Organic Chemistry 2 Exam 1
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
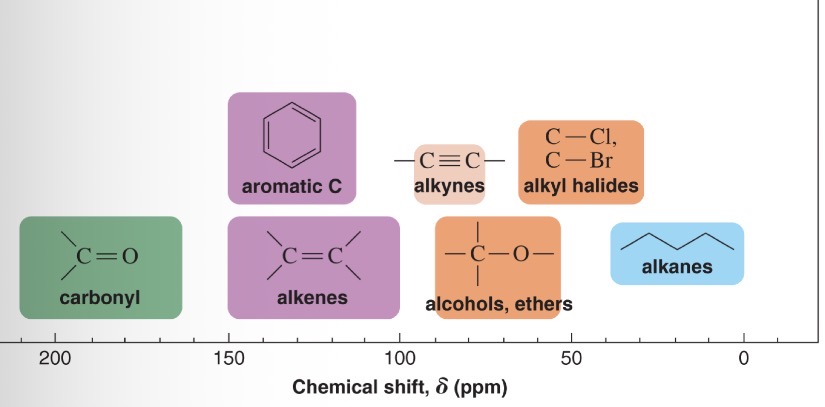
0-40 ppm Chemical shift
Sp3 C-C
40-100 ppm chemical shift
Sp3 C-X (X = electronegative atom)
80-100 ppm chemical shift
CC triple bond
100-150 ppm chemical shift
C=C, aromatic ring
150-200 ppm chemical shift
Acid halide
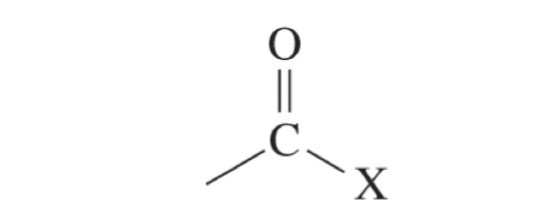
>200 ppm chemical shift
Chemical shifts (REVIEW)
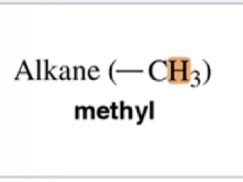
0.9 ppm chemical shift
Type of Proton
Methyl
1.3 ppm chemical shift
Type of Proton
Methylene
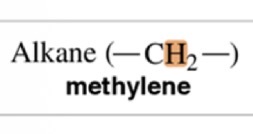
1.4 ppm chemical shift
Type of Proton
Methine
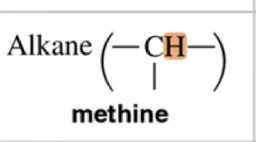
2.1 ppm chemical shift
Type of Proton
Methyl Ketone
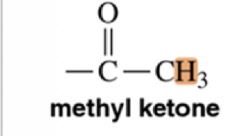
2.5 ppm chemical shift
Type of Proton
Acetylenic
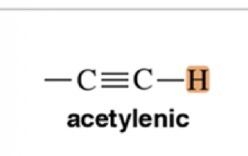
3-4 ppm chemical shift
Type of Proton
(X=halogen, O)
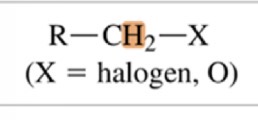
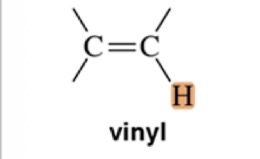
5-6 ppm chemical shift
Type of Proton
Vinyl
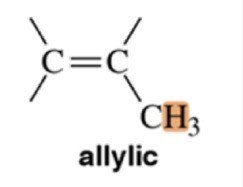
1.7 ppm chemical shift
Type of Proton
Allylic Hydrogen
7.2 ppm chemical shift
Type of Proton
Aromatic

2.3 ppm chemical shift
Type of Proton
Benzylic
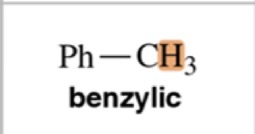
9-10 ppm chemical shift
Type of Proton
Aldehyde
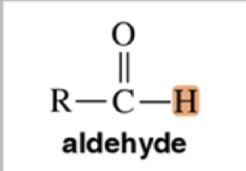
10-12 ppm chemical shift
Type of Proton
Acid
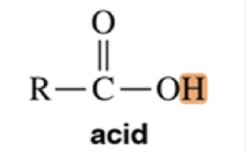
Variable ~2-5 ppm chemical shift
Type of Proton
Alcohol
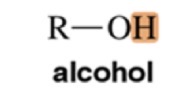
Variable, ~4-7 ppm chemical shift
Type of Proton
Phenol
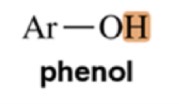
Variable, ~1.5-4
Amine
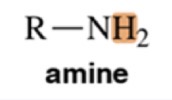
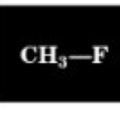
Chemical Shift of methyl H
4.3 ppm
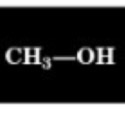
Chemical Shift of methyl H
3.4 ppm
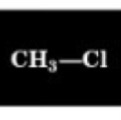
Chemical Shift of methyl H
3.0 ppm
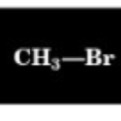
Chemical Shift of methyl H
2.7 ppm
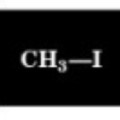
Chemical Shift of methyl H
2.2 ppm
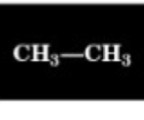
Chemical Shift of methyl H
0.9 ppm
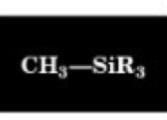
Chemical Shift of methyl H
0.0 ppm
Wave number of H3-CH3 Bond
995 cm-1
Wave number of H2C=CH2 Bond
1650 cm-1
Wavenumber of HC triple bond CH
2181 cm-1
Wavenumber of C-F
1049 cm-1
Wavenumber of C-Cl
732 cm-1
Wavenumber of C-Br
611 cm-1
Wavenumber of carbonyl
1715 cm-1
Wavenumber of C(sp3)—H
2900cm-1
Wavenumber of C(sp2)—H
3100 cm-1
Wavenumber of C=C
1660cm-1
Wavenumber of Terminal Alkynes (2 kinds)
C triple bond C 2200cm-1
C(sp)-H 3100cm-1
Wavenumber of Internal Alkynes
No Csp-H bond stretch around 3100cm-1 and C TRIPLE BOND C stretch (2100cm-1) —» OFTEN MISSING IF MOLECULE ISN’T POLAR
Wavenumber of Alcohol
O-H stretch 3400cm-1 (very intense bc of polarity)
(Only fingerprint areas of IR to pay attention to is the C-O bond)
Characteristic broad OH band is result of H-bonding; “free OH” is not H-bonded to other molecules (Rounded tips = broad bands; sharp ended possibly indicates “free OH” but this is rare)
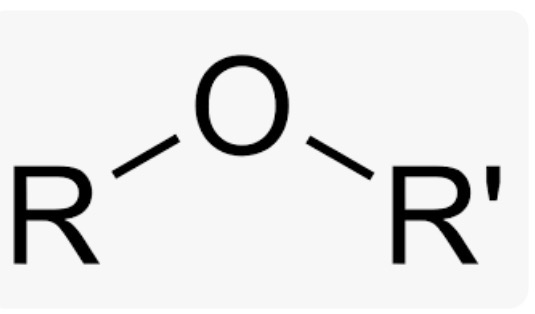
Wavenumber of Ethers
C-O stretching band around 1100cm-1 —» will look jagged like ^^^^^ or flat like ———
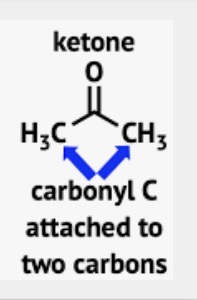
Wavenumber of Ketones
C=O stretch around 1715 cm-1 (carbonyl)
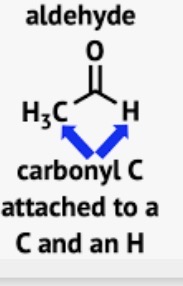
Wavenumber of Aldehydes
C=O stretch around 1735cm-1
Two distinct aldehyde C-H bands at 2840cm-1 and 2710cm-1
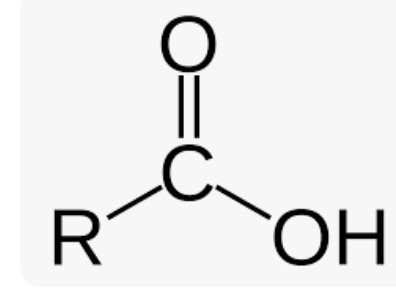
Wavenumber of Carboxylic Acid
Broad O-H band extends from 3600-2400cm-1 (broad range due to high polarity)
C=O stretch around 1715cm-1
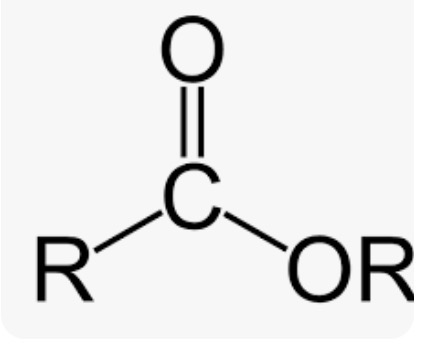
Wavenumber of Esters
C=O stretch around 1740cm-1, two C-O stretching bands around 1100 cm-1 in fingerprint regions (C-O bond)
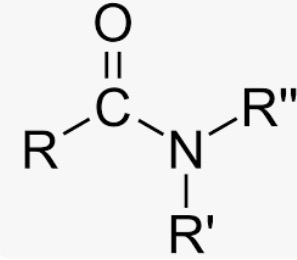
Wavenumber of Amides
C=O stretch below 1700cm-1; N-H if there’s H atom in N, visible at 3300cm-1
Wavenumber of Aromatic
Always looks more complex than other functional groups; overtone region contains several (usually 4 → index of H deficiency) low intensity peaks between 2000-1600cm-1
=C–H stretch is observed at 3100-3000 cm-1
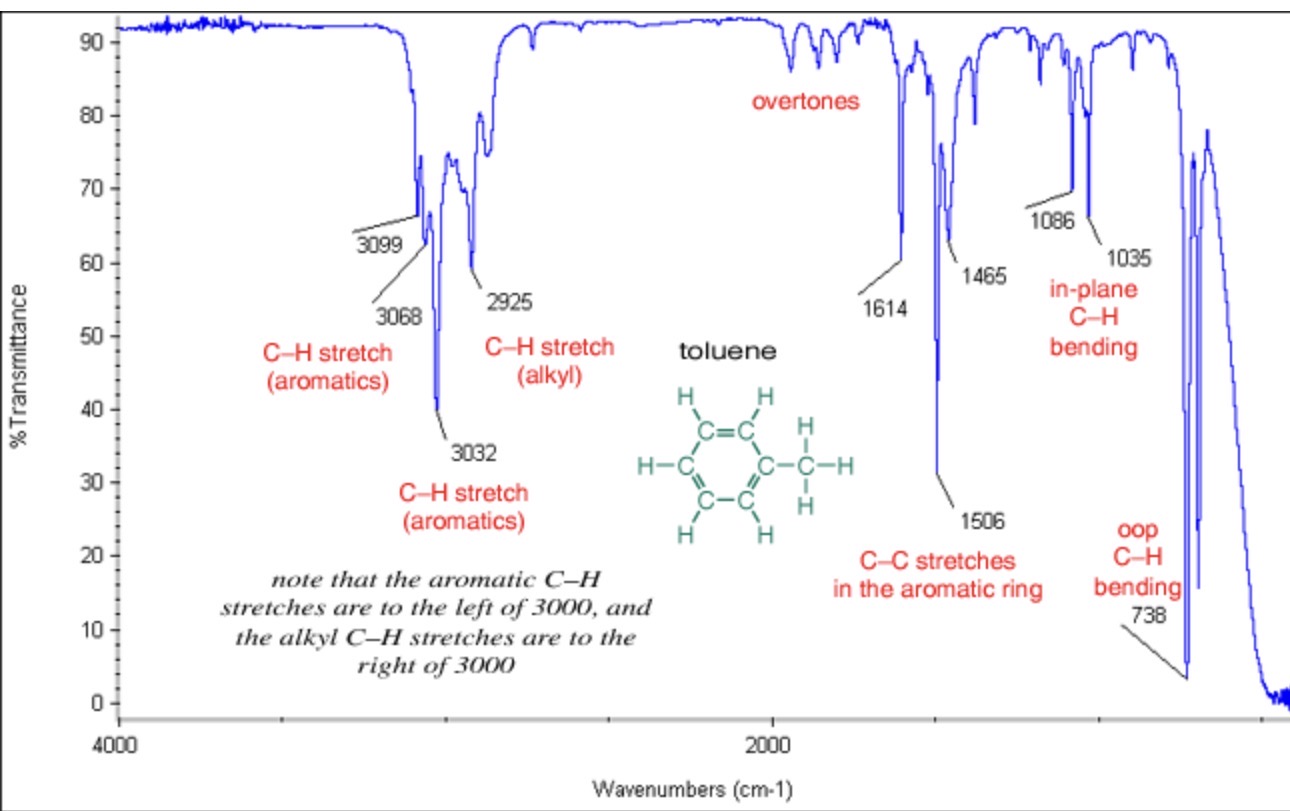
what does wavenumber tell you about bonds?
Indicates the energy of the bond vibrations and the strength of bond and atomic mass. Higher wavenumbers = stronger bonds and lighter atoms, lower wavenumbers = weaker bonds and heavier atoms
Single bonds: below 1500cm-1
Double bonds: ~1700cm-1
Triple bonds: ~2200cm-1
What does chemical shift tell you about bonds and molecules"?
Local electron environment, the magnetic shielding, and nuclei structure
Identifies functional groups; e withdrawing groups deshield nuclei moving peaks downfield/higher ppm and vice versa with e donating groups (shielding)
Common wavenumbers
4000-2500 cm-1: O−H, N−H, 𝐶−𝐻 stretching (light atoms)
2500-2000 cm-1: C≡C, 𝐶≡𝑁 stretching (triple bonds).
2000-1500 cm-1: C=O, C=C, C=N stretching (double bonds).
Below 1500 cm-1: Fingerprint region (single bonds, bending motions)