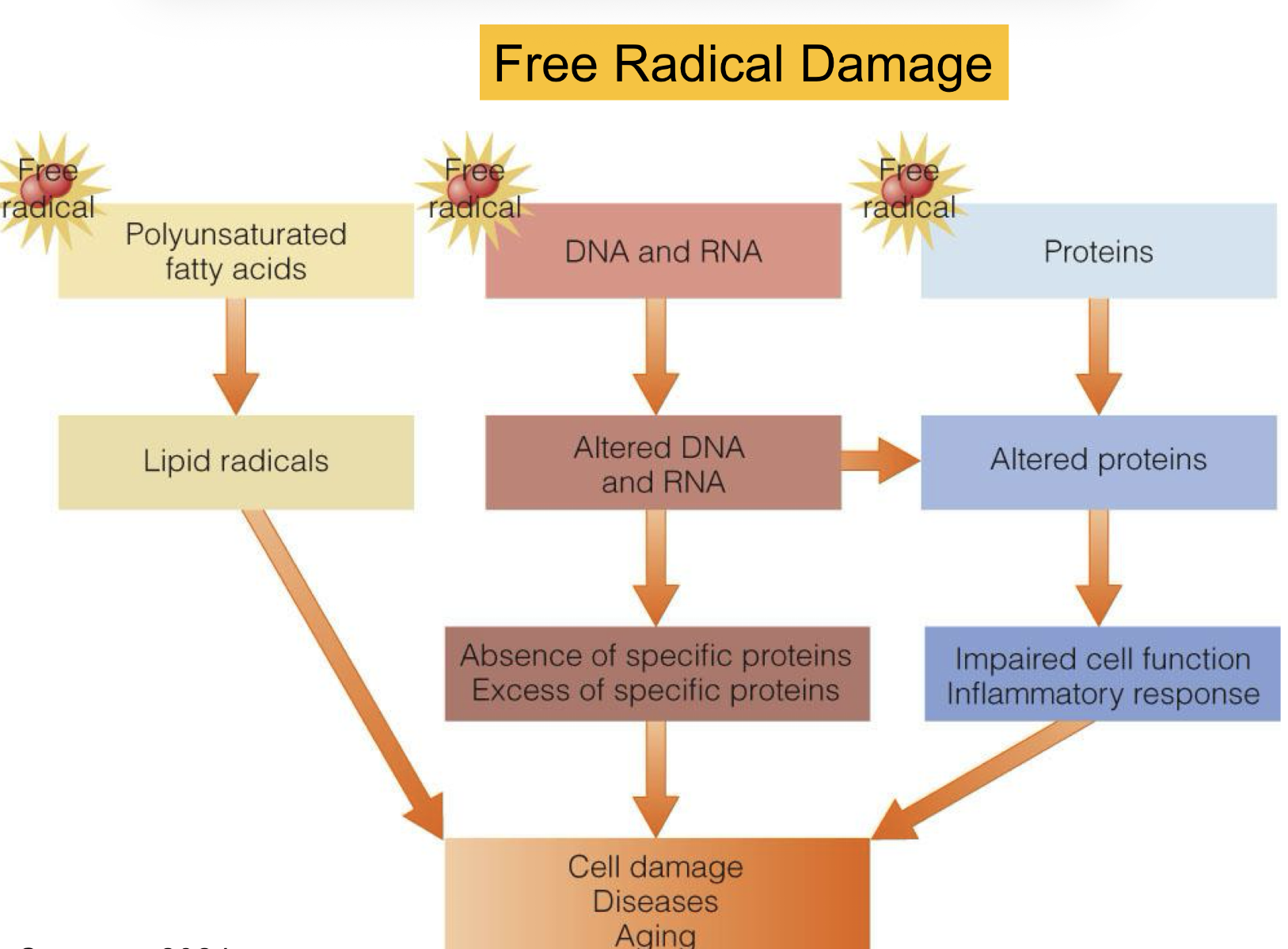
how does free radical damage affect DNA and RNA, PUF, vs proteins? what does it all lead to?
ALL leads to cell damage, aging, diseases
what is vit. C functions, what is it a cofactor for? how does it act as antioxidant? how can it be ‘reactivated, what is this process called?
Cofactor For
1)Collagen
bone, teeth development
“cement”, scar tissue, wound healing
2) Many rxn
hormone synthesis
Synthesis of neurotransmitters
Role as antioxidant:
Immune system antioxidant
Defends against oxidative stress, ree radicals to help prevent disease
Recycling process= recycling active forms of Vit. C
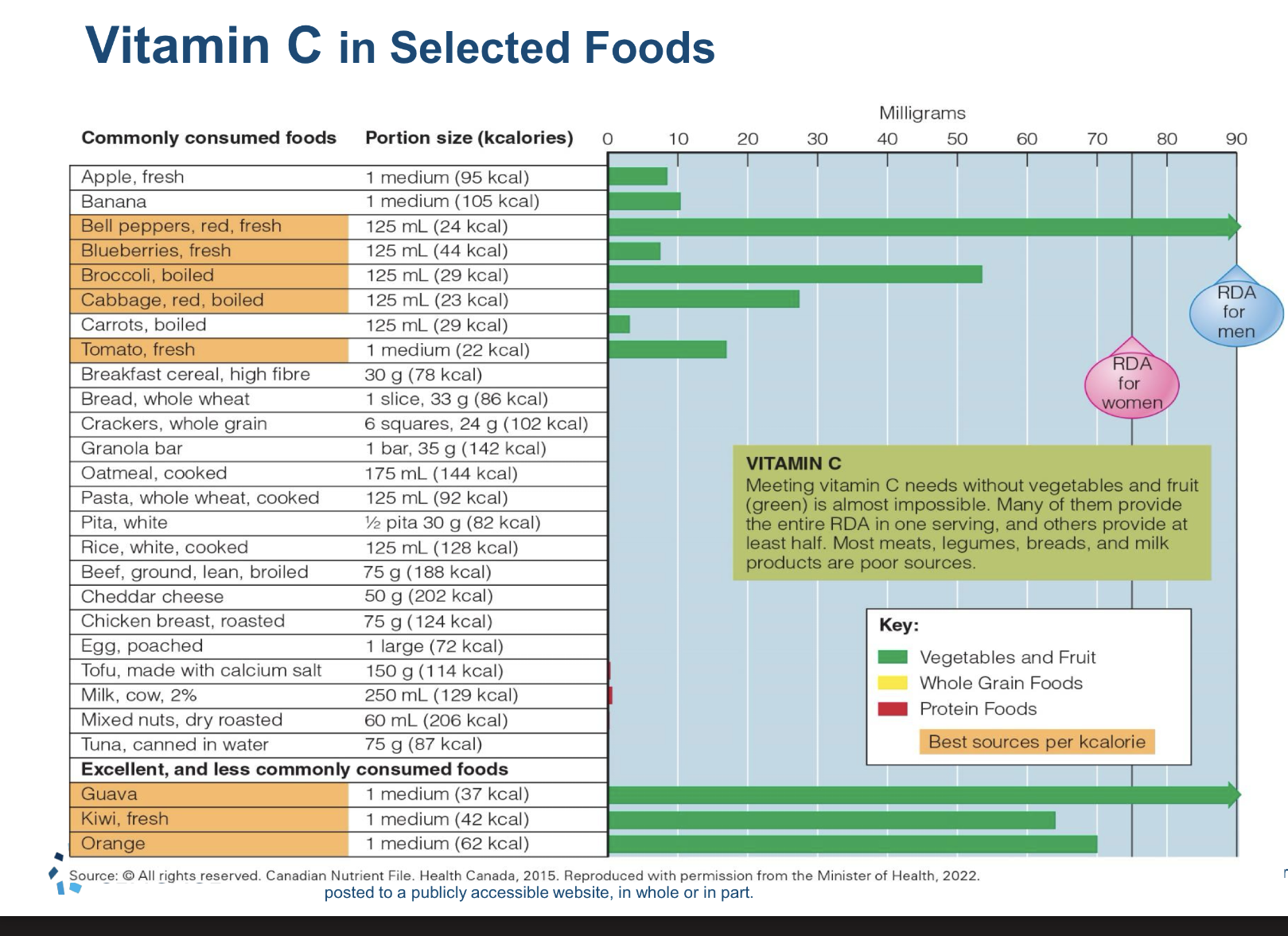
what are specific roles of vit C? what prevents scurvy and when does it apprea, what is max absorption? what is relationship to smoking?
Roles:
Enhances iron absorption
Stressed state increases vitamin C needs—> When stressed: Adrenal glands secrete vit C
Common cold
◦ Slight but consistent shortening of cold duration —> Deactivates histamine
Scurvy:
-10mg prevents scurvy symptoms, but
-scurvy appears visible @ 1/5 optimal lvls
-symptoms=Bleeding gums, breaking of capillaries (smell red spots) Inadequate collagen, wound healing ceases, teeth become loose, skin
becomes dry, rough, and scaly, Sudden death from massive internal bleeding
Absorption:
-200ug max absorption, rest is excreted
-Smoking cigs increases needs: bc it increases oxidants so antioxidants are needed
what happens with vitamin C overdose/ what are thoughts?
Pharmacological vs Nutritional Supplement
Could Decrease length and severity of colds?
◦ placebo effect OR actual histamine affect as Vit C deactivates histamine??
◦ May relieve some symptoms…
Disadvantages:
◦ False positive urinalysis
◦ Drug interactions
◦ Oxidative stress: interaction with iron
◦ Kidney stones
◦ Rebound deficiency when pills stopped???
◦ Vit C UL- 2000mg
what are common forms of vit and mineral supplements? what are some dangers? how big of an industry?
Form (chewable, liquid, pill)
Content of dose(below UL)
Misleading claims (organic, natural, high potency)
50 billion in N.A, expensive
how are vit and mineral regulated in canada? what is NNHP? NPN?? DIN?
regulated by health canada

who actually needs supplements?
Specific nutrient deficiencies
Low energy intakes
Vegans and older adults with atrophic gastritis
Lactose intolerance/milk allergies
Certain medications
Certain stages of life cycle
Inadequate milk intake, sun exposure, dark
skin
People w diseases, infections, injuries
who should NOT take supplements -4
men—> iron
smokers—> beta carotene
post-menopausal women—> iron, vit A
Surgery patients, vit E