Male Reproductive System and Cell Division Overview
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
What are the main components of the male reproductive system?
The main components include the testes, epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct, urethra, and accessory glands (seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbo-urethral glands).
What is the structure and function of the scrotum?
A hairy sac that hangs outside the pelvic cavity at the root of the penis. The scrotum regulates the temperature of the testes, keeping it 2-3°C lower than core body temperature for optimal sperm survival. When cold the cremaster muscle pulls them closer to body. Increased surface area means more room for sweating when hot.
What are the two types of cells found in the seminiferous tubules of the testes?
Spermatogenic (sperm-forming) cells and Sustentacular (Sertoli) cells.
What is spermatogenesis and when does it begin?
Spermatogenesis is the formation of sperm by meiosis, beginning around age 14.
What hormones are involved in initiating and maintaining spermatogenesis?
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Testosterone.
Describe the process of spermatogenesis from spermatogonia to sperm.
Spermatogonia (2n) undergo mitotic division to become primary spermatocytes (2n), which undergo the 1st meiotic division to form secondary spermatocytes (n), then the 2nd meiotic division produces spermatids (n), which mature into sperm (n).
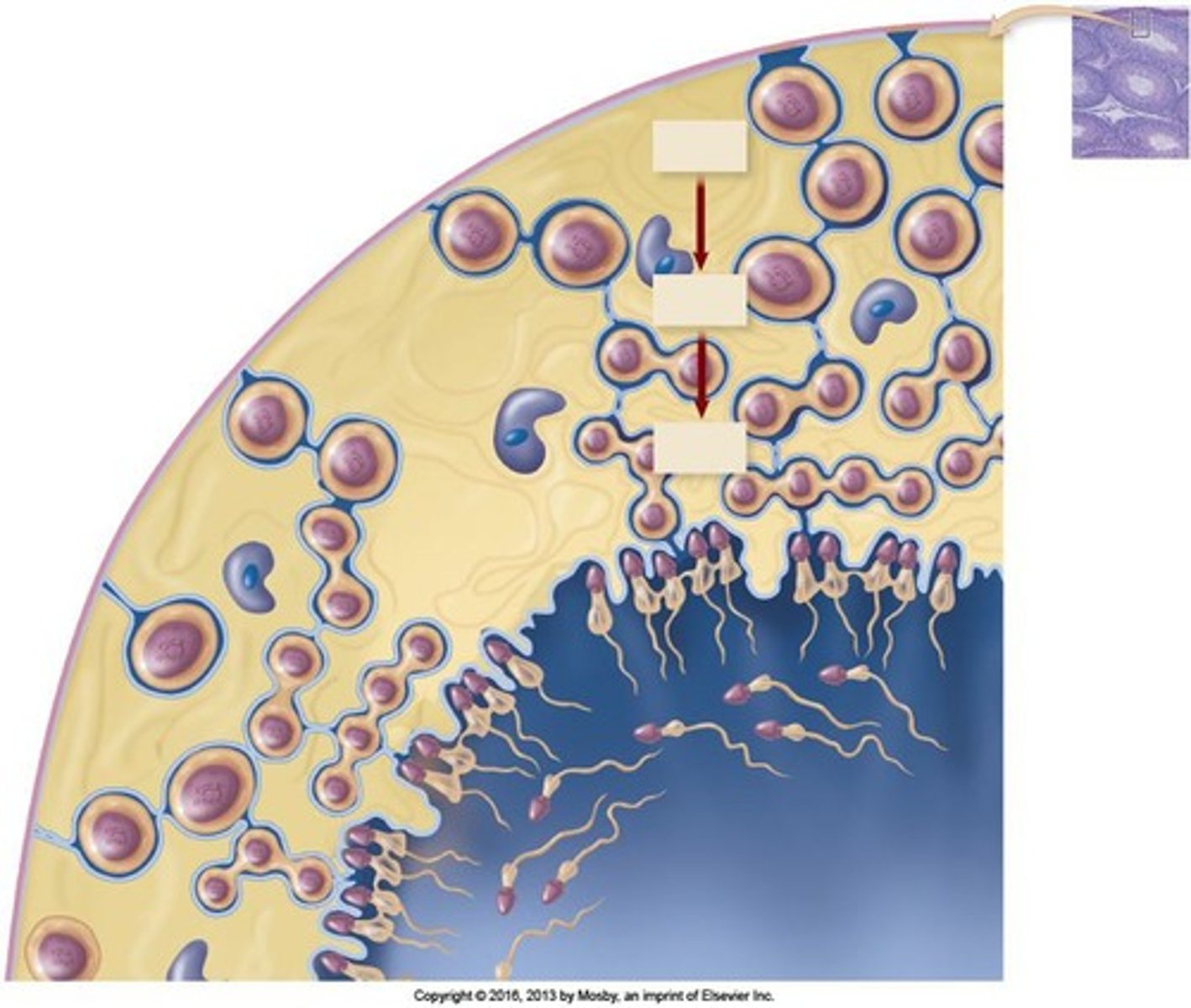
What role do Sustentacular (Sertoli) cells play in sperm development?
They nurture developing sperm cells, provide nutrients for about 70 days, produce testicular fluid for sperm transport, and control the release of sperm into the seminiferous tubule lumen.
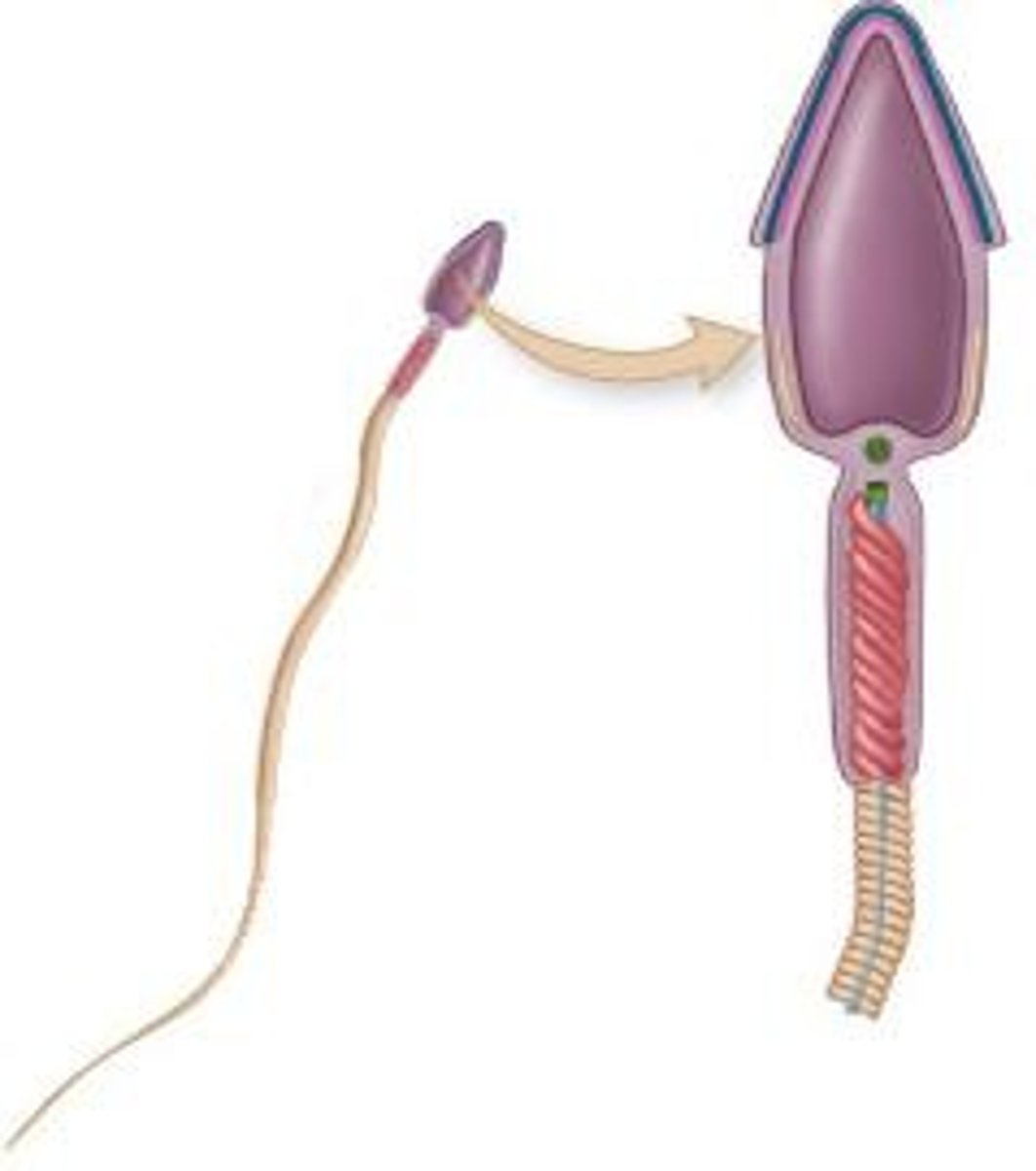
What is the acrosome and its function in sperm?
The acrosome is a cap-like vesicle containing enzymes that help the sperm penetrate the secondary oocyte for fertilization.
What are the main parts of a sperm cell?
The main parts include the acrosome, nucleus, midpiece (containing mitochondria), and tail.
What is the role of the epididymis in the male reproductive system?
The epididymis stores and matures sperm produced in the testes.
What is the pathway of sperm from the testes to the exterior of the body?
Sperm travels from the testes to the epididymis, then to the ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct, and finally through the urethra to the exterior.
What are the accessory glands of the male reproductive system?
The accessory glands include the seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbo-urethral glands.
How do the accessory glands contribute to semen production?
They secrete fluids that mix with sperm to form semen, providing nutrients and a medium for sperm transport.
What factors can affect male fertility?
Factors include age, hormonal levels, lifestyle choices, and environmental influences.
What age-related changes occur in the male reproductive system?
Age-related changes may include decreased testosterone levels, reduced sperm production, and changes in the structure and function of reproductive organs.
What is the function of the midpiece of the sperm?
The midpiece contains mitochondria that provide energy for the sperm's movement.
What is the role of the tail in sperm?
The tail propels the sperm through the female reproductive tract. A flagella
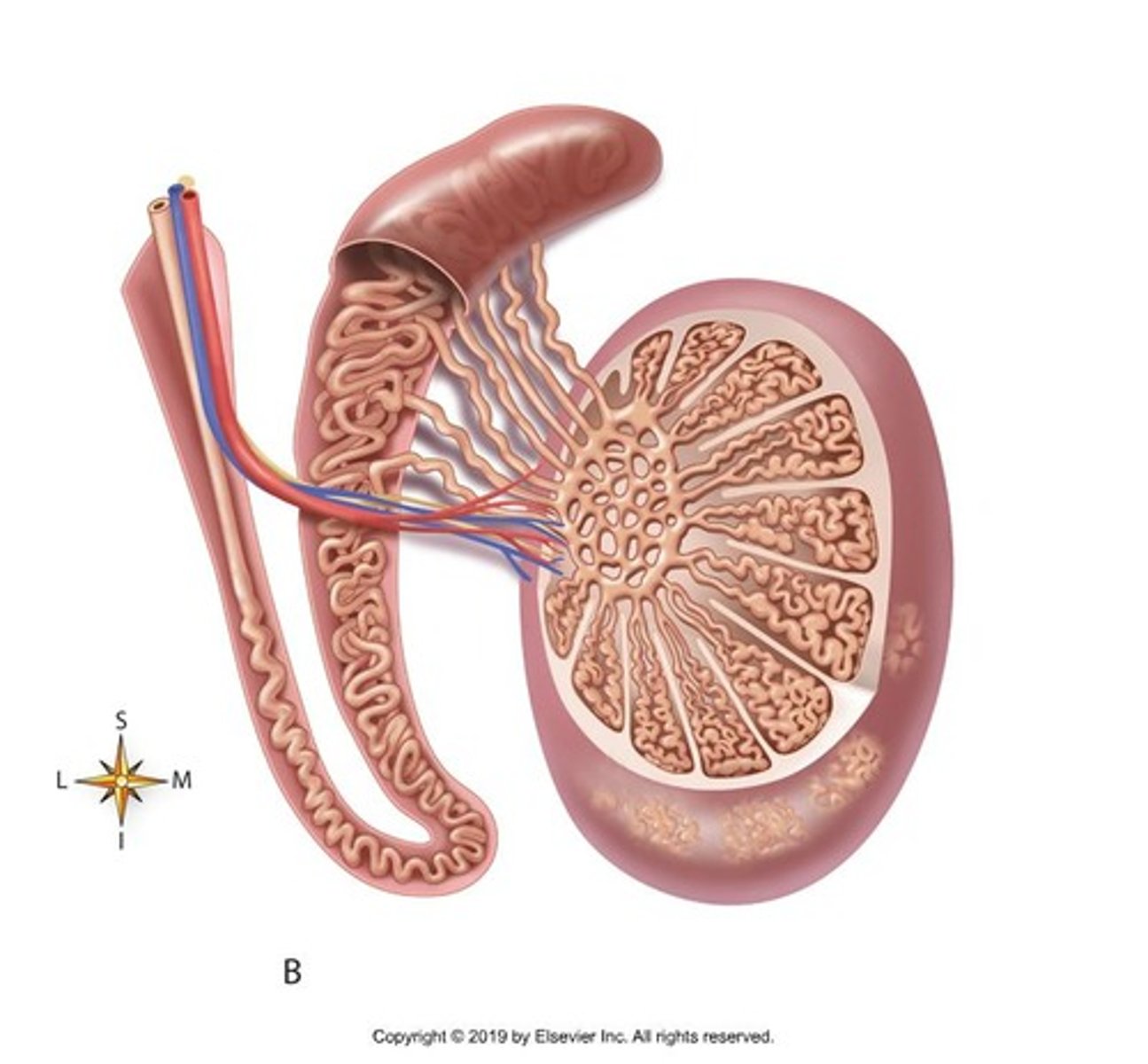
What is the structure of the testes?
The testes are divided into lobules containing seminiferous tubules where sperm production occurs.
What is the role of smooth muscle in the seminiferous tubules?
Smooth muscle contracts rhythmically to move sperm and testicular fluid through the tubules to the epididymis.
What is the composition of semen?
Semen consists of sperm, testicular fluid, and secretions from the accessory glands, which provide nutrients and a medium for sperm transport. Slightly basic to neutralize acid in vagina. Clotting factors coagulate after ejaculation so it sticks in vagina, after ~20 minutes fibrinolysin liquifies it.
What hormone does the hypothalamus secrete to initiate spermatogenesis?
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
What is the role of GnRH in the hormonal control of spermatogenesis?
GnRH stimulates the anterior pituitary to increase secretion of LH (Luteinizing Hormone) and FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone).
What do LH and FSH stimulate in the testis?
LH stimulates interstitial (Leydig) cells to secrete testosterone, while FSH, along with testosterone, stimulates spermatogenesis.
What is the function of testosterone in males?
Testosterone controls the growth, development, functioning, and maintenance of sex organs, stimulates sperm maturation, bone growth, protein synthesis, and the development of male secondary sex characteristics.
What are the effects of rising testosterone levels on GnRH production?
Increased testosterone levels create negative feedback to reduce GnRH production by the hypothalamus.
Where are spermatogenic (germ) cells located and what is their function?
Spermatogenic cells are located in the walls of the seminiferous tubules and produce sperm cells.
What is the role of sustentacular (Sertoli) cells in the testes?
Sustentacular cells nourish developing sperm and control the release of sperm into the lumen of the seminiferous tubule.
What is the function of interstitial (Leydig) cells?
Leydig cells are located between seminiferous tubules and secrete testosterone.
What is the most common form of cancer in males aged 15-35?
Testicular cancer.
What are the clinical manifestations of testicular cancer?
A painless, solid mass in the testis.
What is a major risk factor for testicular cancer?
Undescended testes.
What is the function of the epididymis?
The epididymis is the site for sperm maturation and storage, allowing sperm to gain mobility over 14 days.
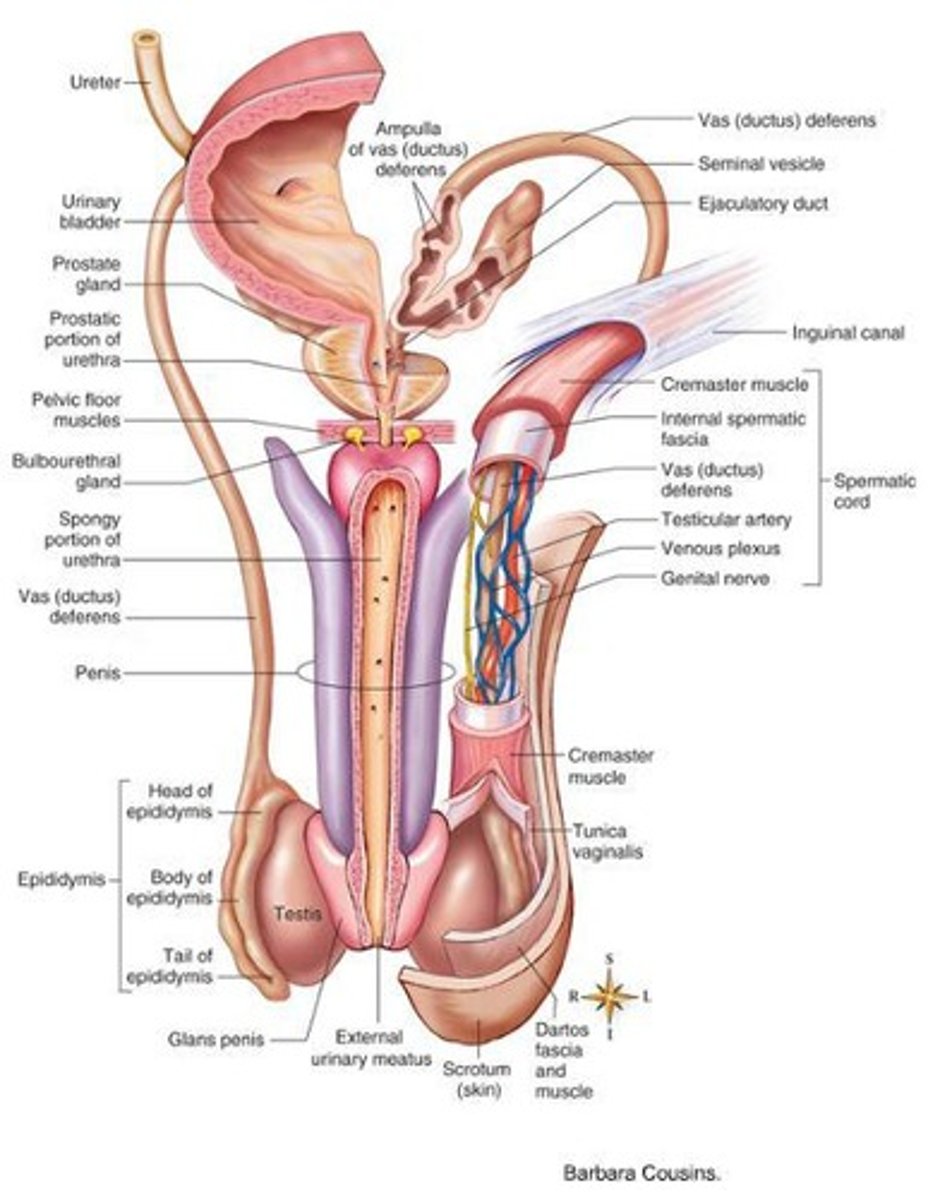
How does the ductus (vas) deferens function in the male reproductive system?
It transports sperm from the epididymis to the urethra by peristalsis and can store sperm for several months.
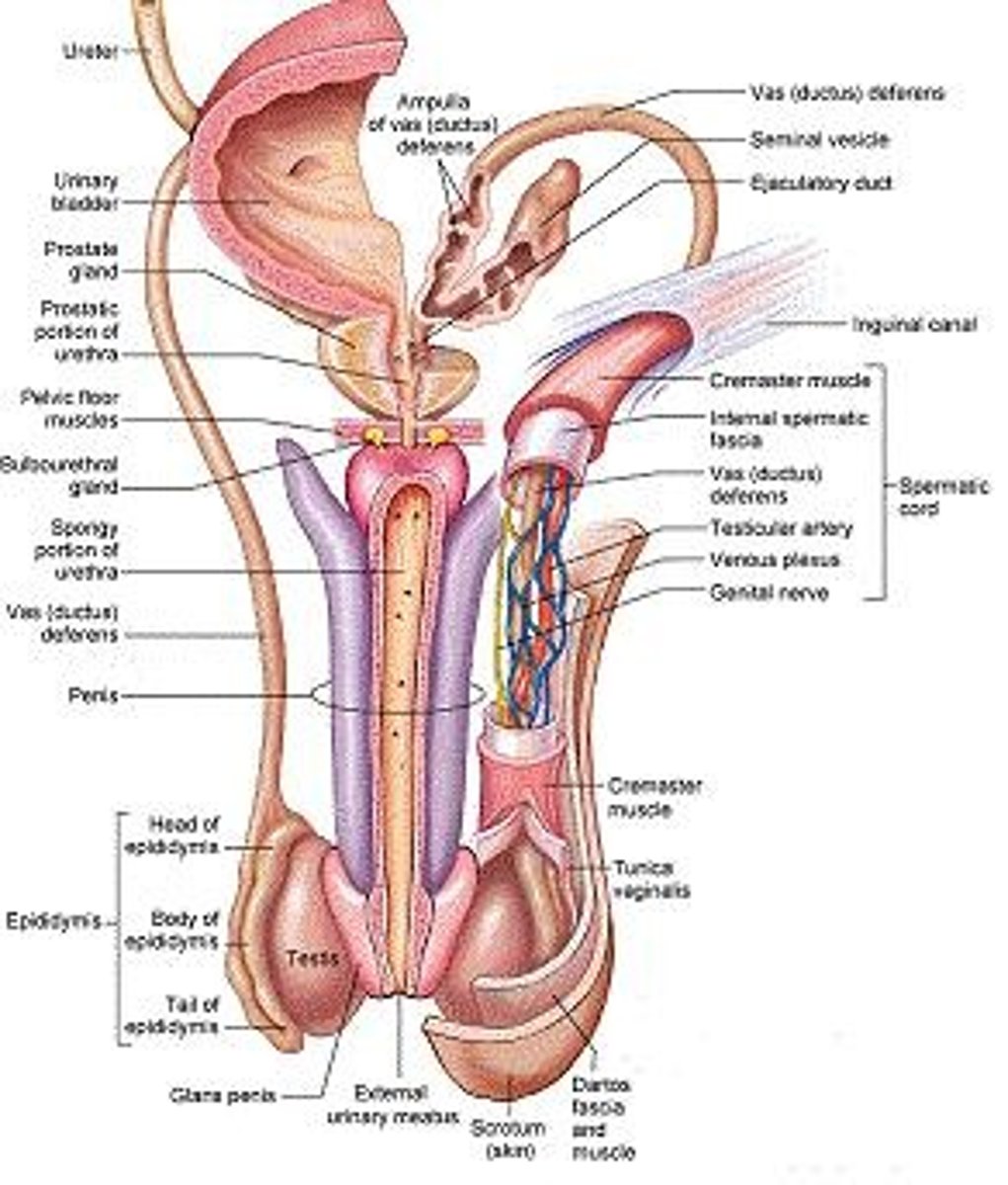
What structures are contained within the spermatic cord?
The spermatic cord contains testicular blood vessels, autonomic nerves, lymphatic vessels, the ductus deferens, and the cremaster muscle.
What is the role of seminal vesicles in male reproduction?
Seminal vesicles add an alkaline, viscous fluid to sperm, which contains fructose for ATP production.
What is the function of the ejaculatory duct?
The ejaculatory duct ejects sperm and seminal vesicle secretions into the urethra just before ejaculation.
Where is the prostate gland located and what is its significance?
The prostate gland encircles the urethra just inferior to the urinary bladder and consists of 20-30 glands embedded in smooth muscle and connective tissue.
What is the approximate length of the coiled duct in the epididymis?
Approximately 6 meters.
What are the characteristics of the prostate gland?
It is a golf-ball sized gland that encircles the urethra and is comprised of smooth muscle and connective tissue.
What is the function of the cremaster muscle?
The cremaster muscle helps regulate the temperature of the testes by raising or lowering them.
What occurs during ejaculation in terms of smooth muscle activity?
Smooth muscle contracts, squeezing glandular secretions into the urethra via several ducts.
What are the components of glandular fluid that accounts for up to 1/3 of the volume of semen?
It includes nutrients and several enzymes, such as prostate-specific antigen (PSA).
What is prostate cancer and how is it detected?
A common form of cancer in males, often growing slowly; detected by digital examination, assessment of blood PSA levels, and ultrasound.
What is benign prostatic hyperplasia and its effects?
A condition where the prostate doubles to quadruples in size, affecting most males over 60 years, distorting the urethra and urine flow.
What is the function of the bulbourethral glands?
They produce a thick, clear, alkaline mucus that lubricates the male urethra and neutralizes acidic urine.
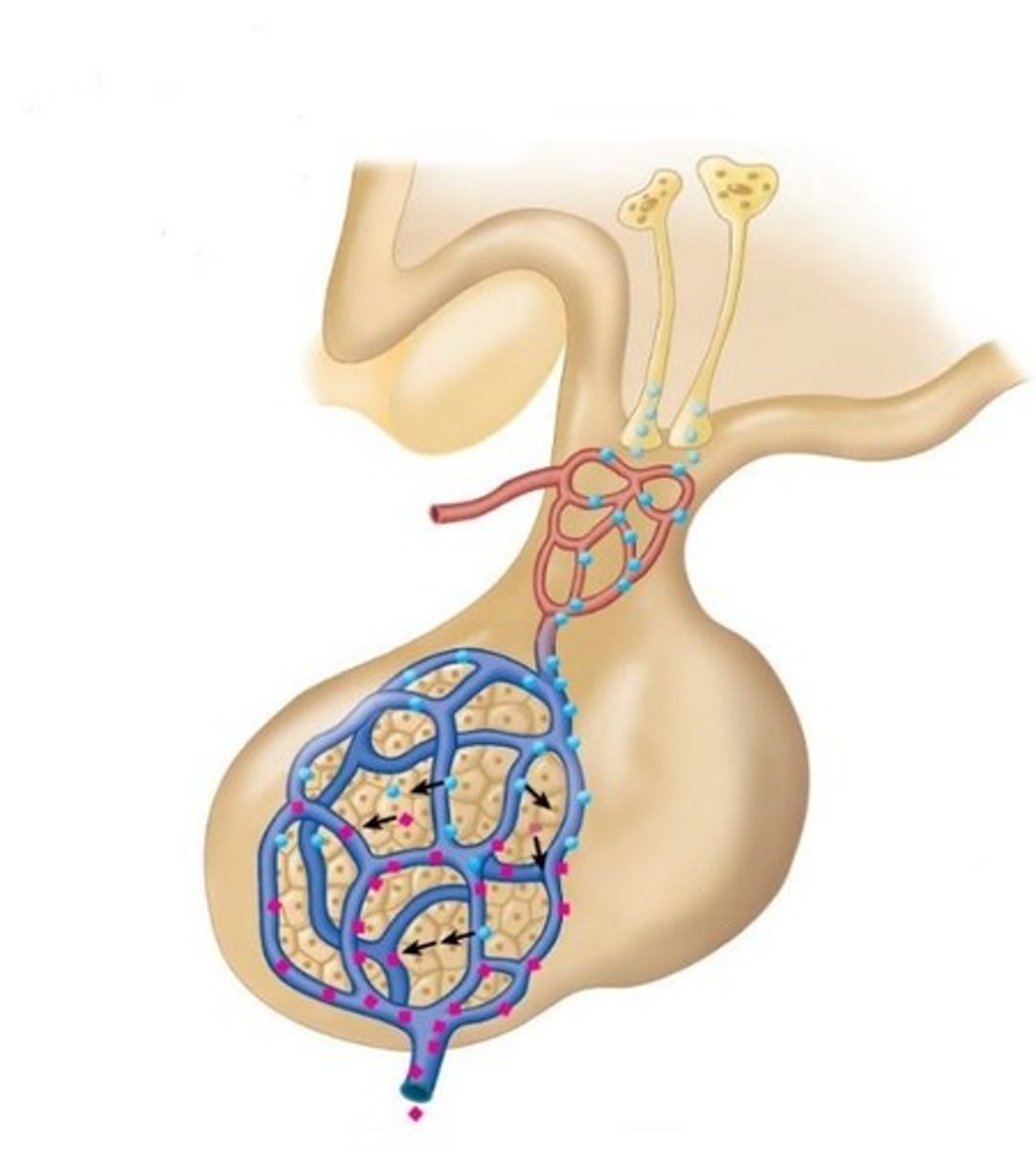
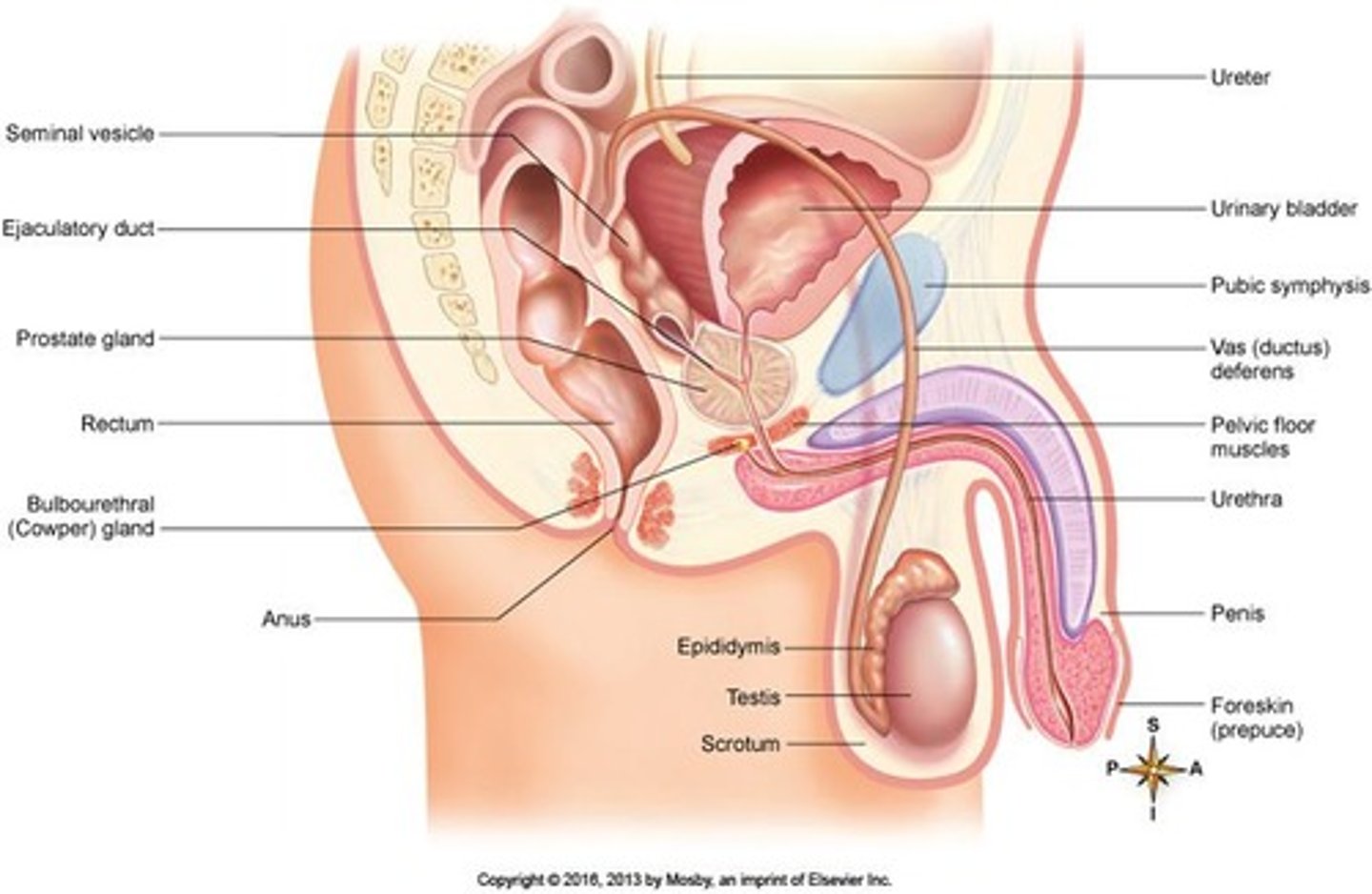
What is the length and function of the urethra in males?
The urethra is a 20 cm-long passageway that carries urine out of the bladder and propels semen during ejaculation.
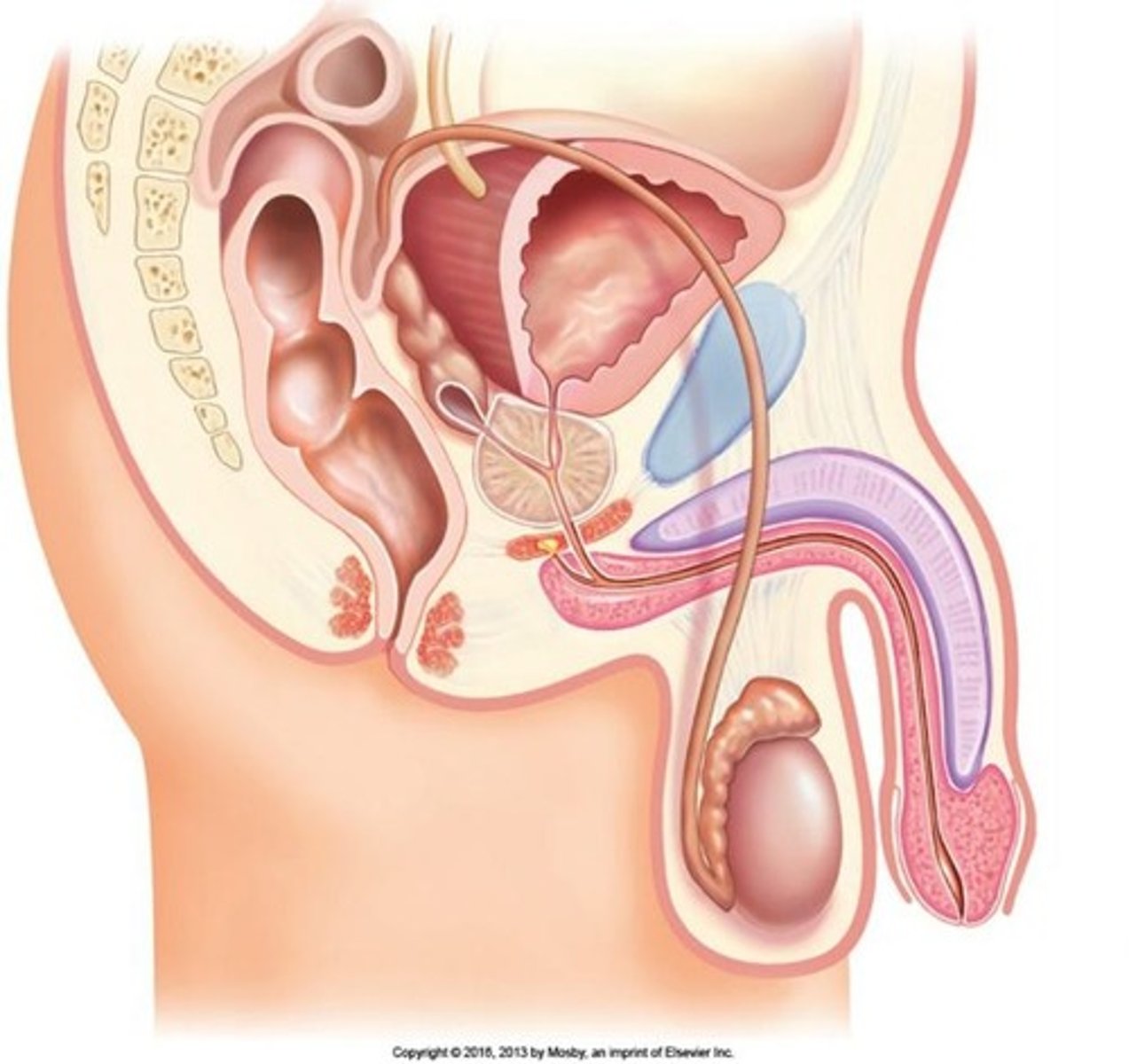
What prevents urine from entering the urethra during ejaculation?
A smooth muscle sphincter at the base of the urinary bladder closes reflexively.
What are the main components of the penis?
The penis consists of an attached root, a free shaft, and an enlarged tip called the glans penis.
What is circumcision and its potential benefits?
The removal of the foreskin for social, cultural, or religious reasons, which may reduce some infections.
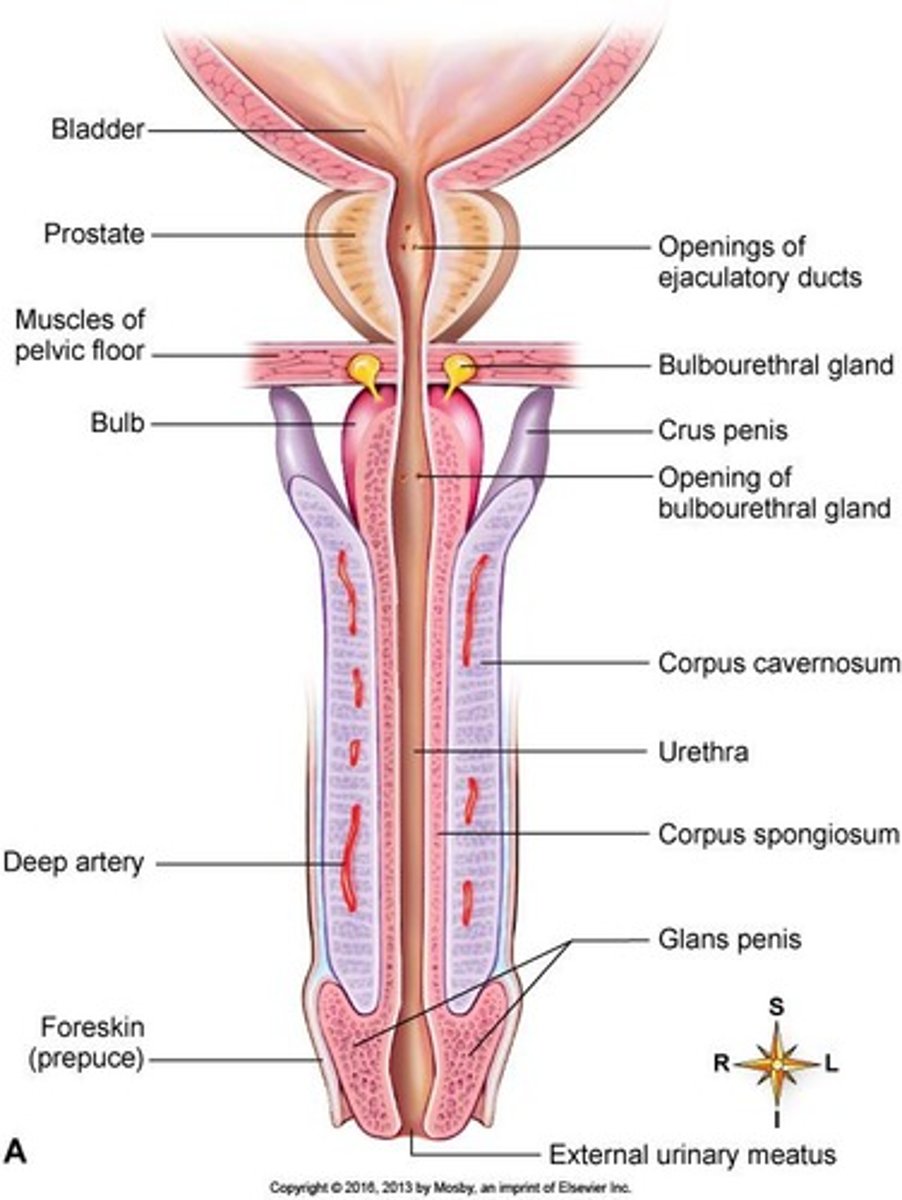
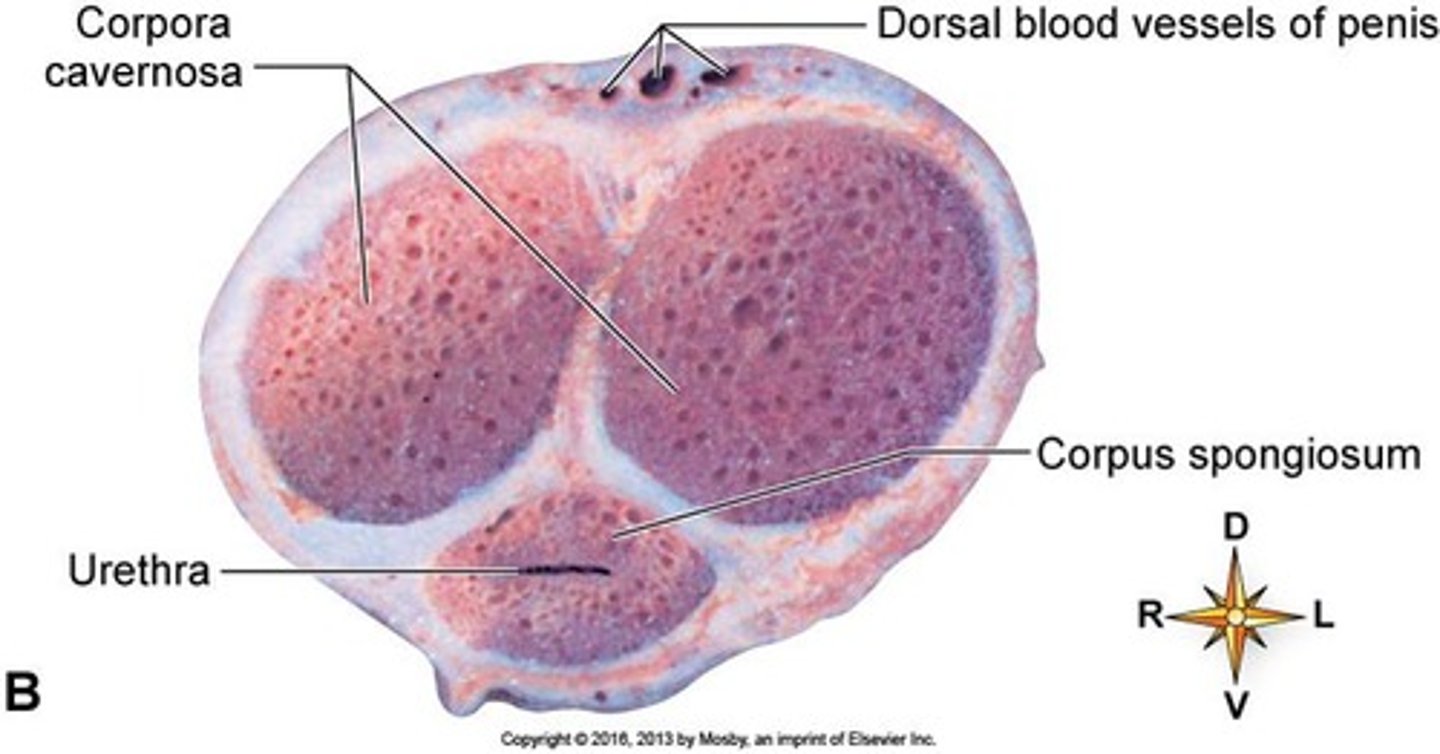
What are the three cylindrical bodies of erectile tissue in the penis?
Two corpora cavernosa and one corpus spongiosum.
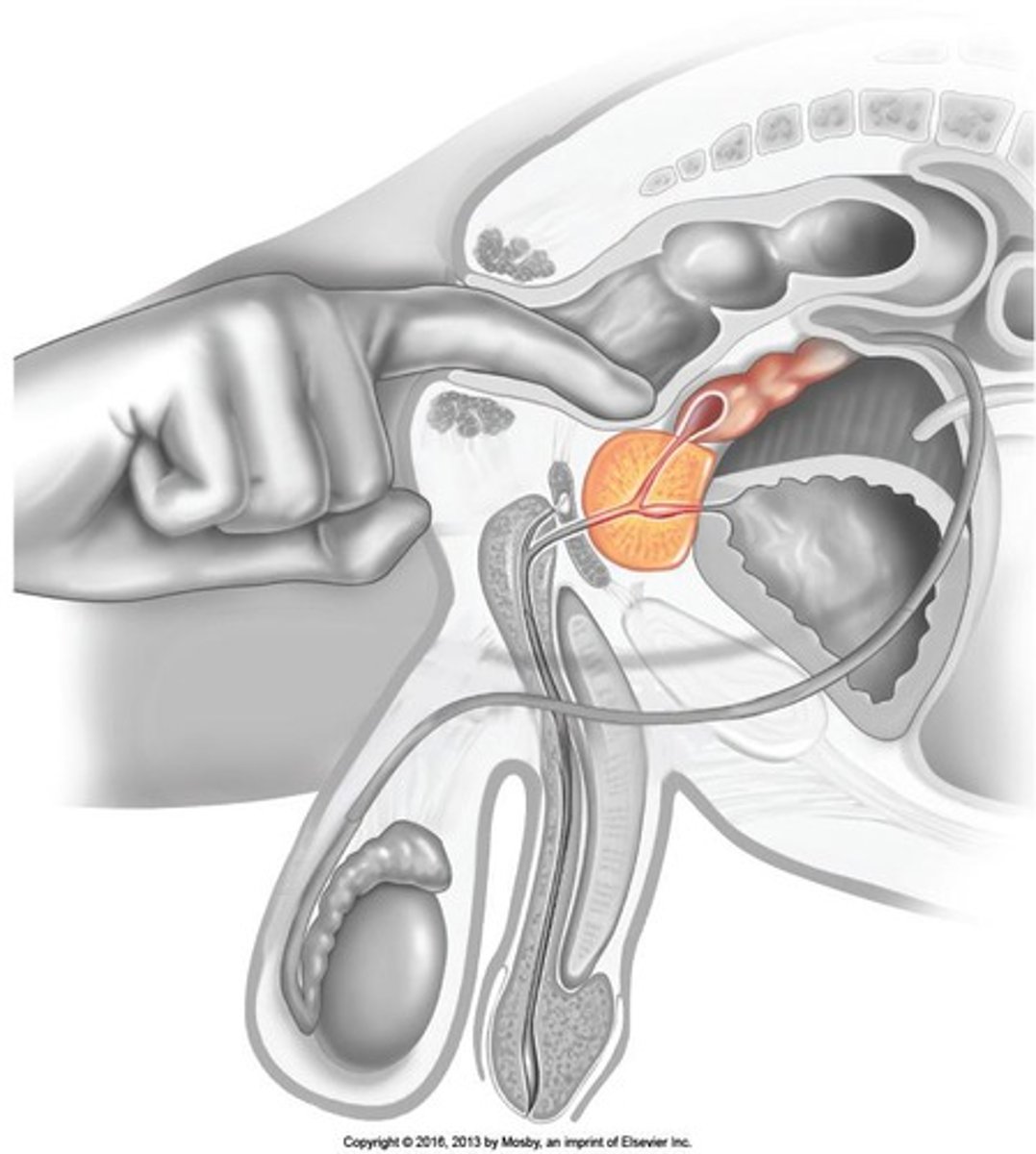
How does erectile tissue function during sexual excitement?
Vascular spaces fill with blood, causing the penis to enlarge and become rigid.
What is the volume of semen released during ejaculation?
About 2.5 - 5 mL.
What is the composition of semen?
A thick, milky white fluid mixture of sperm, testicular fluid, and accessory gland secretions.
What is the pH of semen and its purpose?
Semen has a pH of 7.5 to neutralize the acidic pH of the vagina.
What happens to semen after ejaculation?
It coagulates to stick to the vaginal wall and then liquefies after 15-20 minutes due to fibrinolysin.
What is the typical survival time of sperm in the female reproductive tract?
Sperm usually survive for about 48 hours, but some can survive longer.
What is the viability period of the secondary oocyte?
The secondary oocyte is viable for about 24 hours.
When does fertilization typically occur in relation to ovulation?
Fertilization usually occurs 12 to 24 hours after ovulation.
What factors affect male fertility?
Adequate production of normally formed sperm with normal motility; affected by X-rays, infections, toxins, malnutrition, and raised temperature.
What hormonal changes occur during puberty in males?
Pulses of GnRH trigger production of FSH and LH.
What age-related changes occur in male testosterone levels?
Around age 55, testosterone levels decline, resulting in decreased muscular strength, fewer viable sperm, and decreased sexual desire.
What symptoms can benign prostatic hyperplasia cause?
Frequent urination, decreased force of stream, bed-wetting, and sensation of incomplete emptying.
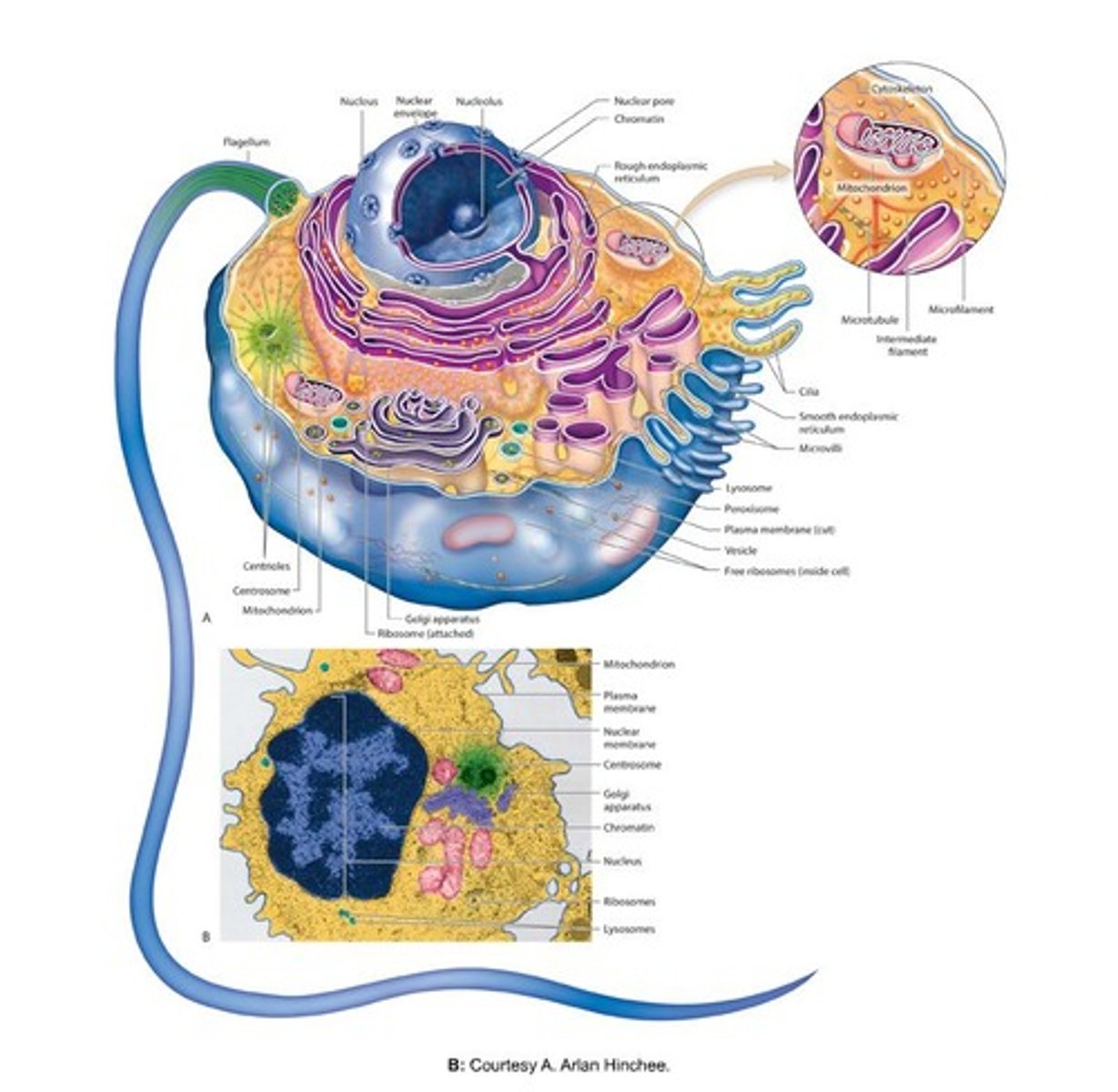
What is the function of the nucleus in a cell?
It controls cellular structure, directs cellular activities, and produces ribosomes.
What are chromosomes made of?
Chromosomes are long molecules of DNA coiled around proteins.
How many pairs of chromosomes do body (somatic) cells have?
Body cells have 23 pairs of chromosomes.
What are homologous chromosomes?
Homologous chromosomes are the two chromosomes making up a chromosome pair, one from each parent.
What is the difference between homozygous and heterozygous alleles?
Homozygous alleles have identical information for a trait, while heterozygous alleles have different information for a trait.
What are the two types of cell division?
Somatic cell division and reproductive cell division.
What is the aim of somatic cell division?
To replicate cells to replace dead or injured cells or to add new cells during tissue growth.
What is the aim of reproductive cell division?
To produce gametes (sperm and oocyte) for the next generation and ensure genetic variation in offspring.
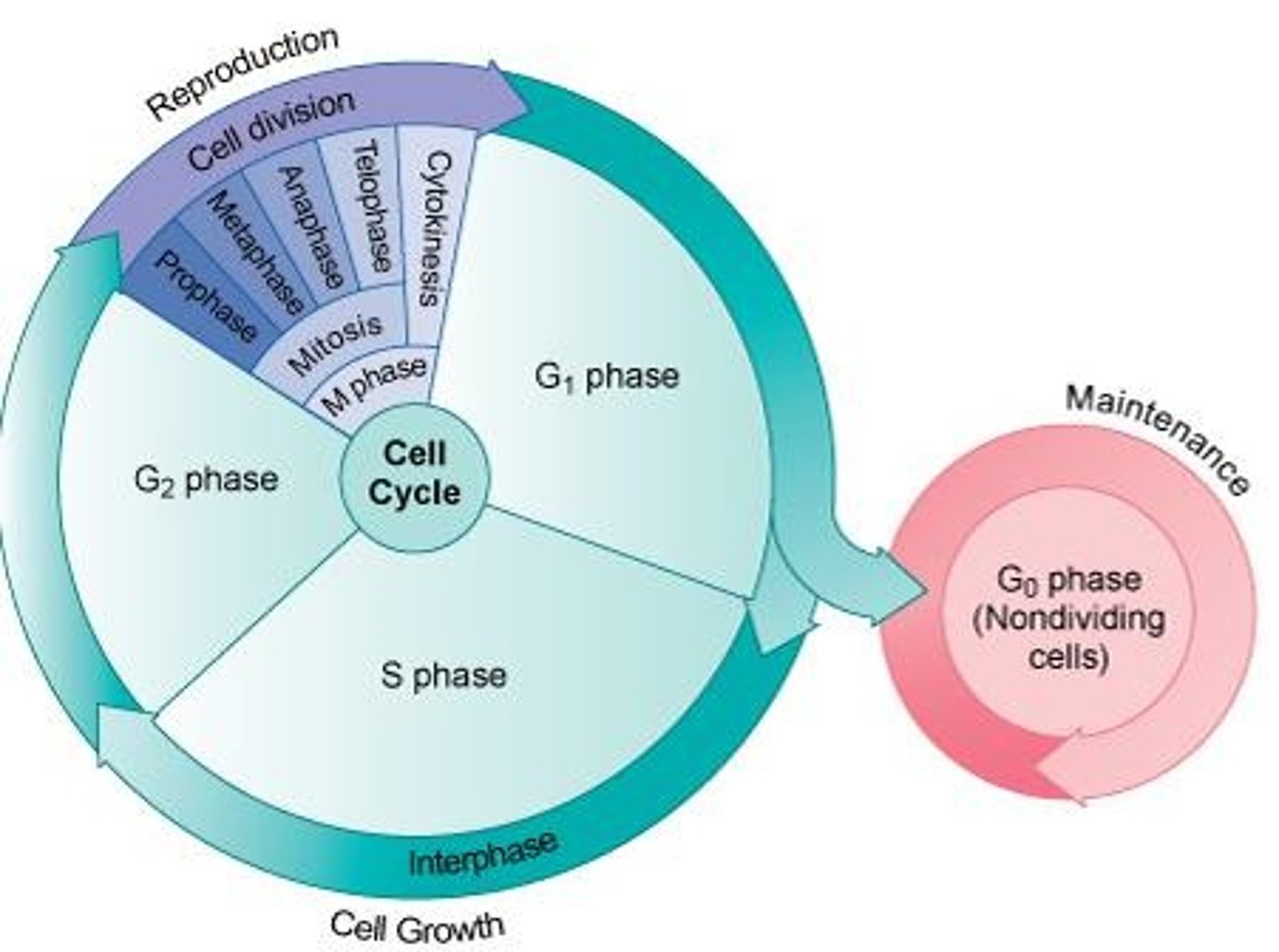
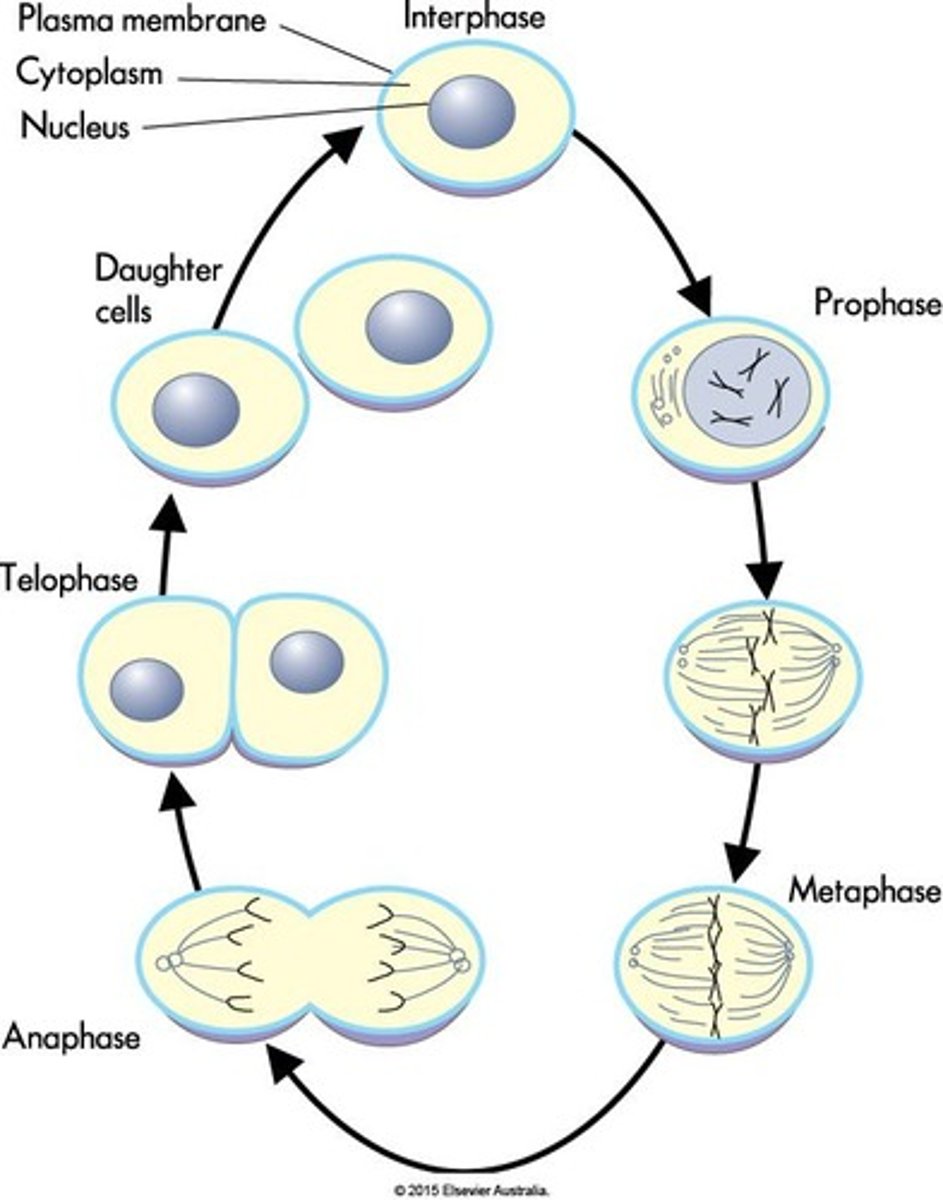
3 stages of somatic cell division
interphase, mitosis, cytokinesis
What occurs during interphase?
Cell growth, metabolism, duplication of chromosomes, and production of more organelles.
What are the phases of interphase?
G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase, and G0 phase.
What happens during the 4 phases of interphase?
1. G1 is duplication of organelles etc.
2. G2 is cell growth and protein synthesis
3. S1 creation of identical daughter cells
4. rest/maintenance
What is mitosis?
The process where the parent cell produces two identical cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
How many stages are there in mitosis?
There are four stages in mitosis.
What is cytokinesis?
The division of the cytoplasm following mitosis.
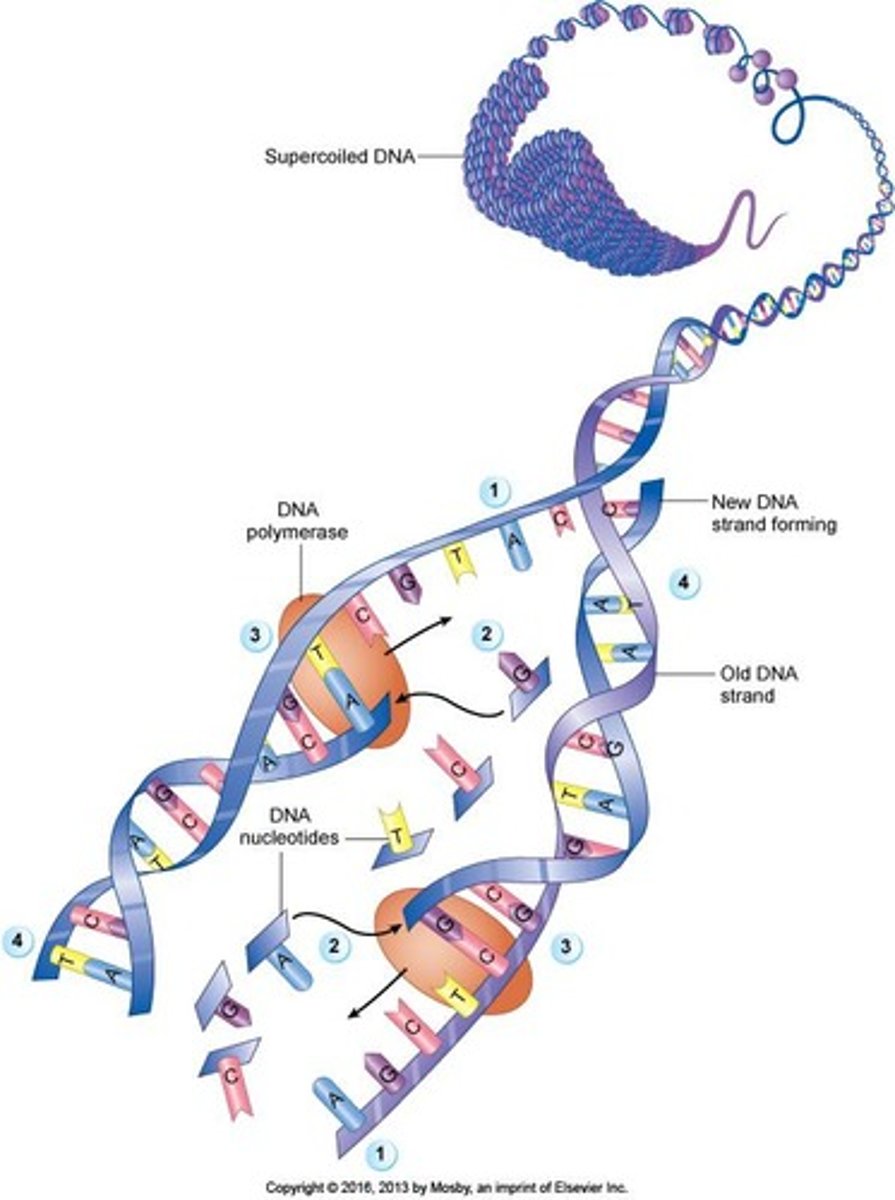
What happens to DNA during replication?
DNA molecules unzip, and complementary bases pair to form identical copies along each strand.
What are the four stages of mitosis?
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
What is the role of enzymes in DNA replication?
Enzymes help unzip DNA and facilitate the pairing of complementary bases.
What are the components of DNA?
DNA is made of a base, pentose sugar, and a phosphate group.
What is the significance of crossing over in reproductive cell division?
Crossing over ensures genetic variation in offspring.
What are alleles?
Alleles are alternative versions of a gene.
What is the result of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle results in the duplication of cellular contents and division into two cells.
What is cytokinesis?
The division of the cytoplasm to create 2 new identical cells (daughter cells). Each new cell has 23 pairs of chromosomes (46).
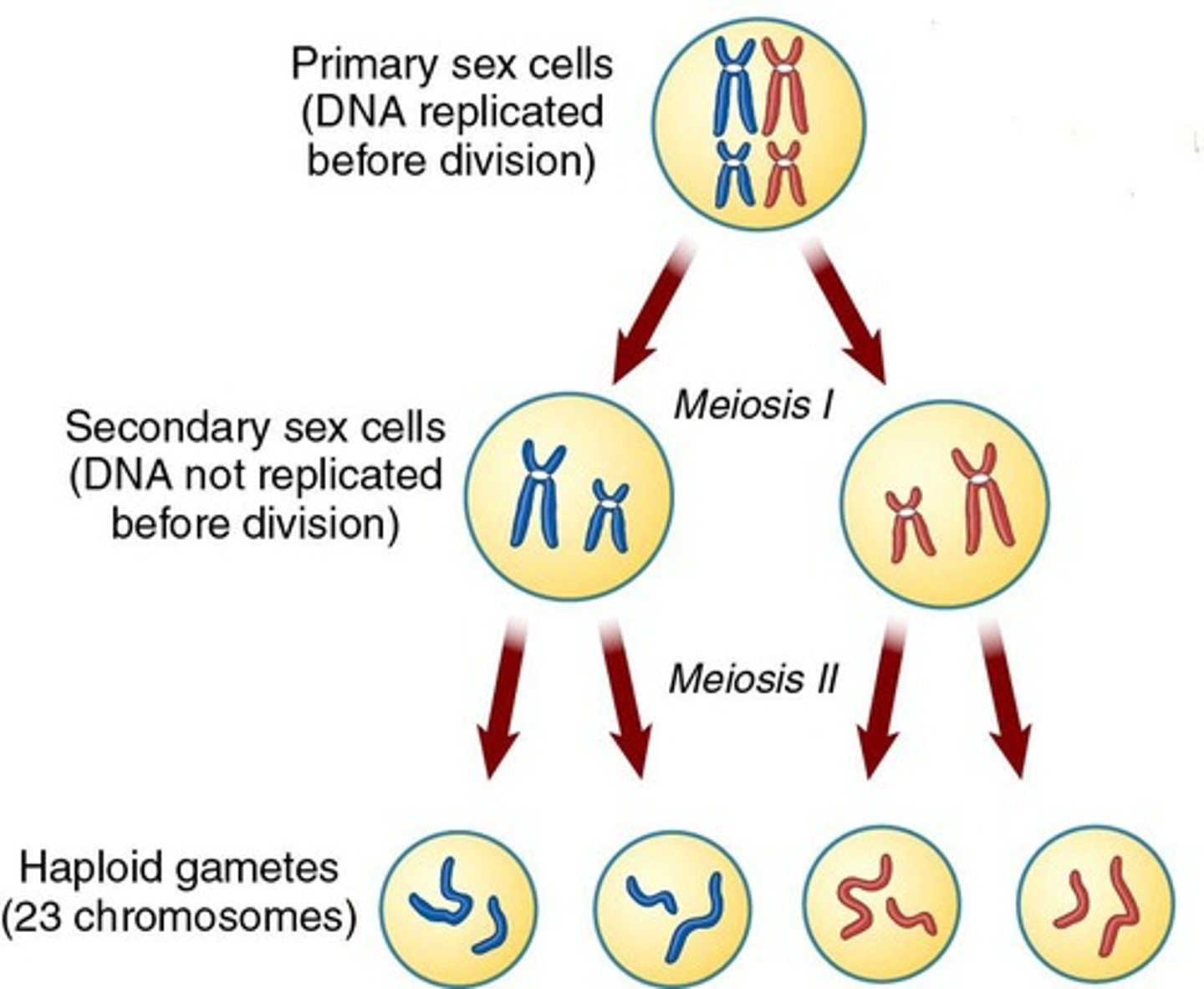
What type of cell division occurs in the gonads?
Meiosis, which results in the production of haploid cells (n) containing only 23 single chromosomes.
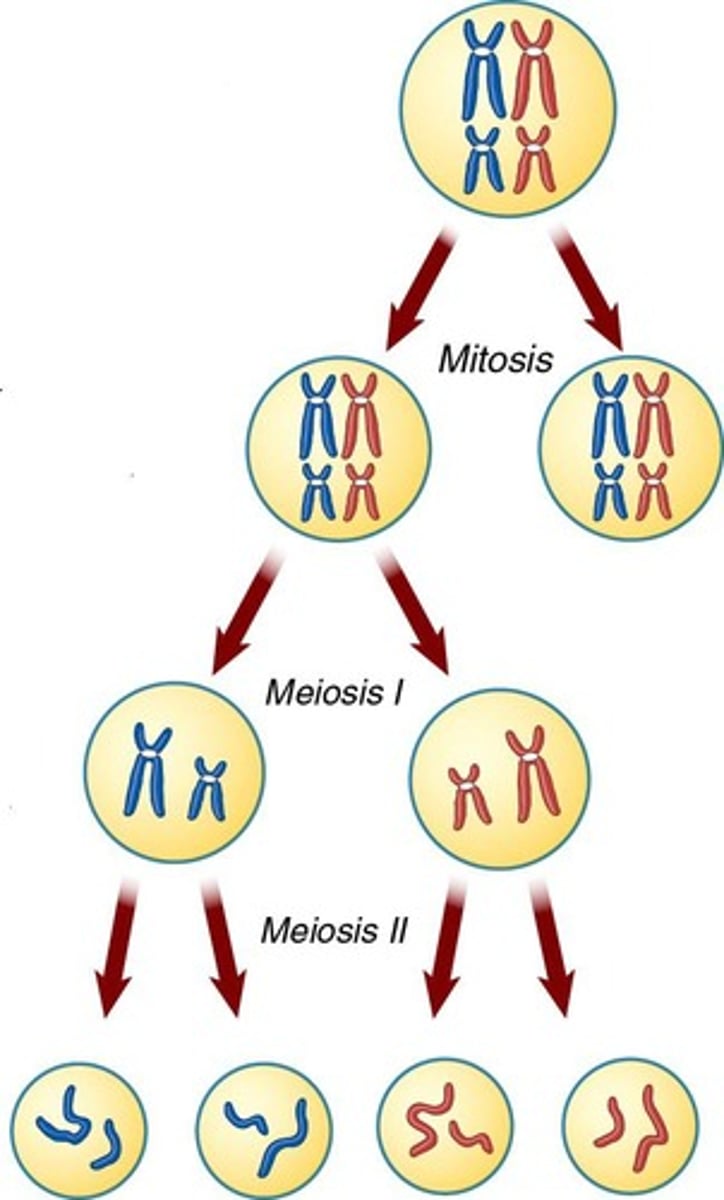
What restores the diploid number of chromosomes after meiosis?
Fertilization restores the diploid number of chromosomes (46 / 23 pairs).
What are the two stages of meiosis?
Meiosis I and Meiosis II.
What happens during Meiosis I?
It occurs following the interphase stage, has 4 stages, and produces 2 genetically different cells that contain 23 chromosomes.
How does meiosis differ from mitosis in terms of daughter cells?
Mitosis produces 2 genetically identical daughter cells (2n=46), while meiosis produces 4 genetically variable daughter cells (n=23).
What is the outcome of meiosis in males?
In males, meiosis occurs in the testes and results in 4 daughter cells maturing into 4 sperm cells.
What is the outcome of meiosis in females?
In females, meiosis occurs in the ovaries and results in 1 secondary oocyte and 3 polar bodies (which are discarded).
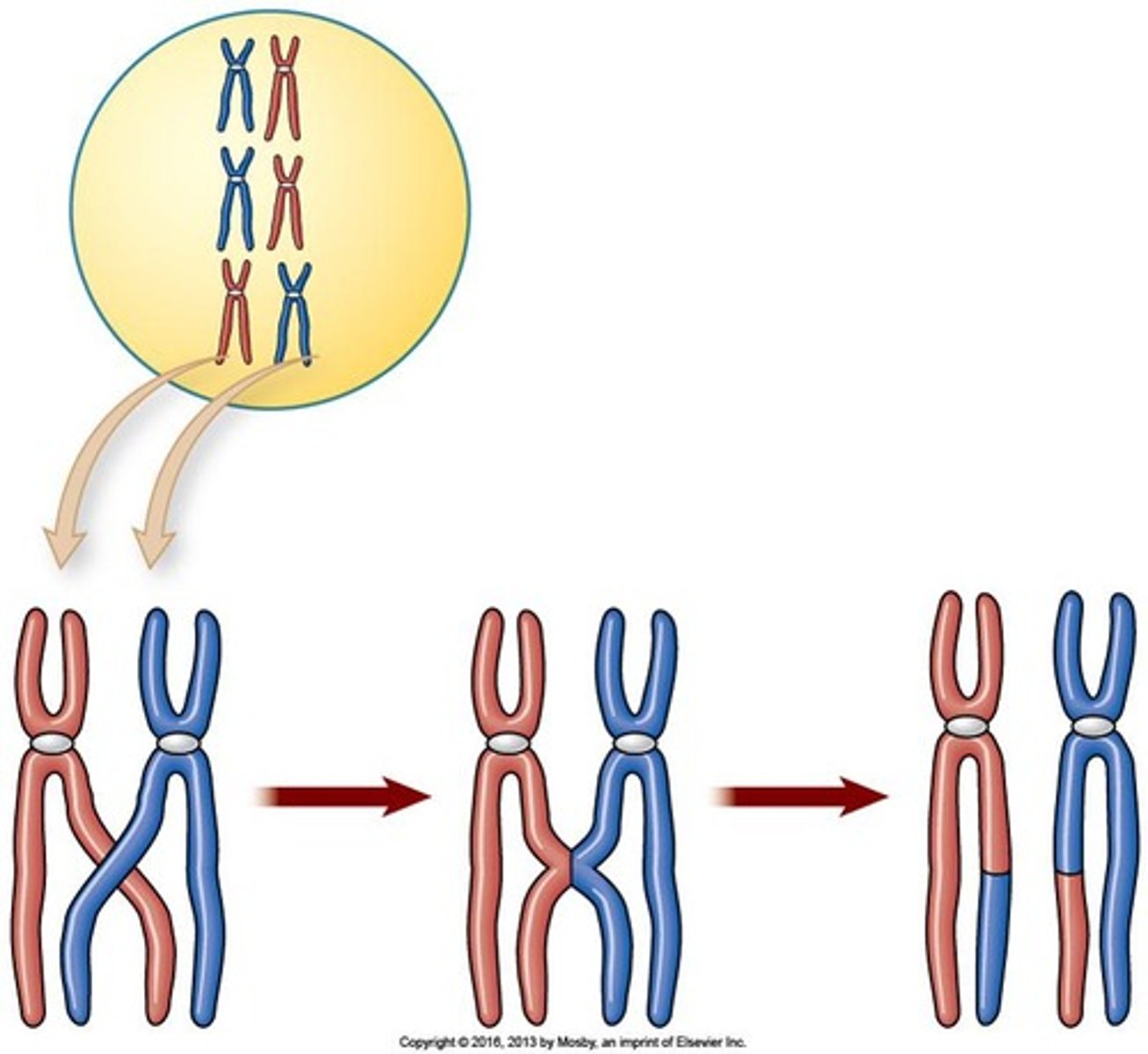
What is crossing over in meiosis?
Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes, increasing genetic variation.
When does crossing over occur?
Crossing over occurs during Meiosis I.
What is the significance of genetic variation in offspring?
Genetic variation allows offspring to be genetically different from their parents, which is essential for evolution and adaptation.
What are the potential genotypes of offspring resulting from crossing over?
Gametes can have various combinations of alleles, such as blonde hair & blue eyes, blonde hair & brown eyes, brown hair & blue eyes, and brown hair & brown eyes.
What is cancer in relation to cell division?
Cancer is a group of diseases resulting from uncontrolled or abnormal cell proliferation. Or from mutation of DNA.
What is a tumor?
A tumor (or neoplasm) is excess tissue resulting from uncontrolled cell division.
What is the difference between malignant and benign tumors?
Malignant tumors undergo metastasis (spread of cancerous cells), while benign tumors do not metastasize.
What is carcinoma?
Carcinoma is a type of cancer that arises from epithelial tissue.