ruminant nutrition 1 - grass and forages
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
How many litres is the rumen in an adult sheep?
10-15
How many litres is the rumen in an adult cattle ?
150-200 litres
How much water does the rumen contain?
850-930g/kg water
what type of environment is the rumen?
Anaerobic
true or false: in cattle there is usually a caudal mat of fibre
True
each mL contains;
10^9 to 10^10 bacteria
10^6 protozoa
10^3 to 10^5 fungi
True or false?
True
True or false: there are as many bacteria in 1mL of rumen fluid as people on the planet
True
What are the evolutionary features of the rumen?
Bacteria and fungi enzymatically break down B-glycosidic linkages in fibre under anaerobic conditions
Rumen bacteria break down most of the protein in the rumen to ammonia, which they use to synthesise their own amino acids
what does fermentation of sugars, starch and fibre in the rumen produce ?
Short chain, “volatile” fatty acids (acetate, propionate and butyrate), as well as methane
Excess ammonia in the rumen is absorbed and converted to urea in liver, what happens after this ?
The urea can be recycled to the rumen via saliva or the rumen epithelium, or excreted in urine
What are the common forages?
Grass, grass silage , maize silage, whole crop wheat, hay, straw, kale/rape/fodder/beet/turnips
What are the concentrates ?
Cereals (barley, wheat, oats), by-products (sugar beet pulp, soya hulls), protein (soyabean meal, rapeseed meal), minerals/vitamins
What can concentrates be used for ?
Can be ground and mixed and pelleted to form a concentrate pellet (or cake )
All ruminant nutrition is undertaken on a _____ ____ basis ?
Dry matter
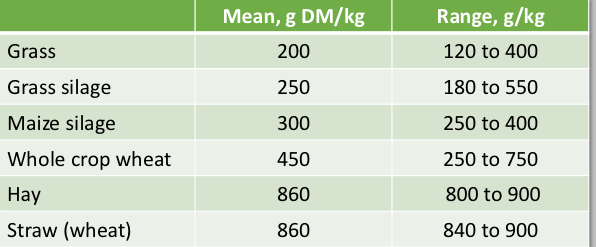
What does this table tell you?
That there is large variation in the dry matter content of ruminant forages
How to work out crude protein?
Nitrogen x 6.25
Why is there a large range of crude protein in grass/grass silage ?
Large range due to stage of maturity
Is there a big range in crude protein for maize silage/whole crop cereals ?
No, there is a lesser range
Are legume forages high or low in crude protein?
High (mean of 180-220g CP/kg DM)
How is fibre measured in forages?
Neutral detergent fibre (NDF)
What is NDF made up of ?
Cellulose + hemicellulose + lignin
true or false: NDF content does not indicate how lignified the fibre is
True
What does more nature grass mean about lignification ?
More mature grass is more lignified
which has less lignin in the fibre ; dicotyledons or monocotylendous plants ?
Dicotylendous plants
what does ME stand for? And what units is it measured in?
Metabolisable energy (megajoules/kg DM)
what does the total energy in feed =? And what is important to note about this ?
Gross energy
Not all is available to the animal
What is the ME equation?
ME = gross energy - faecal energy - urinary energy - methane energy
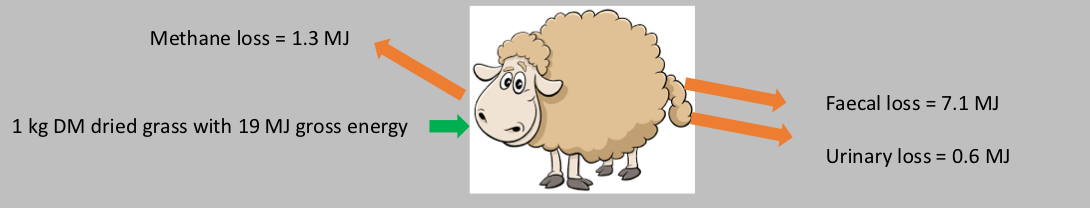
What would be the ME here ?
ME= 19 - 7.1 - 0.6 - 1.3 = 10.0 MJ/kg DM
How does lignin prevent bacteria from adhering to fibre ?
Lignin coats the outside of fibre
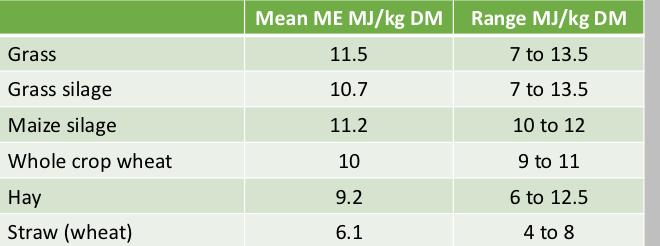
What can we learn from this table ?
Animal requirements are calculated on an ME basis
How can excvsss grass growth be conserved?
As hay or silage and fed when grass growth is below requirements
What grazing systems are there ?
Set-stocking
Rotational
Strip grazing
Zero grazing (or cut and carry)
Out wintering sheep and cattle (feeding forages over winter)
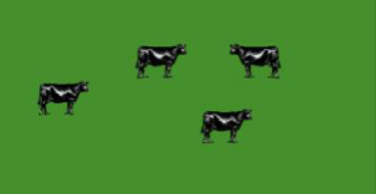
What grazing system is this ?
Continuous grazing or set stocking
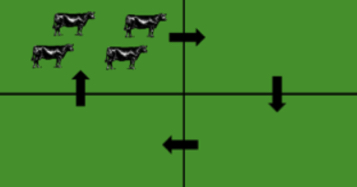
What grazing system is this ?
Paddock or rotational grazing
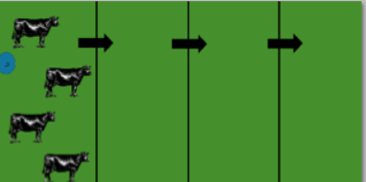
What grazing system is this ?
Strip grazing
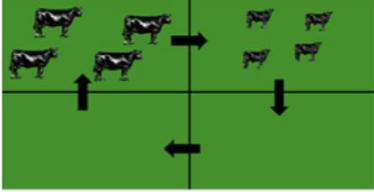
What grazing system is this ?
Forward or creep grazing
What are some health issues with grazing?
Bloat (especially if pasture clover content is high)
Nitrate poisoning
Intestinal parasites (“clean grazing”)
Liver fluke
Clostridial diseases (e.g. pulpy kidney, black leg)
Mineral deficiency
What are some mineral deficiency’s that can be caused from grazing?
Magnesium (staggers/tetany)
Calcium (hypocalcaemia: milk fever)
Copper (swayback)
Colbalt (pine)
What grazing system is used for ewes, store lambs, beef and dairy heifers and cows between September and march?
Outwintering
What are advantages of outwintering?
Less building (capital) and fewer respiratory problems
What is a major forage that is grazed?
Grass (deferred grazing)
What are some forages that are specifically grown?
Stubble turnips
Turnips
Kale
Forage rape
Forage rape/kale hybrid
Fodder beet
What are the two ways lambs can be “stored” and grown? (Depending on herbage allowance )
Slowly (e.g. 50g/d) to finish late winter
Or rapidly (250g/d) and finish earlier
How much of the dry matter intake do beef and dairy cattle usually provide ?
1/3 a big bale silage placed in field
What are cattle growth rates?
0.6-1.2 kg/d but can be variable
How to provide a dry bed?
Field selection, run back or provision of straw bedded area
There is a lower critical temperature from studies with suckler cows , what is it acclimatised (still, dry) and unacclimatised (windy, wet)?
Acclimatised = -18 degrees
Unacclimatised = + 7 degrees
What are some health issues when outwintering?
Photosensitisation
Nitrate poisoning
Kale anaemia factor
CCN
goitre
Bloat
Mineral deficiency
When do you get nitrate poisoning when outwintering?
Particularly when crop is growing quickly following fertiliser or overcast. Symptoms include muscle tremor, drooling and death
What animals are most susceptible to photosensitisation when outwintering?
In sheep and cattle grazing brassicas, particularly young cattle with white hair
What is kale anaemia factor caused by when outwintering?
Due to the amino acid S-methyl cysteine sulphoxude (SMCO) which causes anaemia and aperture loss
What causes CCN while outwintering?
Due to degradation of vitamin B1 in the rumen following dietary change, results in blindness, uncoordination, head held back.
What causes goitre when outwintering?
Kale is low in iodine, and high in goitrogejs, resulting in swollen thyroid gland , reduced fertility and still births
What causes bloat when outwintering?
Fodder beet and kale are very high in sugars and can reduce rumen PH
What mineral deficiency’s are caused in outwintering?
Copper, colbalt, selenium and iodine
What are the main methods of feed preservation?
Drying, ensiling, alkaline treatment, crimping and addition of an organic acid
What is drying hay made up of ?
Variety of grasses e.g. ryegrass, Timothy, bro,e. Fescue, clover (or mixtures)
How long is drying hay cut and left to airdry in the field ?
4-5 days , turning occasionally (weather dependent)
when is hay baled?
At around 850g DM/kg
Why is grass left?
To become mature (stemmier and higher in DNF than grass)
Grass can also be artificial dried then _____ ?
Pelleted
What are some health issues with hay?
Spontaneous combustion
Moulds such as fescue poisoning in tall fescue grass caused by an endophyte fungus
Affects ears, tail and cause lameness and reduced performance in cattle and sheep
Mould spores resulting in bovine allergic pneumonitis
Botulism, associated with dead birds or rodents in the hay bale, or if pasture fertilised with chicken litter
To feed the cow/sheep you have to feed the ______
Rumen
When are mould and mycotoxins health challenges with hay?
If it’s poorly dried
outwintering is undertaken to reduce costs but has what issues?
Health
What does a large range of dry matter and nutritive content of forages depend on?
Species
Stage of maturity at harvest
Degree of wilting
What is TMR?
Total mixed ration