AP PSYCHOLOGY VOCAB — SCIENTIFIC FOUNDATIONS OF PSYCHOLOGY
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
Gestalt Psychology
How the brain organizes and structures our perceptions of the world; we typically perceive organized patterns or wholes— NOT pieces
Behavioral Approach
John Watson: Only environments molds behavior; psychology should only study observable behaviors without references to mental processes
Operant Conditioning/Reinforcements
B.F. Skinner: Behavior is shaped by reinforcements and punishments
Classical Conditioning/Reinforcements
Ivan Pavlov: When person/animal associates specific stimulus with response; if a stimulus occurs before another, personal/animal may associate it with the response
Biological/Neurobiological Approach
How genetics, hormones, brain structures, etc. influence a person’s thinking and behavior
Examples: bad eyesight, ADHD, fight or flight response
Cognitive Approach
How we process, perceive, store, and recall info (memory); language developments and use, decision-making, and learning are observed
Examples: study methods, underdeveloped language, dyslexia
Humanistic Approach
How people pursue their goals that give their lives a sense of meaning and purpose; focuses on need for love, acceptance, and self-fulfillment
Examples: happiness with friends, acceptance from them
Socio-Cultural Approach
Study of how situations and cultures affect our behavior and thinking
Examples: cultural punishment, being in the wrong crowd, parents fighting
Evolutionary Approach
Behavior reflects inherited pre-dispositions or tendencies that increase the likelihood of ancestor’s survival; traits passed down for survival and reproduction
Darwin’s natural selection: traits can influence animal structures and behaviors
Psychodynamic Perspective
Sigmund Freud: Psychoanalysts look for impulses/memories pushed into the unconscious mind through repression
Sigmund Freud
Developed the psychoanalytic theory
B.F. Skinner
A leading behaviorist who studied how rewards and consequences influence behavior, especially through his analysis of rodents in an electrified box
Ivan Pavlov
Studied classical conditioning experiments
Clinical Domain
Helps those with psychological disorders such as anxiety, depression, etc.
Psychiatrist
Medical doctor
Can use drugs to treat
Uses psychotherapy
Psychologist
No medical degree
Can’t prescribe drugs
Uses psychotherapy
Counseling Domain
Helps those going through difficult times in life with coping strategies; doesn’t help with mental illnesses
Biological Domain
Studies how structures of the brain and human anatomy influence behavior and thought processes
Developmental Domain
How people change and grow in their lifetime; studies topics like changes in cognition, linguistics, motor or moral development, etc.
Educational Approach
How people learn and process information; for teachers implementing effective teaching
Experimental Domain
Researching spectrum of human behaviors, mental processes, orders, etc. to expand psychological scientific knowledge base
Industrial-Organizational Domain
How to maximize employee performance at work
Personality Domain
How it affects the way people navigate the world
Psychometric Domain
The creation and implementation of tests to study behavior and mental processes
Social Domain
How culture, religion, family, peers, income, and environment shape beliefs, goals, and behaviors
Positive Domain
Broadening the number of people that psychology helps to help them live their best life
Applied Research
Scientific study that aims to solve or help people with specific problems
Clinical, counseling, industrial-organizational, positive, educational domains
Basic Research
Pure science that aims to increase the scientific knowledge base
Focuses on the big picture
Biological, experimental, psychometric, social, cognitive, personality, and developmental domain
Stratified Sampling
Requires close to/equal amount of people in different groups; each subgroup is a “strata”, each one being grouped by a characteristic; once grouped, each subgroup is randomly sampled
Cross Sectional Study (Adj.)
A study of people with different ages compared to one another; results may not be accurate
Longitudinal Study (Adj.)
Research where the same period are restudied and retested over a long period of time; costs a lot of money
Scientific Method
Question + Theory
Hypothesis: If → Then statement
Reliable Experiment
Reliable Experiment
Results can be replicated by someone else; experiments need to be written down with every single step taken with precise and detailedness for it to produce exact results
Operationalize
A definition of something in terms of the operations (procedures, actions, processes) which it can be observed and measured; if variables aren’t operationalized, the experiment can’t be replicated
Good Operational Definition:
Amount
Time/Duration
Change
Validity
Extent of which a test/instrument measures what the researchers set out to measure; if inaccurate, conclusions can’t be drawn
Confounding Variable
An extraneous variable that impacts the variables studied so the results produced don’t reflect the actual relationship between independent and dependent variables
Psychology
The science of behavior and mental processes
Nature-Nurture Issue
The longstanding controversy over the relative contributions that genes and experience make to the development of psychological traits and behaviors
Natural Selection
The principle that, among the range of inherited trait variations, those contributing to reproduction and survival will most likely be passed on to succeeding generations
Hindsight Bias
The tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it. AKA the l-knew-it-all-along phenomenon
Critical Thinking
Thinking that does not blindly accept arguments and conclusions. Rather, it examines assumptions, discerns hidden values, evaluates evidence, and assesses conclusions
Theory
An explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes and predicts observations; something that’s already tested and researched
Hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory that expresses a relationship between two variables
Replication
Repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding extends to other participants and circumstances
Case Study
An observation technique in which a person or small group is studied in depth
Survey
A technique for ascertaining the self-reported attitudes or behaviors of people, usually by questioning a representative, random sample of them; people can skew the results
False Consensus Effect
The tendency to overestimate the extent to which others share our beliefs and behaviors
Population
All the cases in a group, from which samples may be drawn for a study; except for national studies, this does not refer to a country's whole population
Random Sample
A sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion; allows for generalization
Naturalistic Observation
Observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation; DESCRIBES behavior, not study; can’t use surveys
Correlation Effect
A statistical measure of the extent to which two factors vary together, and thus of how well either factor predicts the other
Does NOT equal to causation due to third variable problem, which only applies to correlational studies
Scatterplot
A graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the values of two variables; the slope of the points suggests the direction of the relationship between the two variables
The amount of scatter suggests the strength of the correlation (little scatter indicates high correlation)
Illusory Correlation
The perception of a relationship where none exists
Experiment
A research method in which an investigator manipulates one or more factors (independent variables) to observe the effect on some behavior or mental process (the dependent variable); by random assignment of participants, the experiment controls other relevant factors
Only this can prove cause and effect as it can
Manipulate variables
Control the setting
Downside: Can be too artificial and doesn’t always replicate real world
Double-Blind Procedure
An experimental procedure in which both the research participants and the research staff are ignorant (blind) about whether the research participants have received the treatment or a placebo; commonly used in drug-evaluation studies
Placebo Effect
Experimental results caused by expectations alone; any effect on behavior caused by the administration of an inert substance or condition, which is assumed to be an active agent
Experimental Condition
The condition of an experiment that exposes participants to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable
Control Condition
The condition of an experiment that contrasts with the experimental condition and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment
Random Assignment
Each participant has an equal chance of being placed into either experimental or control group so that comparisons can be made; helps eliminate confounding variables
Mode
The most frequently occurring score in a distribution
Statistical Significance
A statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance
Mean
The arithmetic average of a distribution, obtained by adding the scores and then dividing by the number of scores
Median
The middle score in a distribution; half the scores are above it and half are below it
Range
The difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
Standard Deviation
Measure of spread; how close the values in a data set are to the mean
Culture
The enduring behaviors, ideas, attitudes, and traditions shared by a large group of people and transmitted from one generation to the next
Objective
Based on quantifiable things; facts
Subjective
Personal opinions, beliefs, assumptions
Empiricism
Knowledge stems from experience
Directionality Problem
When two variables correlate and might actually have a casual relationship, but it’s impossible to conclude which variable causes changes in the other
Falsifiability
Finding evidence that refutes the hypothesis; this makes a good hypothesis
Extraneous/Lurking Variable
Any variable not being investigated that has the potential to affect the outcome of a research study
Sampling Bias
Statistical error that occurs when the sample selected to collect data is NOT representative; can lead to inaccurate results and conclusions due to segments of the population being excluded
Convenience Sample
Researchers use subjects who are easy to contact for participation in their study; can’t generalize findings from this
Self-Report Bias
People not giving answers that are fully correct, either because they do not know the full answer or because they seek to make a good impression
Social Desirability Bias
Example: How often do you attend a religious service?
Frequency Distribution
Plotting how often certain pehnomena occur
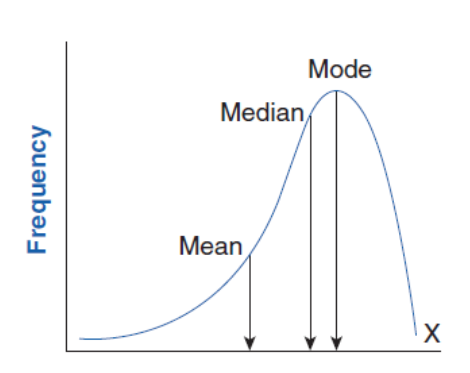
Negatively Skewed
Measure of central tendency: Median
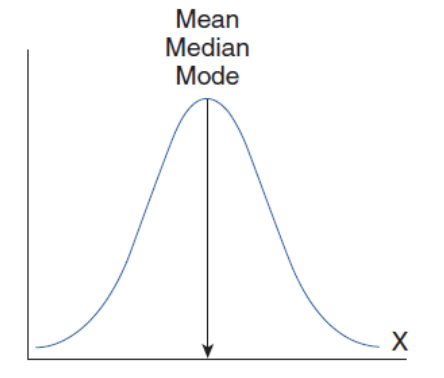
Normal (No Skew)
Measure of central tendency: Mean
Positively Skewed
Measure of central tendency: Median

Z-Scores
Measures the distance of a score from the mean in units of standard deviation
Percentile (Rank)
Indicates the % of scores that fall below a specific score
Z-Score of -3
0.13%
Z-Score of -2
2.28%
Z-Score of -1
15.87%
Z-Score of 0
50%
Z-Score of 1
84.13%
Z-Score of 2
97.72%
Z-Score of 3
99.87%
Single-Bind Experiment
Doesn’t disclose if people are in control/experimental group; prevents participant bias
Pseudo-Psychology
An approach to understanding or analyzing the mind or behavior that uses unscientific or fraudulent methods
Regression Toward the Mean
In any event where luck/chance is involved, extreme outcomes tend to be followed by more average ones (closer to the mean) the second time around
Descriptive Statistics
Organizing and summarizing data using…
Measures of variability
Range, variance, and standard deviation
Frequency distribution
How often something occurs
Central tendency
Mean, median, mode
Normal, positive, and negative distribution
Inferential Statistics
Taking findings and “inferring” (generalizing) characteristics from your sample onto the population
Uses probability to determine confidence of conclusions being correct
Guaranteeing that a sample is 100% representative of a total population is IMPOSSIBLE due to sampling error
P < 0.5
Statistically significant
P > 0.5
NOT statistically significant
Effect Size
Magnitude of difference between the experimental and control group; practical significance
Practical Significance
Shows that the effect is large enough to be meaningful in the real world; effect size
Statistical Significance
There’s a high probability that the independent variable caused changes to the independent; results of study did not occur by chance